Method for improving low-temperature impacting power of 17-4 PH maraging stainless steel forged piece based on organization control
A low-temperature impact and martensite technology, which is applied in the field of improving low-temperature impact energy of 17-4PH maraging stainless steel forgings based on structure control, improving low-temperature impact energy of 17-4PH maraging stainless steel forgings, and can solve the problem of unclear direction and other problems to achieve the effect of eliminating directionality and improving low temperature impact energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0024] Example one.
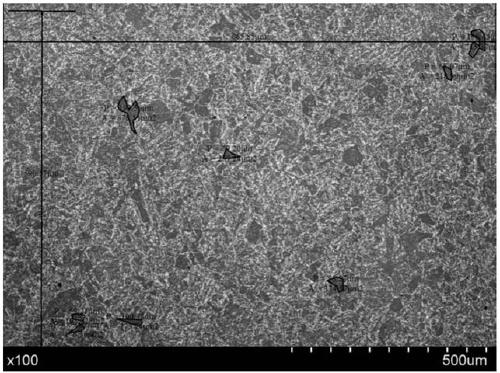
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown.
[0026] A high and low temperature impact energy 17-4PH maraging stainless steel forging, its chemical composition (in mass percentage %): carbon (C) 0.040, chromium (Cr) 15.25, nickel (Ni) 4.75, copper (Cu) 3.35, manganese (Mn) 0.65, niobium (Nb) + tantalum (Ta) 0.3, silicon (Si) 0.30, titanium (Ti) 0.025, molybdenum (Mo) 0.15, aluminum (Al) 0.010, nitrogen (N) 0.040, phosphorus (P) 0.020, sulfur (S) 0.015, the balance is iron (Fe), the sum of each component is 100%. Its forging process is forging heating (forging billeting) temperature ≤ 1200℃, forging deformation adopts three upsetting and three drawing, total forging ratio is 5; its heat treatment process is two solid solution + aging heat treatment, of which the first solid solution + aging The treatment process is: solid solution at 1050°C, air cooling until the core temperature of the forging is below the martensite transformation starting temperature (Ms point), over-a...
Example Embodiment
[0028] Example two.
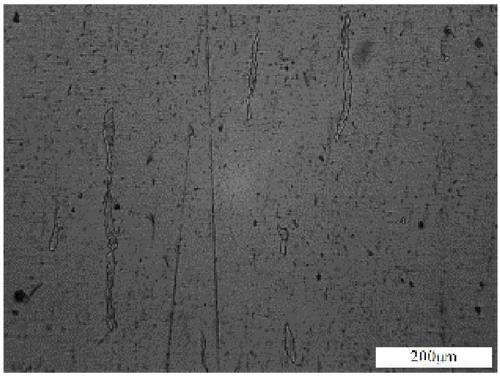
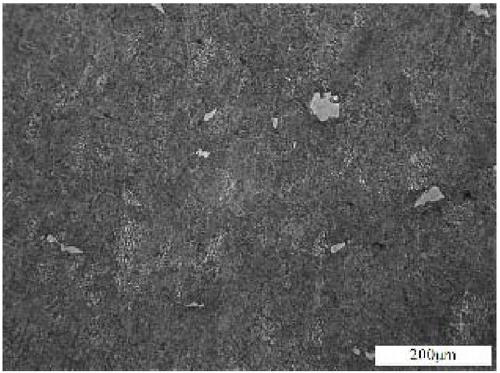
[0029] Such as figure 2 , 3 Shown.
[0030] figure 2 It is the metallographic structure before forging with positive pressure applied along the direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the elongated high-temperature ferrite. image 3 It is the metallographic structure after forging with positive pressure along the direction perpendicular to the length of the long strip high-temperature ferrite. By forging along the direction perpendicular to the length of the long high-temperature ferrite in the 17-4PH maraging stainless steel forging, the long high-temperature ferrite is upset and its directionality is effectively eliminated. Significantly improve the low-temperature impact energy.
Example Embodiment
[0031] Example three.
[0032] A high and low temperature impact energy 17-4PH maraging stainless steel forging, its chemical composition (in mass percentage %): carbon (C) 0.030, chromium (Cr) 15.00, nickel (Ni) 4.50, copper (Cu) 3.20, manganese (Mn) 0.80, niobium (Nb) + tantalum (Ta) 0.45, silicon (Si) 0.35, titanium (Ti) 0.030, molybdenum (Mo) 0.20, aluminum (Al) 0.015, nitrogen (N) 0.050, phosphorus (P) 0.030, sulfur (S) 0.020, the balance is iron (Fe), the sum of each component is 100%. Its forging process is forging heating (forging billeting) temperature ≤ 1200℃, forging deformation adopts three upsetting and three drawing, total forging ratio is 6; its heat treatment process is two solid solution + aging heat treatment, of which the first solid solution + aging The treatment process is: solid solution at 1050°C, air cooling until the core temperature of the forging is below the martensite transformation starting temperature (Ms point), over-aging at 650°C; the second sol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com