Power distribution network confidence peak clipping benefit assessment method capable of considering distributed photovoltaic randomness
A distributed photovoltaic and distribution network technology, applied in computing, instrumentation, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient peak shaving benefit evaluation, difficulty in determining the value of distribution network, randomness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
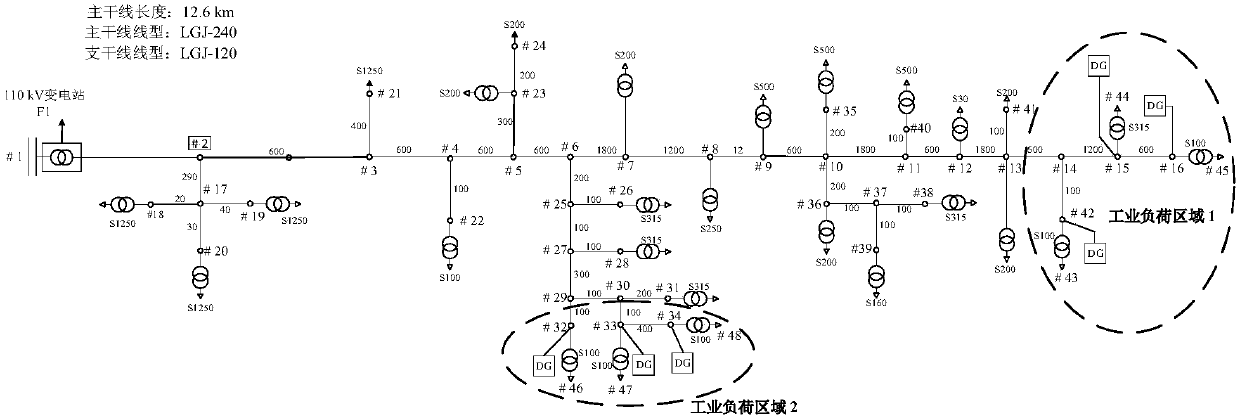
[0032] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example, and it should be pointed out that if there are no special details (such as figure 2 The symbols in ) can be understood or implemented by those skilled in the art according to the prior art.
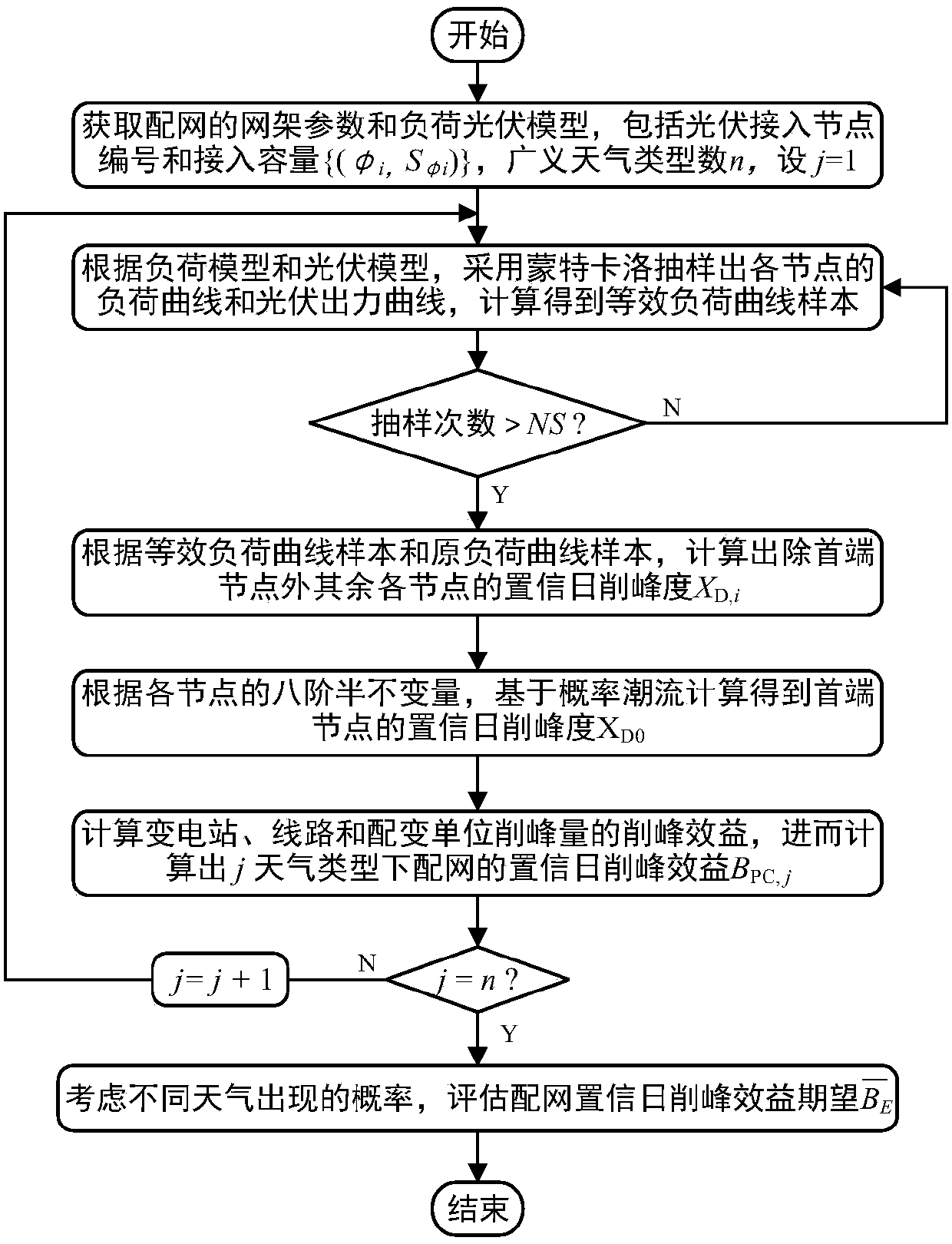
[0033] figure 1 It reflects the specific process of the distribution network confidence peak shaving benefit evaluation method considering the randomness of distributed photovoltaics, including the following steps:
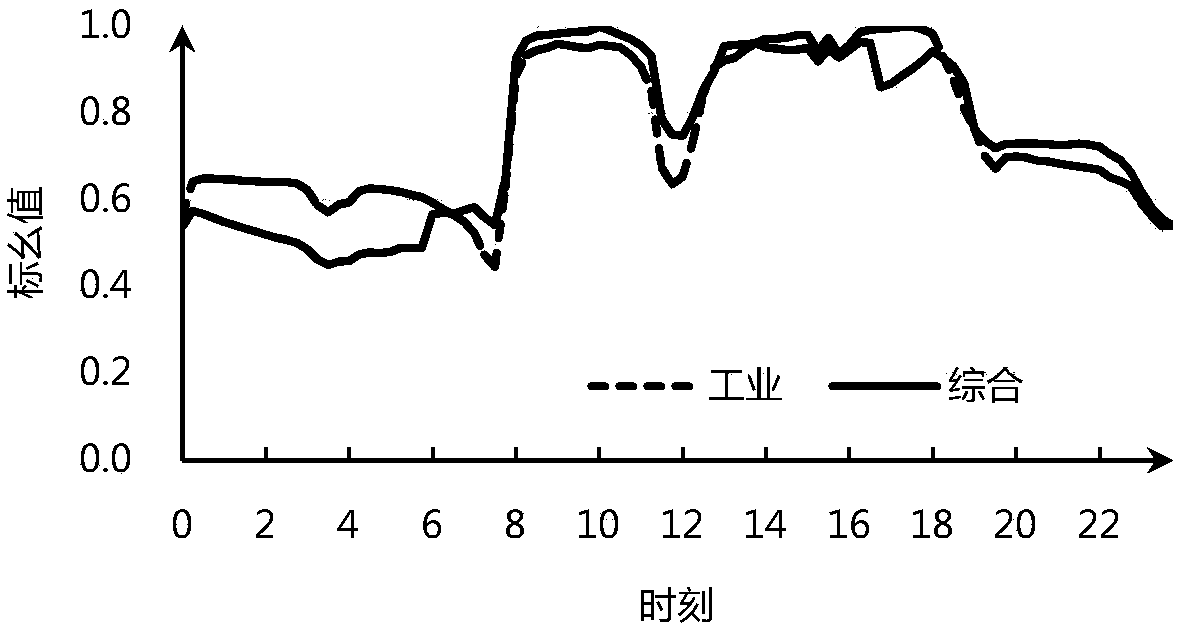
[0034] (1) Obtain the grid parameters, load model and photovoltaic output model of the distribution network. The grid parameters include the line impedance of the distribution network and the impedance of each distribution transformer; the load model is a load probability model considering the load prediction error; The output model is a photovoltaic output probability model that considers the fluctuation and timing of photovoltai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com