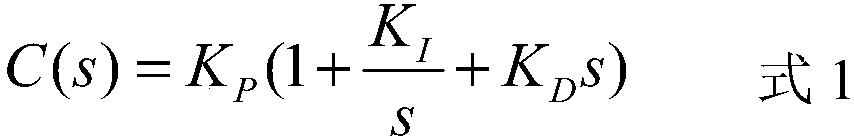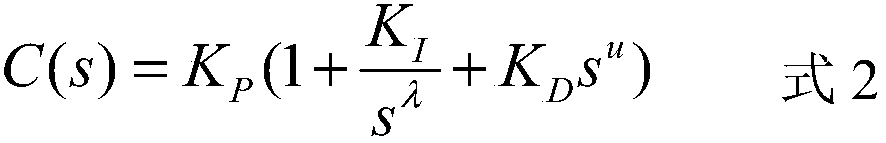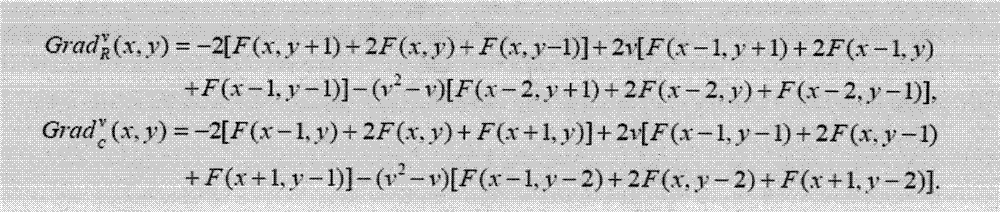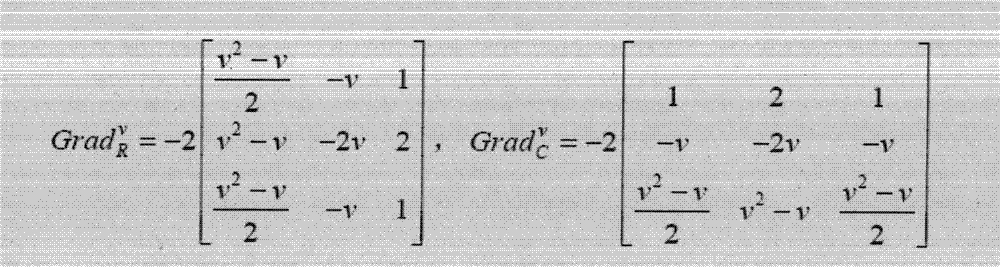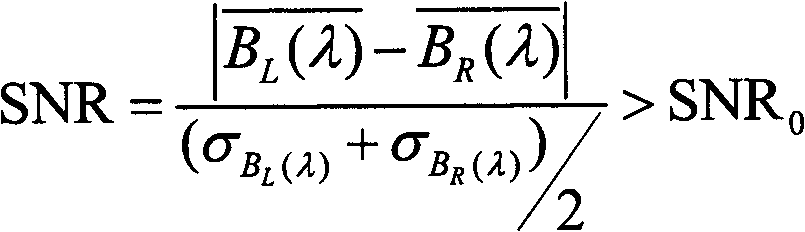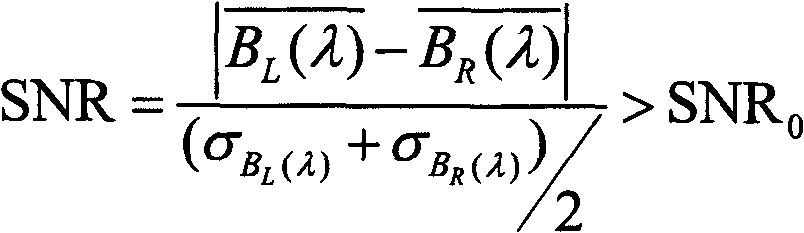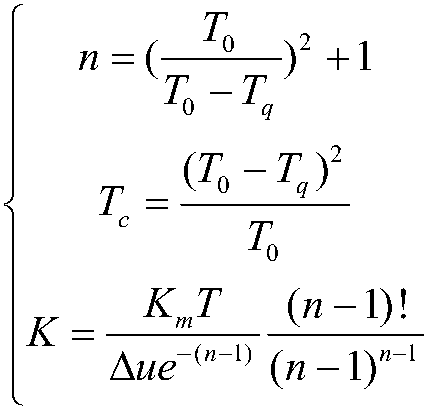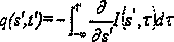Patents
Literature
52 results about "Differential of a function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = f(x) with respect to changes in the independent variable. The differential dy is defined by dy=fʼ(x) dx, where fʼ(x) is the derivative of f with respect to x, and dx is an additional real variable (so that dy is a function of x and dx). The notation is such that the equation dy=dy/dx dx holds, where the derivative is represented in the Leibniz notation dy/dx, and this is consistent with regarding the derivative as the quotient of the differentials.
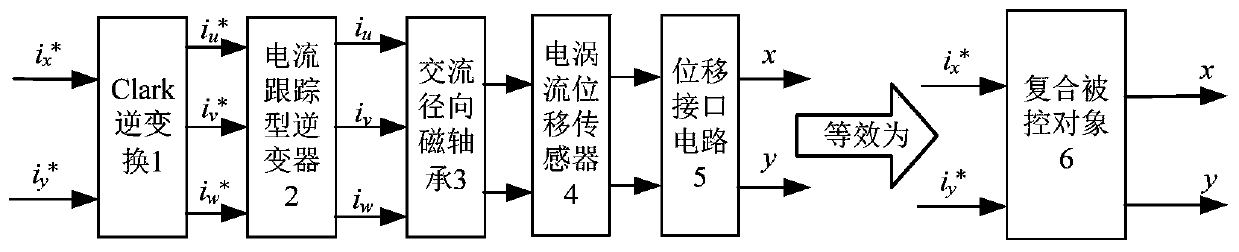
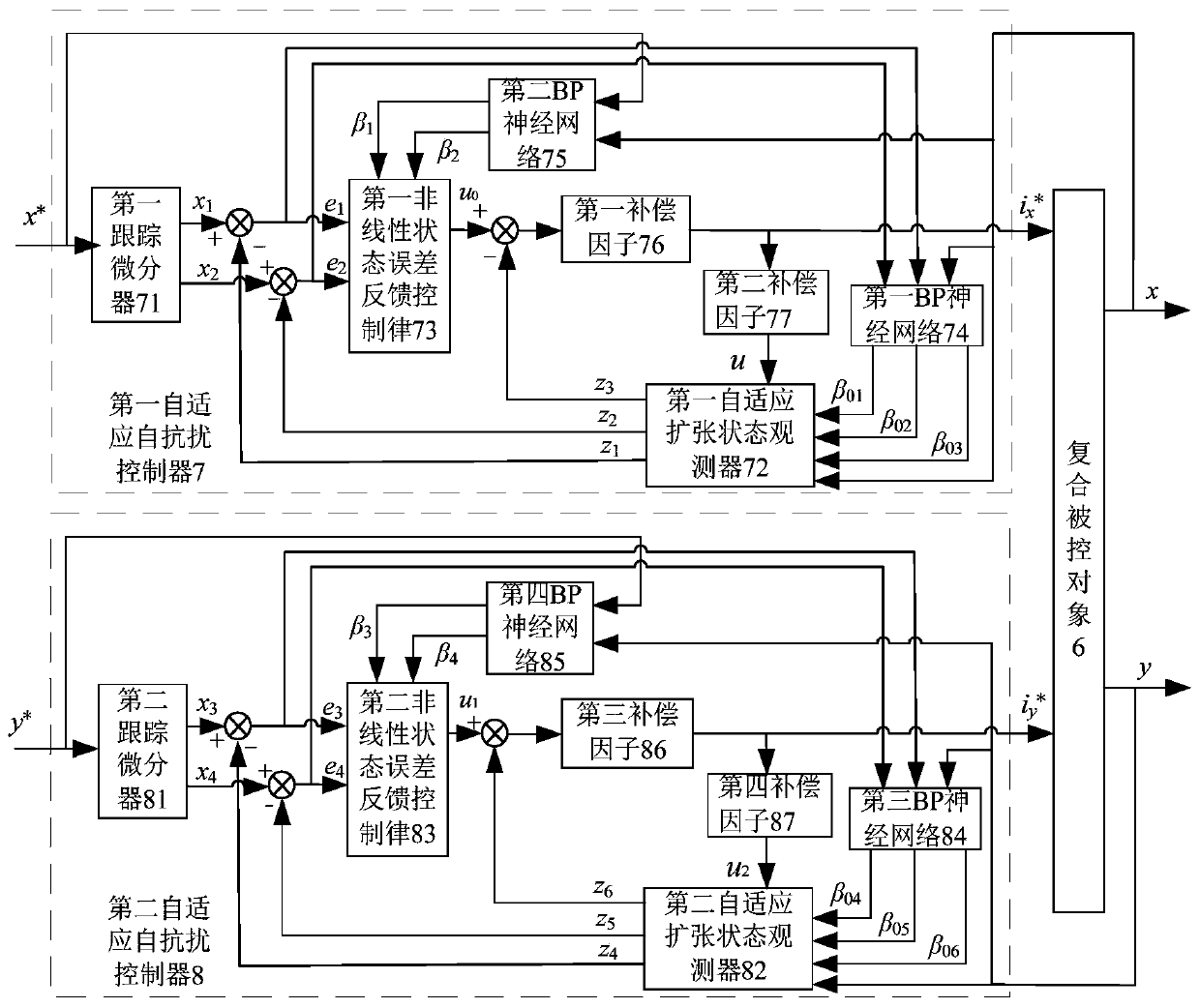
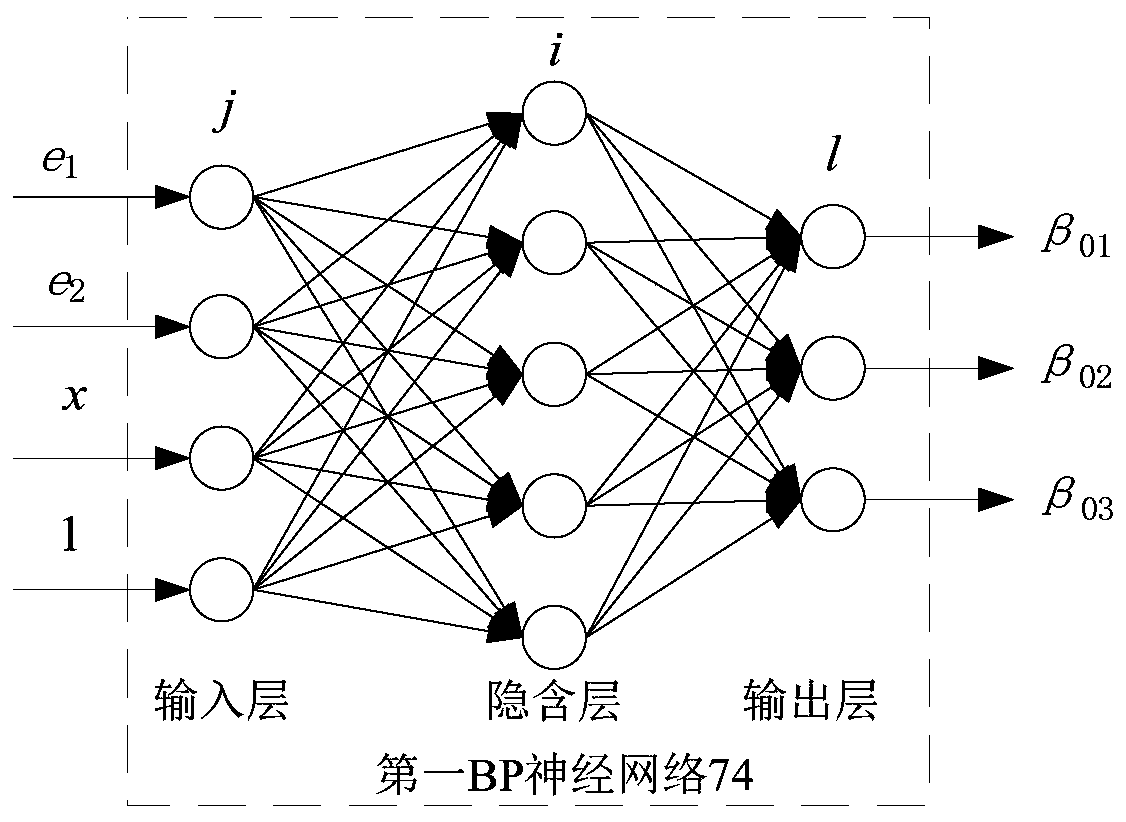
Neural network active-disturbance-rejection controller for AC radial magnetic bearing, and construction method thereof
PendingCN110018638AImprove controlCompensation internalMagnetic bearingsAdaptive controlDifferentiatorMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses a neural network active-disturbance-rejection controller for an AC radial magnetic bearing, and a construction method thereof. The input of a first tracking differentiator is given radial displacement x*, and the output is a tracking signal x1 and a differential signal x2; the input of a first self-adaptive expanded state observer is controlling quantity u, radial displacement x and three parameters beta01, beta02 and beta03, the other two inputs of a first nonlinear state error feedback control rule is parameters beta1 and beta2, and the output is the controlling quantity u0; the difference of the controlling quantity u0 and an estimation value z3 is the input of a first compensation factor, the output of a second compensation factor is the controlling quantity u,and the controlling quantity u is used as one input of a first self-adaptive active-disturbance-rejection controller. By constructing the self-adaptive extended state observer, the internal disturbance and the externa disturbance of the controlled object are automatically controlled, and the online automatic adjusting of the three parameters beta01, beta02 and beta03 can be realized along the system disturbance change, the estimation and compensation precision on the disturbance by the extended state observer are increased, and the control performance of the active-disturbance-rejection controller is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Time delay system PID controller stabilization method based on data drive
Provided is a time delay system PID controller stabilization method based on data drive. The time delay system PID controller stabilization method based on the data drive comprises the steps of firstly using relay identification of multiple frequency points, giving input frequency domain response data of a controlled time delay object and output frequency domain response data of the controlled time delay object, and extracting characteristic parameters; then obtaining the maximum permissible stabilization range of proportional gain k in a PID controller through necessary conditions of PID stabilization; for a fixed k value, obtaining a necessary and sufficient condition which can enable a closed-loop system to be stable, and determining a two-dimensional parameter domain which can enable the closed-loop system to be stable and relates to differential gain k<d> in the PID controller and integral gain k in the PID controller; and determining a two-dimensional stabilization domain with a convex polygon characteristic of the (k<d>, k) to ergodic points of each k through going through the maximum permissible stabilization range of the k, and obtaining a stabilization set of the PID controller. As long as a control parameter is selected from the obtained stabilization set of the PID controller, the stability of the closed-loop system can be ensured. According to the time delay system PID controller stabilization method based on the data drive, under the condition that a transfer function of the time delay object or a state space model of the time delay object does not need to be obtained, the PID controller stabilization method is offered based on frequency response data, complex calculation processes of pattern identification are avoided, and an approach which is simple and effective is offered for the design of a PID controller without a model time delay system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of modifying dynamic performance of phase-locked loop on basis of sliding filter
ActiveCN104811188AReduce window widthImprove dynamic performancePulse automatic controlMoving averageVoltage amplitude
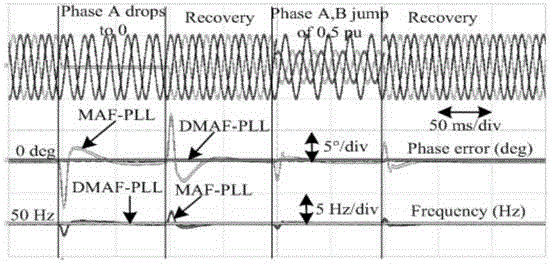
The invention discloses a method of modifying dynamic performance of a phase-locked loop on basis of a sliding filter. The method includes: sampling three-phase grid voltage, and performing Park coordinate transform to obtain voltage components v<q> and v<d> in a two-phase dq rotating coordinate system; subjecting the voltage component v<d> to differentiation and then to dividing by an angular frequency parameter, and summing a quotient and the voltage component v<q> to obtain q ; subjecting q to differentiation and then to dividing by the angular frequency parameter, and summing a quotient and the voltage component v<d> to obtain d; subjecting d to the sliding filter to obtain a fundamental wave positive-sequence voltage amplitude V<1><+>; subjecting q to the sliding filter and a PI (proportion integration) regulator, and summing an output of the PI regulator and a preset angular frequency to obtain a grid voltage angular frequency , with the preset angular frequency being power frequency usually; subjecting to differentiation to obtain a grid voltage phase 1+; feeding back 1+ to the input end to finish closed-loop control. The method has the advantages that a proportional algorithm of input signal frequency changes is introduced to MAF-PLL (moving average filter-phase-locked loop), the lowest frequency fluctuation component in the PLL is eliminated, the window width of the MAF is decreased, and dynamic performance of the MAF-DLL is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
PID controller design method
InactiveCN108803311ALess freedomReduce the difficulty of settingSampled-variable control systemsControllers with particular characteristicsControl systemDifferential of a function
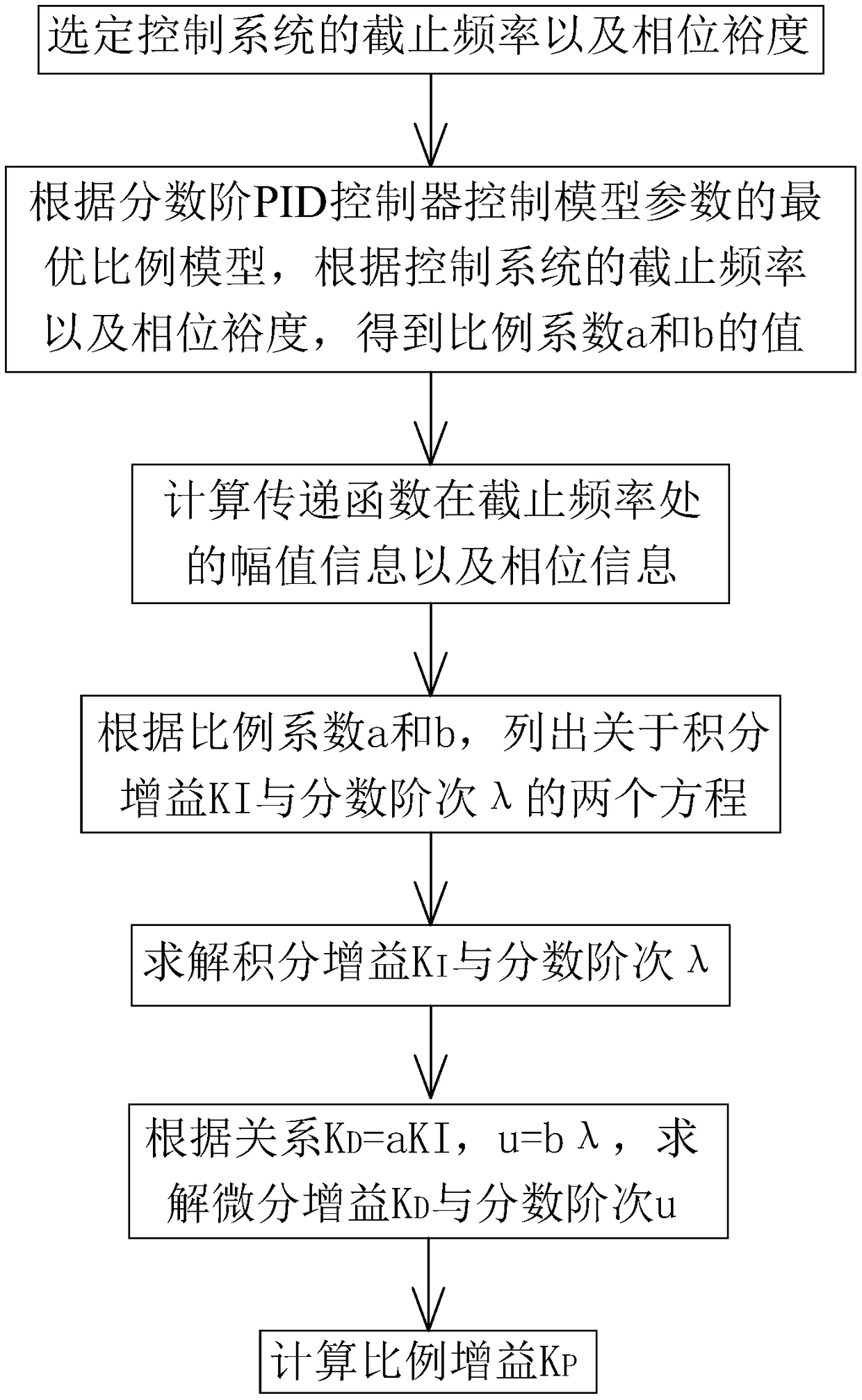
The invention discloses a PID controller design method. A control model of a PID controller is C(s)=Kp(1+K / S<lambda>+K<D>S) in which K<D>=aK, u=blambda, and a and b represent proportional coefficients respectively, and the control model of the PID controller is reset as C(s)=Kp(1+K / S<lambda>+ aKS<blambda>). A transfer function of a controlled object in the control system is set as G(s)=K / (S<3>+tau1S<2>+tau2S). According to the method, the cutoff frequency omegac and phase margin phim are selected; an optimal proportion model of model parameters is controlled according to the fractional order PID controller, and values of the proportional coefficients a and b are obtained according to the cutoff frequency omegac and phase margin phim; amplitude information and phase information of the transfer function in the cutoff frequency omegac are calculated; two equations related to the integral gain KI and the fractional order lambda are listed; the integral gain KI and the fractional order lambda are solved; a differential gain KD and a fractional order u are solved; and the proportional gain KP is calculated. The proportional relation between the integral gain KI and the differential gain KD of the fractional order PID controller as well as the proportional relation between the integral order lambda and the differential order u are established, the freedom degree of parameters of the fractional order PID controller is reduded, and the difficulty in parameter setting is reduced.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Crude oil type near infrared spectrum identification method
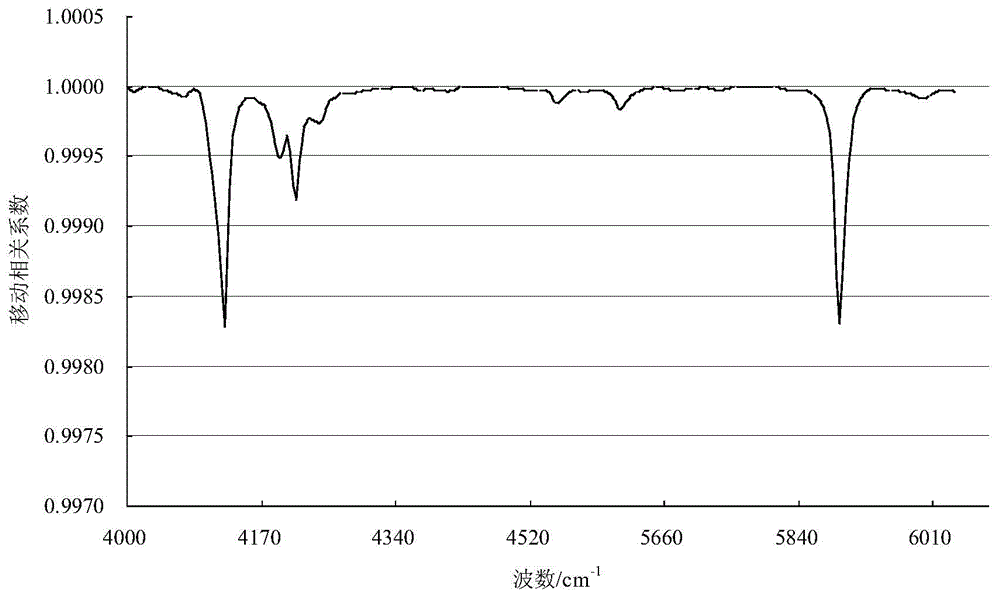
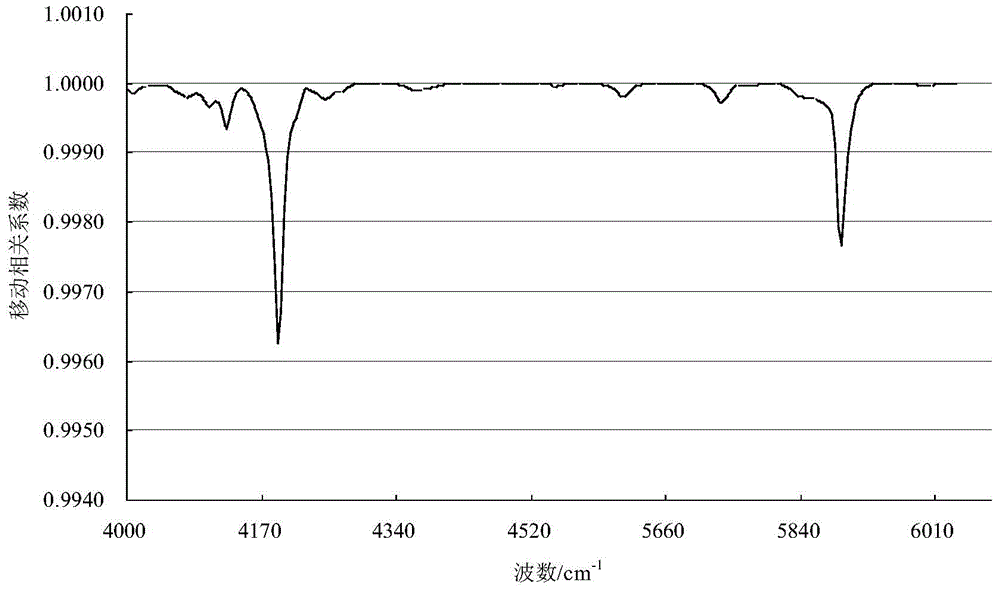
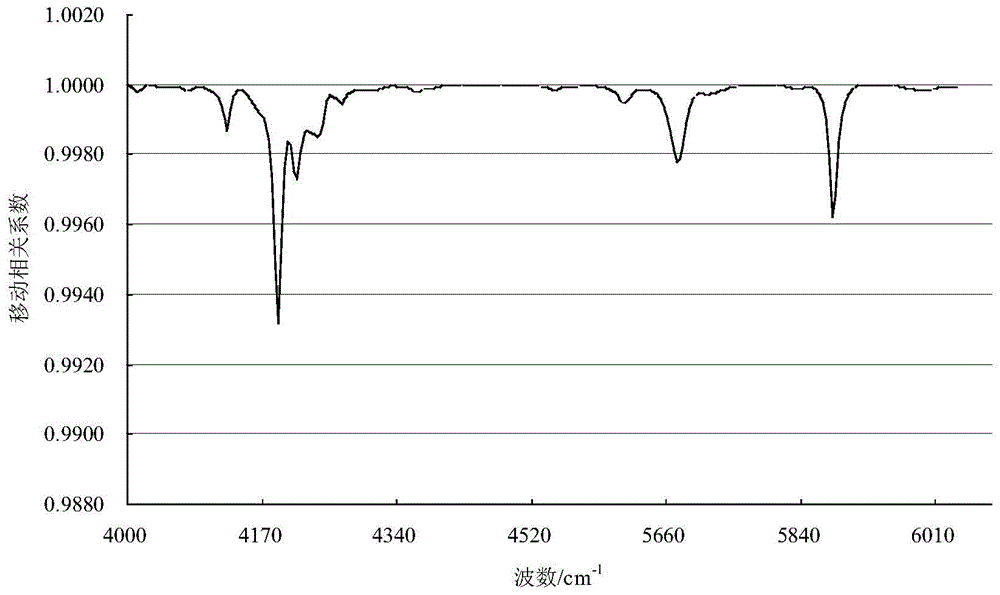
ActiveCN105424641ASmall amount of calculationFast recognitionMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientSpectral database
The invention relates to a crude oil type near infrared spectrum identification method, which comprises that various crude oil samples are collected; after a second order differentiation treatment, the absorbance of the spectrum regions 4628-4000 cm<-1> and 6076-5556 cm<-1> are taken to establish a crude oil sample near infrared spectrum database; the near infrared spectrum database is subjected to main component analysis, and the spectrum database scoring matrixes T and the spectrum database loading matrixes P of the first 14-16 main components are taken; after the second order differentiation treatment, the absorbance of a crude oil sample to be identified in the characteristic spectrum regions form vector x, the main component scoring vector t is calculated, 10-14 crude oil samples having the similar scoring vector t are selected from the spectrum database scoring matrixes T, the spectrums of the samples form an adjacent spectrum database, and the identification parameters of various samples in the adjacent spectrum database on the x are calculated; and the sample same to the crude oil to be identified does not exist if all Qi values are not more than Qi, and if Qi is more than Qt and each mobile correlation coefficients of the sample i is not less than 0.9900, the crude oil to be identified and the sample i in the adjacent database are the same. With the method of the present invention, the identification speed of the unknown crude oil sample can be improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Image edge detection method based on fractional order partial differential
InactiveCN103247047AEasy extractionEasy to detectImage analysisPattern recognitionFractional differential
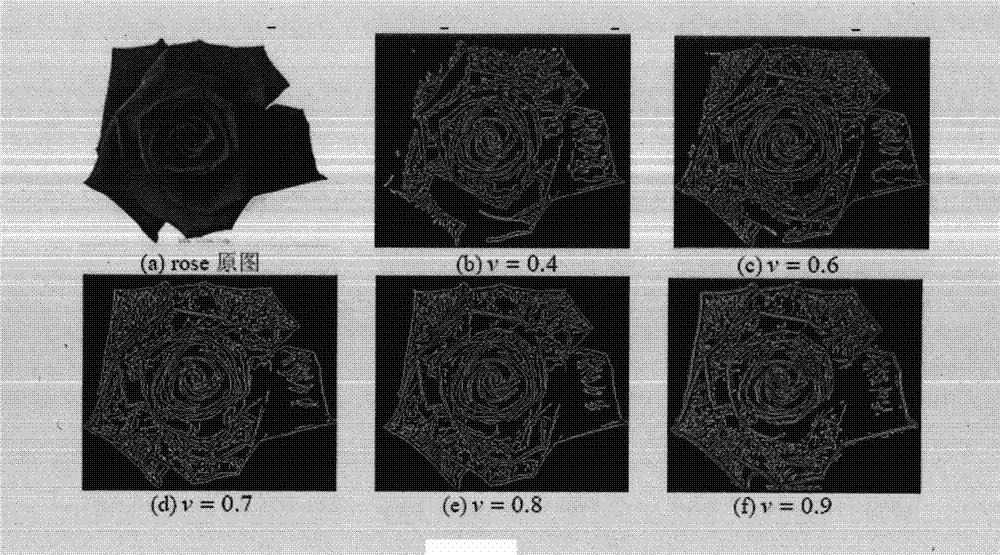
The invention discloses an image edge detection method based on fractional order partial differential, which comprises the following steps: the Sobel operator and a 3*3 pixel neighborhood with the gray-scale function of F (x, y) are subjected to convolution; the convolution sum is subjected to central difference to obtain an integral order differential expression; the integral order differential expression is replaced by a v order differential expression; based on definition of fractional differential, first three items of the fractional differential expression of a digital image substitute values in the v order differential expression; and different results can be obtained through regulation parameter, namely the differential order v. The method can satisfactorily extract edge contour information, has an excellent effect on texture detail detection, is superior to conventional edge detection methods, and satisfactorily achieves the purpose of image edge detection.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Portable human joint parameter estimation method based on IMU (inertial measurement unit)
InactiveCN106344026AHigh precisionReduce mistakesInertial sensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringKinesiologyHuman motion
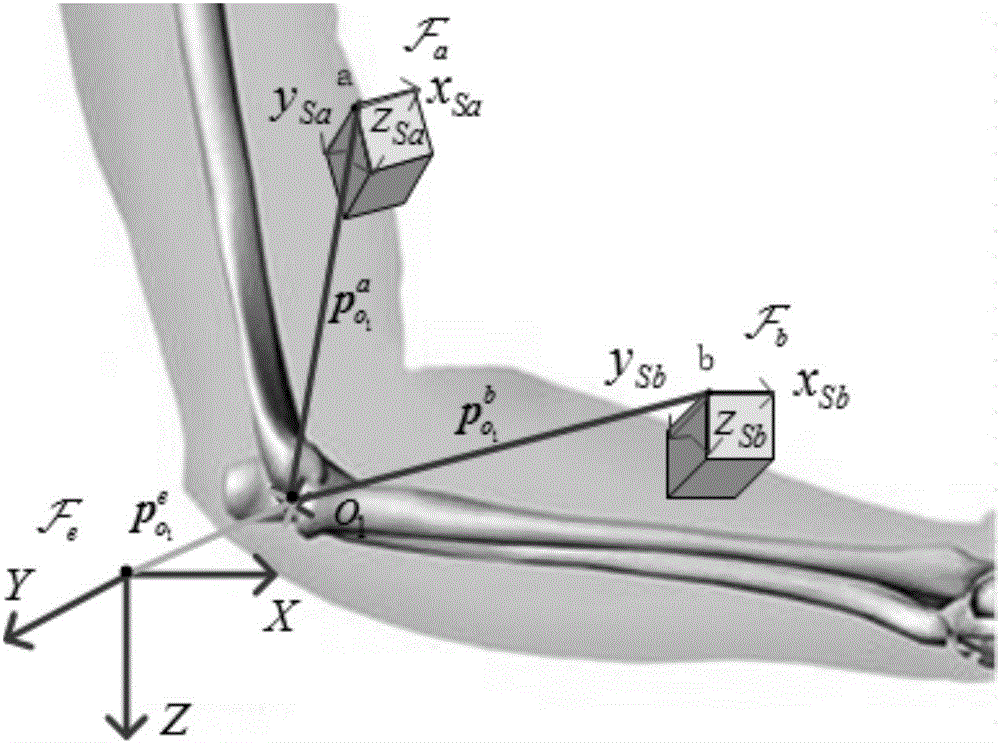
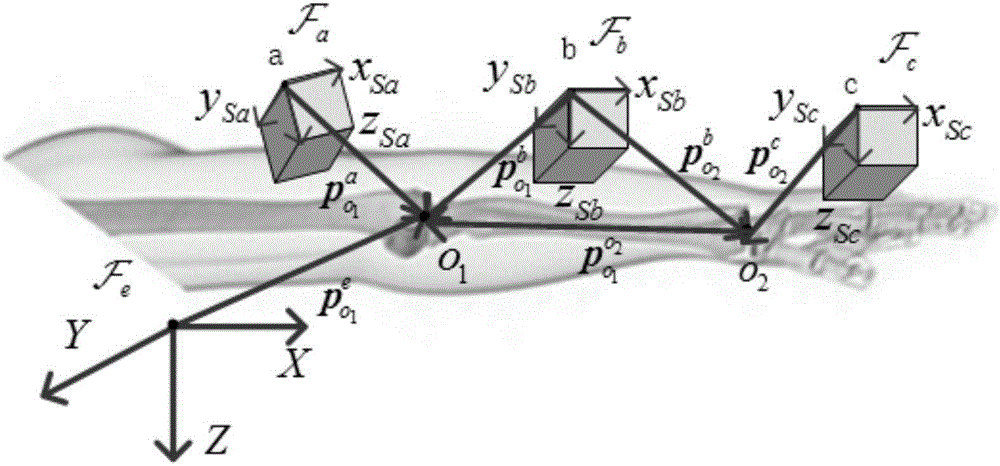
The invention provides a portable human joint parameter estimation method based on an IMU (inertial measurement unit) and relates to a human joint parameter estimation method in order to solve the problems of low precision, high price, inconvenient operation, high time consumption and the like in the prior art. The method comprises steps as follows: step one, a human arm is equivalent to be hinged by three rigid bodies including an upper arm, a front arm and a palm through an elbow joint and a wrist joint, and a coordinate system is defined; step two, a position vector of o1 in Fa is analyzed according to kinesiology, and a second-order differential form, shown in the specification, of P<o1><e> is obtained; step three, a position vector of o1 in Fb is analyzed according to kinesiology, and a second-order differential form, shown in the specification, of P<o1><e> is obtained; step four, a kinematic constraint relation, caused by ball joints, of P<o1> and P<o1> is obtained; step five, an equation set is solved with the least square method, and P<o1> and P<o1> are obtained; step six, the step two to the step five are executed again, and values of P<o2> and P<o2><c> are obtained; step seven, the length of the forearm is calculated. The method is applied to the field of limb measurement.
Owner:苏州坦特拉智能科技有限公司
A method of geostationary satellite orbit uncertainty evolution based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109255096AReduce computing timeHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsNatural satelliteDynamic models
The invention discloses an orbital uncertainty analysis method based on differential algebra technology. Based on Taylor expansion of multivariate functions and polynomial operation framework, and based on the dynamic model of geosynchronous satellite orbit element description, solar pressure to the kinetic model, the third gravitational perturbation and the three perturbation terms of the Earth'soblateness are added in the dynamic model , the right term of the dynamic model is expanded along the nominal orbit by Taylor expansion, the expansion polynomial with initial deviation as variable isobtained, Under the frame of differential algebra, the orbital state expressed by the polynomial with the initial deviation as variable at any time is obtained, and the concrete value of the initialdeviation is brought into the polynomial result to obtain the state of the final spacecraft. The invention analyzes the optimal expansion order, the balance calculation time and the calculation precision according to different perturbation forces. The method can be used to analyze the orbit evolution of geostationary satellites with initial state deviation and parameter uncertainty, and can also be used in other spacecraft orbit evolution and attitude evolution missions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Engine bench system control system
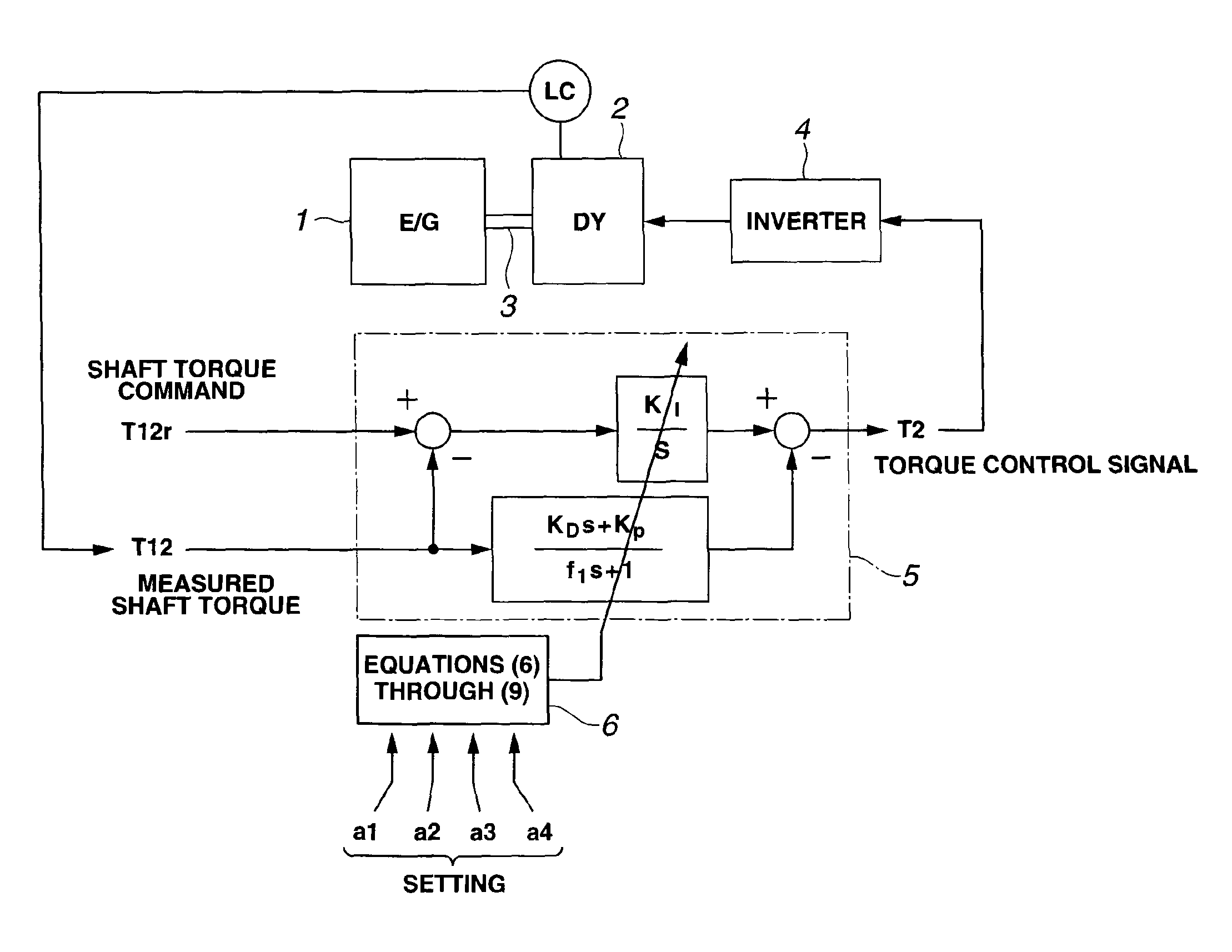
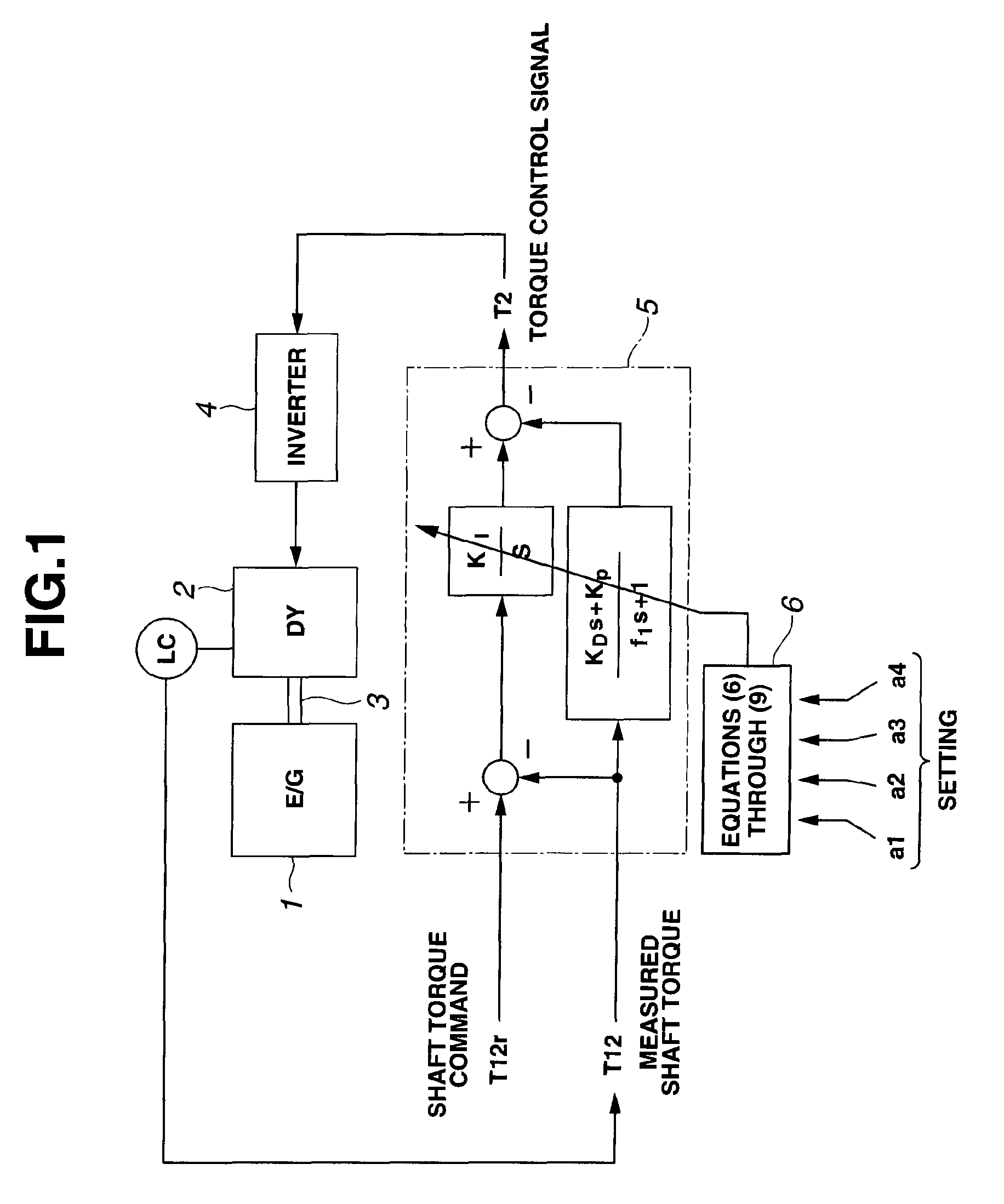
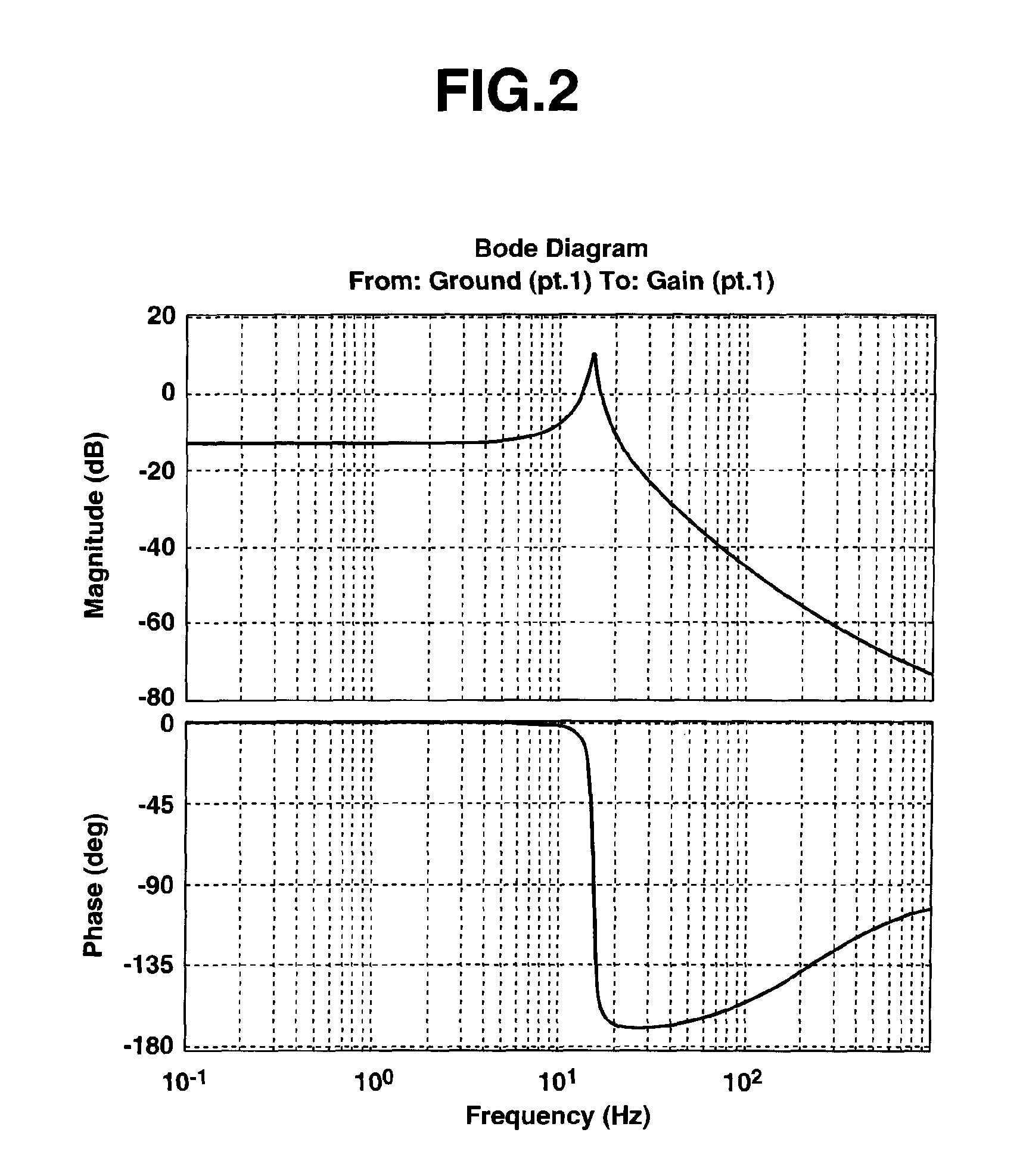
It is a challenge to make it possible to produce a resonance suppression effect, and perform a stable control even in a case where a spring rigidity of a shaft significantly varies. The challenge is achieved as follows. In an engine bench system in which an engine 1 to be tested and a dynamometer 2 are coupled together by a coupling shaft 3, and a shaft torque control of the dynamometer is performed, a controller 5 includes: an integral element having an integral coefficient KI for a deviation (T12r−T12) between a shaft torque command T12r and a measured shaft torque T12; a differential element having a differential coefficient KD for the measured shaft torque T12; and a proportional element KP for the measured shaft torque T12. The controller 5 obtains a torque control signal T2 by subtracting the differential element and the proportional element from the integral element. Control parameters (KI, KP, KD, f1) are determined according to control characteristic parameters (a4, a3, a2, a1) set in a function calculation section 6, inertia moments J1, J2 of the engine and the dynamometer, and spring rigidity K12 of the coupling shaft.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Method of on-track detection for MTF (modulation transfer function) of interference hyperspectral imager
ActiveCN102692273AImproved method for calculating MTFControl impactInterferometric spectrometrySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Data graph
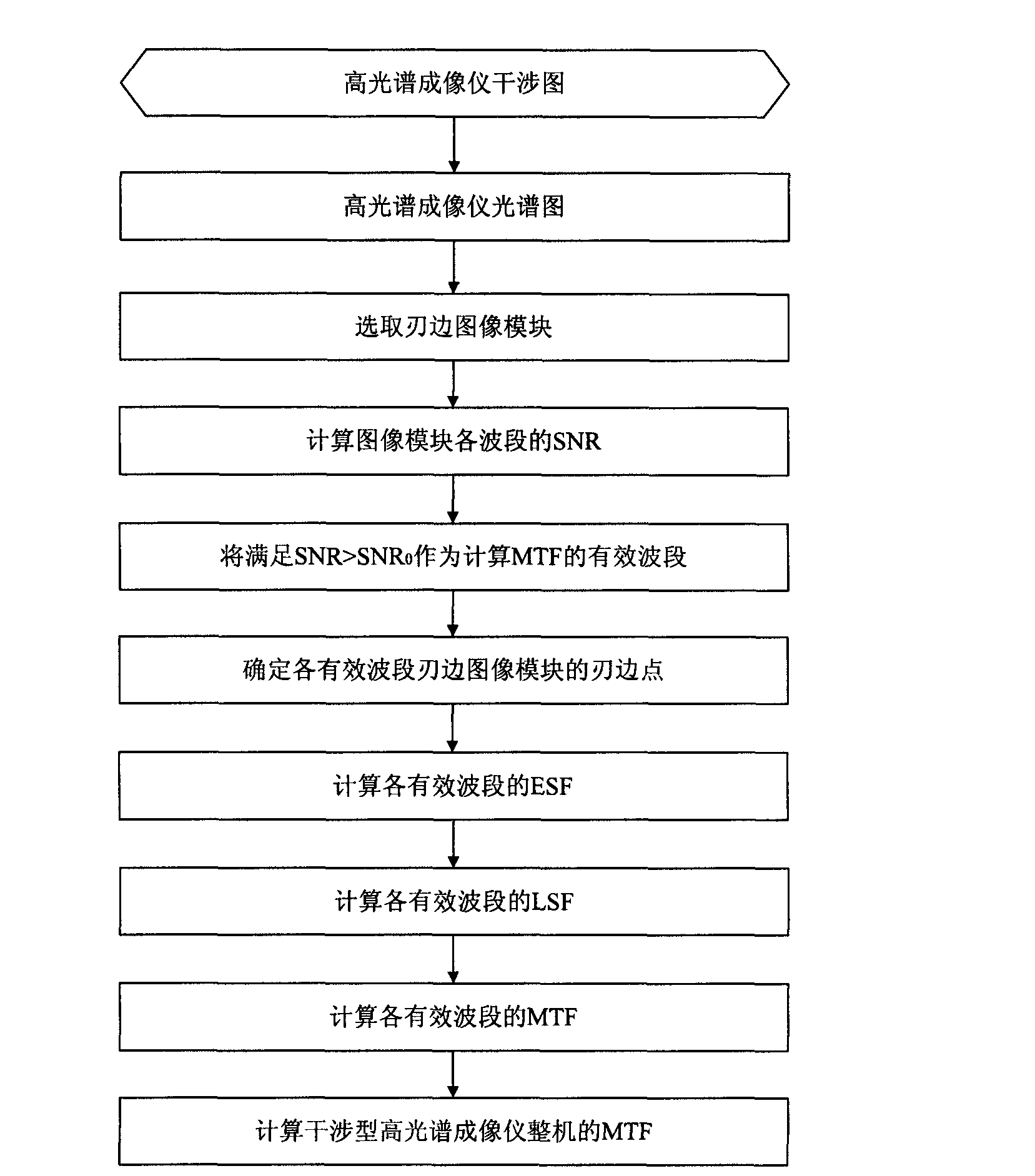
A method of on-track detection for MTF (modulation transfer function) of an interference hyperspectral imager includes: firstly, reading an interference data graph of the hyperspectral imager and subjecting interference data of the hyperspectral imager to discrete inverse discrete Fourier transformation to obtain a spectral data graph of the interference hyperspectral imager; secondly, selecting a 'knife-edge' image module from the spectral data graph of the hyperspectral imager and calculating proper effective wavebands of the MTF of the interference hyperspectral imager according to SNR (signal to noise ratio) of the image module; thirdly, extracting knife-edge points from the knife-edge image module in the effective waveband, and fitting the knife-edge points to form ESF (edge spread function); fourthly, subjecting the ESF to differential computing, fitting results of differential computing to obtain LSF (linear spread function), and subjecting the LSF to discrete Fourier transformation to obtain the effective wavebands of the MTF of the interference hyperspectral imager; and fifthly, averaging the effective wavebands of the MTF to finally obtain overall MTF of the interference hyperspectral imager.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Fractional differential-based multi-feature combined sparse representation tracking method
InactiveCN106530329AImplement Adaptive UpdatesOvercoming the poor ability of single feature to describe the targetImage enhancementImage analysisFractional differentialFeature extraction
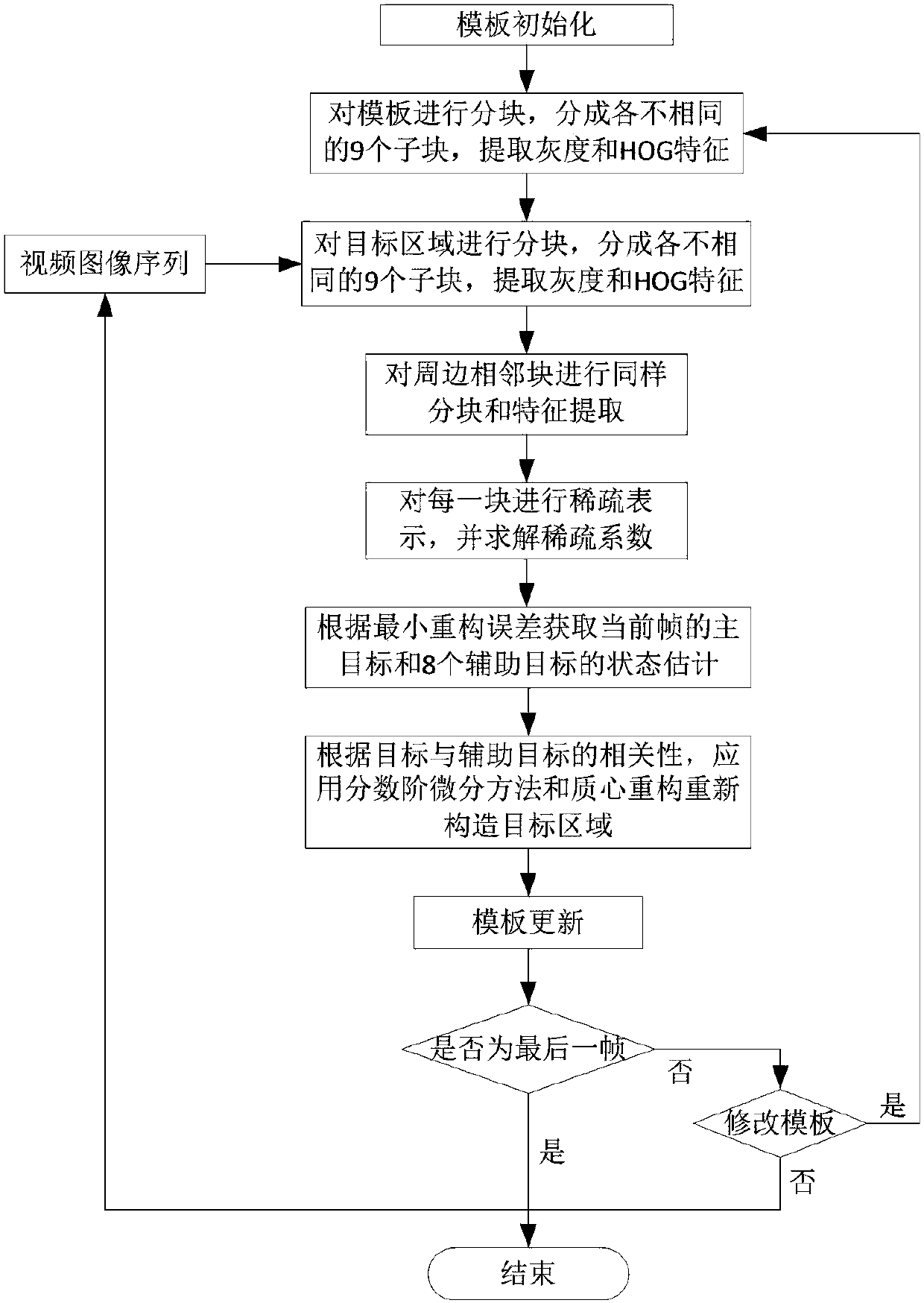
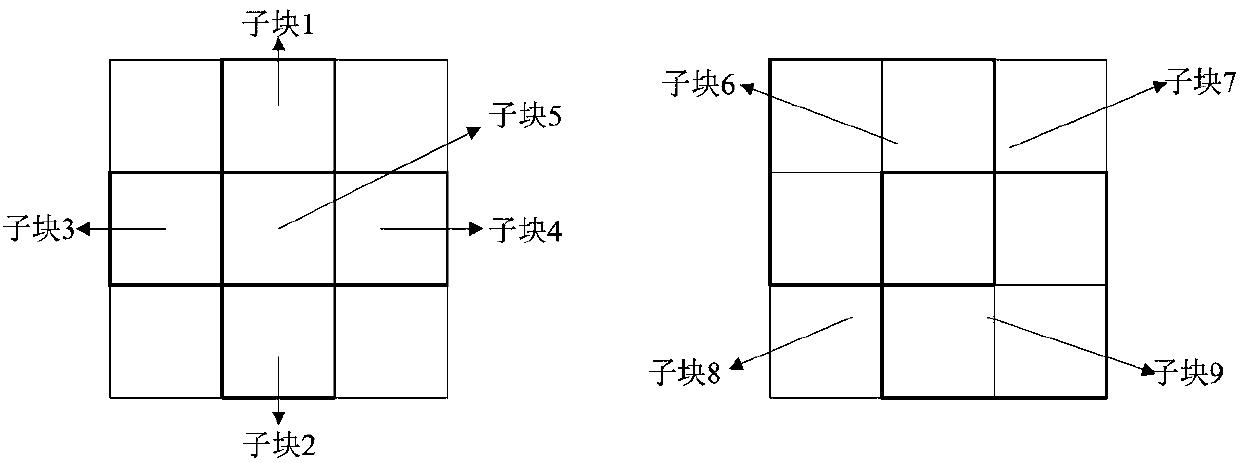
The invention provides a fractional differential-based multi-feature combined sparse representation tracking method. The method includes the following steps: in a frame of particle filtering, first, performing partitioning processing on a target image region, dividing the target region into 9 related and unequal subblocks according to the features of the target region, extracting the gray scale feature and HOG feature of each subblock, combining the two features to perform sparse representation on a target subblock, and also performing the same feature extraction and sparse representation on 8 adjacent regions around the target; then, adopting a nucleating accelerated neighbor gradient algorithm to jointly solve sparse coefficients of 9 candidate particles; and finally, regarding target blocks in different positions as different categories, utilizing a block of the same category as a candidate particle block and a representation coefficient in a dictionary to reconstruct the block, and building a likelihood function according to a reconstruction error to determine an optimal candidate particle, thereby realizing accurate tracking of a main target and 8 auxiliary targets.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
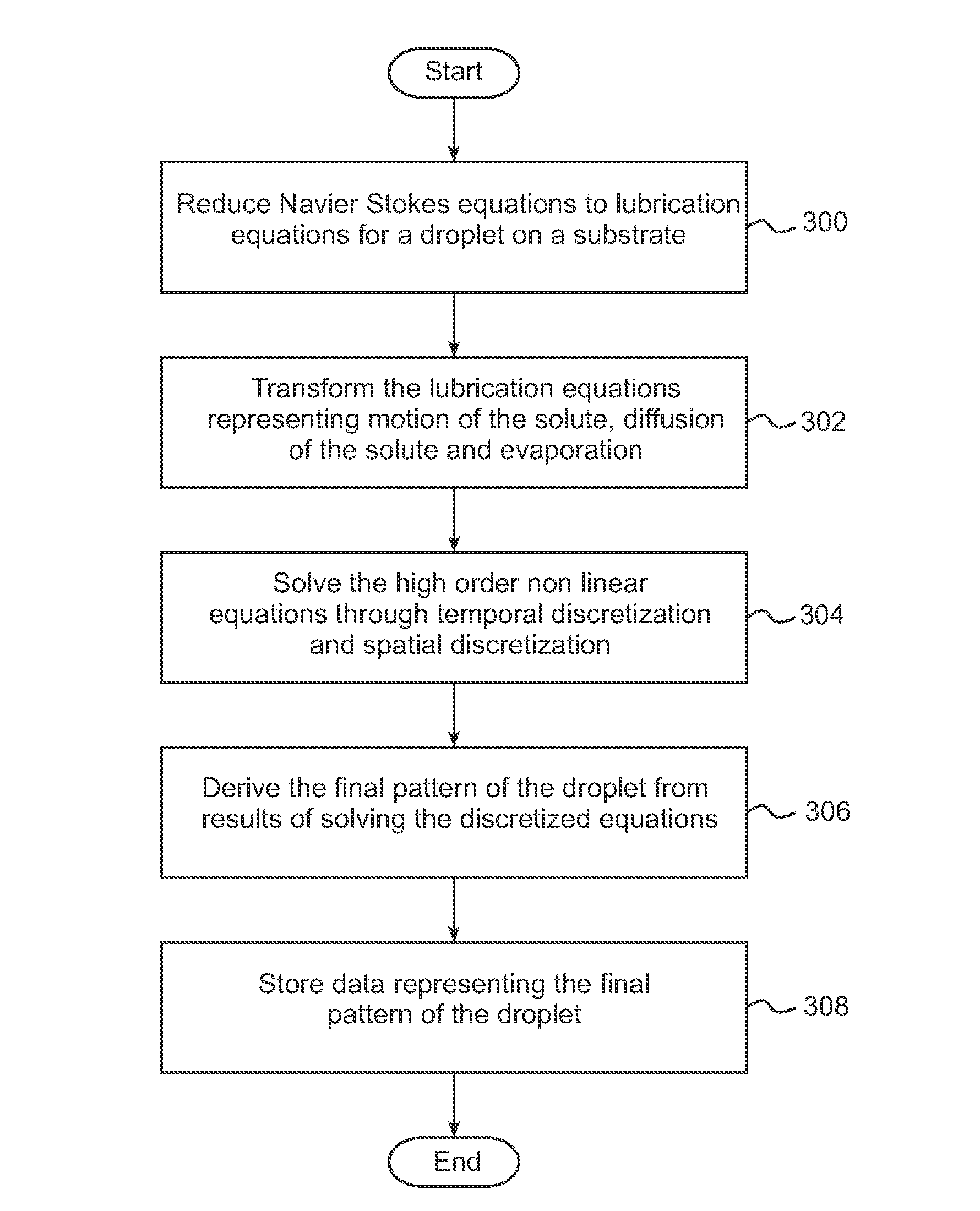
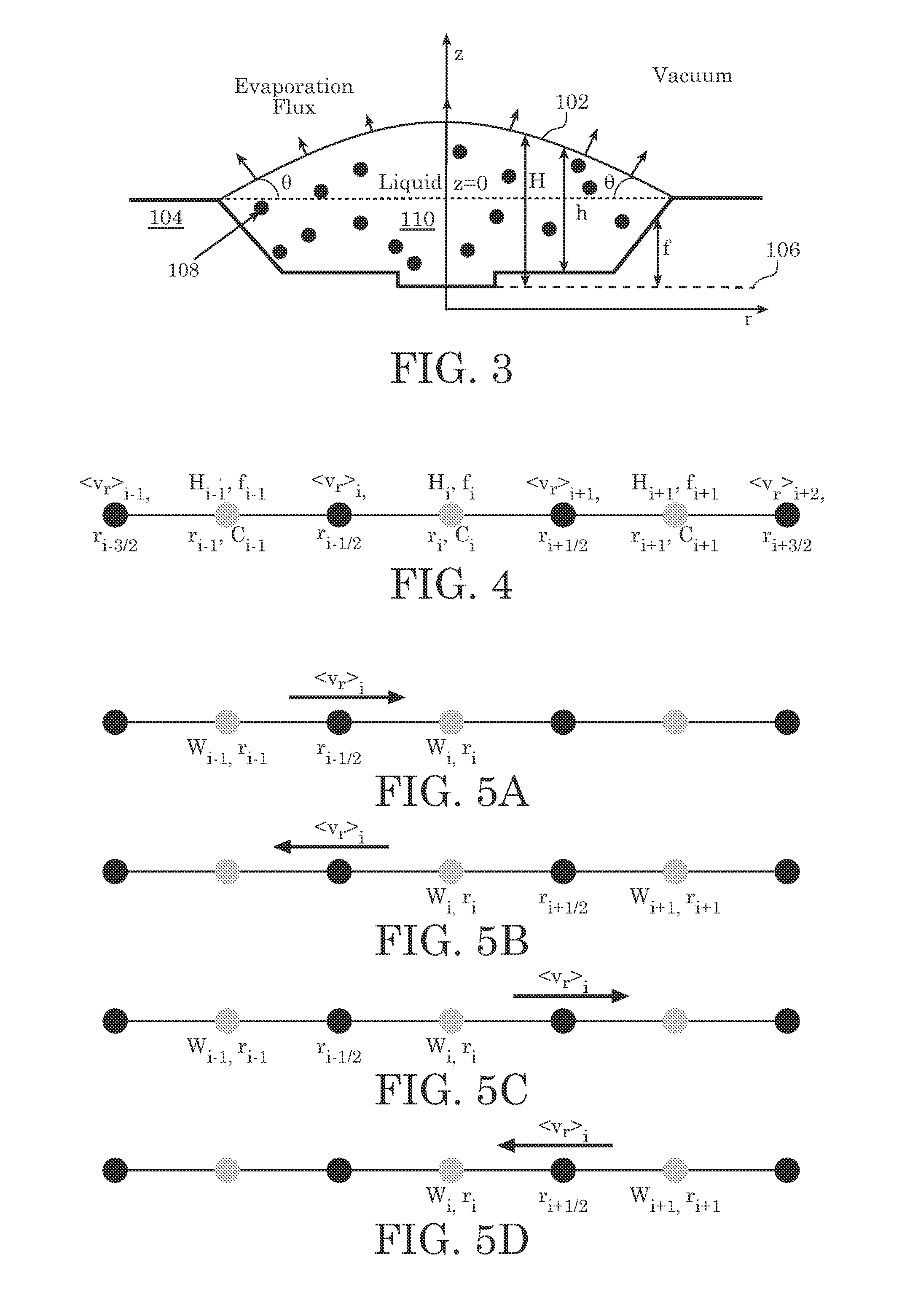
Upwind Algorithm for Solving Lubrication Equations
InactiveUS20110093241A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationFinite difference equationsDifferential of a function
An embodiment of the present invention may be a system or method for simulating a physical process. The physical process being simulated may be in a droplet. The process being simulated may be the drying of a droplet on a substrate. Simulating the physical process may include using a finite difference scheme to approximate a differential of a function. The function may be dependent on a plurality of variables. The location in space at which one or more of the variables is evaluated may depend on the sign of one or more of the variables and upon which portion of the finite difference equation is being evaluated.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
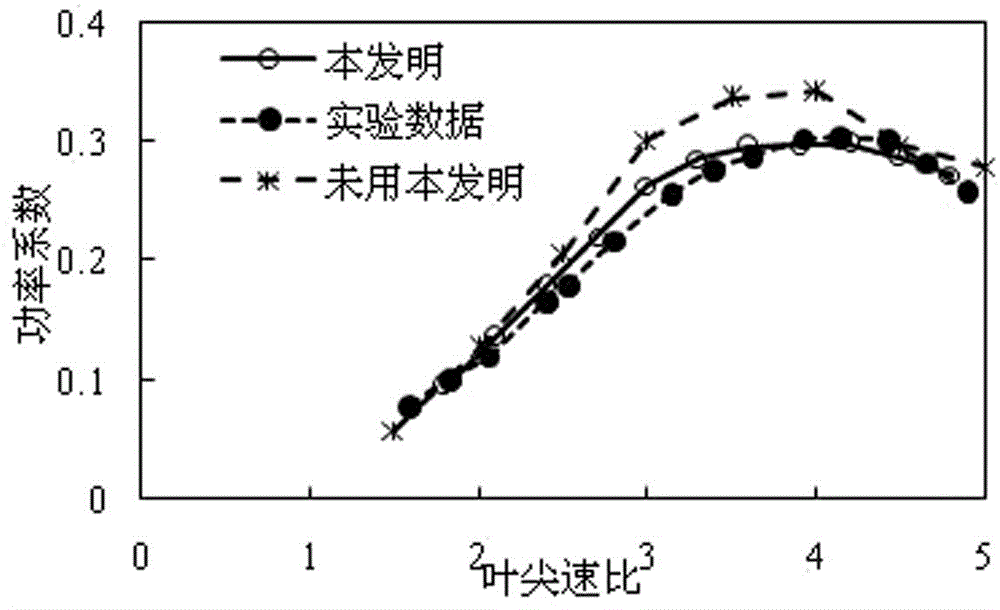
Three-step three-order pre-estimation correcting method for wind wheel vortex line control equation discretion
InactiveCN104832370AImprove stabilitySpeed up iterationWind motor controlMachines/enginesDifferential of a functionTurbine
The invention discloses a three-step three-order pre-estimation correcting method for wind wheel vortex line control equation discretion. According to the method, when a vortex convection control equation is solved according to a free vortex back track method, a linear display three-step method is adopted for a time step differential for pre-estimation, an implicit linear three-step method is used as a corrector step, a three-step pre-estimation correcting differential format for solving a vortex line control equation is formed, and three-order precision is obtained. By the adoption of the method, iteration stability and iteration speed are improved when the non-constant aerodynamic characteristic of a wind turbine is calculated according to the free vortex back trace method, the calculation time is greatly shortened, and the calculation accuracy can be improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
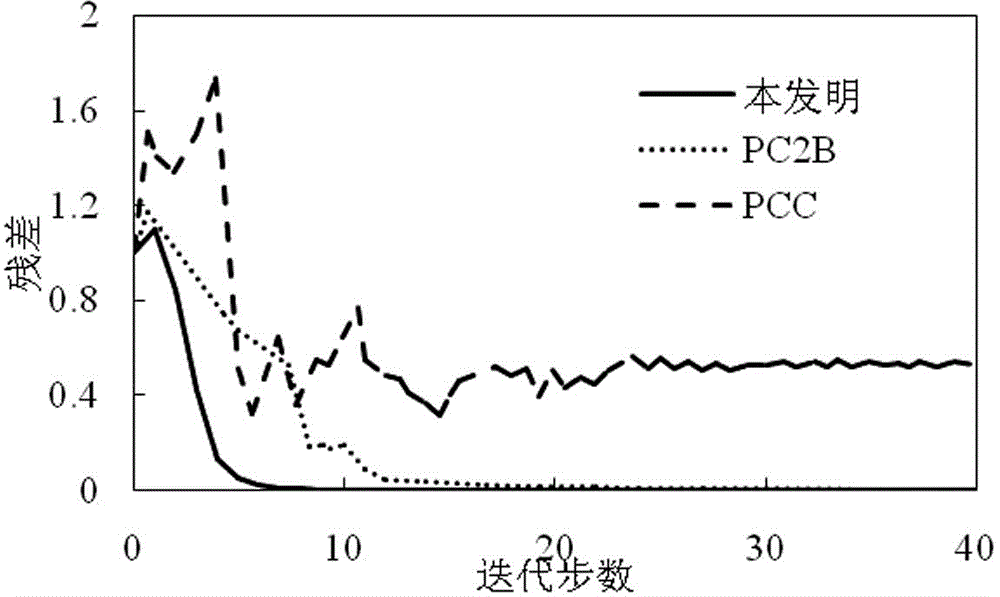
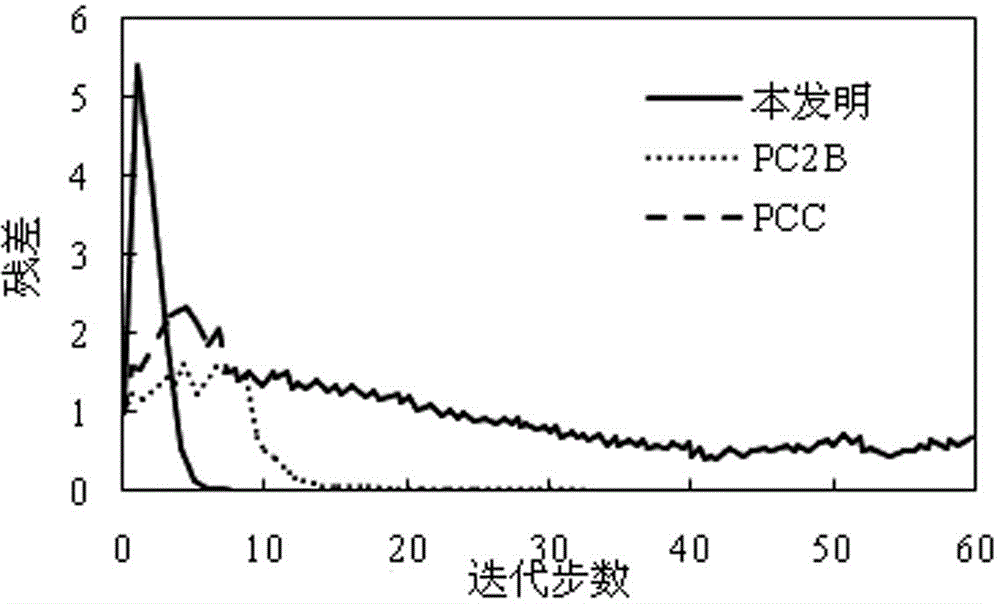
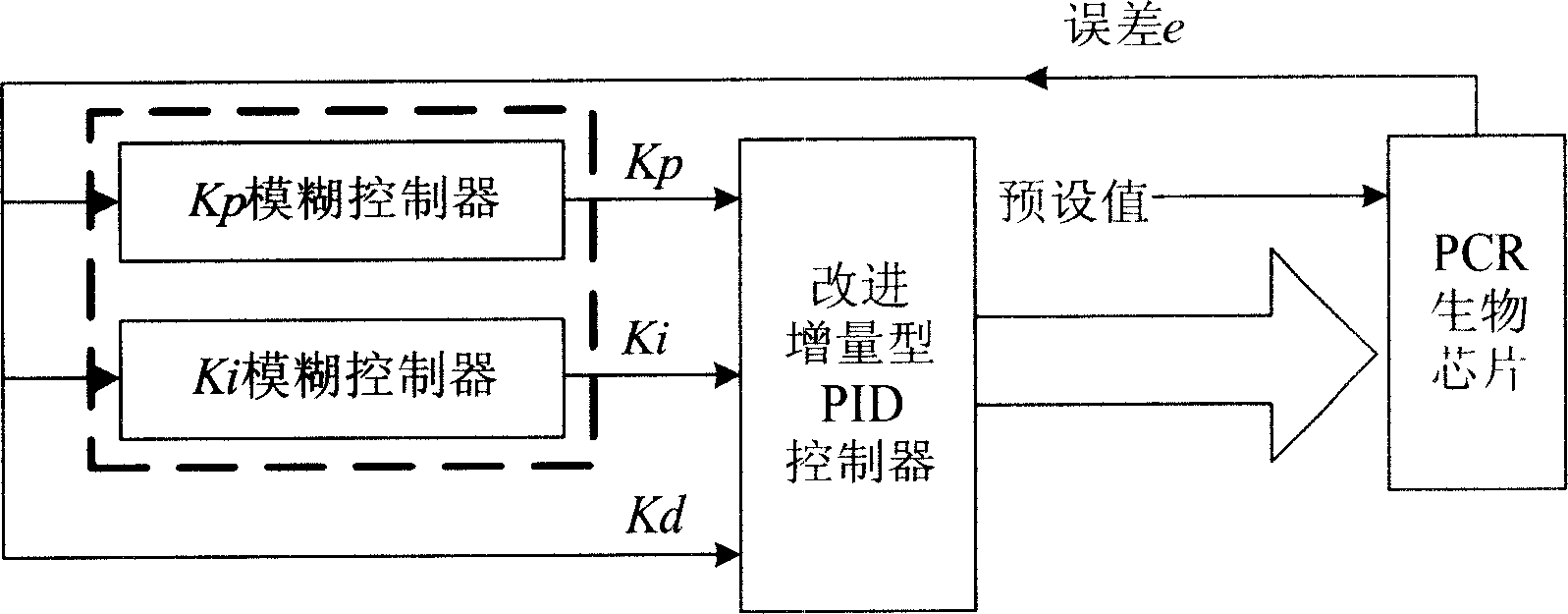
Polymerase chain reaction biochip temperature control method
InactiveCN1710090AHigh amplification efficiencyGood temperature control effectFermentationTemperature controlStable state
The polyase chain-reaction biochip temperature control method includes: Set up integrating factor, when the error is greater, make the controller reach output saturation in a short time, the temperature rises or drops at full speed, relatively weaker controller saturation degree has guaranteed very fast speed of desaturation. When the error is less, uses ordinary integrating function to dispel the stable state error after the desaturation. Set up suitable factor of proportionality, enter the false integrating saturated condition fast with the auxiliary controller when the error is greater. Use the integrating function to resist the exceed adjusting when the error is less, uses ordinary proportion function to output steadily after the desaturation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
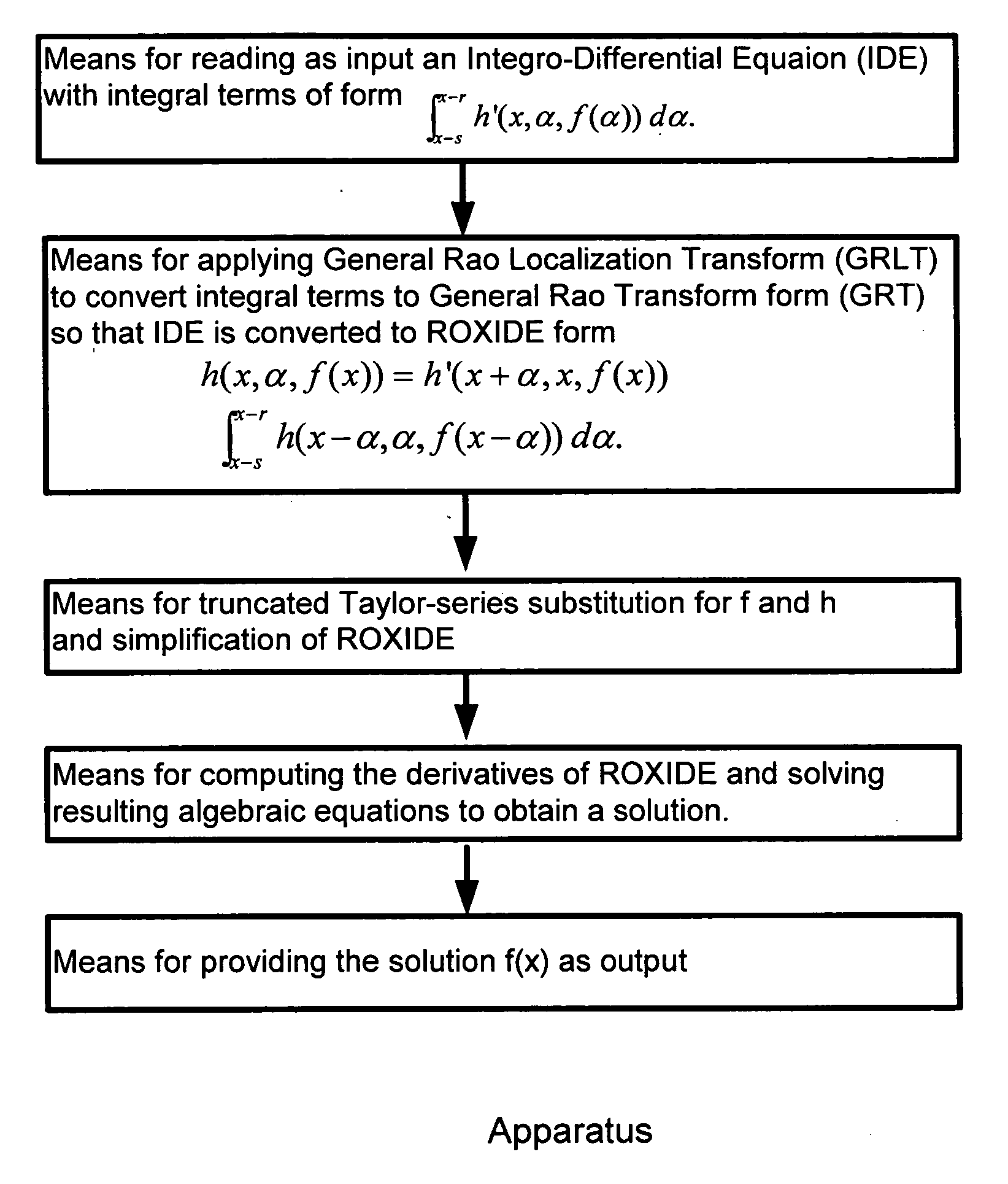
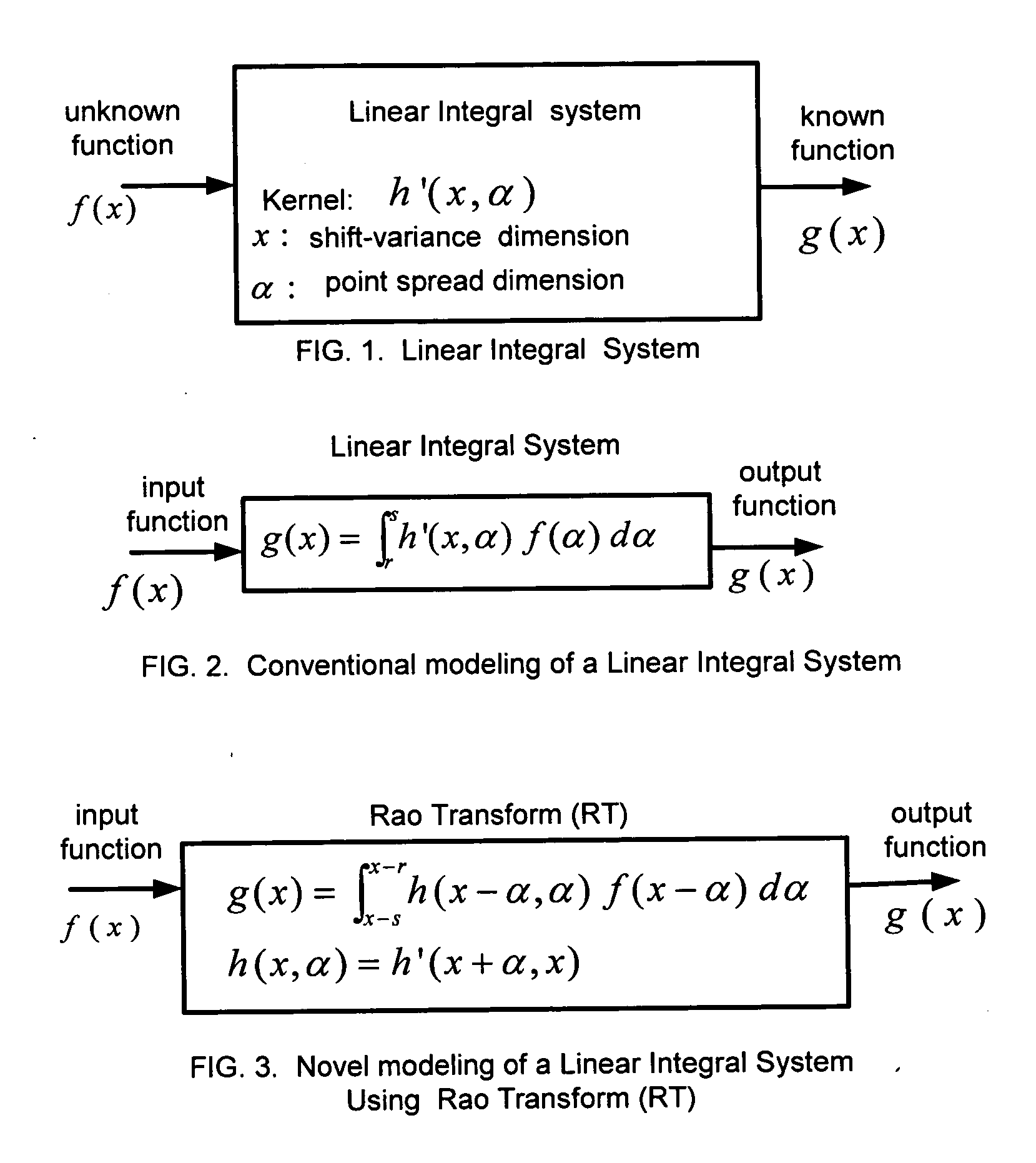
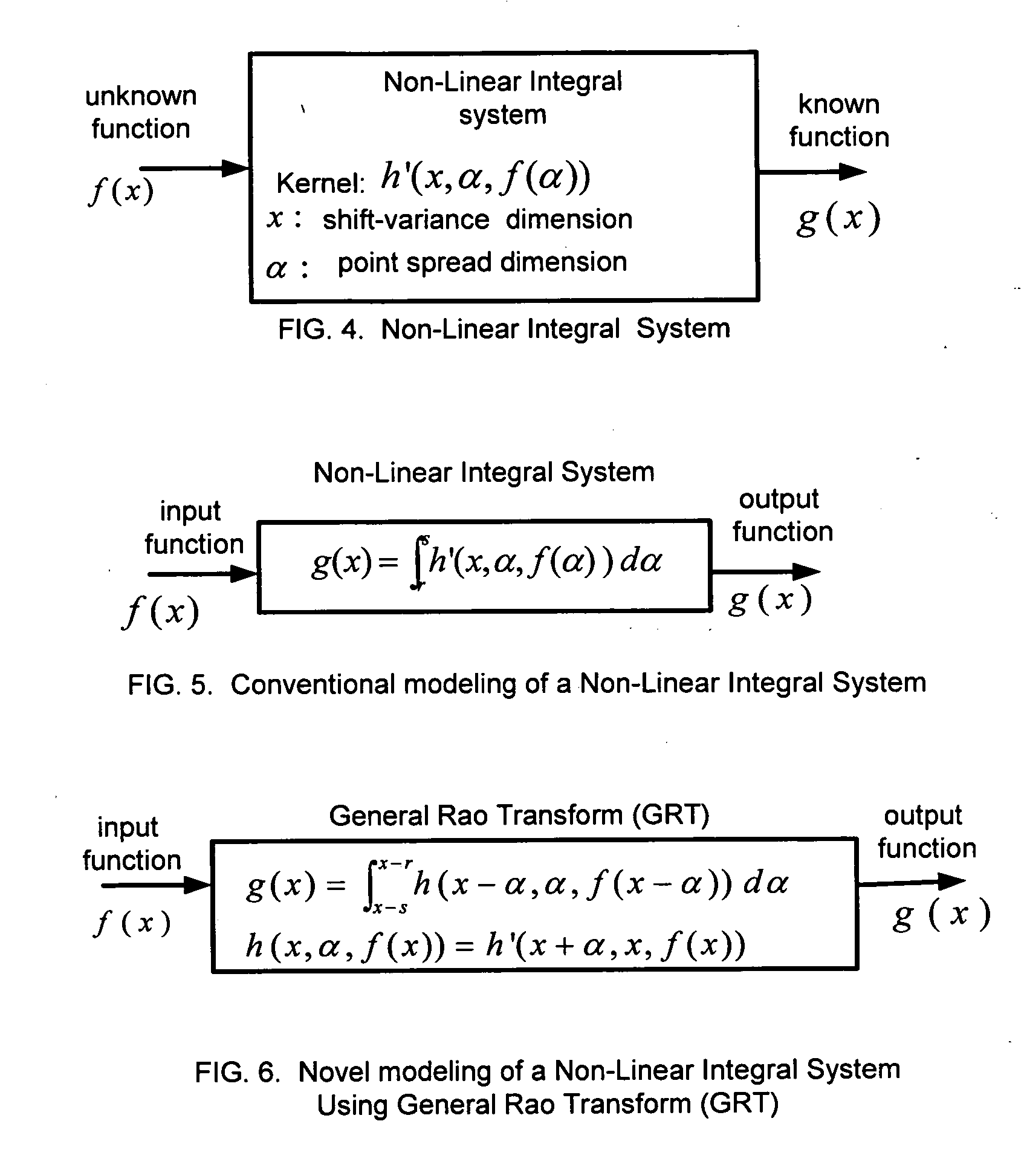
Unified and localized method and apparatus for solving linear and non-linear integral, integro-differential, and differential equations
InactiveUS20060111882A1Efficiently compute valueComplete efficientlyComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmDifferential of a function
This invention is based on a new class of mathematical transforms named Rao Transforms invented recently by the author of the present invention. Different types of Rao Transforms are used for solving different types of linear / non-linear, uni-variable / multi-variable integral / integro-differential equations / systems of equations. Methods and apparatus that are unified and computationally efficient are disclosed for solving such equations. These methods and apparatus are also useful in solving ordinary and partial differential equations as they can be converted to integral / integro-differential equations. The methods and apparatus of the present invention have applications in many fields including engineering, science, medicine, and economics.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
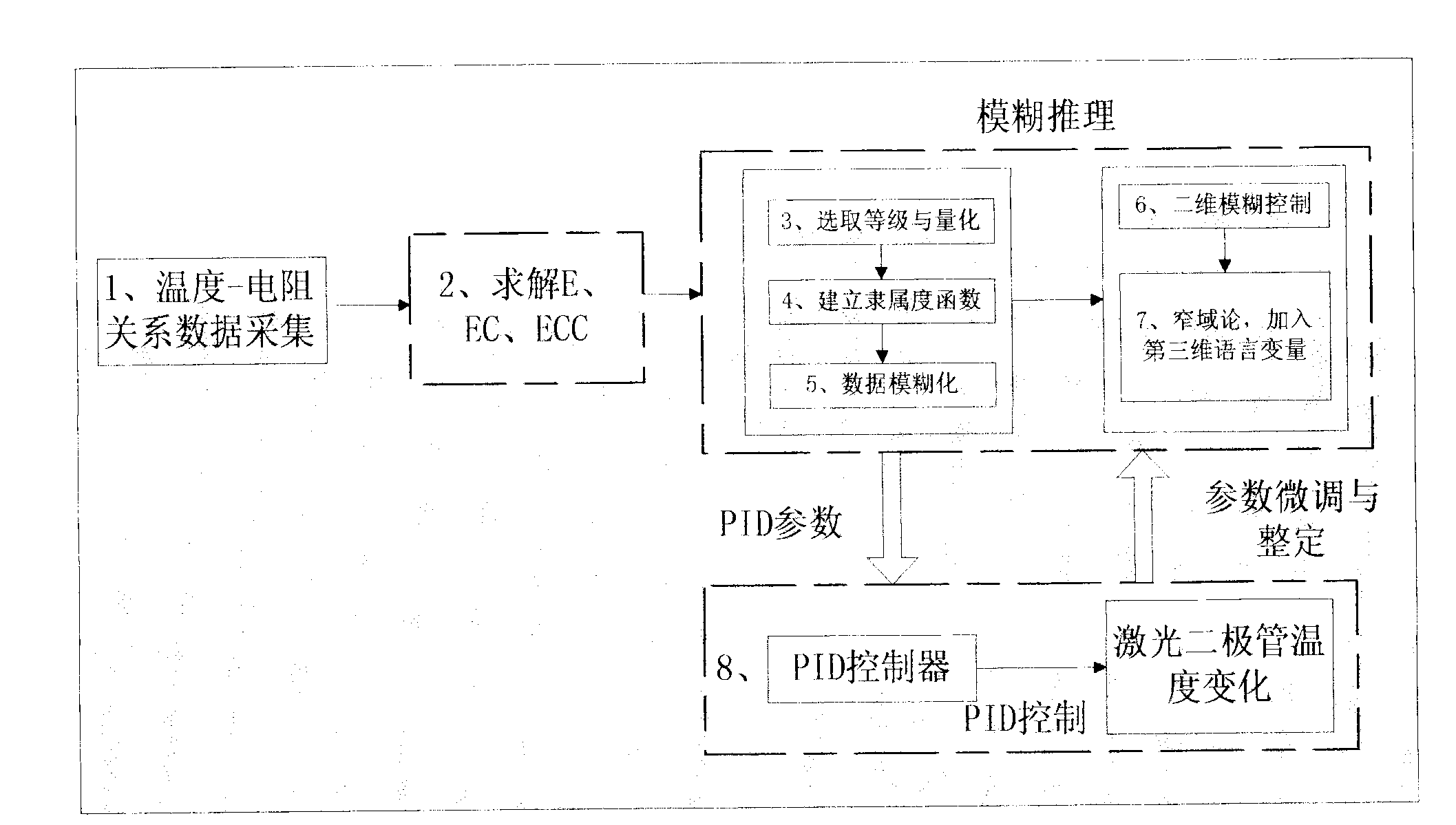
Approximate three-dimensional setting method of proportion integration differentiation (PID) temperature control parameters of laser device based on narrow field theory
ActiveCN103064447AReduce shockQuick responseLaser detailsTemperature control using electric meansTemperature controlProportion integration differentiation
The invention discloses an approximate three-dimensional setting method of proportion integration differentiation (PID) temperature control parameters of a laser device based on a narrow field theory. The method is presented when PID temperature control is carried out to the temperature of a laser diode, considering control precision and system expense. The method optimizes the tracking error terms of performance indicator function, introduces the differential term of the tracking error to the indicator function, presents an approximation algorithm based on a first dimension E and a second dimension EC variable to set up an approximate third dimension linguistic variable ECC, through the introduction of the third dimension ECC, and sets up a fuzzy rule to control, wherein the E stands for the deviation of a measure value and a set value, the EC stands for the deviation of the E, and the ECC stands for the deviation of the EC. The method measures fitting data and carries out fuzzy reasoning, carries out fuzzy judgment by optimizing the fuzzy rule, and carries out fuzzy control.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
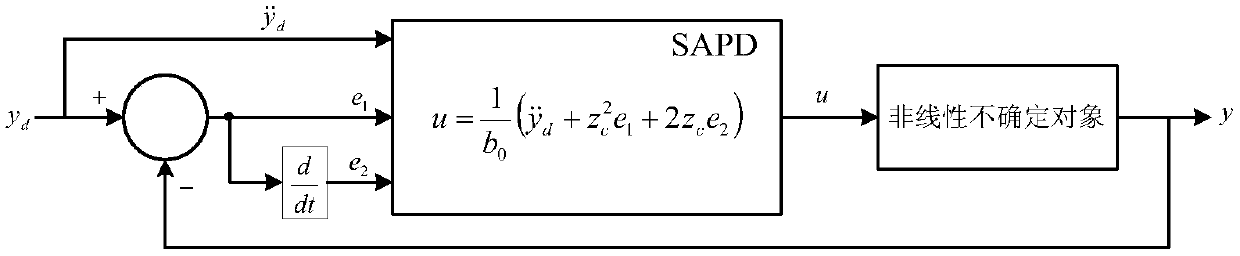
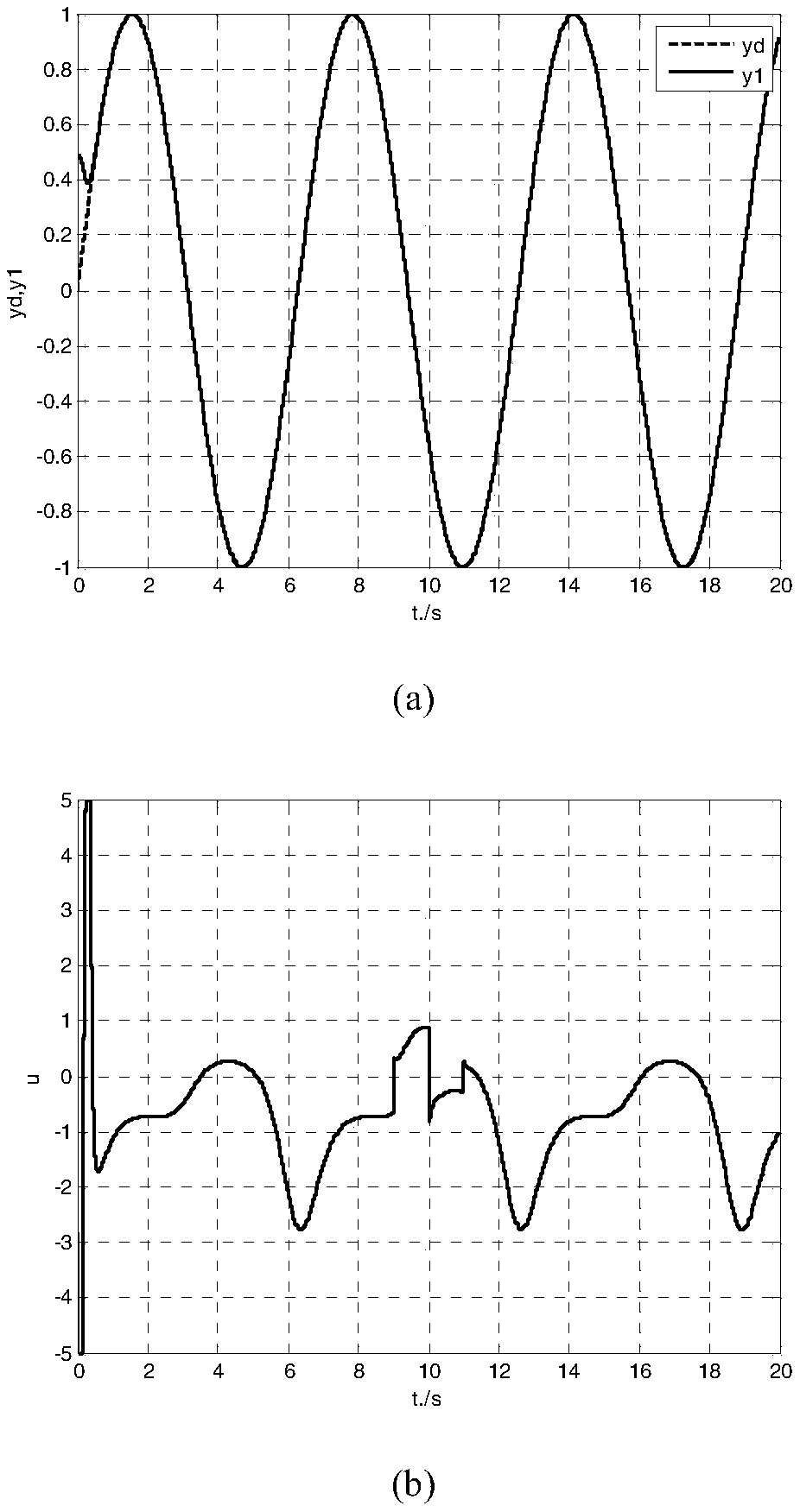
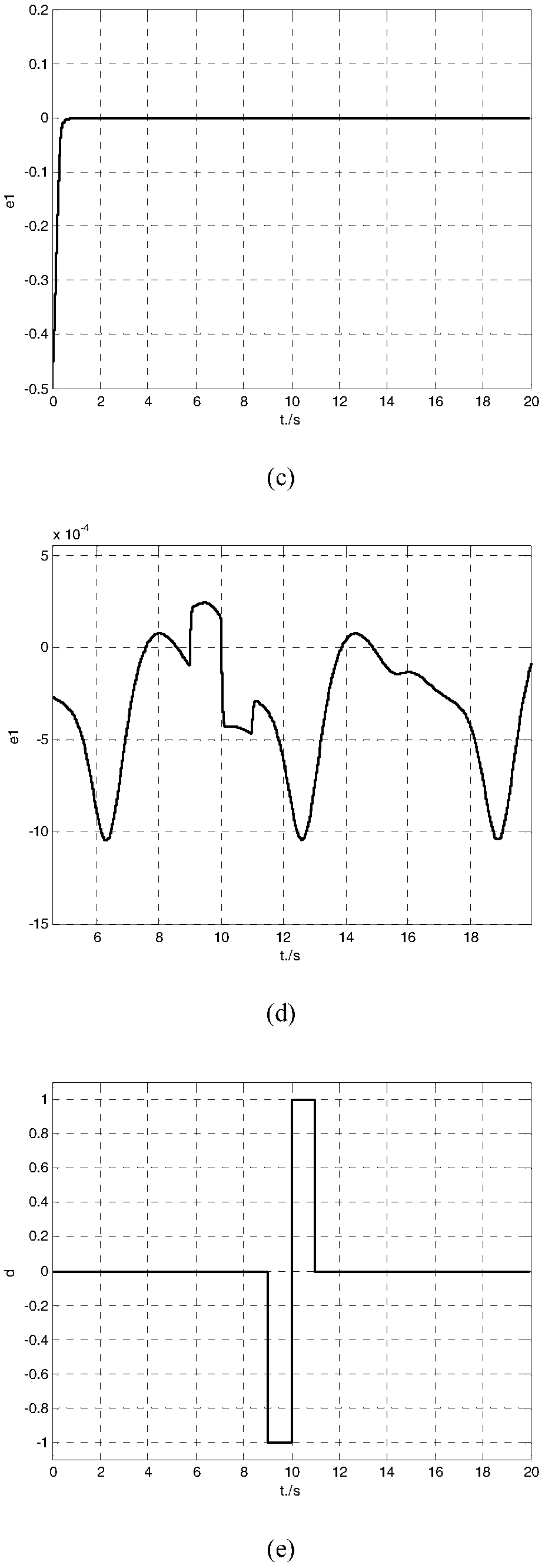
Two-speed adaptive proportional-derivative control method
InactiveCN109254529AGood anti-disturbance robust performanceSimple structureControllers with particular characteristicsAviationComponent Object Model
For the control problem of a non-affine nonlinear uncertain system, the invention relates to a two-speed adaptive proportional-derivative (2SAPD) control method independent of a controlled object model. According to the control method in the invention, system dynamics and internal and external uncertainty are defined as total disturbance; therefore, the non-affine nonlinear uncertain system is converted into a linear uncertain system, so that an error dynamics system under total disturbance excitation is constructed; thereby, a two-speed adaptive proportional-derivative control model by takingthe central speed factor as the core is designed; the facts that a closed-loop control system composed of a 2SAPD controller has the global asymptotic stability robustness and the 2SAPD controller also has good anti-disturbance robustness are theoretically analyzed; and the two-speed adaptive proportional-derivative control method in the invention has wide application value in the fields of power, mechanisms, chemical engineering, traffic, aviation, spaceflight and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Inductance current interrupted mode fractional order switch converter symbol analysis method
ActiveCN106227925AAvoid deep discussionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement OrderPeak value
The invention discloses an inductance current interrupted mode fractional order switch converter symbol analysis method combining a harmonic wave balance principle; the method converts differential operation relating to status variable fractional order in a converter into differential operators, and combines all differential operators into an opposite angle symbol matrix, thus converting a non-integer order calculus operation solving process into a matrix operation and linear equation (group) solving process. Compared with a conventional normal analysis method, aiming at the fractional order switch converter, of building an Oustaloup filter approximation model in a Matlab / Simulink, the novel method can parse and analyze converter status variable ripple peak-to-peak value size and influences on converter work status by energy storage element order changes, can fast obtain a status variable stable state periodic analytic solution, and can parse status variable harmonic wave components.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
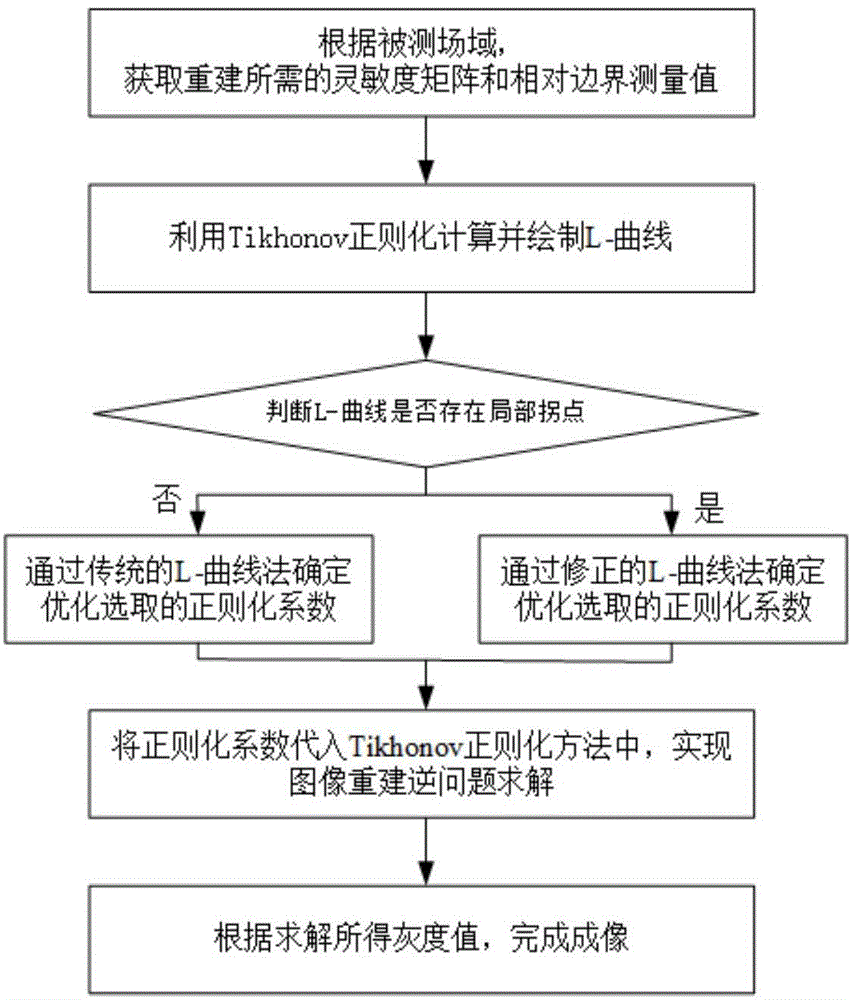
Corrected L-curve electrical tomography reconstruction method based on second-order differential
ActiveCN104535294ABroaden model applicabilitySolve non-applicable problemsHydrodynamic testingReconstruction methodPeak value
The invention provides a corrected L-curve electrical tomography reconstruction method based on the second-order differential. The method is suitable for bubble flow tomography and includes the steps that according to a measured field domain, a relative boundary measured value vector b and a sensitivity matrix A which are needed for reconstruction are acquired; through Tikhonov regularization, an L-curve is calculated and drawn; whether a local inflection point exists in the L-curve or not is judged; if the local inflection point does not exist, an optimally-selected regularization coefficient is determined through an L-curve method; if the local inflection point exists, an optimally-selected regularization coefficient is determined through the corrected L-curve method. The method includes the steps that the local inflection point of the curve is determined by calculating a second largest peak value of the L-curve second-order differential, and the regularization coefficient corresponding to the local inflection point serves as the optically-selected coefficient; the regularization coefficient is substituted into Tikhonov regularization, and an image reconstruction inverse problem is solved; imaging is conducted. By the adoption of the method, the electrical tomography inverse problem can be accurately solved, and image reconstruction quality is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Single-speed adaptive proportional-derivative control method
InactiveCN109541936AGood anti-disturbance robust performanceGlobal stabilityControllers with particular characteristicsAviationChemical industry
The invention discloses a single-speed adaptive proportional-derivative control method which does not rely on a controlled object model for the control difficulty of the non-affine nonlinear uncertainsystem. According to the control method, the system dynamic and internal and external uncertainty are defined as sum disturbance, so that the non-affine nonlinear uncertainty system is transformed into a linear uncertainty system, and then an error dynamic system under the sum disturbance excitation is constructed, and the single-speed adaptive proportional-derivative controller model with the speed factor as the kernel is designed accordingly. Theoretical analysis shows that the closed-loop control system composed of SAPD controller not only has global asymptotic stability and robustness, but also has good anti-disturbance robustness. The invention has wide application value in the fields of electric power, machinery, chemical industry, transportation, aviation and aerospace.
Owner:曾喆昭
Nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum
ActiveCN107402903AImprove calculation accuracyEasy to useComplex mathematical operationsNormal densityAnalytical problem
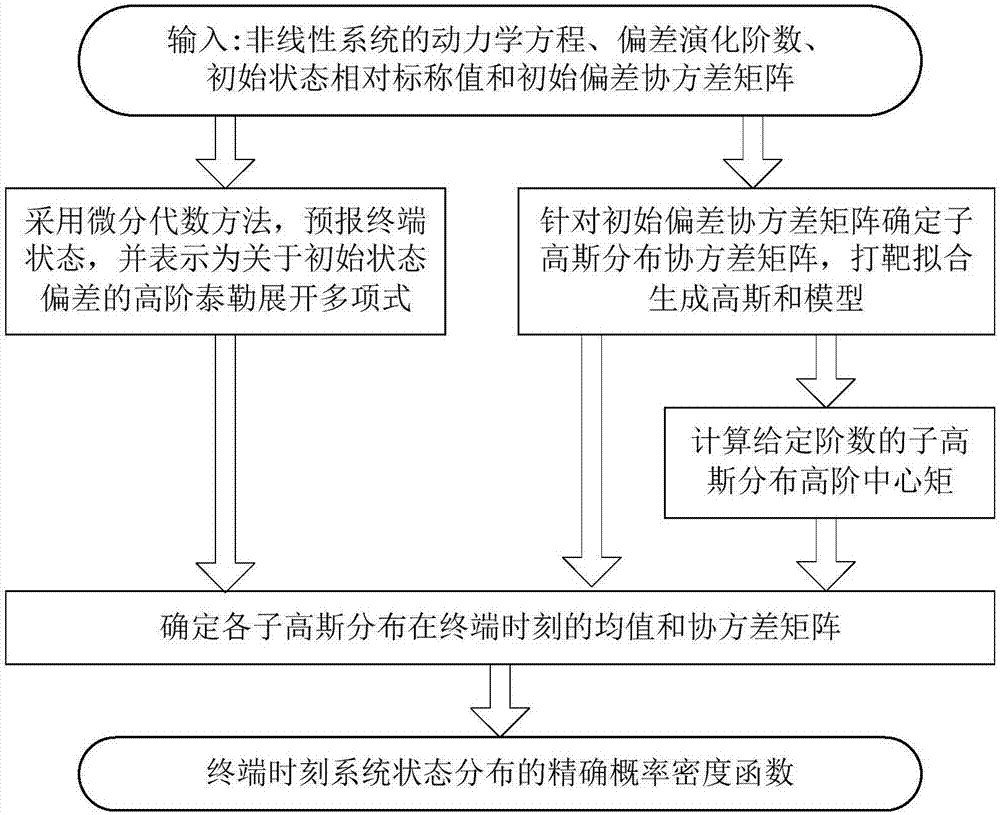
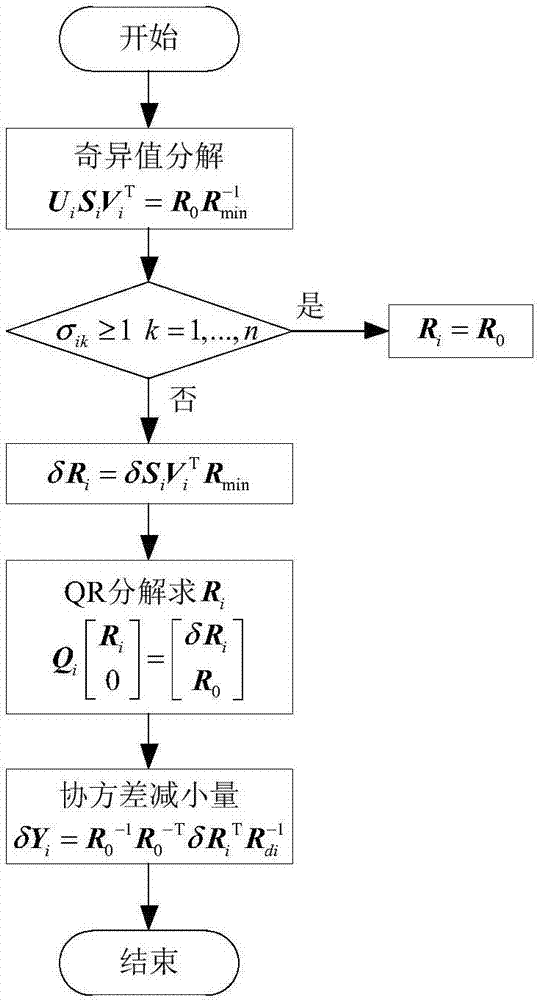
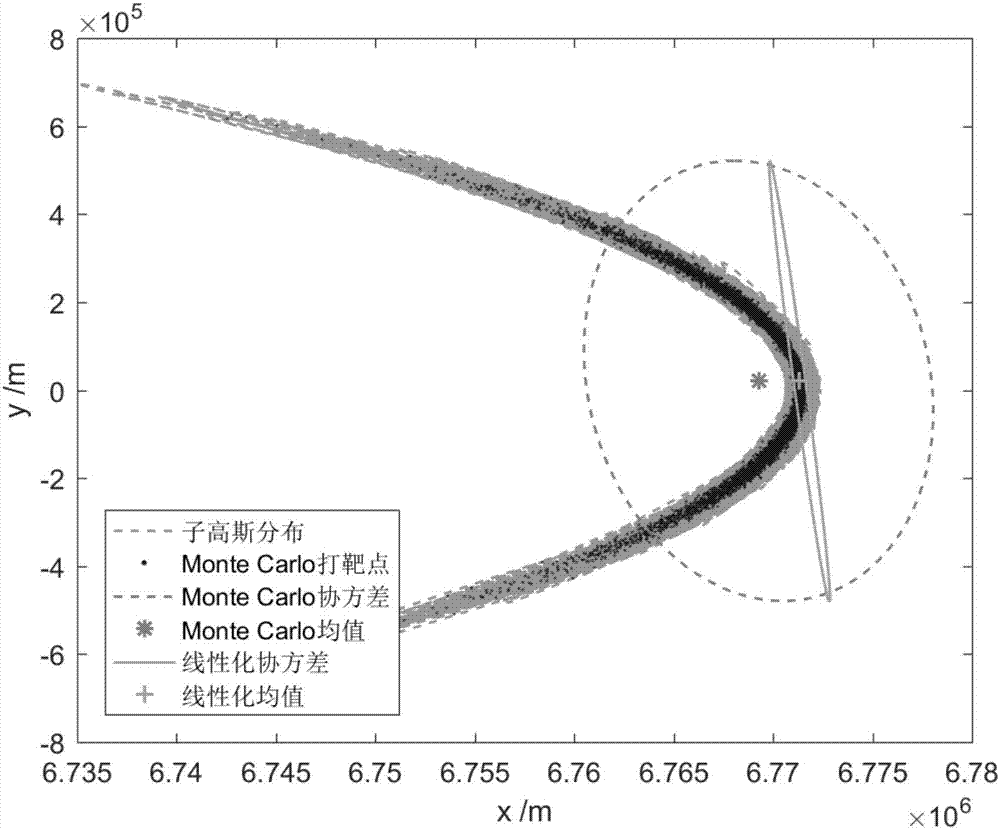
The invention discloses a nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum. The method includes forecasting the terminal state of a nonlinear system according to a differential algebra method, and representing it as a high-order Taylor expansion polynomial related to original-state deviation; determining a sub Gaussian distribution covariance matrix, and fitting a Gaussian sum model for each sub Gaussian distribution through shooting; calculating the high-order central moment of the sub Gaussian distributions; determining the mean value and the covariance matrix of each sub Gaussian distribution at the terminal moment, and providing a terminal-state deviation distribution probability density function in the form of the Gaussian sum. The method can be extended to any designated-order deviation evolution accuracy automatically, manual derivation of high-order partial derivatives of kinetic equations is not needed, the method is applicable to long-term forecasted nonlinear system deviation evolution analysis problems with high nonlinearity, the remarkable efficiency advantages of the method can be still maintained as compared to the Monte Carlo simulation method while deviation distribution and non-Gaussianity thereof are described accurately, and accordingly, the method has the advantages of convenience in use and high calculation accuracy.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
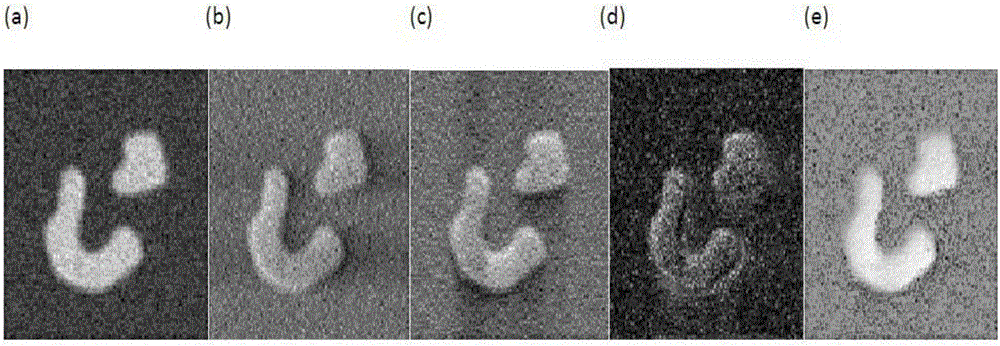
Adaptive weight activity contour model construction method based on fractional order differential information and system
The invention provides an adaptive weight activity contour model construction method based on the fractional order differential information and a system. The system comprises an input module, an initiation module, a first calculation module, a second calculation module, a determination module and an output module. The system is advantaged in that fractional order differential is introduced, a new difference image is constructed, a local term is constructed by utilizing the difference image, and a new activity contour model is proposed; by utilizing the fractional order gradient mode information, one adaptive weight is proposed, so local and global terms of the model can be dynamically adjusted; by utilizing change of an inner area of an evolution curve, a new evolution stop standard is proposed, and the evolution curve can automatically stop at a correct boundary.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
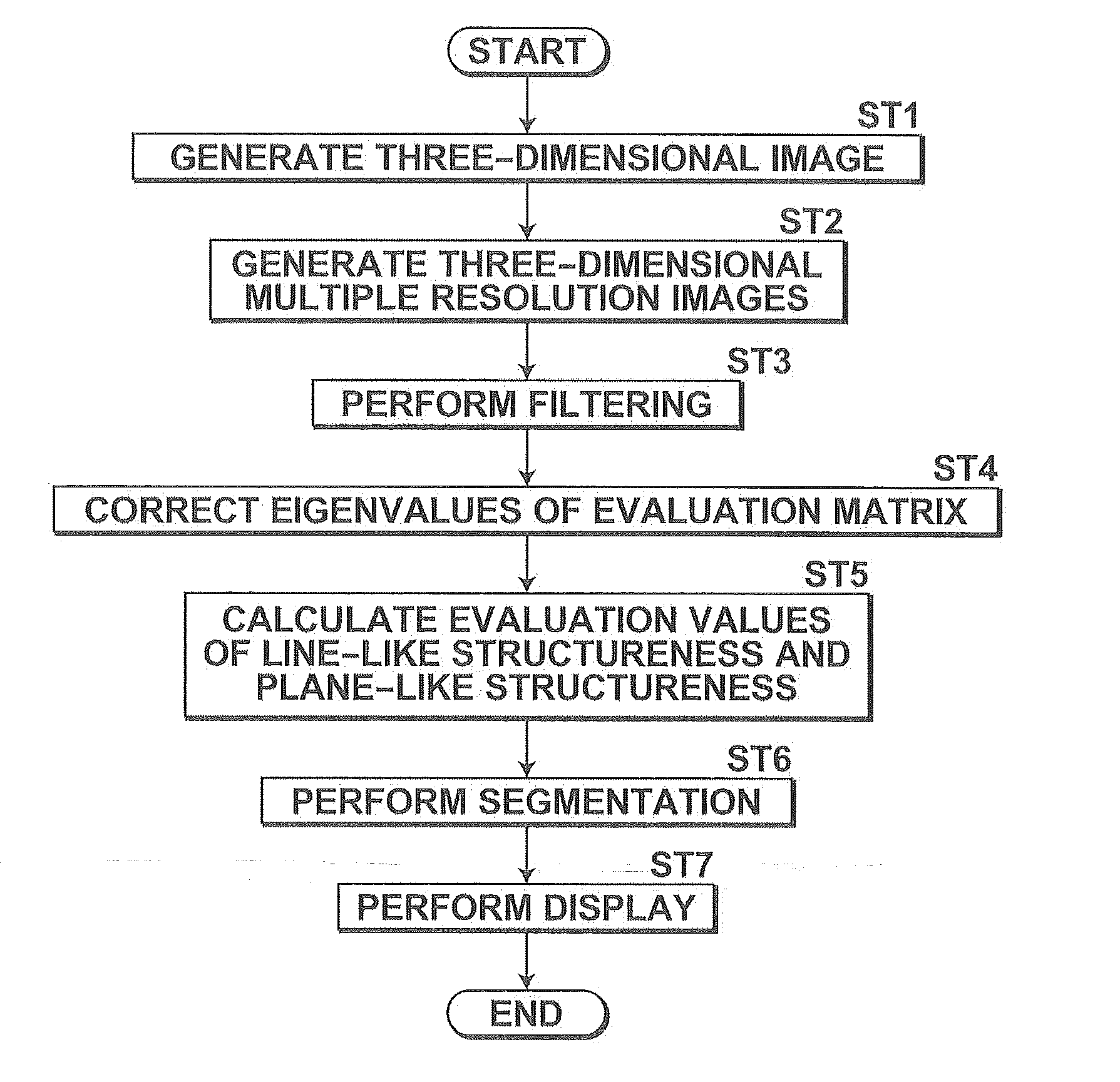
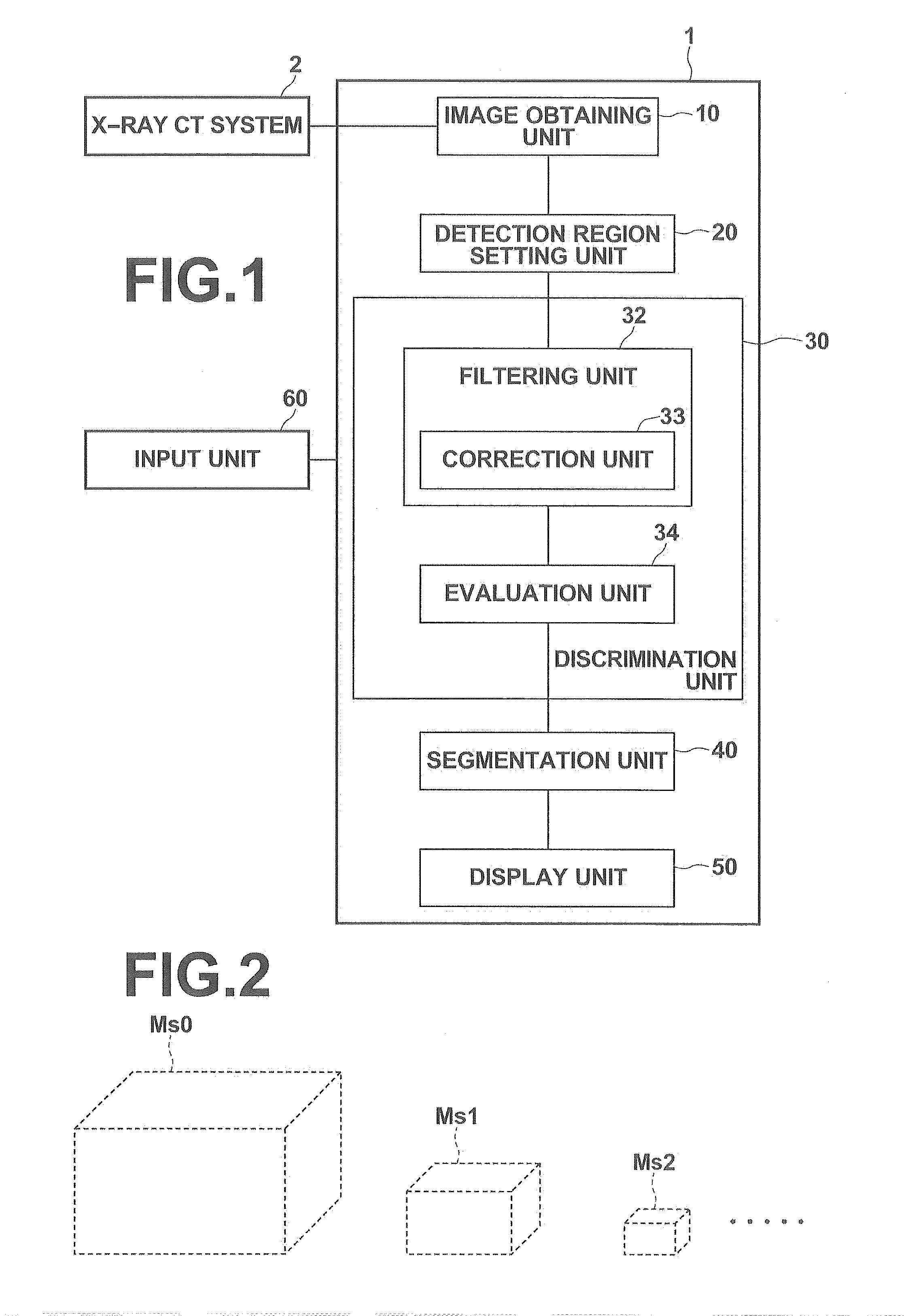
Image processing apparatus, method, and program
ActiveUS20150016686A1Inhibit discriminationImprove assessment accuracyImage enhancementMedical imagingFeature vectorImaging processing
An image processing apparatus, including a filtering unit that performs filtering on an image using a second order partial differential and calculates a Hessian matrix and an evaluation unit that discriminates a structure included in the image using eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the Hessian matrix, in which the filtering unit includes a correction unit that performs filtering on the image using a first order partial differential of a function representing a hollow sphere having the same radius as the radius of the solid sphere and obtains first order partial differential vectors, and carries out correction to cancel out one of response waveforms of the function representing the solid sphere in each direction, the response waveforms appearing at two positions symmetrically separated with respect to the center of the solid sphere, using values obtained by projecting the first order partial differential vectors onto directions of the eigenvectors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
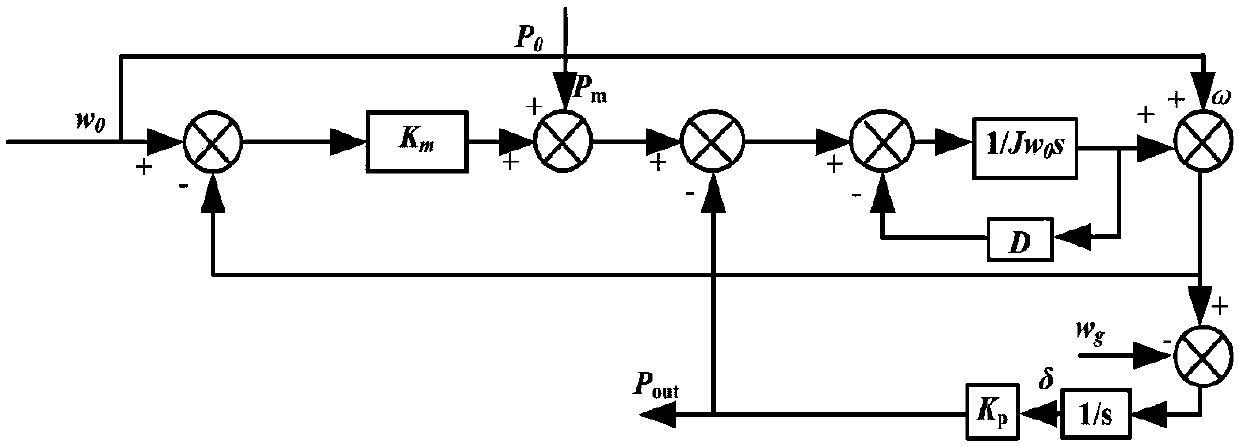
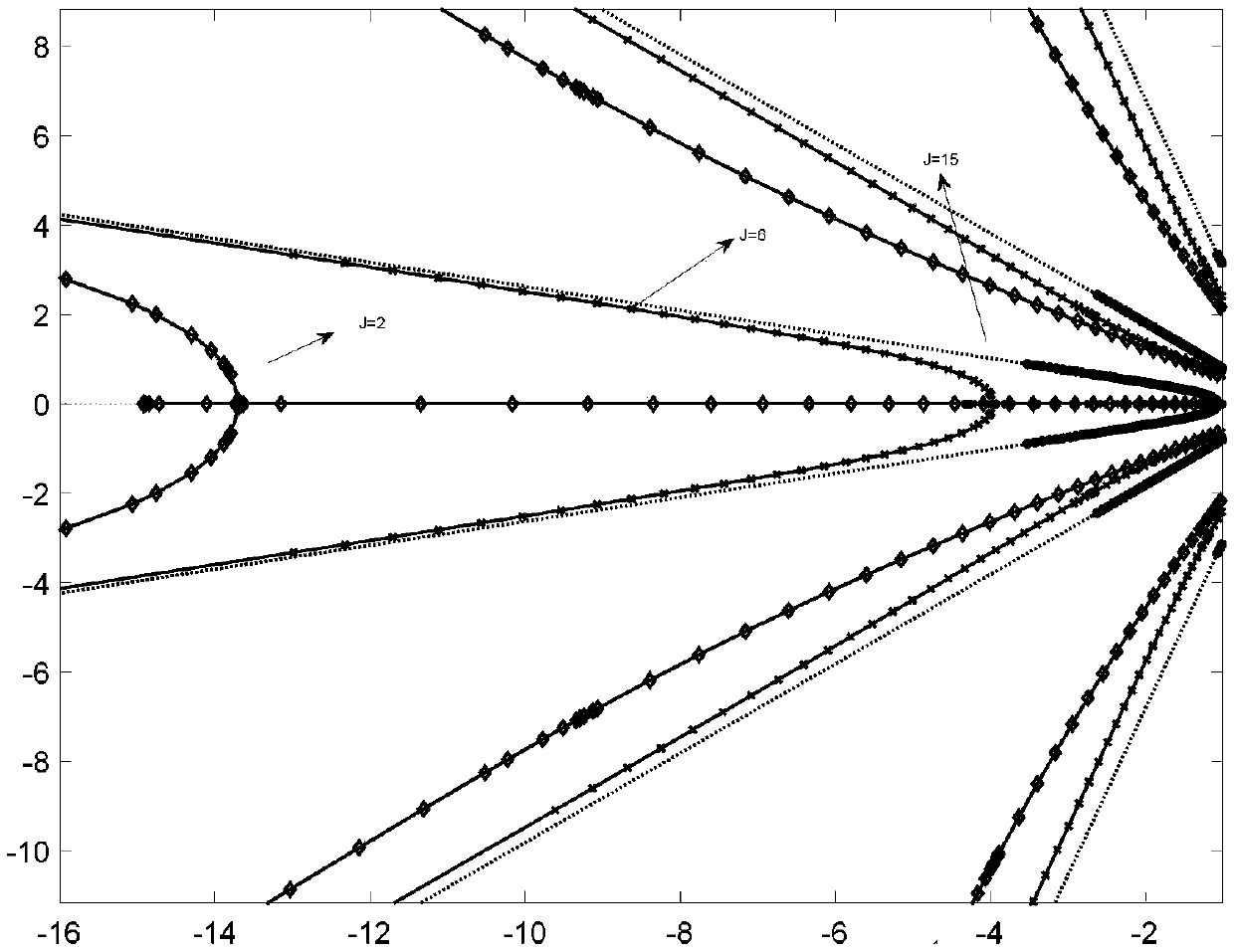
Fractional order differential compensation type VSG control method
InactiveCN109656140AImprove dynamic performanceImprove steady state performanceAdaptive controlClosed-loop poleBiogeography
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Transfer function model identification method with differential characteristic process
ActiveCN108170637ASimple calculationPromote engineering applicationComplex mathematical operationsTransfer function modelRC time constant
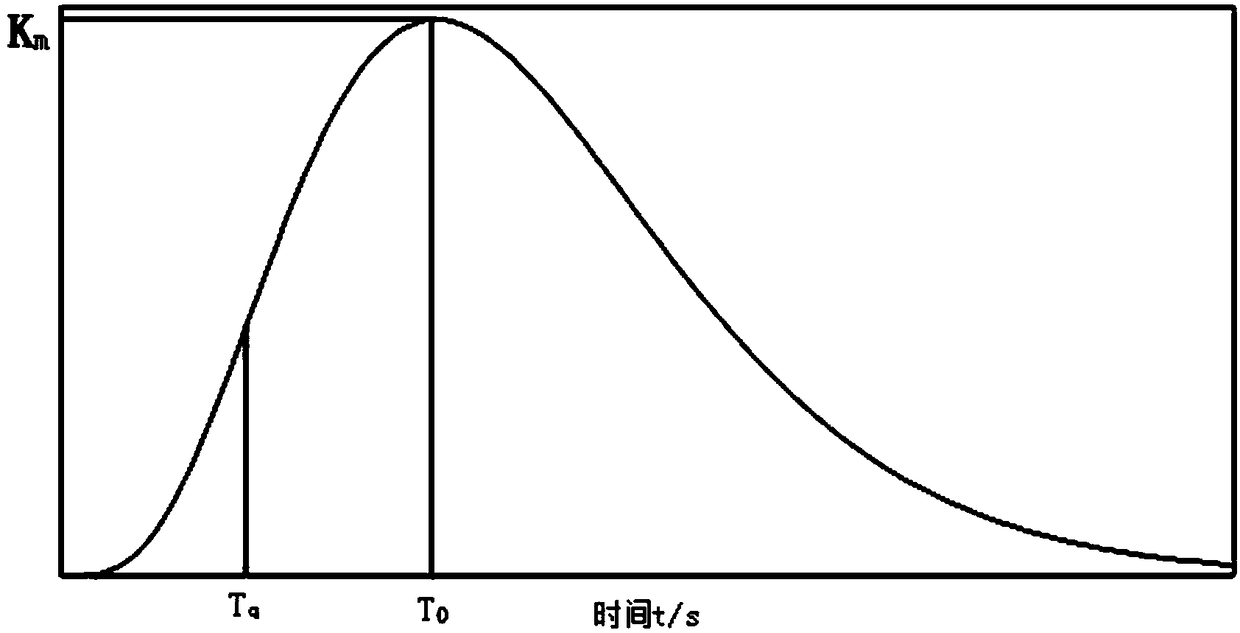
The invention discloses a transfer function model identification method with a differential characteristic process. According to the method, first, step response dynamic characteristic test data of the process is acquired through a field test; second, three characteristic parameters of a step response curve of the process are calculated according to the test data, wherein the three characteristicparameters include time T<0> corresponding to an extreme point of the curve, a corresponding extreme value K<m> and time T<q> corresponding to an inflection point of the curve before the moment T<0>;and last, according to the characteristic parameters T<q>, T<0> and K<m>, parameters of a process transfer function model (shown in the description) are calculated, wherein the parameters include a transfer coefficient K, a time constant T<c> and an order n. The method is simple and easy to implement and brings convenience to engineering application.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
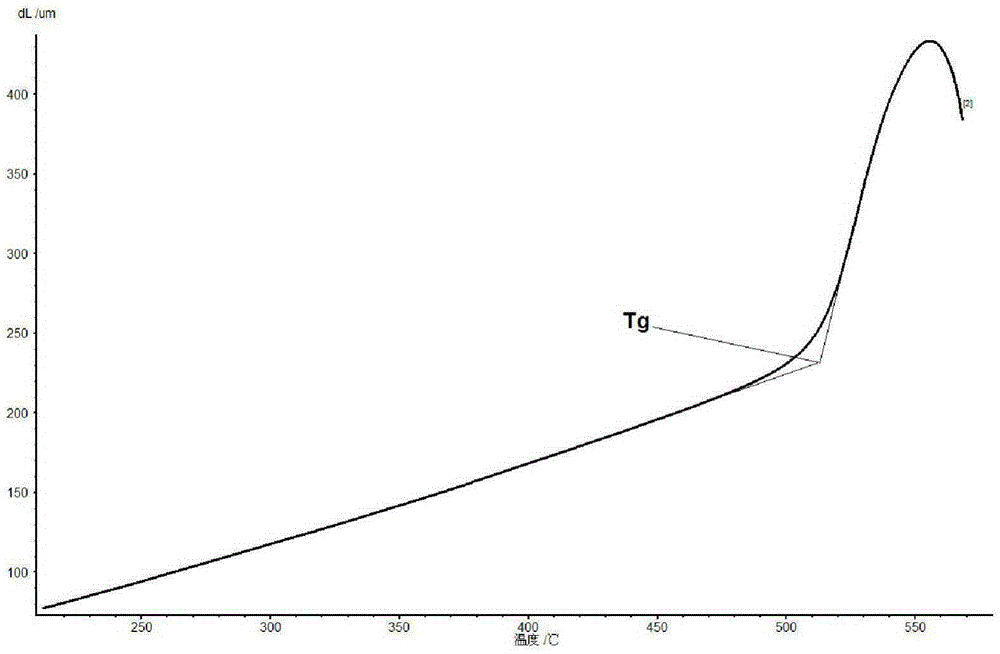
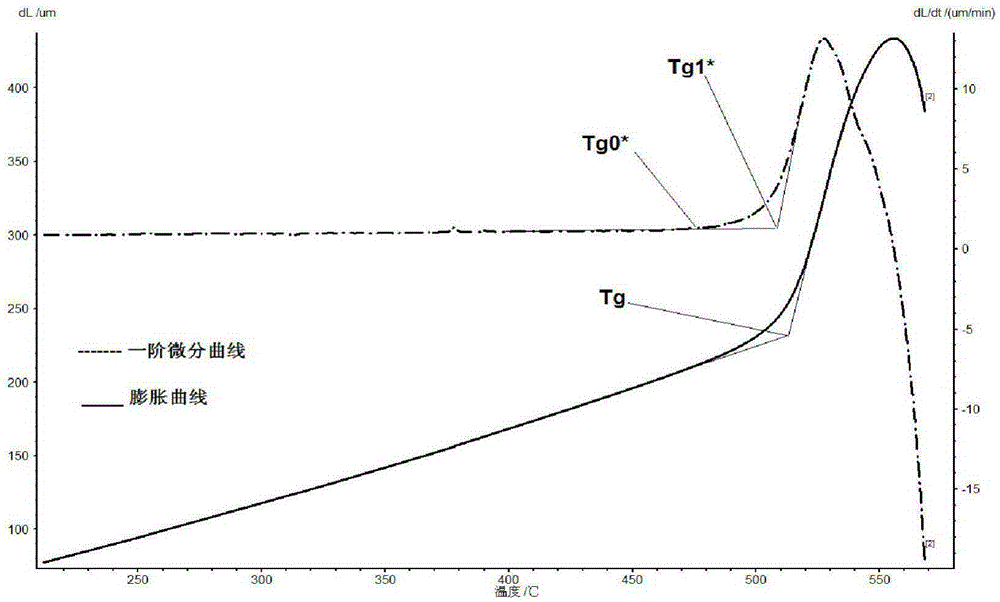
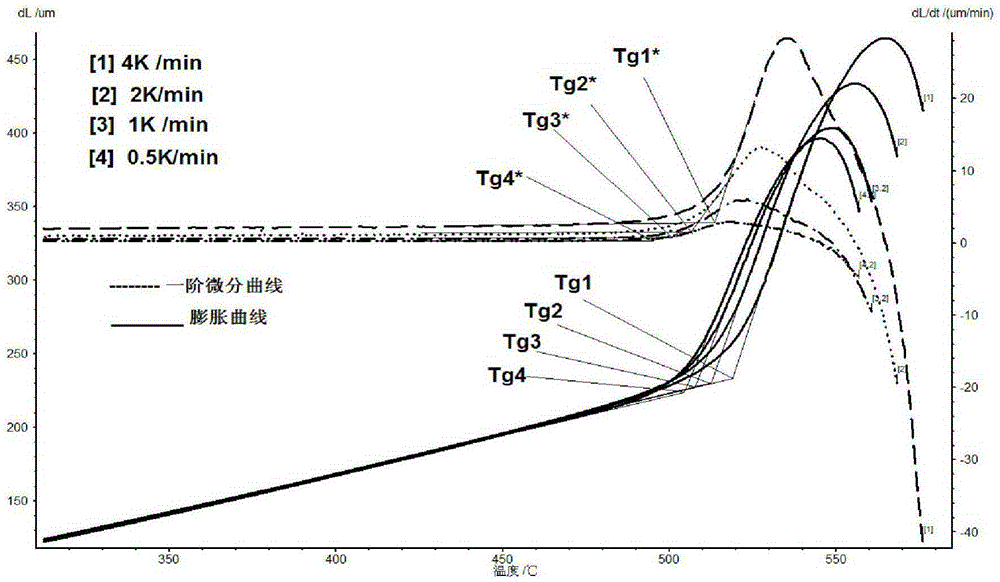
Acquisition method for precision annealing temperature
The invention provides a method capable of accurately acquiring a precision annealing temperature. The acquisition method for the precision annealing temperature comprises the following steps: (1) heating a material, and obtaining a heat expansion curve; (2) carrying out first-order differential on the heat expansion curve to obtain a heat expansion first-order differential curve; (3) when a beginning conversion temperature Tg0* of the heat expansion first-order differential curve is a lowest annealing temperature, the first-order differential curve displays that length variation occurs per unit time; when the conversion temperature Tg1* of the heat expansion first-order differential curve is a best annealing temperature, determining the relaxation state of the material to be optimal, wherein the relaxation state of a glass micro structure is an optimum value eliminating the stress. By utilizing the first-order differential curve of the heat expansion curve, the lowest and optimum annealing temperatures needed in a glass or ceramic annealing process can be rapidly and accurately obtained.
Owner:CDGM OPTICAL GLASS
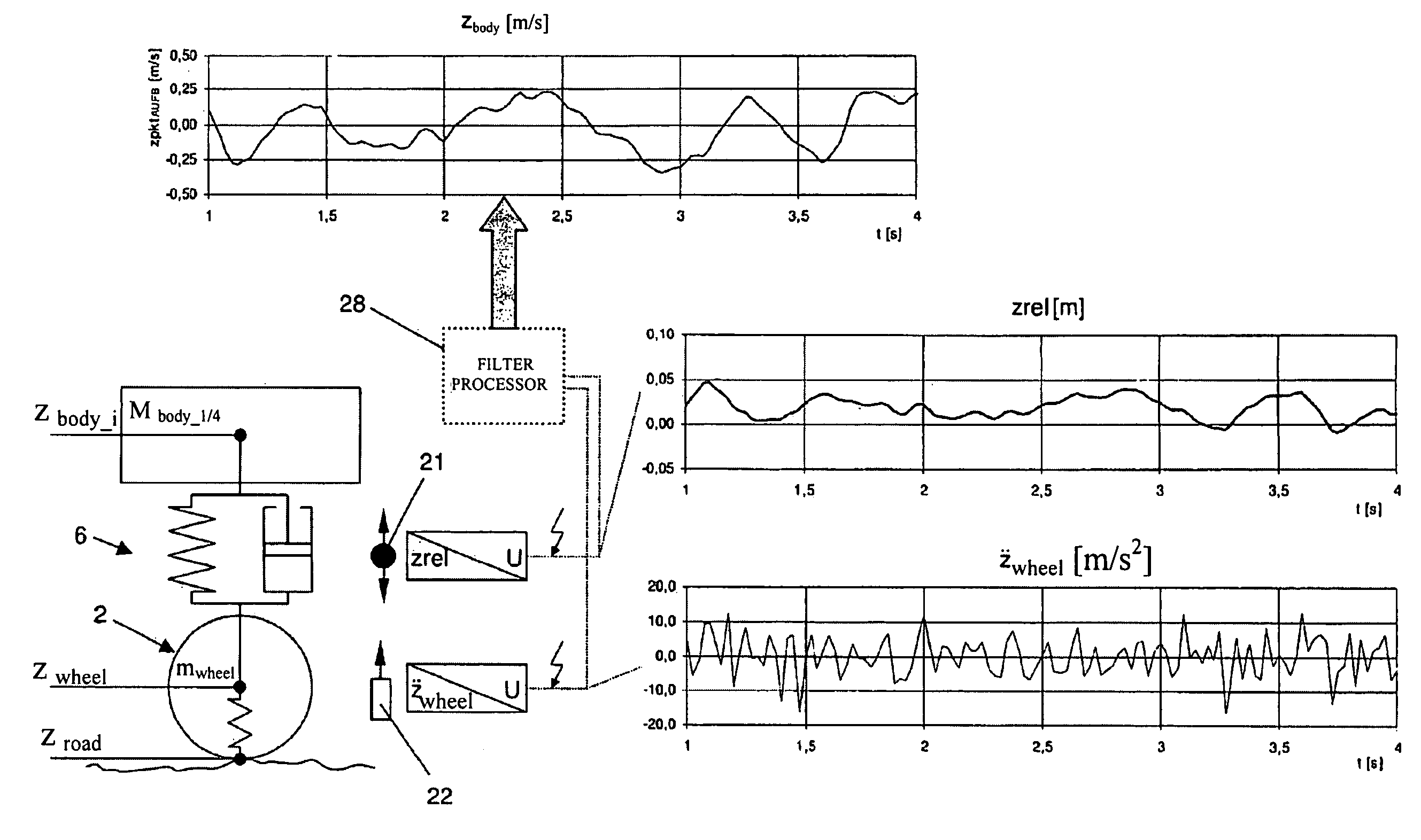
Method for determining at least one displacement state of a vehicle body
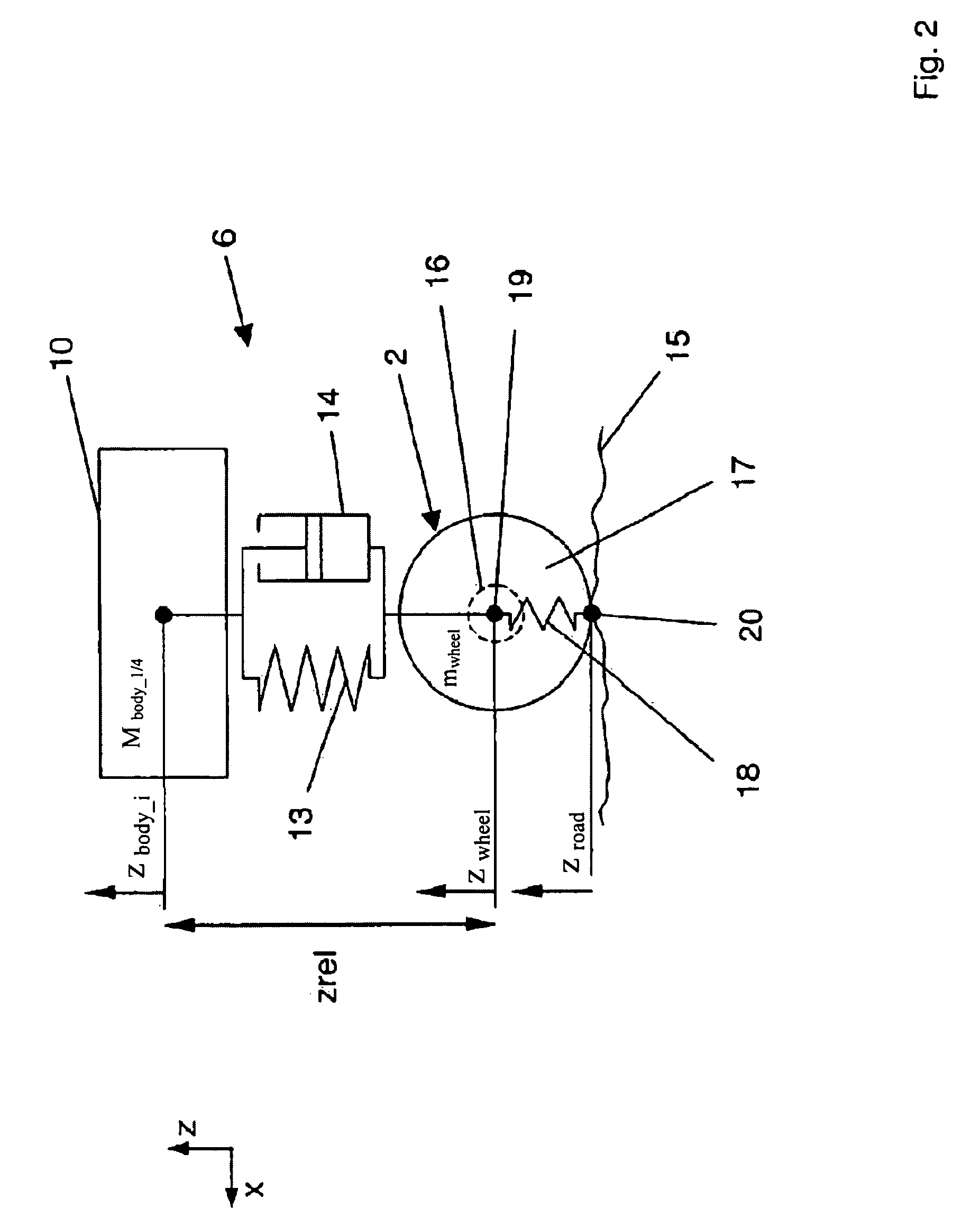
ActiveUS8428807B2Control suspensionImprove accuracyVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringDifferential of a function
Process for determining at least one state of motion of a vehicle body (10) of a vehicle (1), which has at least one wheel (2) spring-mounted on the vehicle body (10) via a wheel suspension (6), whereinan inward deflection (zrel) of the wheel (2) is measured by means of a path or angle sensor (21),an inward deflection velocity (żrel) of the wheel (2) is determined by differentiating the inward deflection (zrel) of the wheel (2) over time,a vertical acceleration ({umlaut over (z)}wheel) of the wheel (2) is measured by means of an acceleration sensor (22),a vertical velocity (żwheel) of the wheel (2) is determined by integrating the vertical acceleration ({umlaut over (z)}wheel) of the wheel (2) over time, anda vertical velocity (żbody) of the vehicle body (10) is calculated by forming a difference of the vertical velocity (żwheel) of wheel (2) and the inward deflection velocity (żrel) of wheel (2).
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
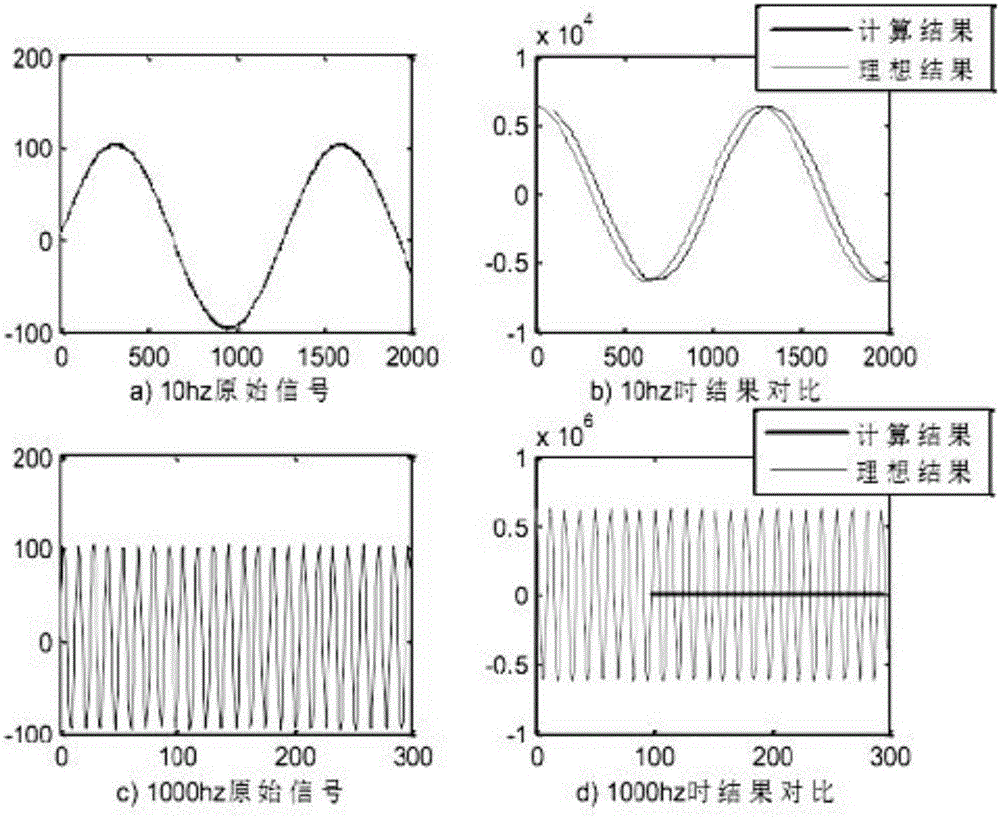
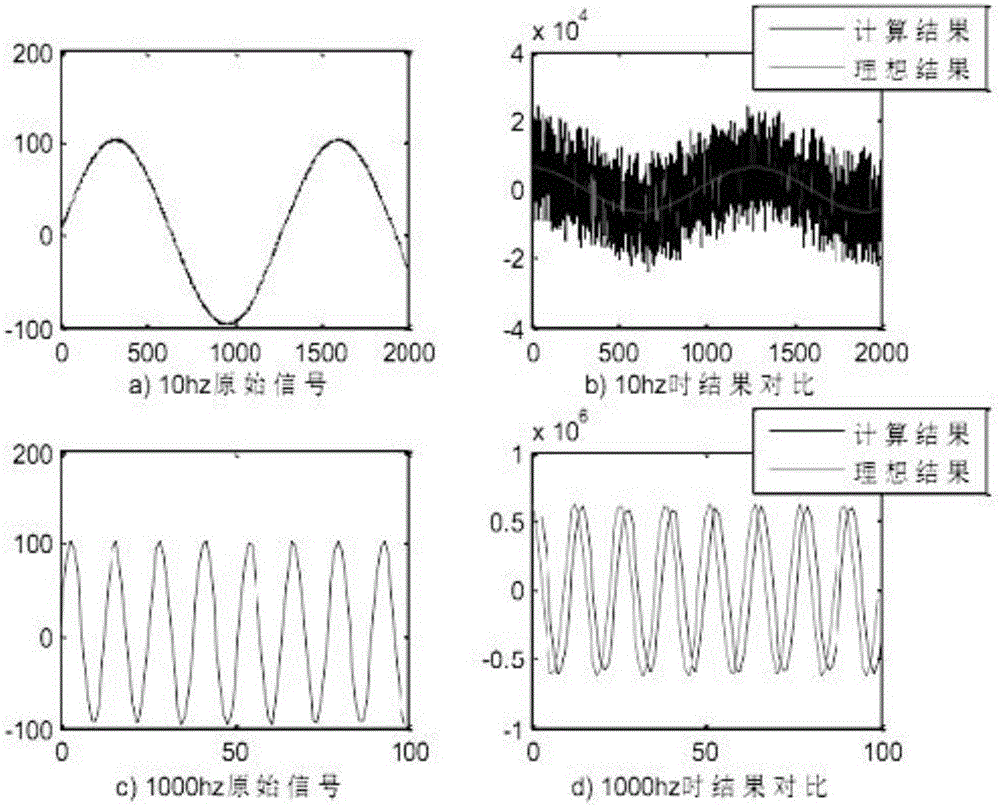
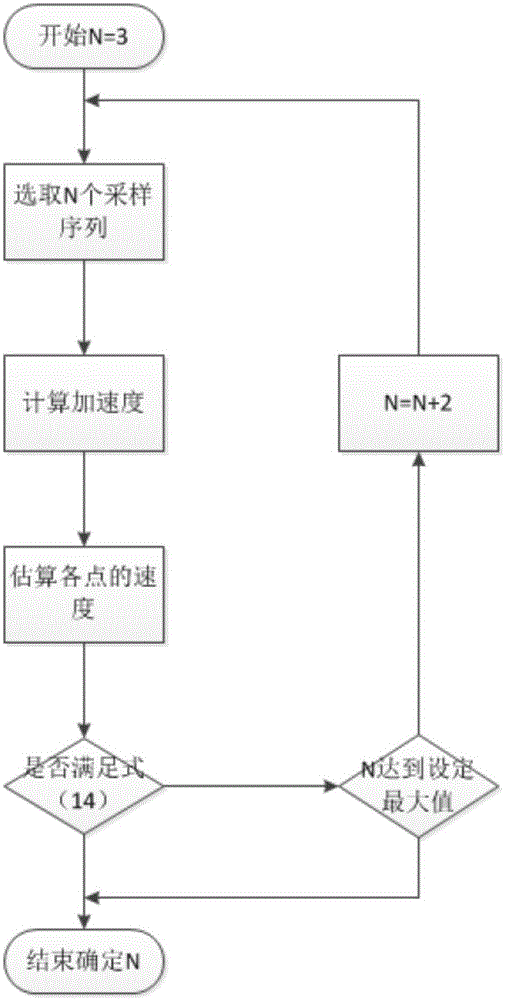
FIR filtering differential algorithm applicable to research on transformer vibration signal
InactiveCN105159866AConvenient lengthComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseTransformer
The present invention discloses a differential algorithm based on an FIR (finite impulse response) filter. The differential algorithm based on the FIR filter is a novel differential computation method designed according to features of an actual transformer vibration signal and an idea of a minimum mean square error; a filter length self-adjusting strategy is adopted; the length of the filter is gradually changed and finally, a differential result is optimized (as shown in figures) by a linear adjusting method; the problem of a large result error span, which is obtained in different frequency ranges, of differential computing results obtained by conventional FIR filtering is solved; and the differential algorithm is applicable to research on the power transformer vibration signal.
Owner:广州普瑞电力控制系统设备有限公司
A method for stably solving an electric field integral equation in a time domain
InactiveCN108984472AEfficient solutionAvoid cumbersomeComplex mathematical operationsTime domainEngineering
A method for stably solving an electric field integral equation in a time domain is disclosed. Another form of a thin-line time-domain electric field integral equation suitable for a finite differencesolution is deduced, and in the fine wire structure, symbols shown in the description are considered to be the line current and charge density respectively. The invention does not need to introduce an expansion function, directly discretizes the temporal and spatial differentials of the unknown current, and further advances the solution in time.
Owner:苏州峰极电磁科技有限公司
Multi-mode Lamb wave signal separation method based on fractional differential
PendingCN108921113AAchieve separationEfficient extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsFractional differentialPhase spectrum
The invention discloses a multi-mode Lamb wave signal separation method based on a fractional differential. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) calculating the Fourier transform of a multi-mode signal; (2) calculating the fractional differential of an amplitude spectrum; (3) calculating the multinomial coefficient of the fractional order and the fractional differential maximum valueof the amplitude spectrum of a Gaussian model; (4) calculating an amplitude spectrum parameter; (5) on the basis of the Gaussian model, calculating the amplitude spectrum; (6) calculating a phase spectrum; (7) extracting a single-mode Lamb wave signal by the amplitude spectrum and the phase spectrum; and (8) removing a mixed signal of which the signal is extracted, and repeating the above steps to realize the separation of each mode. Compared with the prior art, the method can extract the single-mode characteristic parameter of a multi-mode mixed signal through the fractional differential soas to more favorably keep the detail characteristic of each mode signal, each-mode characteristic parameter can be effectively extracted, and each-mode amplitude spectrum reconstruction is realized soas to realize the separation of the multi-mode mixing signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com