Synthesis method of stemona alkaloid
A synthetic method and technology of alkaloids, applied in organic chemistry methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as low natural content, complex structure, and no total synthesis report
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1 Preparation of 4-(1H-pyrrolyl) ethyl butyrate (6)
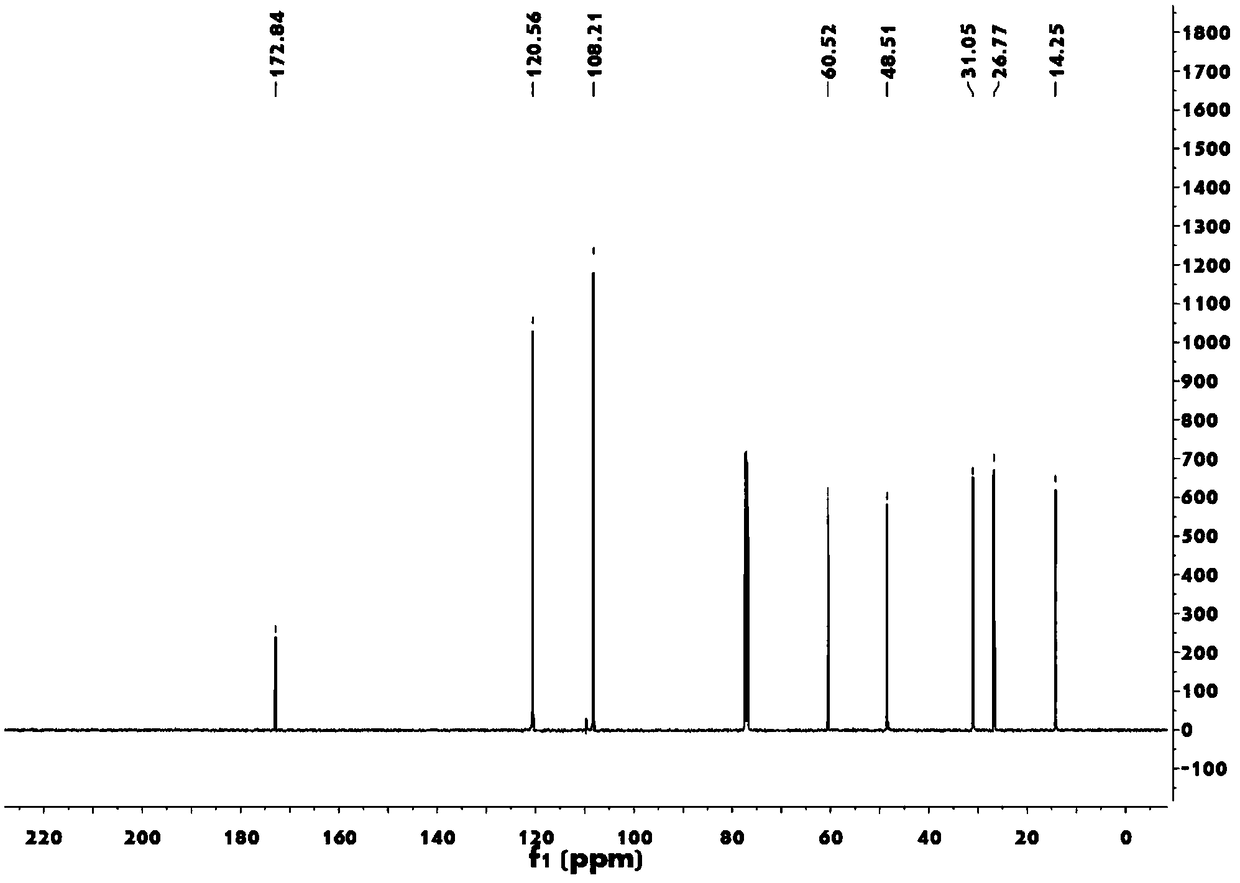
[0055] 2,5-Dimethoxytetrahydrofuran (8.5 g, 63 mmol) was added into water (180 mL), stirred and refluxed under argon for 2 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, and dichloromethane (100 mL), sodium acetate (13 g, 155 mmol) and ethyl 4-aminobutyrate hydrochloride (13 g, 78 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred vigorously in the dark for 15 hours. A 2M sodium carbonate solution (20 mL) was added and extracted with dichloromethane. After drying with magnesium sulfate and filtering, the filtrate was concentrated and the resulting residue was subjected to column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:1) to obtain 9.0 g of pyrrole derivatives (yield: 77%).
[0056] FTIR (neat, cm -1 )ν max 2980, 1732, 1500, 1447, 1375, 1282, 725;
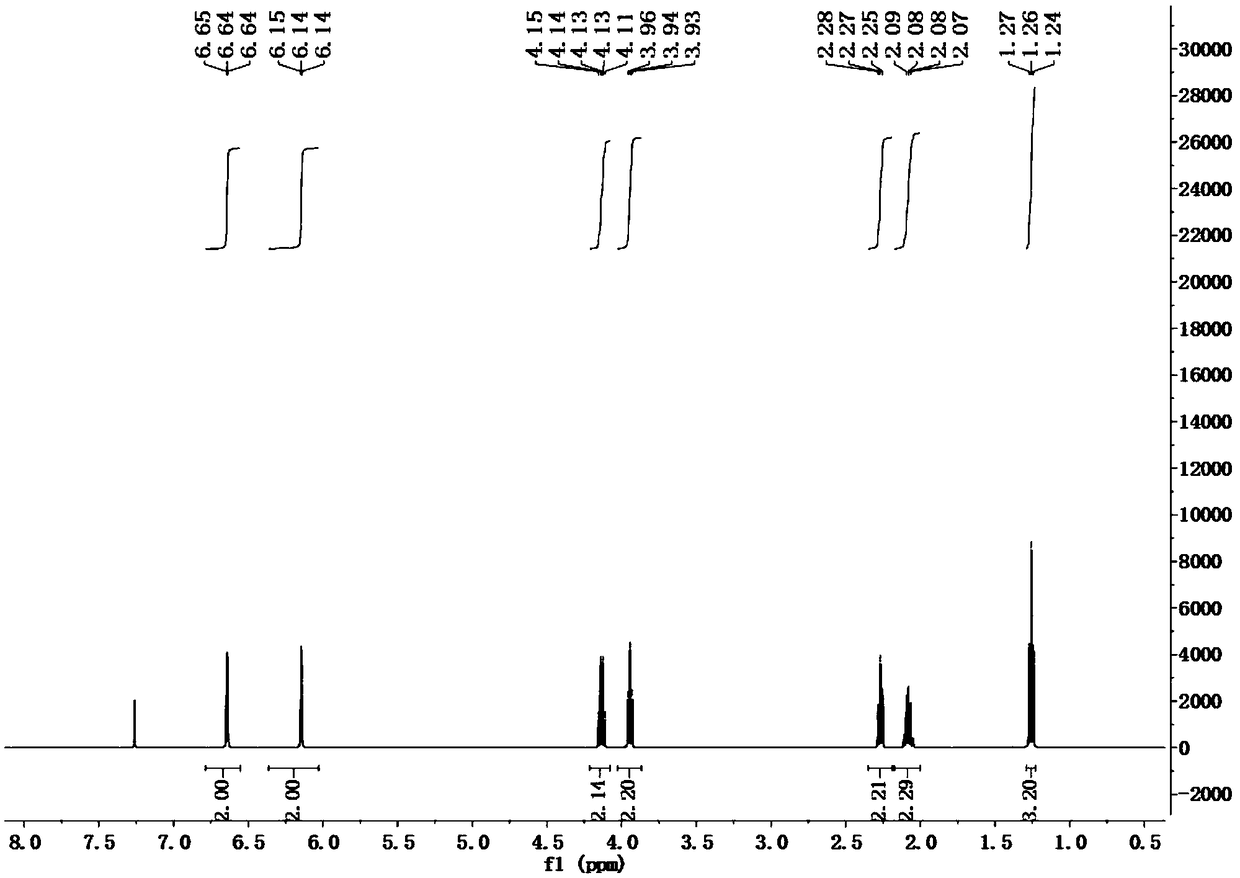
[0057] 1H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 6.64(t, J=2.0Hz, 2H), 6.14(t, J=2.1Hz, 2H), 4.13(q, J=7.1Hz, 2H), 3.94(t, J=6.9Hz, 2H) ,2.27(t,J=7.3Hz,2H),2.13–...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Preparation of N-methoxy-N-methyl-4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)butanamide (7)
[0061] At -20°C, a 2.0M concentration of i-PrMgCl (0.64mL, 1.27mmol) in tetrahydrofuran was added dropwise to ethyl 4-(1H-pyrrolyl)butyrate (6) (0.1g, 0.55mmol) and Me(MeO)NH·HCl (64 mg, 0.66 mmol) in anhydrous THF (1.5 mL). The mixture was slowly warmed to 0°C, stirred at 0°C for 2 hours, then quenched with saturated ammonium chloride solution. The mixture was extracted with EA. The organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, the filtrate was concentrated and the residue obtained was subjected to column chromatography (n-hexane:ethyl acetate=1:1) to obtain N-methoxy-N-methyl-4-(1H -Pyrrol-1-yl)butyramide 0.1 g (yield: 92%).
[0062] FTIR (neat, cm -1 )ν max 29377, 1660, 1500, 1445, 1386, 1281, 726;
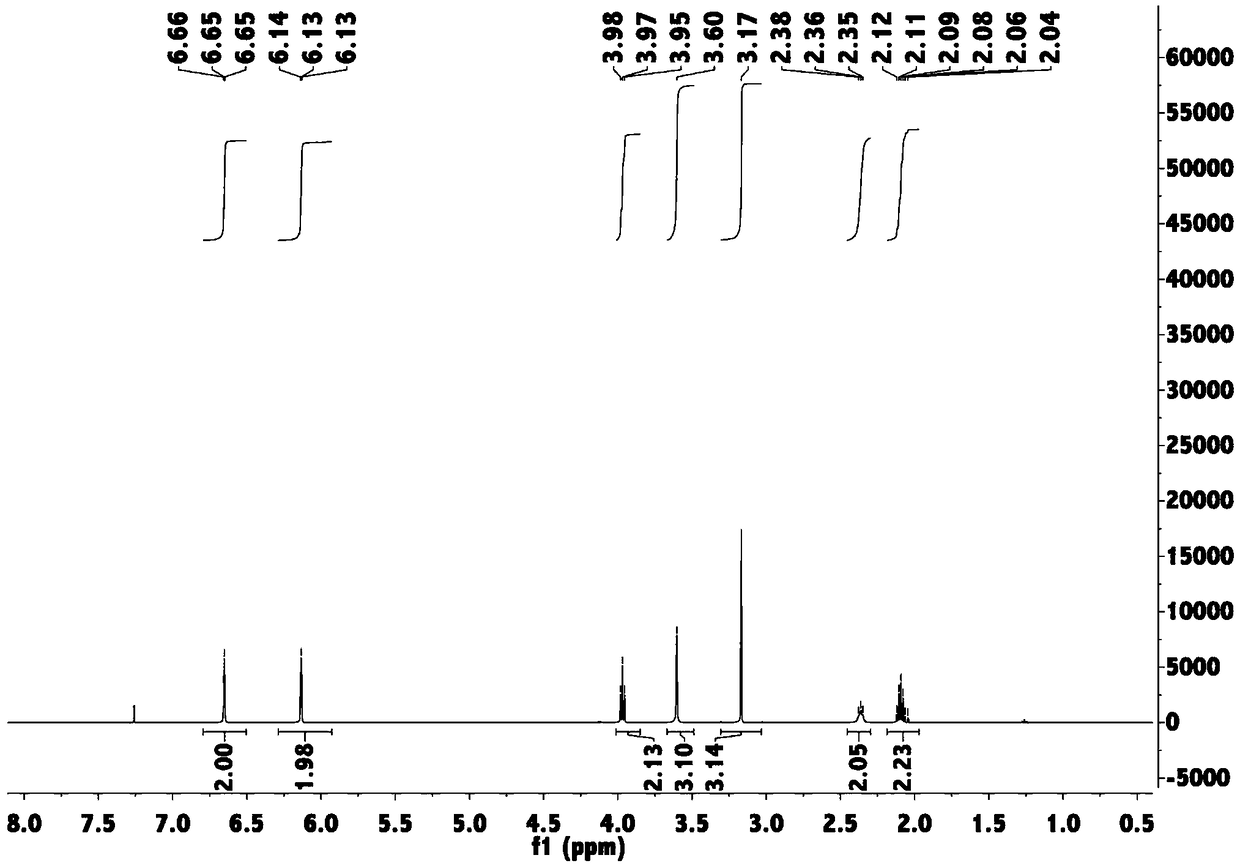
[0063] 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 6.65(t, J=2.1Hz, 2H), 6.13(t, J=2.1Hz, 2H), 3.97(t, J=6.8Hz, 2H), 3.60(s, 3H), 3.17(s, 3H), 2.36(t, J=7.1Hz, 2H),...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Preparation of 6-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)hexyl-1-en-3-one (8)
[0067] To a solution of N-methoxy-N-methyl-4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)butanamide (2.6 g, 13.3 mmol) in THF (120 mL) gradually over 20 minutes at -20°C Vinylmagnesium chloride (1M solution in tetrahydrofuran, 16ml, 16mmol) was added dropwise, and the reaction mixture was stirred at this temperature for 2 hours. Under argon, it was quenched with water (50 mL) at -10 °C. The aqueous layer was extracted with ether, the combined organic layers were washed with saturated sodium chloride solution, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product, which was directly used in the next reaction.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com