Time-frequency-space domain joint weighted circular harmonic domain pseudo-sound intensity sound source positioning method
A sound source localization, time-frequency domain technology, applied in localization, measurement devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the number of microphones or array size, and improving positioning accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
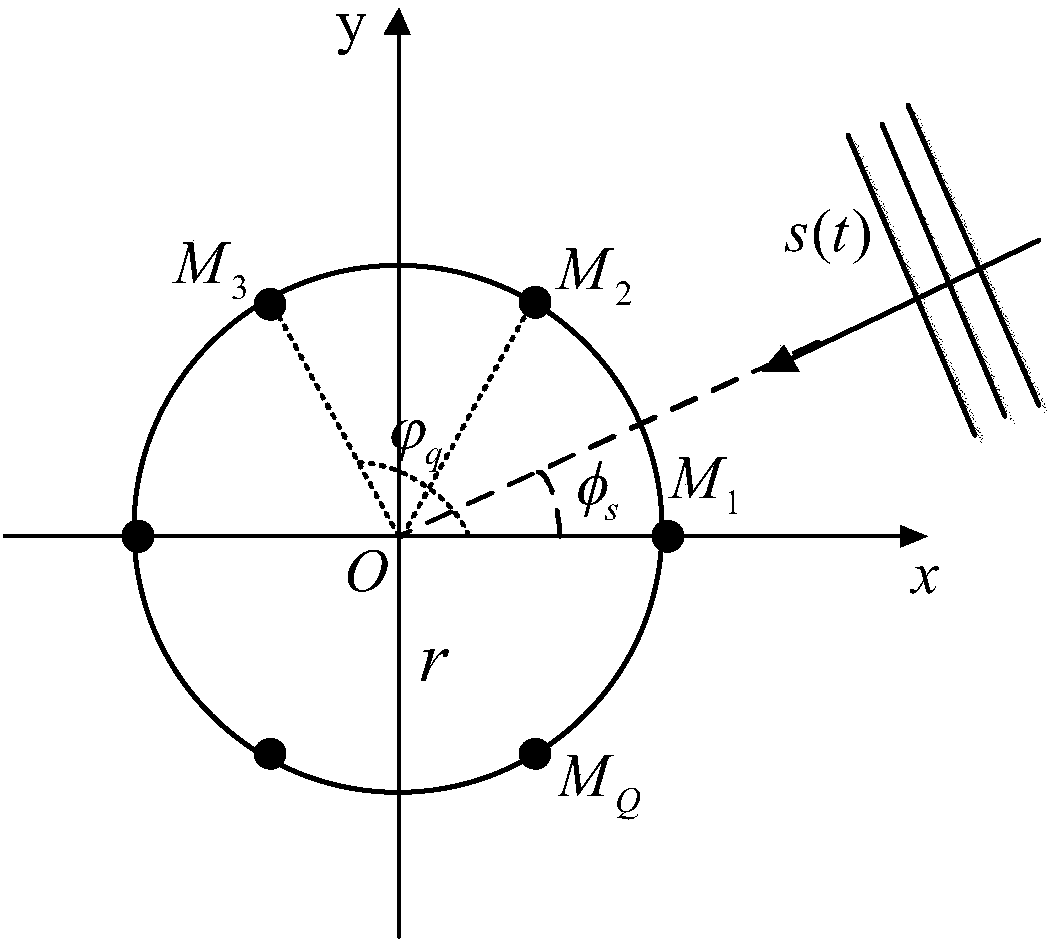
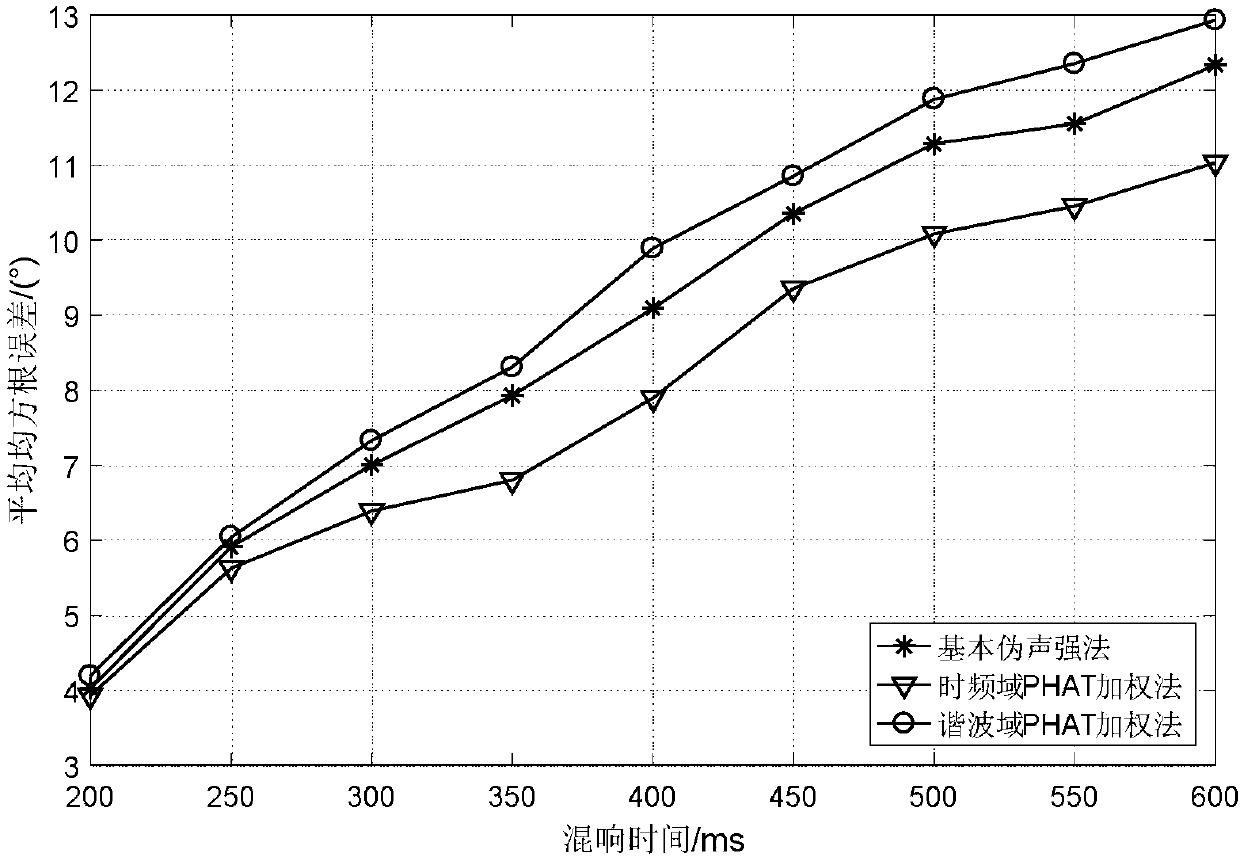
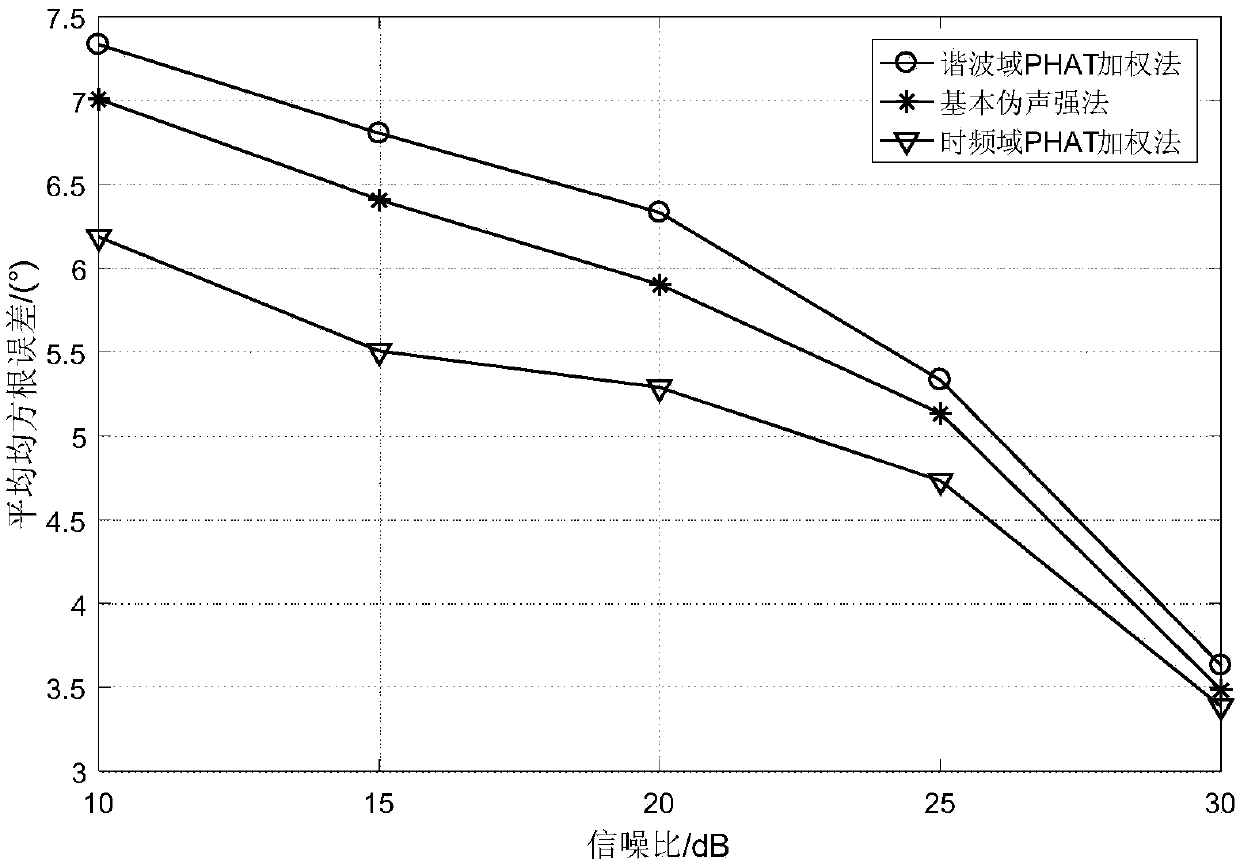
[0060] The present invention is a circular harmonic domain pseudo-sound intensity sound source localization method suitable for time-frequency-space joint weighting of a circular microphone array, using a six-element microphone array and combining voice signal characteristics for sound source localization, Figure 7 Shown is a flow chart of the present invention, and its specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0061] Step 1: Arranging Q identical omnidirectional microphones at equal intervals to form a circular microphone array with a radius of r;
[0062] Create a circular microphone array model, such as figure 1 As shown, there are Q omnidirectional microphones M 1 ,...,M Q Composition, the center of the array is selected as the coordinate origin O, the microphones are arranged counterclockwise and equally spaced on a circle with a rad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com