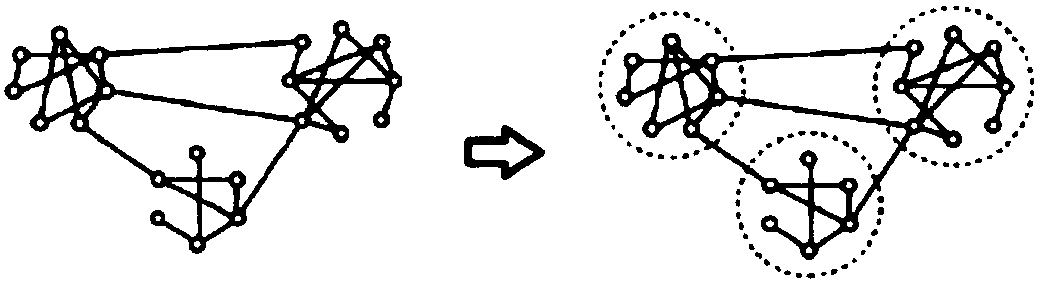
Community discovery method and system based on Louvain algorithm
A community discovery and community technology, applied in the field of community discovery system based on the Louvain algorithm, can solve problems such as inaccurate results, loose structure, unsuitable data, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
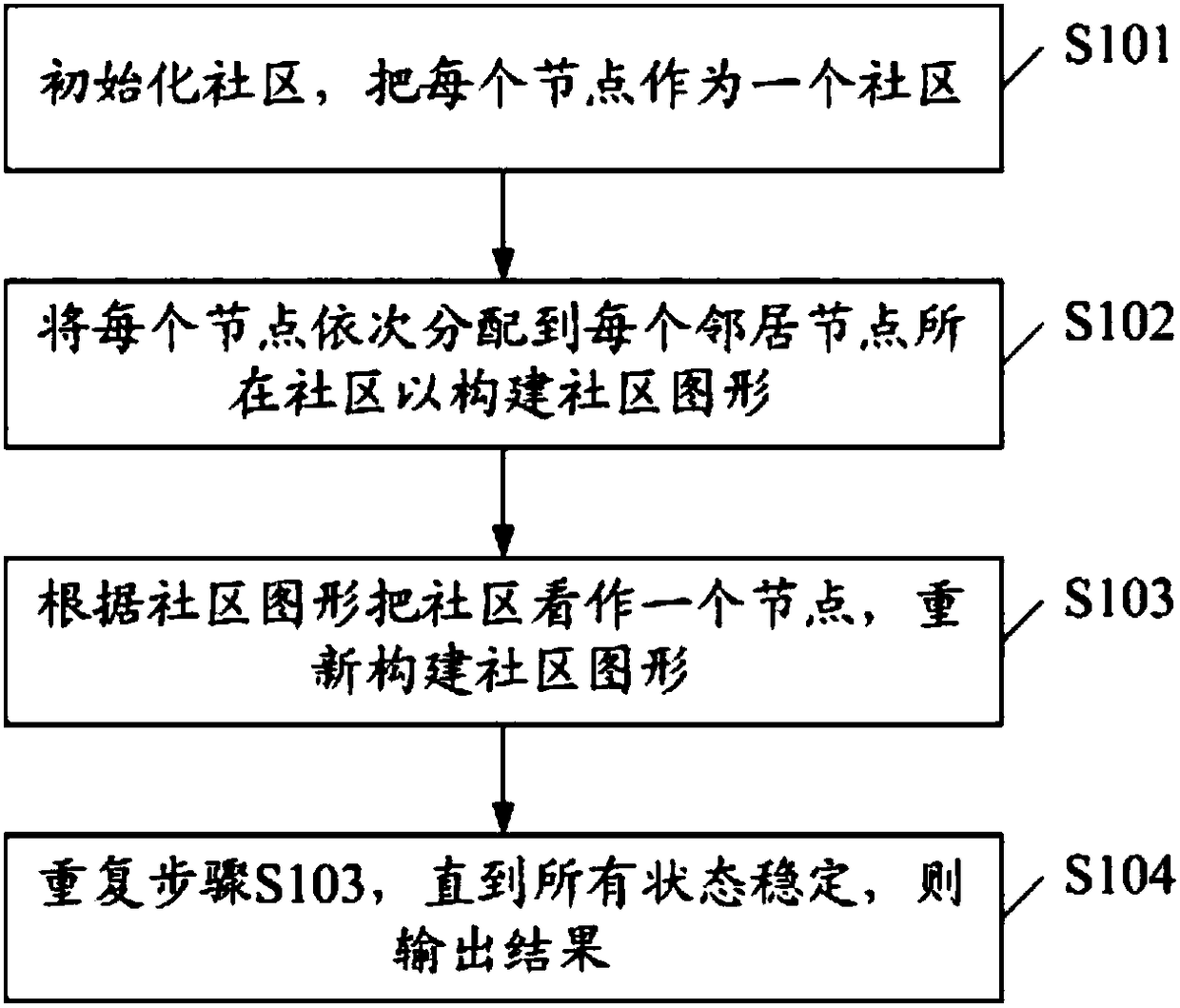
[0036] see figure 2 , figure 2 A flow chart of the first embodiment of a community discovery method based on the Louvain algorithm of the present invention is shown, which includes:
[0037] S101, initialize the community, and regard each node as a community;
[0038] S102, sequentially assigning each node to the community where each neighbor node is located to construct a community graph;
[0039] Specifically, the step S102 includes:
[0040] (1) Try to allocate each node to the community where each neighbor node is located in turn; preferably, the allocation is performed in a round-robin manner.
[0041] (2) Calculate the change in modularity before and after allocation; where the change in modularity before and after allocation refers to the difference between the modularity before and after allocation.
[0042] (3) Extract the maximum value of the variation of modularity;
[0043] (4) If the maximum value of the modularity change is greater than 0, assign the nodes...
no. 2 example
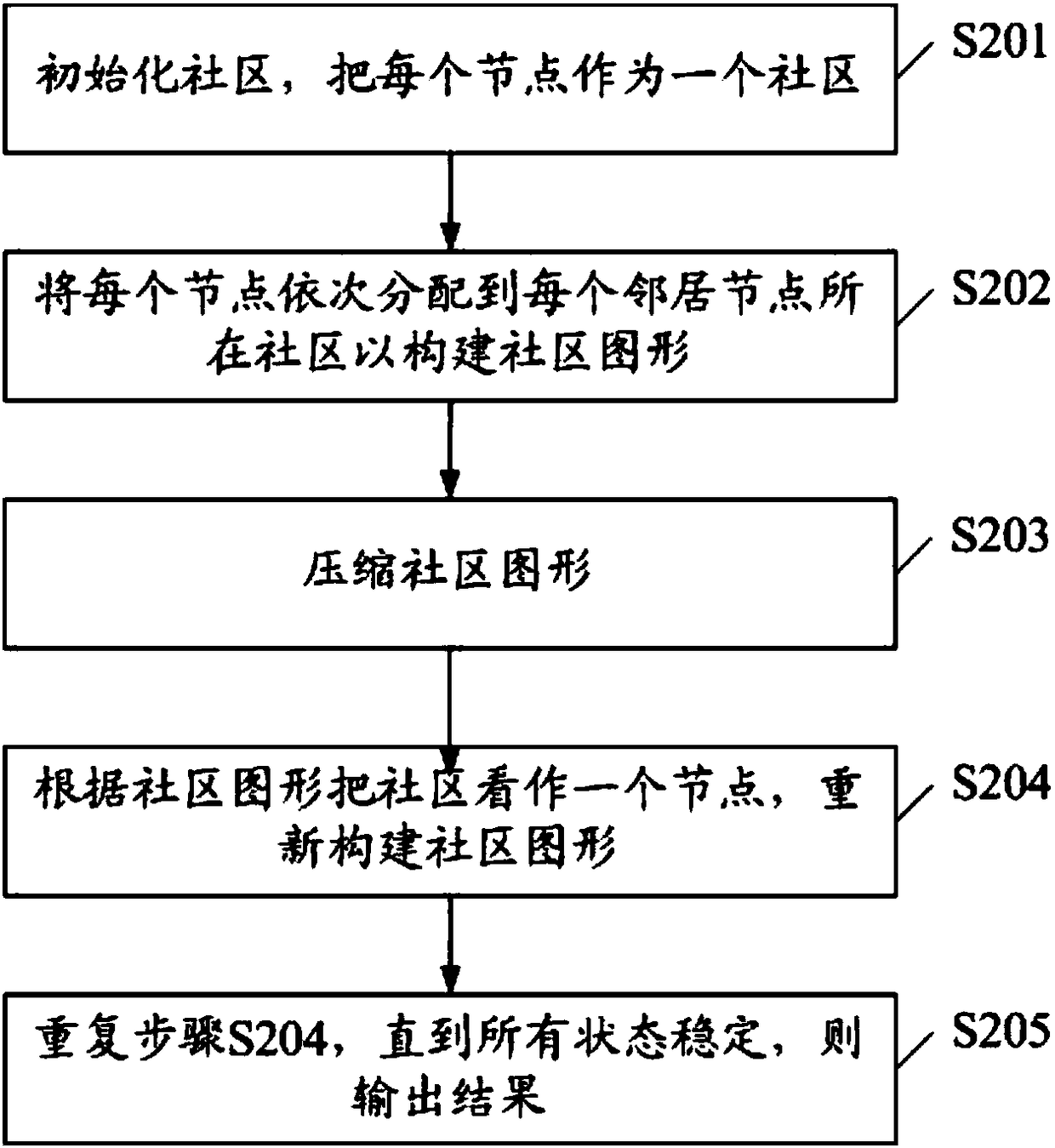
[0057] see image 3 , image 3 A flow chart of the second embodiment of a community discovery method based on the Louvain algorithm of the present invention is shown, which includes:
[0058] S201, initialize the community, and regard each node as a community;
[0059] S202, sequentially assigning each node to the community where each neighbor node is located to construct a community graph;
[0060] Specifically, the step S202 includes:
[0061] (1) Try to assign each node to the community where each neighbor node is located in turn;
[0062] (2) Calculate the change in modularity before and after allocation; where the change in modularity before and after allocation refers to the difference between the modularity before and after allocation.
[0063] (3) Extract the maximum value of the variation of modularity;
[0064] (4) If the maximum value of the modularity change is greater than 0, assign the nodes to the community, and repeat this step until all nodes do not chang...
no. 1 example
[0074] see Figure 4 , Figure 4 A first embodiment of the community discovery system 100 based on the Louvain algorithm of the present invention is shown, which includes:
[0075] Initialization module 1 is used to initialize the community, and each node is regarded as a community;
[0076] The first building block 2 is used to sequentially assign each node to the community where each neighbor node is located to construct a community graph;
[0077] The second building block 3 is used to regard the community as a node according to the community graph, and reconstruct the community graph;
[0078] The output module 4 is used to output the result when all the states are stable.
[0079] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the first building block 2 includes:
[0080] The allocation unit 21 is configured to try to allocate each node to the community where each neighbor node is located in turn; preferably, the allocation is performed in a polling manner.
[0081] The calculation un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com