Mobile robot local motion planning method and device
A mobile robot, local motion technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as nonlinear optimization problems, scarcity hidden dangers of catastrophic events, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
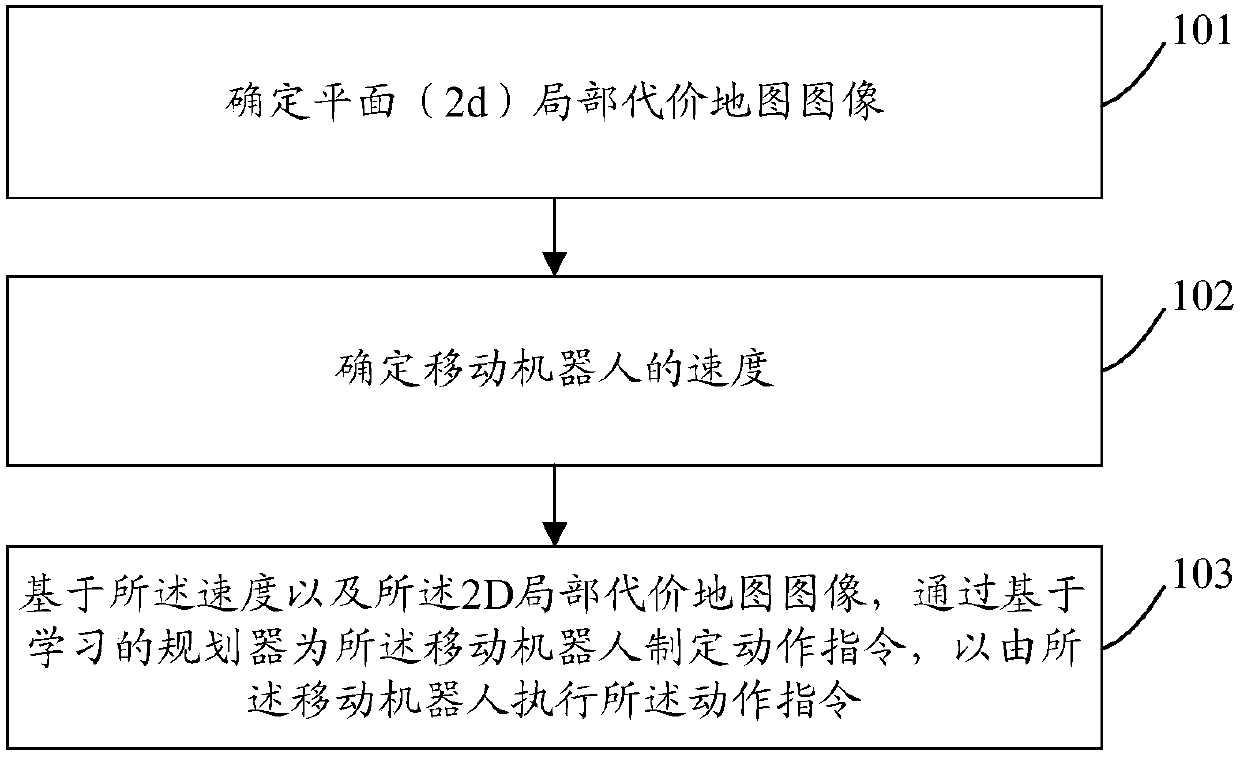
[0118] As an implementation manner, the determining the speed of the mobile robot includes:
[0119] determining the first position information of the mobile robot at the first moment;
[0120] Determining second position information of the mobile robot at a second moment; wherein, the first moment is a moment before the second moment;
[0121] Determine the speed of the mobile robot according to the first position information, the second position information, the first moment, and the second moment.
[0122] For example, the speed of the mobile robot=(second position information-first position information) / (second moment-first moment).
[0123] Certainly, the manner of determining the speed of the mobile robot is not limited to the form listed above, and may also be determined in other manners. For example, data is directly acquired from a speed sensor of the mobile robot to determine the speed of the mobile robot.
[0124] Step 103, based on the velocity and the 2d local ...
Embodiment 2
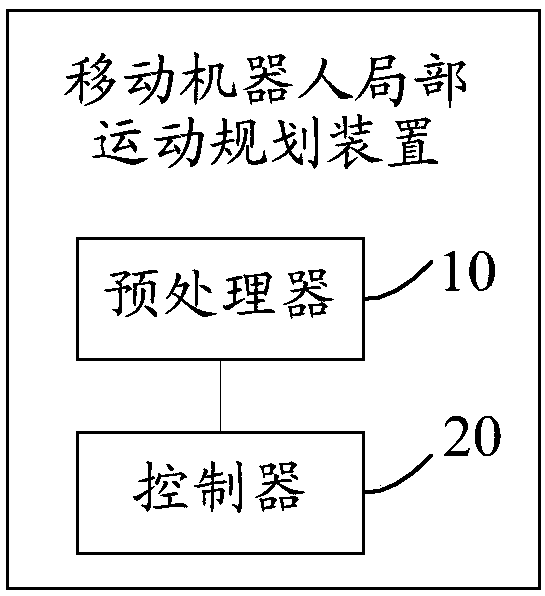
[0169] This embodiment provides a device for local motion planning of a mobile robot, the device comprising:
[0170] Preprocessor 10, used to determine the plane 2d local cost map image; determine the speed of the mobile robot;
[0171] The controller 20 is configured to formulate an action instruction for the mobile robot through a learning-based planner based on the velocity and the 2d local cost map image, so that the mobile robot executes the action instruction.
[0172] In the above solution, the mobile robot includes a learning-based planner.
[0173] As an implementation manner, the preprocessor 10 is specifically used for:
[0174] Obtaining data collected by predetermined sensors on the mobile robot;
[0175] Positioning the mobile robot based on the data, and simultaneously establishing a map of the surrounding environment where the mobile robot is located;
[0176] determining a local target point and a local obstacle map according to a given global path and the...
Embodiment 3
[0214] Based on the mobile robot local motion planning method and device described in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the method for local motion planning and obstacle avoidance of mobile robots proposed by us through deep imitation learning is given below. The main goal is to speed up local motion planning decisions for mobile robots, while making decision making as optimal, safe and general as possible.
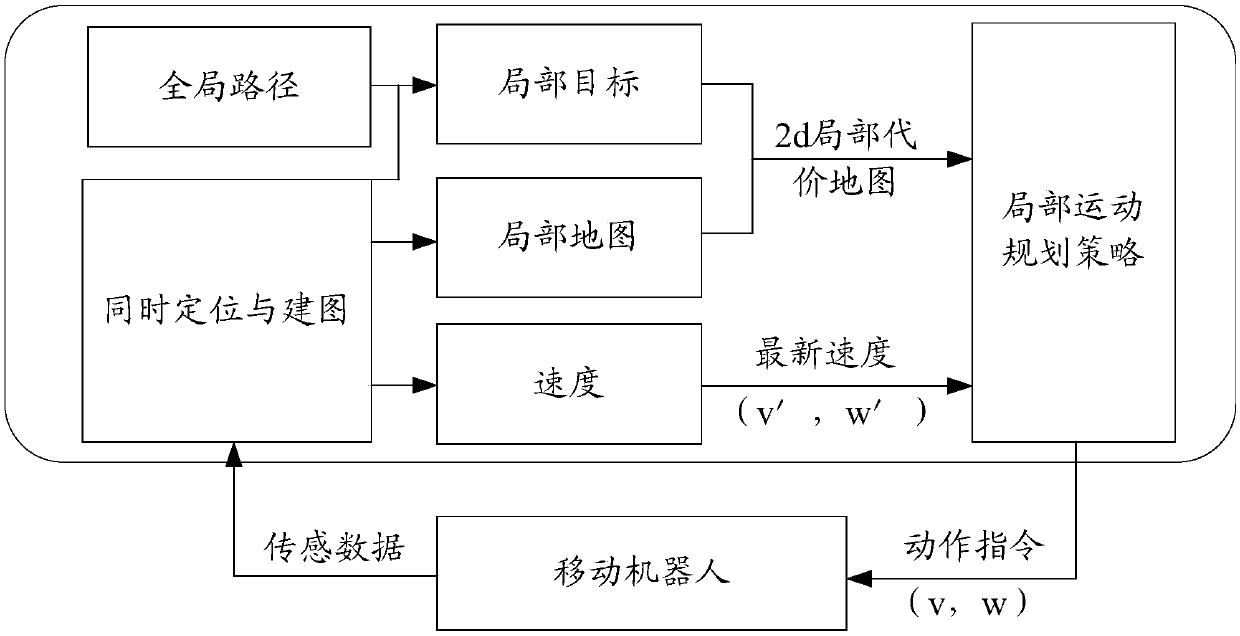
[0215] A. System structure
[0216] image 3 Block diagram for a local mobility planning system with a policy network, from image 3 It can be seen that the system mainly includes two planning blocks. The first planning block is used to preprocess the raw sensing data and generate a local occupancy map describing surrounding obstacles and local target points extracted from the global path according to the robot pose. . These intermediate results are then fed into a second planning block where we employ a deep neural network to simulate a local planning strategy. Addition...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com