A Method of Applying Information Fusion to Radar Signal Sorting
A radar signal sorting and fusion application technology, applied to radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of radar signal sorting difficulty, lack of some characteristic parameters, uncertainty, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
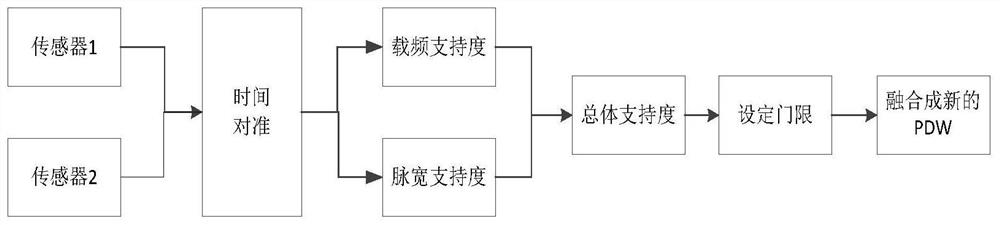
[0103] Embodiment 1: Assume that there are two reconnaissance equipment receivers working at the same time, and the information obtained by each reconnaissance receiving equipment is different from each other. The PDW received by the receiver is fused through a data-level fusion algorithm to form a new PDW. PDW were sorted by conventional SDIF method. The simulation constructs a pulse description word for the mixture of two conventional radar signals, and its parameters are shown in Table 1 below.
[0104] Table 1 Radar simulation parameter settings
[0105]
[0106]
[0107] Under the condition that the pulse deletion rate was 50%, the sorting results of the missing signal and the fusion signal were compared, as shown in Table 2.
[0108] Table 2 Sorting results before and after data level fusion
[0109]
[0110] It can be seen from Table 2 that if there is a lack of received signals, as shown in the first and second signals in the table, radars with PRI parameter...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Embodiment 2: Test the influence of signal capture loss rate on signal sorting. Using the simulation parameters in Table 1, the conventional radar signals under different loss rates and the signals after data-level fusion are conventionally sorted. For single-channel signals with missing pulses and the sorting results after data-level fusion are as follows: Figure 5 and Image 6 shown.
[0112] from Figure 5 It can be seen that when the pulse loss rate is between 10% and 45%, the two lost signals can be successfully sorted to the two radars; when the pulse loss rate reaches 50%, the lost two signals Only conventional radars with a PRI parameter of 500us can be correctly sorted, but radars with a PRI parameter of 400us cannot be correctly sorted. from Image 6 It can be seen that after data-level fusion, the sorting can still be successful when the pulse loss rate reaches 60%, which verifies the effectiveness of the radar signal data-level fusion algorithm in impr...
Embodiment 3
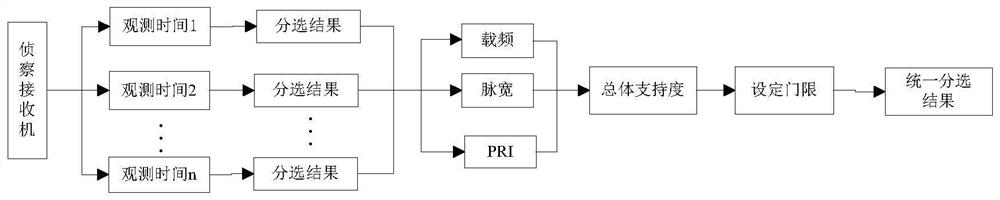
[0113] Embodiment 3: Testing the fusion effect of feature-level sorting results. The simulation first sorts the PDW data packets reported by a reconnaissance receiver after five consecutive observations, and the sorting results are shown in Table 3. The sorting data in the simulation is the measured data, and the sorting algorithm still adopts the SDIF method.
[0114] Table 3 Sorting results under multiple observations
[0115]
[0116] The multiple sorting results obtained in Table 3 are fused at the feature level, and the results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen that although in the observation time period with time number 1, the 76 pulses detected by the receiver describe PRI=1.9613ms, the pulse number of this radar is only 22, even in the observation time period with time number 5 The lower receiver did not detect the pulse signal describing this radar, but after multiple observations and sorting accumulation, we can rule out the possibility of sorting failure an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com