Multi-objective decision-making optimization method for deviation interval preference guidance based on MOEAD
A multi-objective decision-making and optimization method technology, applied in the field of aircraft structure maintenance decision-making, can solve problems such as the small number of effective solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0036] Specific implementation mode one: a kind of deviation interval preference guidance multi-objective decision-making optimization method based on MOEAD comprises the following steps:
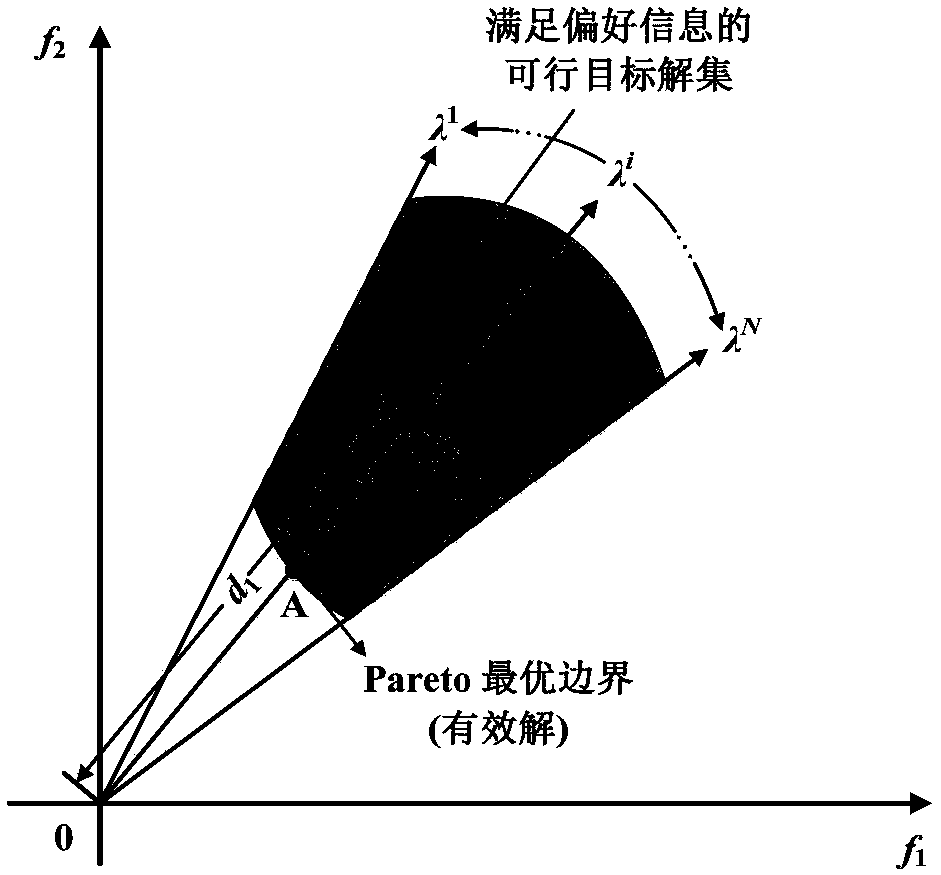
[0037] When the remaining life of the two fleets (the average remaining life of all aircraft in the fleet is used as the remaining life of the fleet) needs to be repaired, due to the limitation of maintenance resources (the maintenance base cannot accommodate the aircraft of the two fleets at the same time overhaul), so it is necessary to reasonably arrange different task volumes for the two fleets so that the remaining life is separated by a certain distance. However, if the remaining service life of the two fleets is too large, it means that after the first fleet is repaired, the maintenance resources that have been prepared will be idle again, and the maintenance resources will not be fully utilized. Maintenance intervals should not be too large. Based on the preference for the remainin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that it is characterized in that: the mathematical model of the normal line boundary intersection method in the step two is:
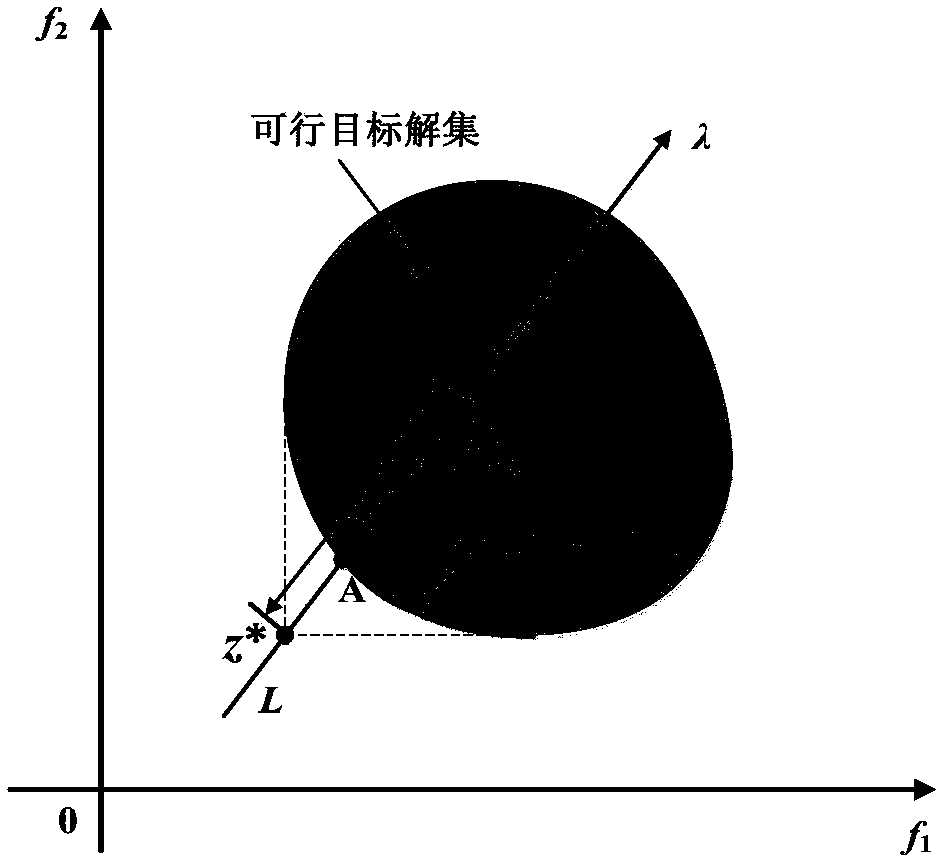
[0049] Traditional BI methods are designed to obtain the non-inferior frontier (ParetoFront, PF) of multi-objective optimization problems with uniform distribution. Such as figure 1 As shown, the PF of the multi-objective optimization problem is the lower leftmost partial convex boundary in the feasible objective space.
[0050] Geometrically, BI finds the lower left boundary in the feasible target space and a series of reference points z*(z*=(minf 1 (x),minf 2 (x),...,minf z (x)), z represents the number of objective functions) to approach the PF by the intersection of uniformly divergent rays. Such as figure 1 , a ray L with a direction of λ is emitted from the reference point z*, where λ is the weight vector λ=(λ 1 ,...,λ z ) T , where λ i ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
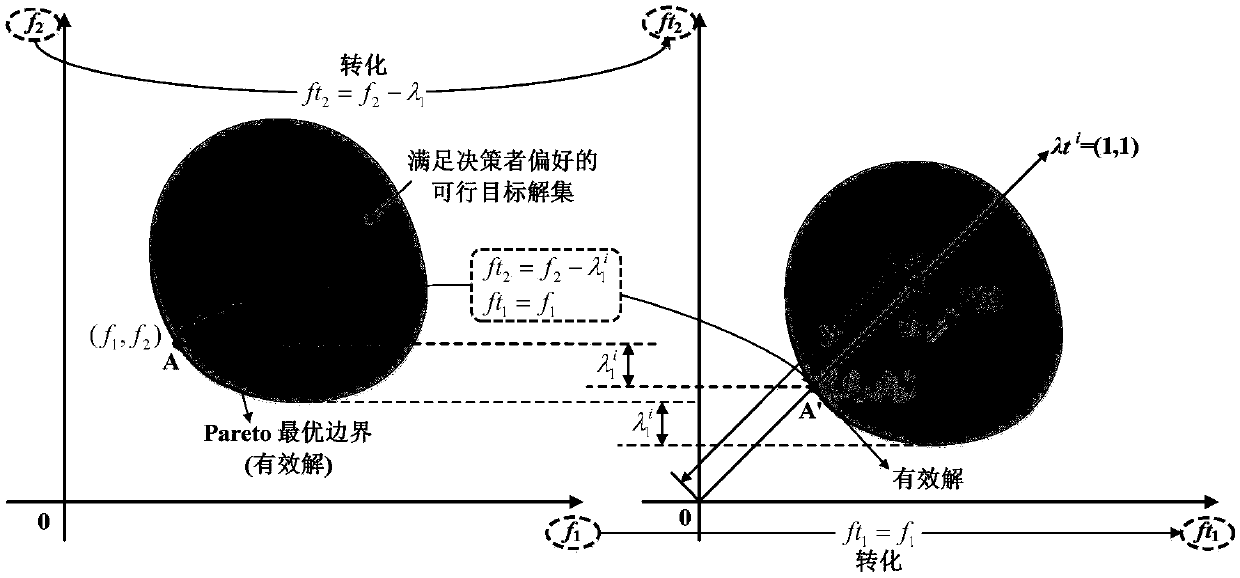
[0056] Specific implementation mode 3: The difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode 1 or 2 is: the specific details of the reconstructed decomposition model obtained by reconstructing the multi-objective decision-making model with deviation relationship interval preference information established in step 1 The process is:
[0057] Since the decision maker's preference information is composed of l deviation relationship intervals, and the deviation relationship intervals can be discretized into deviation preference sets, one preference value is taken in each of the l deviation preference sets to form a preference vector. Therefore, the decision maker's preference information is expressed as a set of N preference vectors, specifically:
[0058]
[0059] Among them, PI represents the set of preference relations between the decision makers for the goals, l represents the number of preference relations (intervals) among the goals in the decisi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com