Carbon nano-material for rapidly detecting residual chlorine in water, and matching device and use method thereof
A carbon nanomaterial and water detection technology, applied in the fields of analytical chemistry and nanometers, can solve the problems of high price, fluorescence quenching, and inability to monitor online, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple operation and wide application range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: carbon dots m -Synthesis of CDs
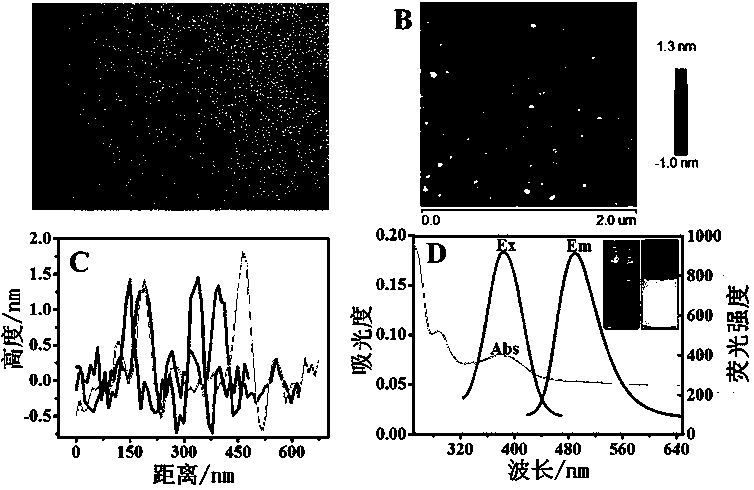
[0025] Firstly, 0.6 g of m-phenylenediamine was dissolved in 60 mL of absolute ethanol, and then the solution was transferred to a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene high-temperature reactor, and the reaction was heated at 180 °C for 12 h, and the reactor was cooled to room temperature. Finally, the resulting product is separated and purified by column chromatography (eluent is dichloromethane:methanol=15:1, v / v), and the obtained solution is spin-dried with a rotary evaporator and vacuum-dried, that is get carbon dots m -Solid crystals of CDs ( m -Relevant characterization of CDs such as figure 1 , where A is m - Transmission electron microscope image of CDs, showing that the particle size distribution is 4-6 nm; B is m -Atomic force microscope image of CDs, characterizing its height; C is corresponding to B m -The height of CDs is displayed as about 1.5 nm; D is the ultraviolet absorption diagram, fluorescence excitation ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: ClO - Drawing of standard curve
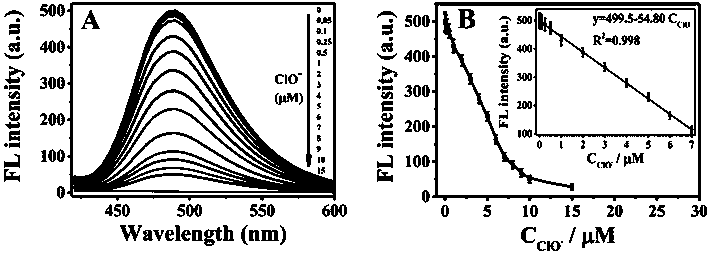
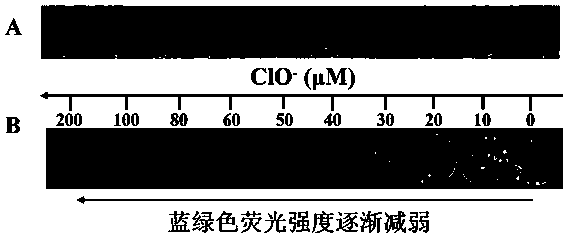
[0027] Use PBS (pH=7.0) buffer to prepare different concentrations of ClO - Solution (ClO - The concentration is 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15 μM), and then at room temperature, to 20 μg / mL m -Add different concentrations of ClO to the CDs solution sequentially - Solution, after mixing and reacting for 5 min m -CDs fluorescence intensity changes and plotted with respect to ClO - Standard curve of response (eg figure 2 , where A is different concentrations of ClO - and m -The change graph of fluorescence intensity after CDs reaction; B is m -CDs respond to different concentrations of ClO - A standard curve with a response range of 0.05-7 μM and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.012 μM).
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: m - Preparation of CDs agarose hydrogel
[0029] Take a certain volume of 20 μg / mL m-CDs solution, add agarose powder to it, and make the agarose evenly distributed in the solution by magnetic stirring, then heat in a microwave oven until the agarose is completely dissolved and forms a viscous colloid, take 300 μL of the sol and drop it evenly in a centrifuge tube In the groove of the lid, after it cools to room temperature, it forms a round cake m - CDs agarose hydrogel. Take it out and put it in a centrifuge tube filled with distilled water and store it in the refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap