An optical path folding device
A technology of optical path and device, which is applied in the direction of optical components, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of astigmatic lenses that are difficult to process, cannot be applied, and does not solve the problem of processing costs of astigmatic lenses, and achieve the effect of multiple reflections
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
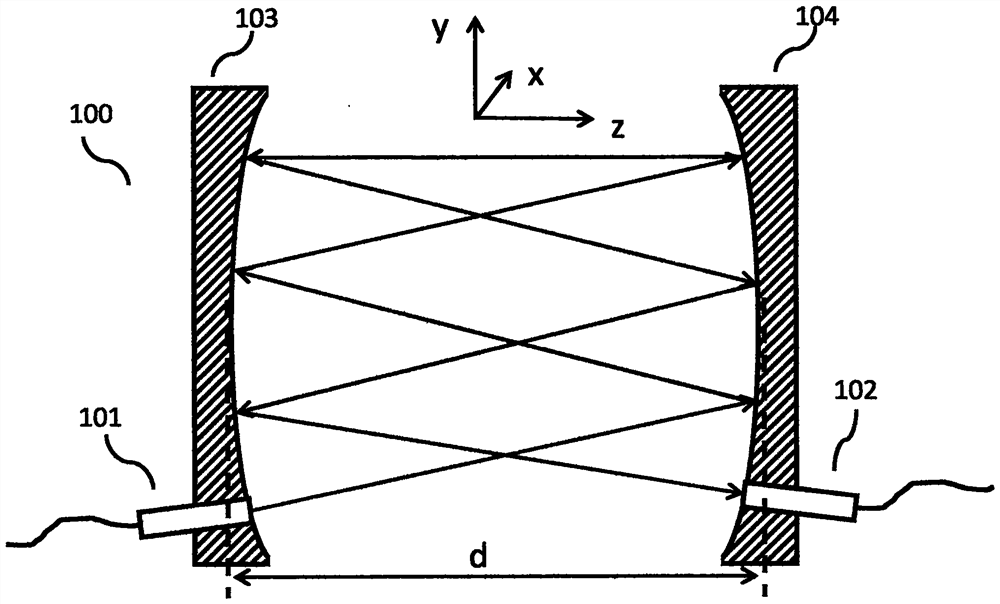
[0054] like Figure 10 As shown, an optical path folding device (1000) provided by the present invention includes:
[0055] An input port (1001) for inputting a light beam;
[0056] an output port (1002), for outputting light beams;
[0057] a principal plane mirror (1004);
[0058]A concave reflector (1003) has a focal plane (1006), and the distance (1007) from the focal plane to the concave reflector is the focal length f of the concave reflector; the focal plane also has an origin (1009), which is The intersection point of the optical axis (1008) of the optical system composed of the main plane reflector and the concave reflector.
[0059] A tilting sub-mirror (1005), which is a facet mirror whose normal line forms an inclination angle θ with the normal line of the main plane mirror;
[0060] The input end, the output end, the main plane reflector, and the inclined sub-reflector are coplanar and located on the focal plane of the concave reflector; the light beam is inpu...
Embodiment 2
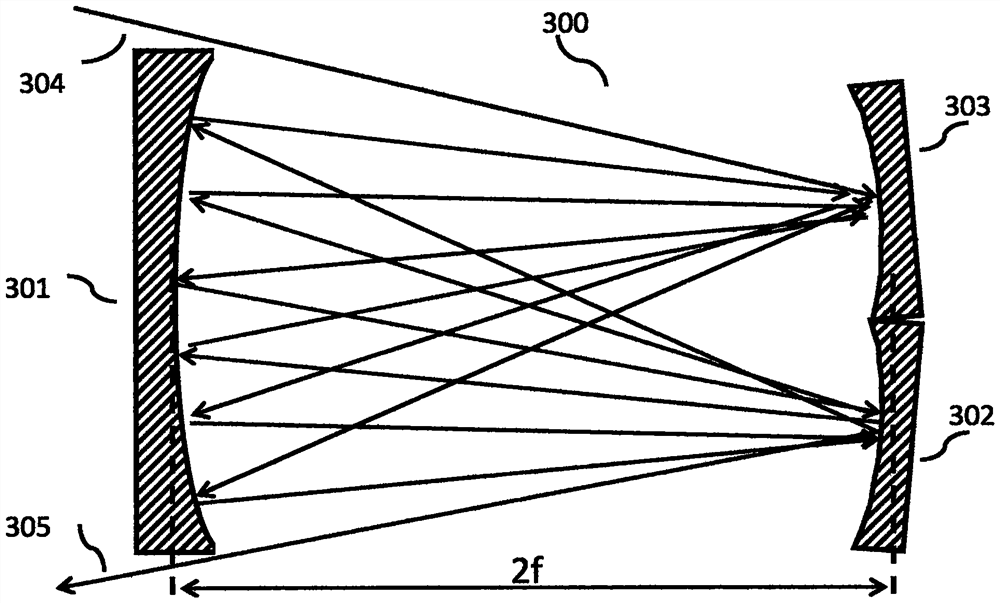
[0065] This embodiment is similar to embodiment 1, as Figure 11 As shown, the difference with embodiment 1 is:
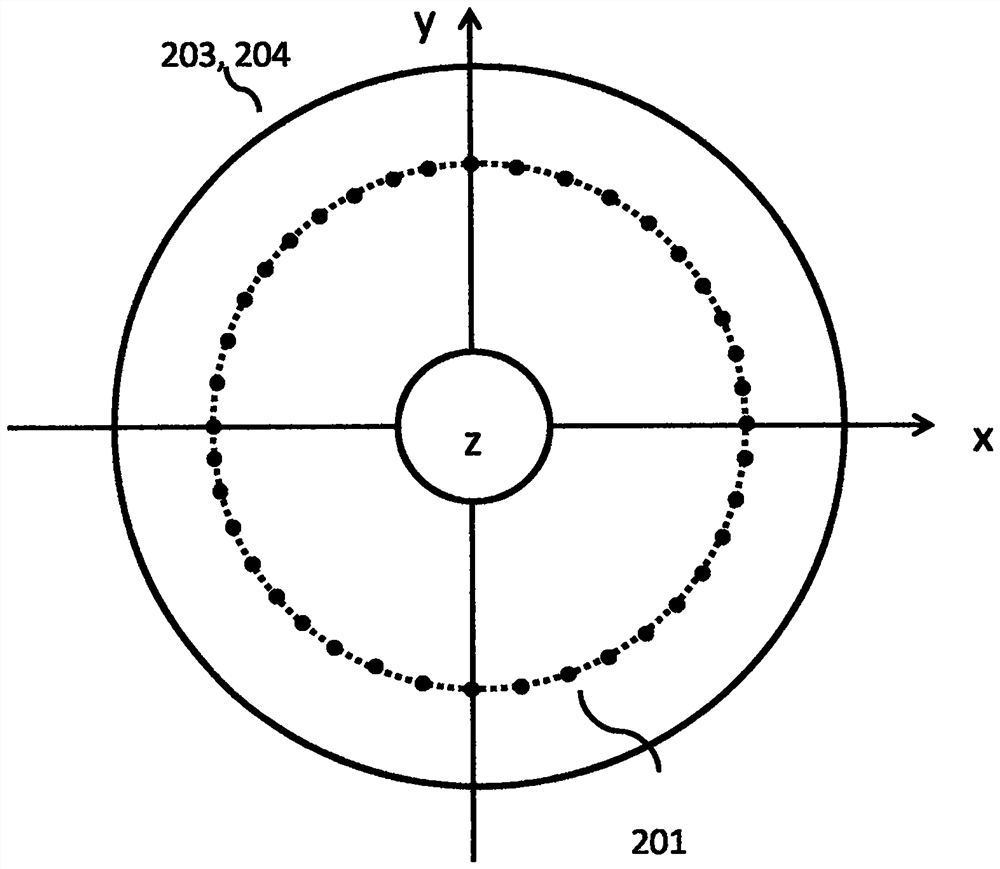
[0066] 1. The input end (1101) and the output end (1102) are fiber collimators with pigtails, the input beam is coherent light, and the beam input from the fiber collimator to the optical path folding device is a Gaussian beam, which has a Gaussian beam The waist radius ω and the far-field divergence half-angle α define the beam radius as A 0 =3ω, divergence half angle β 0 =3α, to cover most of the energy of the Gaussian beam, and thus obtain the distance that the tilted sub-reflector (1105) deviates from the origin (1109) is 6α f, and the aperture is taken as 9α f; the edge distance input of the tilted sub-reflector and The shortest distance of the connecting line at the output end is taken as 6ω.
[0067] 2. The concave reflector (1103) is a spherical reflector.
[0068] In the case of ω=0.2mm, f=200mm, and α=2.5mrad, it can be obtained that the distance of t...
Embodiment 3
[0070] This embodiment is similar to Embodiment 2, as Figure 12 As shown, the difference is that the tilting sub-mirror (1205) can be rotated along the tilting direction to change the size of the tilting angle θ, and its rotation axis (1218) is within the focal plane (1206) where the main plane mirror (1204) is located , and driven by a piezoelectric ceramic driver (1219), the tilt angle θ is measured by an optical angle measuring device (1220) with a measuring laser and a four-quadrant detector. After reflection, it reaches the four-quadrant detector, and the size and direction of the inclination angle θ are obtained after comparison and calculation of the light intensity data of the four-quadrant detector.
[0071] The variable tilt angle θ leads to variable displacement vector ΔP, and the selection of the tilt angle θ makes the distance between the input end and the output end an integer multiple of ΔP, so that the light beam can reach the output end (1202) from the input ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com