A fault line selection method for distribution network based on random matrix and hausdorff distance
A technology of distribution network fault and line selection method, which is applied to the fault location, detects faults by conductor type, and measures electricity, etc., and can solve the problems of system model distribution network fault line selection, distribution network fault line selection dependence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
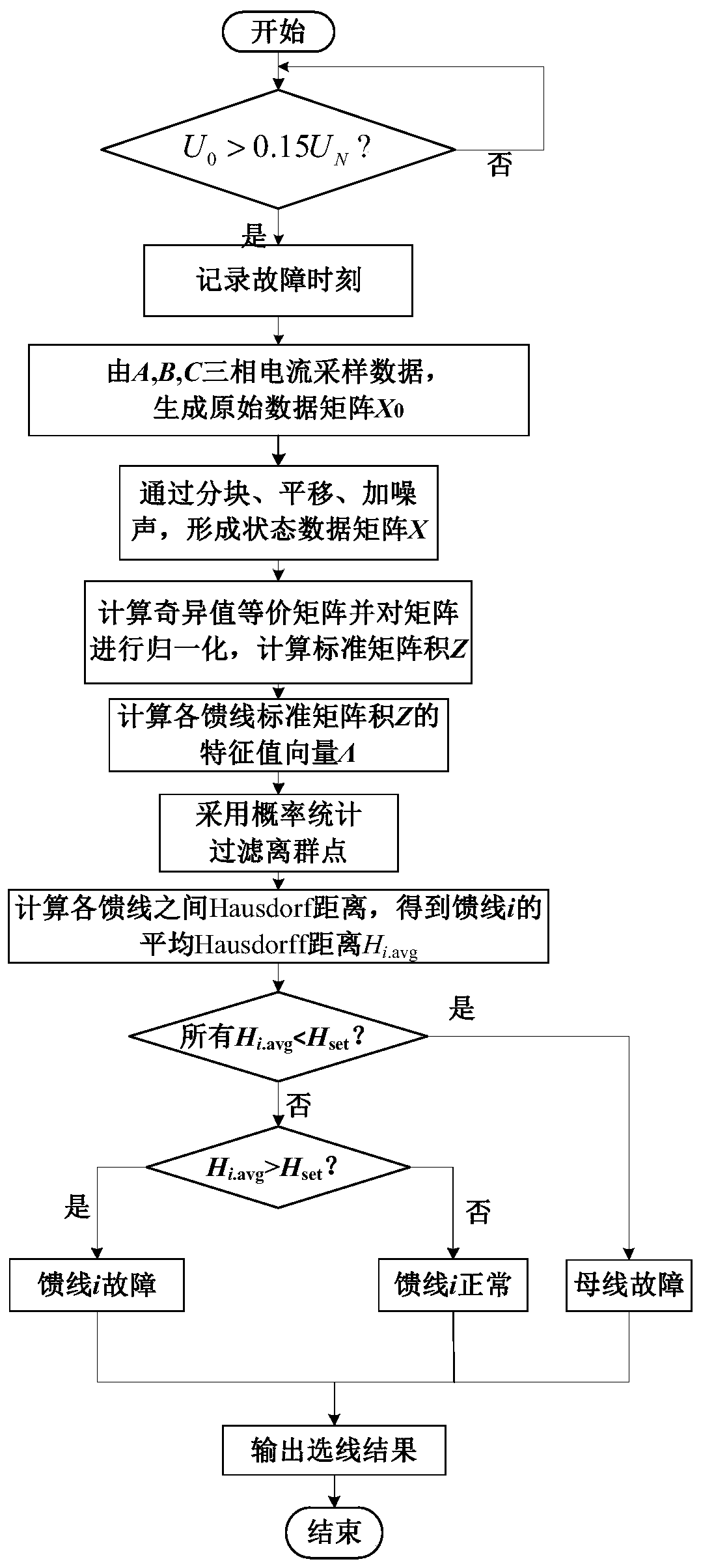
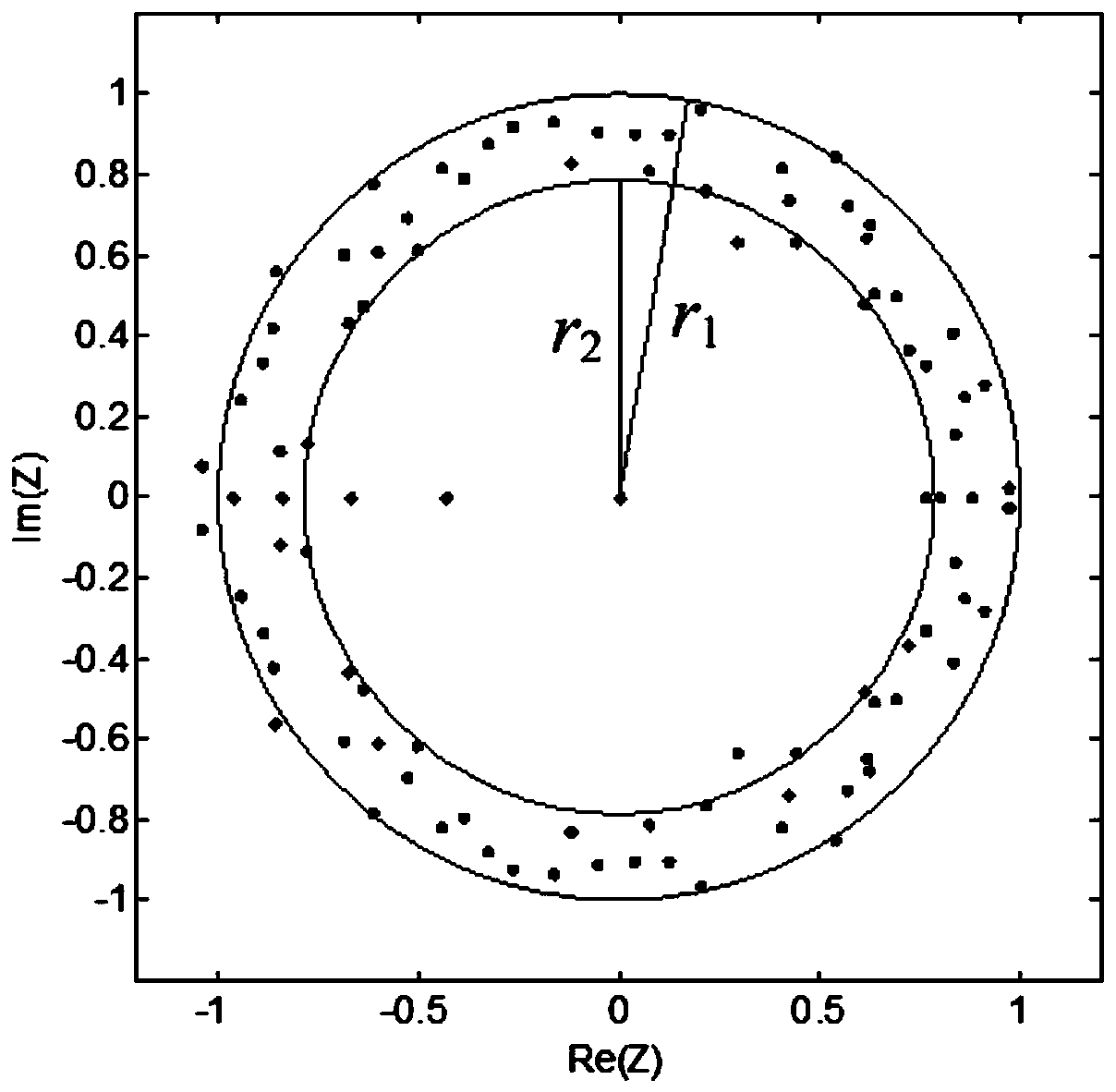
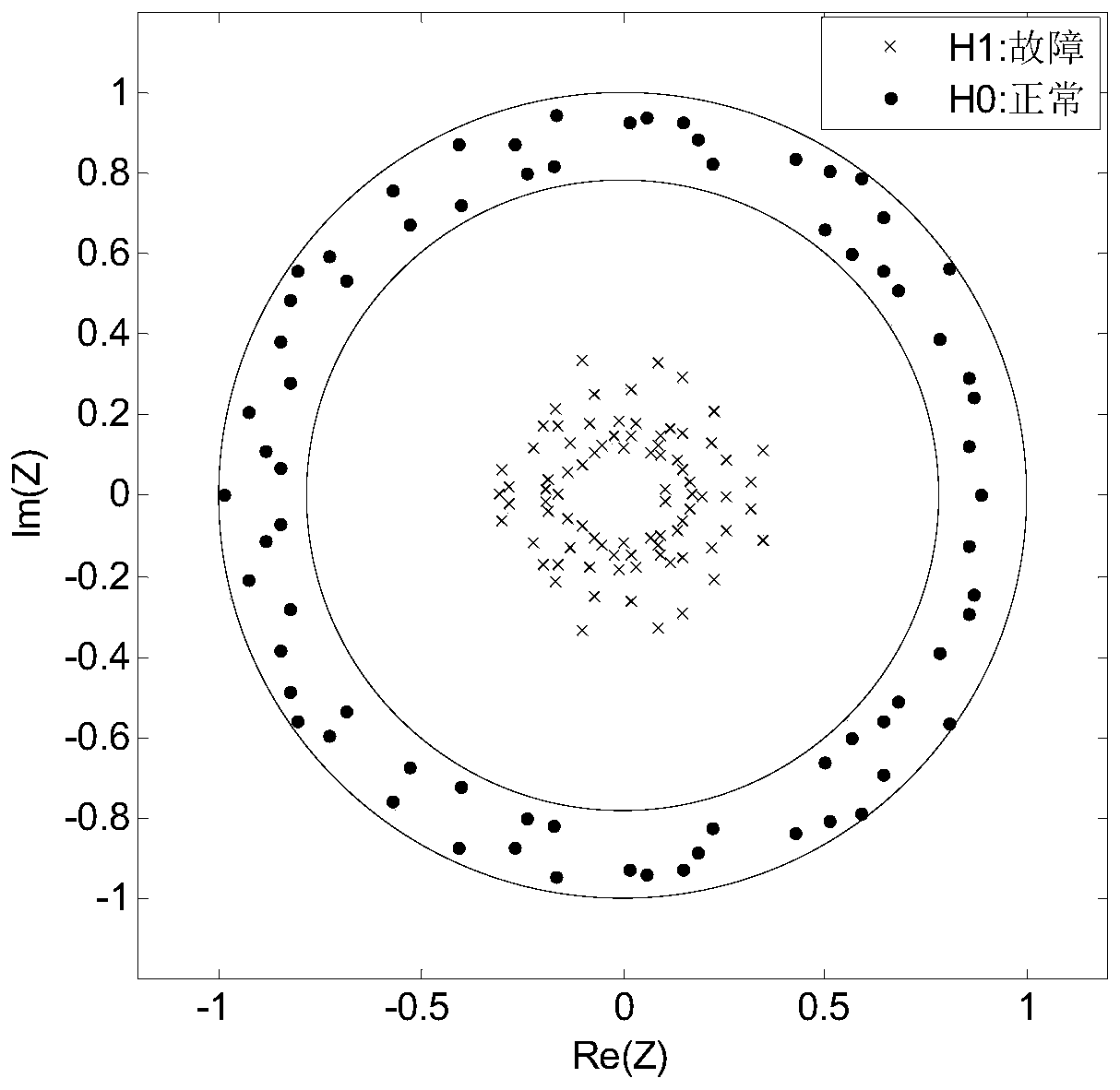
[0157] According to an embodiment of the present application, refer to Figure 4 , using MATLAB / Simulink to build and simulate the distribution network.
[0158] Build 5 distribution networks in MATLAB / Simulink. There are 5 feeders on the low-voltage side of the distribution transformer. The feeder l 1 , l 2 is the overhead line model, l 3 , l 4 is the cable route model, l 5 It is a cable-line hybrid model (75% overhead line + 25% cable). Among them, the positive sequence parameter R of the overhead line 1 = 0.096Ω / km, L 1 =1.22mH / km, C 1 =0.011uF / km; zero sequence parameter R 0 = 0.23Ω / km, L 0 =3.66mH / km, C 0 =0.007uF / km; cable positive sequence parameter R 11 =0.11Ω / km, L 11 =0.52mH / km, C 11 =0.29uF / km; zero sequence parameter R 00 = 0.34Ω / km, L 00 =1.54mH / km, C 00 = 0.19uF / km.
[0159] When simulating the grounding system of the arc suppression coil, the overcompensation mode is used to operate, the overcompensation degree is 8%, the inductance of the arc s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com