A high-resolution SAR image classification method based on sparse features and conditional random fields
A conditional random field and sparse feature technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of not fully considering the correlation of image local features, fuzzy and inaccurate classification results, and inability to obtain segmentation results, etc., to overcome the influence of speckle noise and spatial information Underutilization, the effect of improving classification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
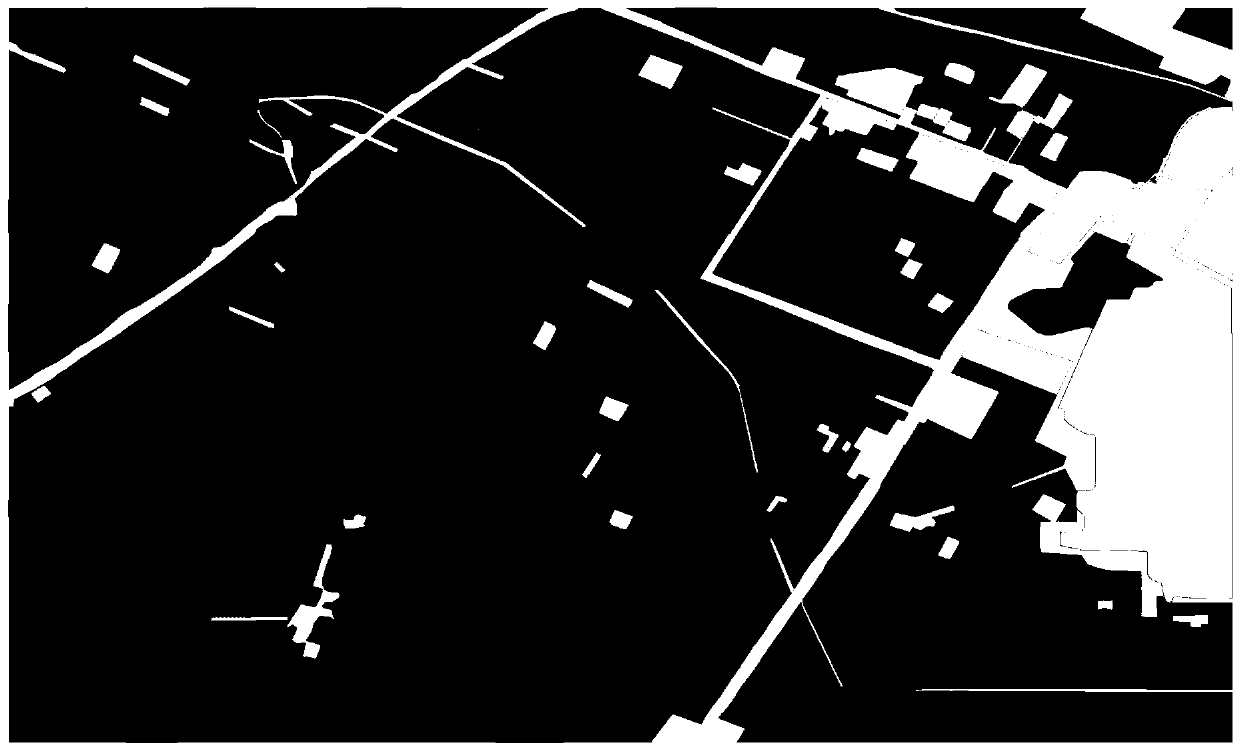
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
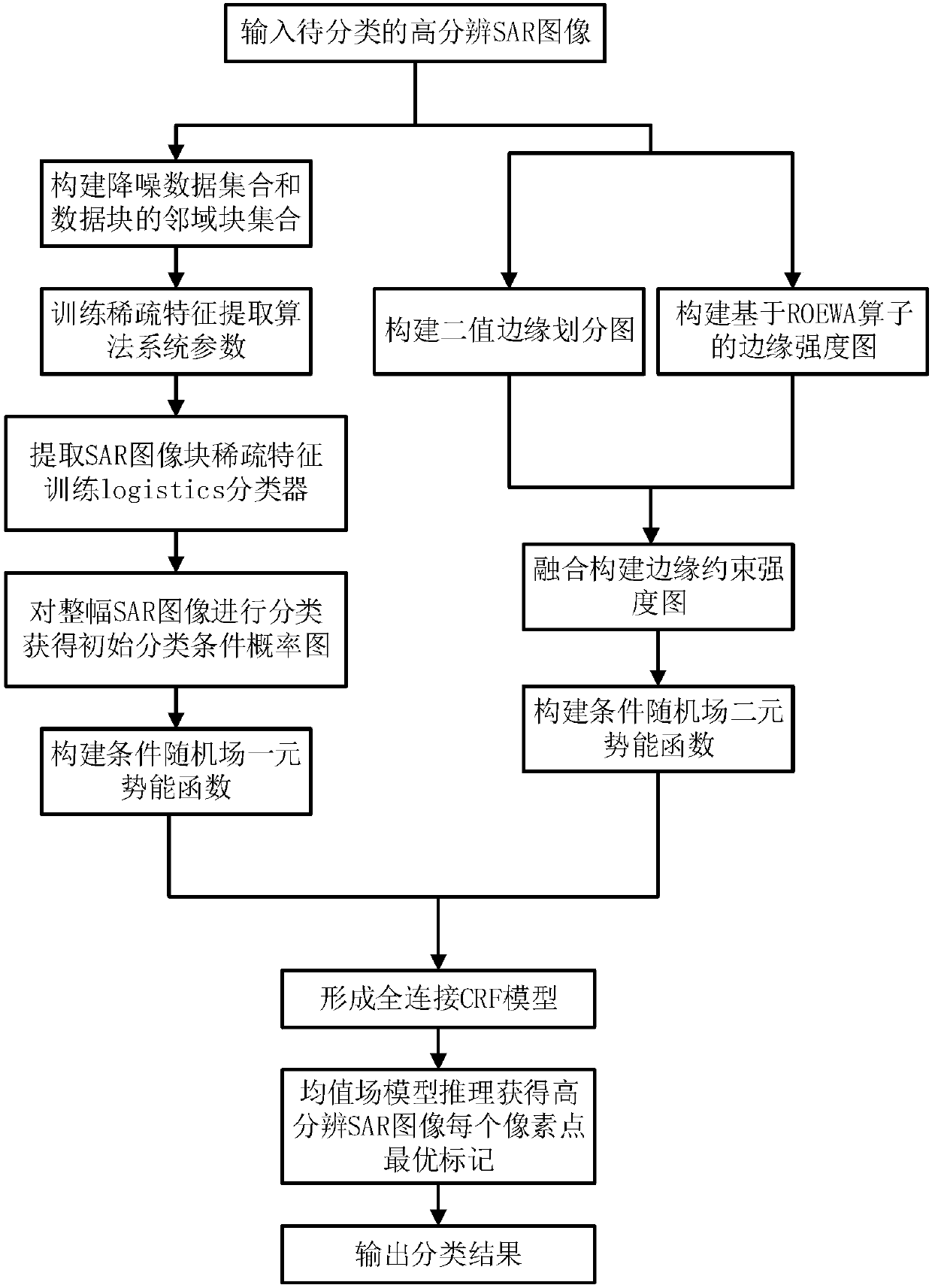
[0038] The specific embodiment and effect of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0039] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0040] Step 1. Input the high-resolution SAR image to be classified.
[0041] The input high-resolution SAR image Y to be classified in this example is a 256 grayscale image, and the grayscale value y of each pixel i i In order to round from 0 to 255, the total number of pixels contained in the SAR image Y is recorded as N, then the SAR image Y is expressed as: Y={y 1 ,...,y i ,...,y N}, i=1,2,...,N.
[0042] Step 2. Select the training noise reduction data block set and the neighborhood block set of the training data block.
[0043] 2a) Randomly select M training data blocks of size w×w from the SAR image Y, where M is set to 30000, w is set to 7, and for each data block d m , with its coordinate position as the center, select a search b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com