Disparity map-based road detection method and device
A road detection and disparity map technology, which is applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of mistakenly deleted obstacle parallax, inaccurate obstacle detection results, and inability to delete distant road parallax, etc., to achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
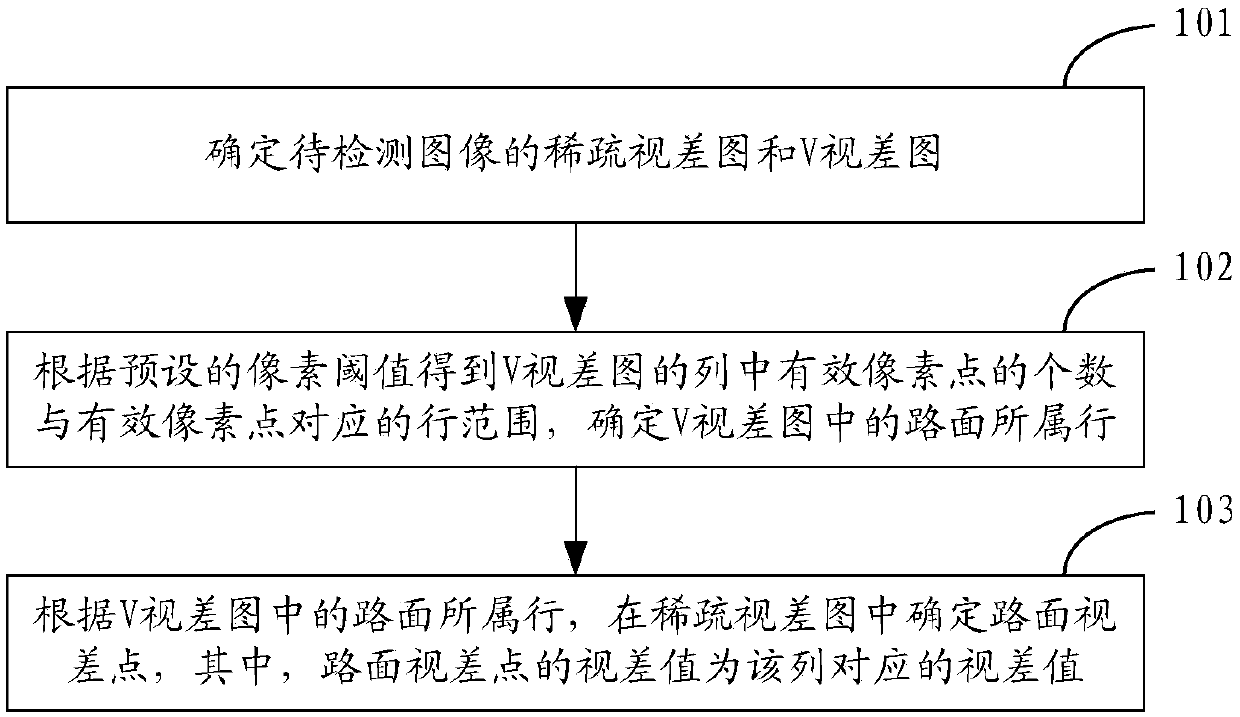
[0040] See Figure 1A , is a flowchart of an embodiment of the road detection method based on the disparity map of the present application, the method includes the following steps:
[0041] Step 101: Determine the sparse disparity map and V disparity map of the image to be detected.
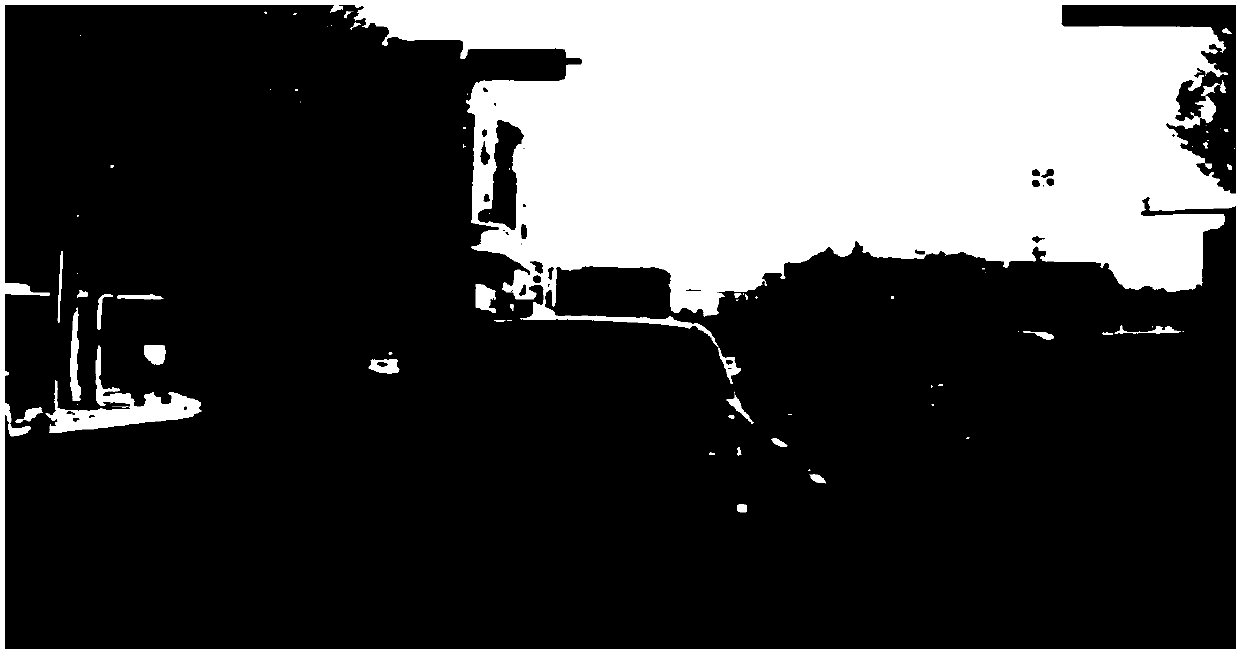
[0042] In the embodiment of the present application, for the convenience of description, the two original images collected by the binocular camera can be referred to as images to be detected, such as Figure 1B Shown is an example of the grayscale image of the image to be detected.
[0043] In related technologies, stereo matching algorithms can be classified according to different primitives used, one of which is feature-based stereo matching algorithms. In the feature-based stereo matching algorithm, the disparity estimation is mainly based on geometric feature information, such as edges, contours, points of interest, lines, corners, etc. Therefore, in the disparity map obtained by the feature...
Embodiment 2
[0051] See figure 2 , which is a flow chart of another embodiment of the road detection method based on the disparity map of the present application, figure 2 The illustrated method focuses on the above step 102 and step 103, that is, the process of determining the road parallax point in the sparse disparity map by processing the V disparity map. The method may include the following steps:
[0052] Step 201: For each column in the V-disparity map, obtain the number of effective pixels in the column and the row range corresponding to the effective pixels according to the preset pixel threshold.
[0053] In the embodiment of the present application, taking one column of the V disparity map as an example, the pixels in the column can be detected line by line from top to bottom, and the pixel value of the detected pixel point can be compared with the preset pixel threshold value. If the pixel value of the detected pixel is greater than the preset pixel threshold, the detected p...
Embodiment 3
[0079] See image 3 , is a flow chart of another embodiment of the road detection method based on the disparity map of the present application, the image 3 The illustrated embodiment focuses on how to determine the row search range in the column, which may include the following steps:
[0080] Step 301: Multiply the preset truncation ratio by the number of effective pixels in the column to obtain the number S of effective parallax.
[0081] In this step, the number S of effective parallaxes can be calculated according to the following formula (3).
[0082] S=A[0][0]*R Formula (3)
[0083] In the above formula (3), R is a preset truncation ratio.
[0084] Those skilled in the art can understand that the above-mentioned number of effective parallaxes S should be an integer. If S calculated by the formula (3) is not an integer, the calculation result can be further "rounded" to obtain the number of effective parallaxes number S.
[0085] Step 302 : In the column, start from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com