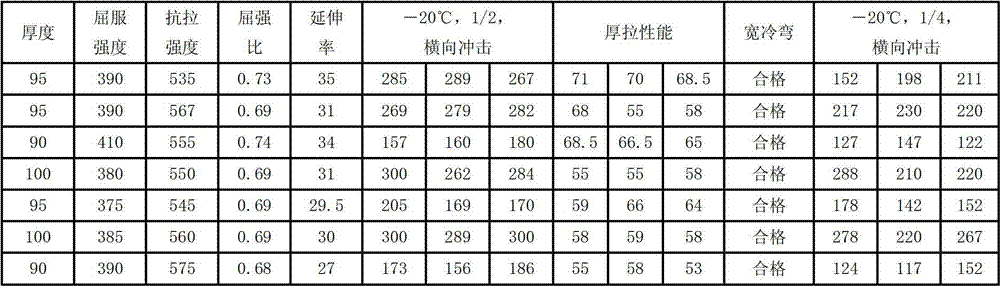
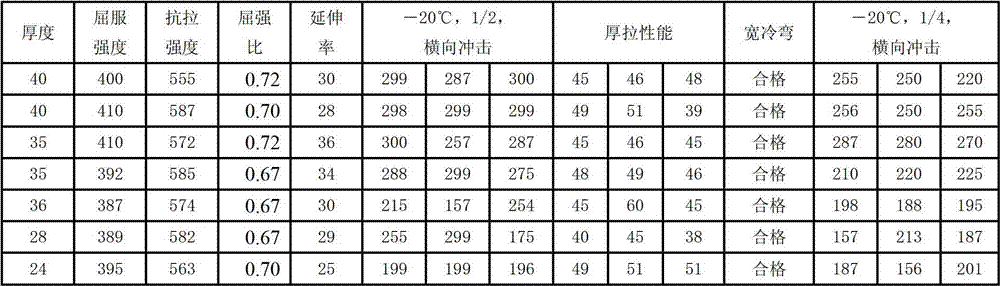
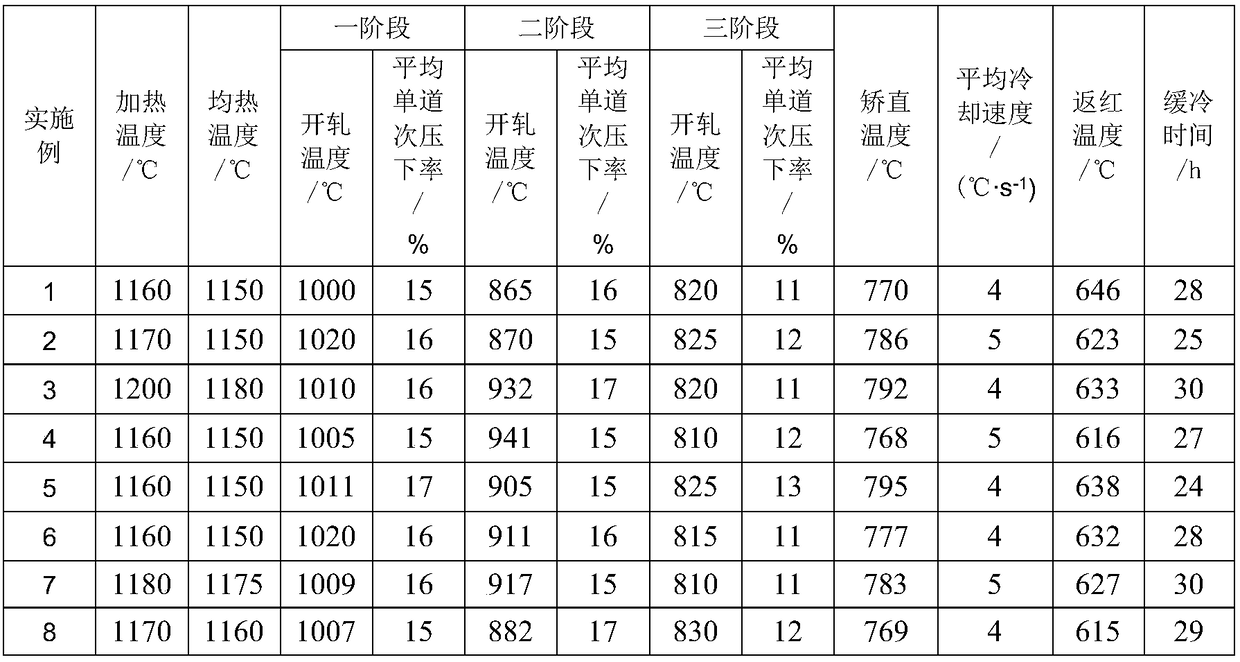
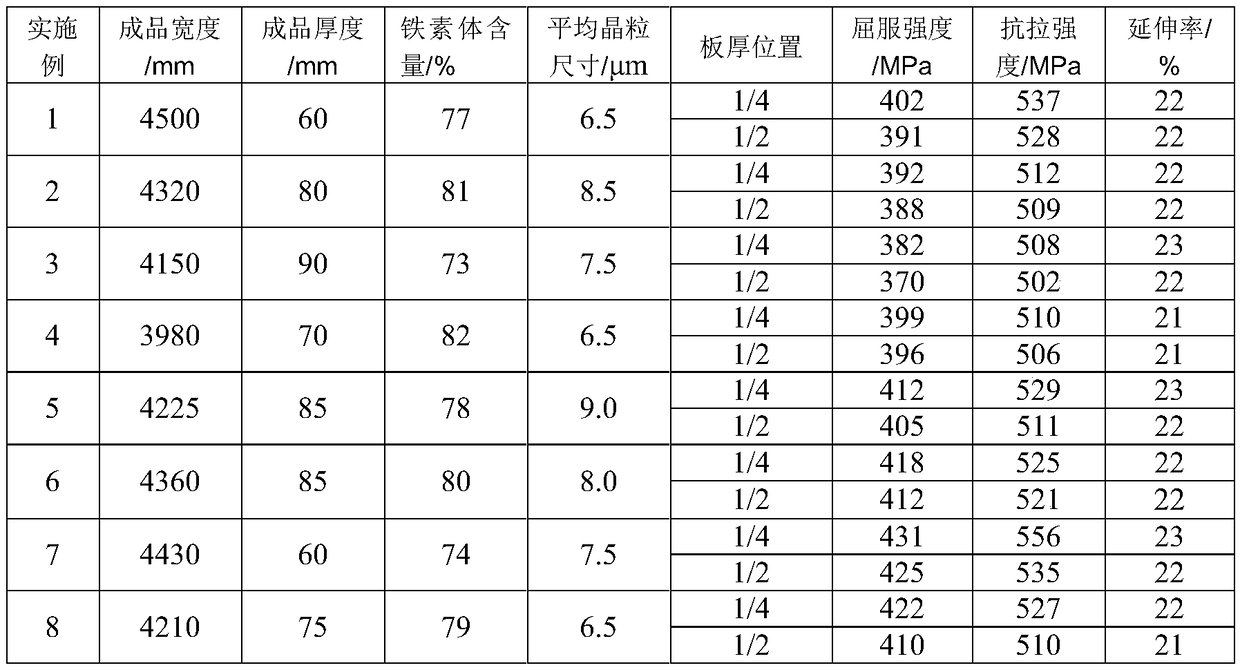
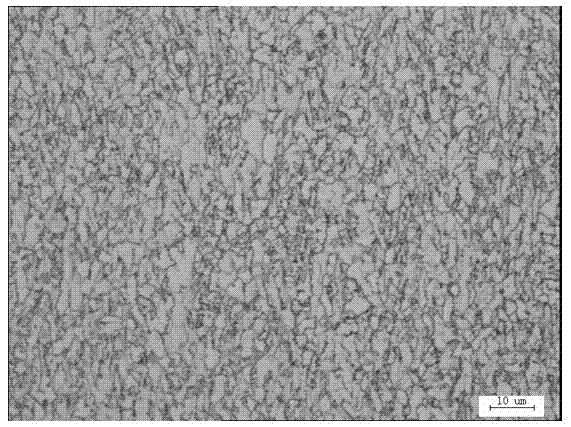
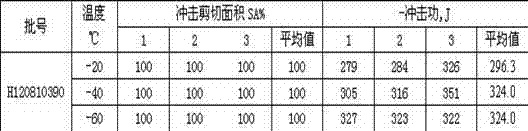
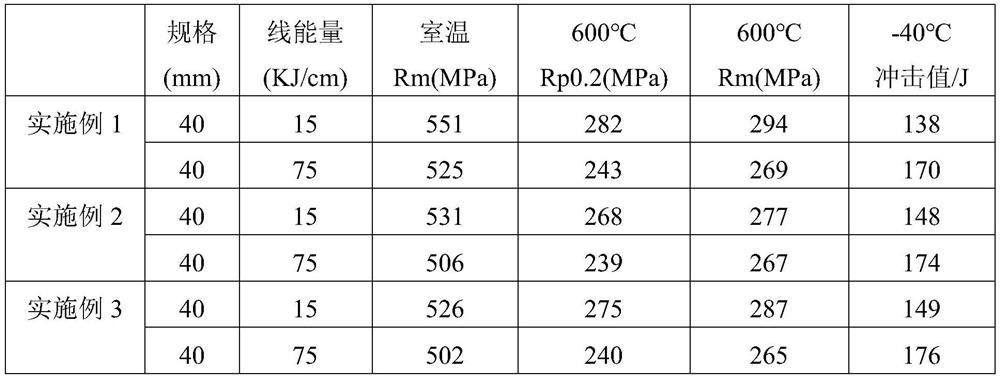
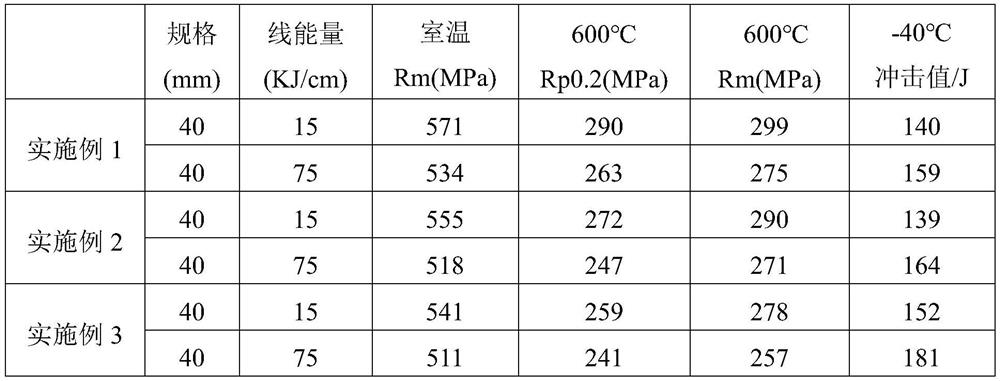
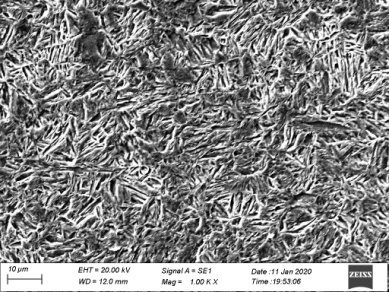
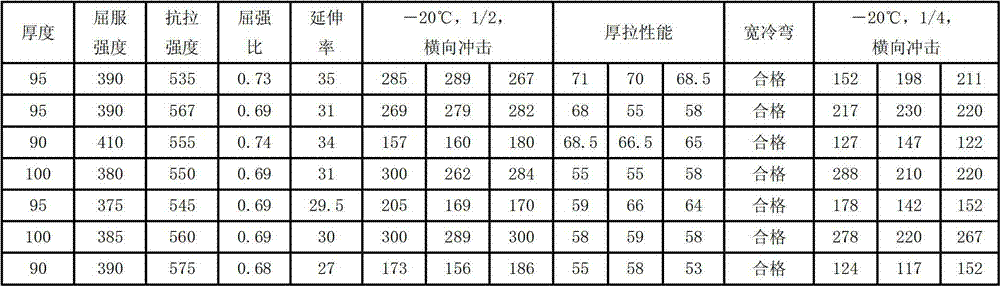
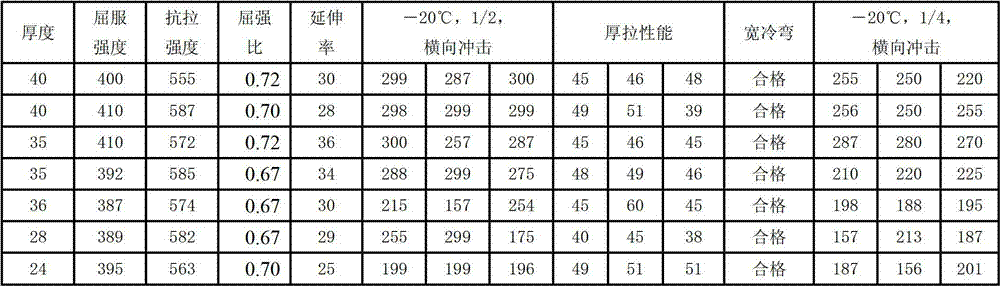
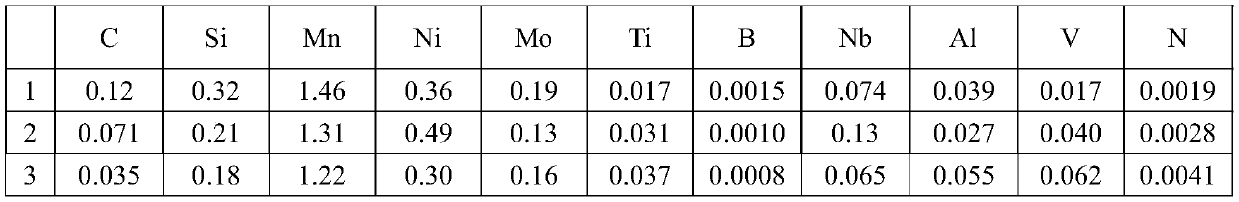
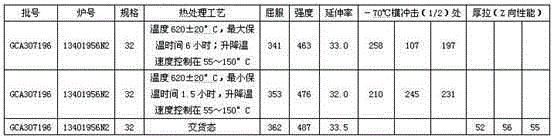
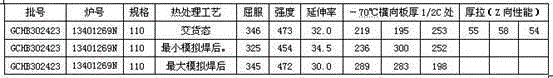
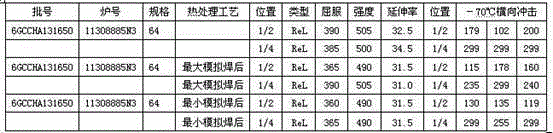
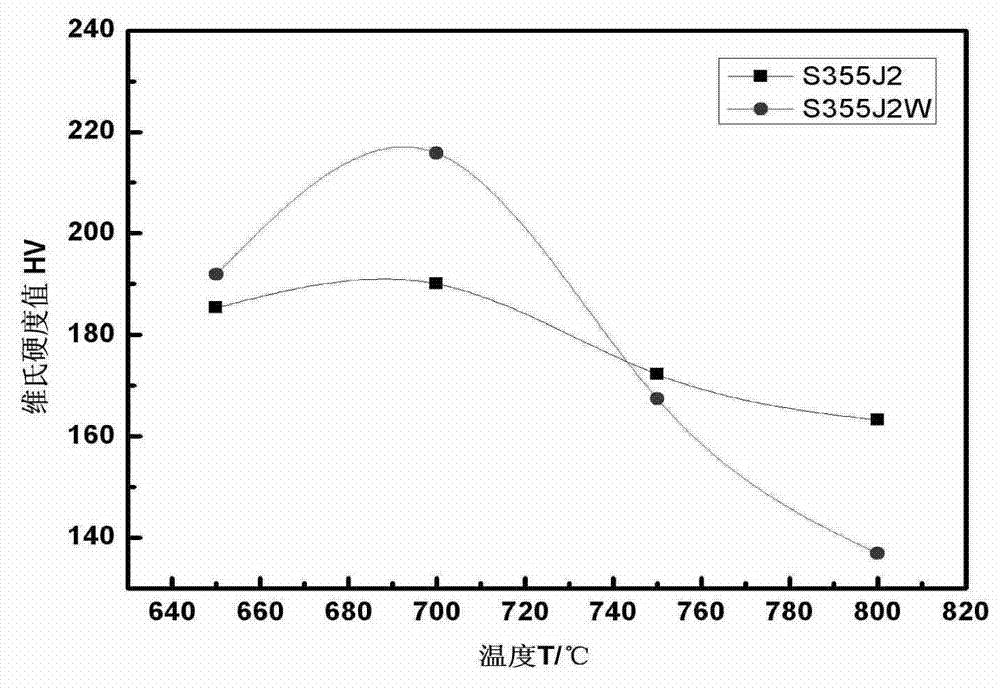
Patents
Literature
35results about How to "High impact energy at low temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
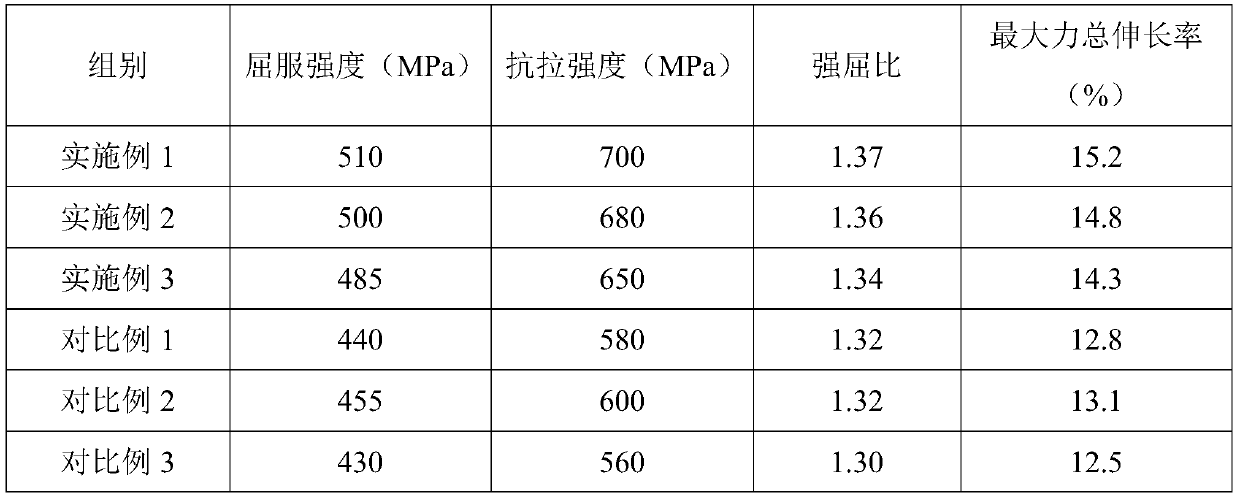
High-performance ocean platform steel and its production method
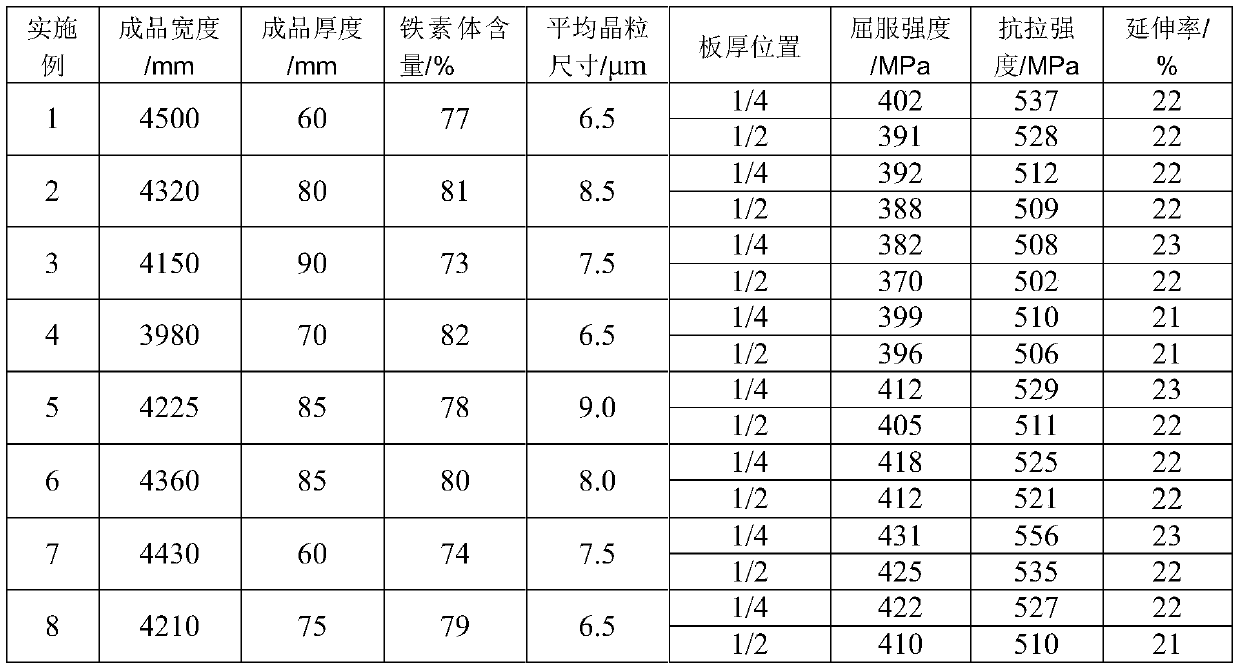
The invention provides high-performance ocean platform steel and its production method. When the thickness of a steel plate is 8-40mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.11-0.13% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.45-1.55% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.035-0.045% of V, 0.025-0.030% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; and when thickness of a steel plate is 40-100mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.10-0.12% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.50-1.60% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.070-0.075% of V, 0.030-0.040% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method of the steel plate of the invention comprises the steps of electric furnace smelting, LF furnace refining, VD vacuum treatment, continuous casting (or die casting), heating, control rolling, cooling, stacking, and normalizing to prepare the steel plate. Through a reasonable component design and process optimization, the steel plate of the invention has excellent mechanical performances, welding performances and processing performances, and has strong market competitiveness.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
Method for improving low-temperature impacting power of 17-4 PH maraging stainless steel forged piece based on organization control
PendingCN109439870AEliminate DirectionalityHigh impact energy at low temperatureMetal-working apparatusDirectivitySmelting process
Owner:JIANGYIN HENGYE FORGING
Heat treatment process for improving low-temperature impact work of 42CrMo bearing
InactiveCN101705342AHigh impact energy at low temperatureImprove reliabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesQuenchingHeating temperature
The invention belongs to the technical field of heat treatment processes, and discloses a heat treatment process for improving the low-temperature impact work of a 42CrMo bearing. The heat treatment process comprises the following quenching and tempering process parameters: the quenching heating temperature of quenching and tempering heat treatment is 840+ / -10 DEG C; the quenching soaking time (h) of the quenching and tempering heat treatment is 3.5 hours; the tempering heating temperature of the quenching and tempering heat treatment is 580+ / -10 DEG C; the tempering soaking time (h) of the quenching and tempering heat treatment is 8 hours; and a coolant adopted by the quenching and tempering heat treatment is F2000 with the concentration of 6 percent. The process solves the important technical problem that the low-temperature impact work cannot meet the requirement after a wind power bearing is treated by adopting a conventional heat treatment process; and the process greatly improves the low-temperature impact work of the wind power bearing, ensures that the wind power bearing has high reliability, and reduces hidden quality danger.
Owner:LUOYANG LYC BEARING
Steel plate for low-temperature spherical tank container and production method thereof
The invention discloses a steel plate for a low-temperature spherical tank container and a heat treatment production method thereof. The steel plate is prepared from less than or equal to 0.12wt% of C, 0.15-0.50wt% of Si, 1.2-1.6wt% of Mn, 0.3-0.8wt% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.010wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.005wt% of S, 0.020-0.045wt% of Al, less than or equal to 0.040wt% of Nb and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities by melting. The steel plate utilizes low-price carbon and manganese solid solution reinforcement, and through adjustment optimization of a ratio of other elements in the steel plate, good steel plate mechanical properties are ensured under conditions of low carbon equivalent, the steel plate has a good microstructure, good comprehensive performances and welding performances, a cost is reduced and market competitiveness is improved. Through a reasonable heat treatment technology, a uniform ferrite-tempered sorbite microstructure is obtained and impact toughness of a large-thickness steel plate is improved. The steel plate has high purity, impact energy greater than 170J at a temperature of -70 DEG C, an elongation rate of more than 25%, good simulation of performances after welding and welding performances, and good mechanical properties.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL
Steel with high low temperature fracture toughness and used for ocean engineering and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN108728743ASolve segregationImprove low temperature fracture toughnessReduction rateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses steel with high low temperature fracture toughness and used for ocean engineering and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the following components: 0.05%-0.10%of C, 0.2%-0.5% of Si, 1.0%-1.5% of Mn, 0.20%-0.50% of Cu, 1.00%-1.50% of Cr, 1.6%-1.8% of Ni, equal to or less than 0.01% of P, equal to or less than 0.01% of S, 0.01%-0.05% of Als, 0.02%-0.04% of Nb, 0.01%-0.02% of Ti, 0.05%-0.07% of V and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. Rolling is controlled by adopting two phases, at the first phase, the rolling temperature is 950-1050 DEG C, andthe single-pass reduction rate is equal to or greater than 15%; at the second phase, the rolling temperature is 840-880 DEG C, and the single-pass reduction rate is greater than 10%; the average cooling rate is greater than 3 DEG C / s, and the self-tempering temperature is 500-600 DEG C; thermal treatment adopts twice quenching and tempering; the yield strength of a steel plate is equal to or greater than 620 MPa, the thickness of the steel plate is 60-100 mm, and the low temperature fracture toughness is high.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Ultra-wide high-strength high-toughness steel for marine engineering and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses ultra-wide high-strength high-toughness steel for marine engineering and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises 0.05 to 0.10% of C, 0.10 to 0.50% of Si, 1.2 to 1.5% of Mn, 0.20 to 0.40% of Cu, 0.10 to 0.30% of Ni, no more than 0.01% of P, no more than 0.01% of S, 0.01 to 0.05% of Als, 0.020 to 0.040% of Nb, 0.010 to 0.020% of Ti and 0.040 to 0.070% of V. According to the invention, a heating temperature is 1,150 to 1,200 DEG C, and heat preservation is performed for 30-60 min; in a first stage, rolling temperature is 1,000-1,050 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is no less than 15%; in a second stage, rolling temperature is 850-950 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is no less than 15%; in a third stage, rolling temperatureis 800-830 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is more than 10%; and an average cooling rate is more than 3 DEG C / s, a self-tempering temperature is 600-650 DEG C, and slow cooling time is no less than 24h. A manufactured steel plate has a width of 3,500 to 4,500 mm and is high in strength and excellent in low-temperature toughness.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Economical fabrication method of high-toughness X70 pipeline hot rolled steel plate coil
ActiveCN103045945AHigh strengthImprove low temperature impact toughnessHeat treatment process controlLaminar coolingToughness
The invention provides an economical high-toughness X70 pipeline hot rolled steel plate coil and a preparation method thereof. The X70 pipeline hot rolled steel plate coil comprise the following chemical components by weight percentage (%) of: 0.060%<C<=0.075%, 0.15%<=Si<=0.30%, 1.20%<=Mn<=1.65%, 0.070<Nb<=0.080%, 0.010%<=Ti<=0.020%, and Cr<=0.25%. The preparation method includes steps of: a heating procedure, a rough rolling procedure, a finish rolling procedure, a cooling procedure and a coiling procedure, wherein in the finish rolling procedure, the rolling temperature of the first pass of finish rolling is not higher than 1050 DEG C, the deformation for the last pass of finish rolling is less than 8%, the accumulated deformation of the last two passes is less than 16%, and the finishing temperature of the finish rolling is 770-850 DEG C; in the cooling procedure: laminar cooling is conducted at a cooling rate of 18-26 DEG C / s after the finish rolling; and in the coiling procedure, coiling is conducted at 300-400 DEG C after the laminar cooling.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Normalization heat treatment method of heavy-gauge low-alloy steel plates
InactiveCN102732696ALow costGuaranteed Yield StrengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNucleationUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a normalization heat treatment method of heavy-gauge low-alloy steel plates. The method concretely comprises the steps of heating, heat insulating and cooling. The steel plates prepared through the method of the invention comprise the following components: 0.18% or less of C, 0.50% or less of Si, 1.60% or less of Mn, 0.020% or less of P, 0.010% or less of S, 0.06% or less of Nb, 0.02-0.06% of Al, 0.03% or less of Ti, 0.08% or less of V, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. Different heat insulation time and cooling technologies are adopted according to different thicknesses of the steel plates, the heat insulation period is 1.8min / mm and a rolling transmission and collector spray water laminar flow mode is adopted to cool when the thicknesses of the steel plates are equal to or less than 100mm, and the heat insulation period is 2.0-2.2min / mm and a water tank cooling mode is adopted to cool when the thicknesses of the steel plates are greater than 100mm. The normalizing heat treatment technology of the invention allows the cooling intensity and the cooling speed of cores of the steel plates to be improved, the nucleation rate of the steel plates to be improved, tissues in the centers of the steel plates to be refined, the quality of the steel plates to be guaranteed and bad tissues and performances caused by uneven heavy-gauge steel plate cooling to be effectively solved, and is especially suitable for heat treatment technologies of thick steel plates.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
High-pressure-resisting and low-carbon alloy steel material
Owner:SJ PETROLEUM MACHINERY CO LTD SINOPEC
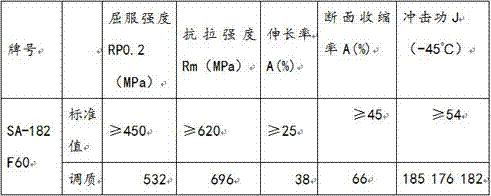
Manufacturing method for high-performance 12Cr2Mo1 forgings
InactiveCN110106308AImprove purityImprove performance and stabilityMetal-working apparatusProcess efficiency improvementMelting tankManufacturing technology
The invention relates to the technical field of metallurgic manufacturing, in particular to a manufacturing method for high-performance 12Cr2Mo1 forgings. The method comprises the following steps: (1)smelting by an electric furnace: molten steel is obtained through charging, slagging, slag discharge, stirring in a molten pool, dephosphorization and desulfurization; (2) furnace external refining:the molten steel obtained in the step (1) is refined, and chemical components thereof are adjusted; (3) vacuum degassing: steel ingots are obtained through vacuumizing and casting; (4) casting: the heating insulation temperature is 1000-1250 DEG C; and the heating time is determined according to 1.5 times of the JB / T6052 standard; and (5) heat treatment: forged forgings are quenched and tempered in sequence; and once annealing or normalization is performed before quenching. The method improves the low-temperature impact power of the 12Cr2Mo1 forgings, reduces the tempering brittleness tendency, improves the performance stability of the forgings, and has the advantages of simple process, excellent comprehensive performances and stability.
Owner:无锡市法兰锻造有限公司
Ocean engineering steel with good low-temperature fracture toughness and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN108728743BImprove low temperature fracture toughnessHigh impact energy at low temperatureReduction rateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses steel with high low temperature fracture toughness and used for ocean engineering and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the following components: 0.05%-0.10%of C, 0.2%-0.5% of Si, 1.0%-1.5% of Mn, 0.20%-0.50% of Cu, 1.00%-1.50% of Cr, 1.6%-1.8% of Ni, equal to or less than 0.01% of P, equal to or less than 0.01% of S, 0.01%-0.05% of Als, 0.02%-0.04% of Nb, 0.01%-0.02% of Ti, 0.05%-0.07% of V and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. Rolling is controlled by adopting two phases, at the first phase, the rolling temperature is 950-1050 DEG C, andthe single-pass reduction rate is equal to or greater than 15%; at the second phase, the rolling temperature is 840-880 DEG C, and the single-pass reduction rate is greater than 10%; the average cooling rate is greater than 3 DEG C / s, and the self-tempering temperature is 500-600 DEG C; thermal treatment adopts twice quenching and tempering; the yield strength of a steel plate is equal to or greater than 620 MPa, the thickness of the steel plate is 60-100 mm, and the low temperature fracture toughness is high.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Preparing method for producing HRB400E fine-grain rebars
ActiveCN110373610AImprove purityImprove performance and stabilityProcess efficiency improvementManufacturing technologyIngot
The invention relates to the technical field of metallurgical manufacturing, in particular to a preparing method for producing HRB400E fine-grain rebars. The method comprises steps of firstly, electric furnace smelting, wherein charging, slagging, deslagging, molten pool stirring and dephosphorization and desulfuration are carried out, and molten steel is obtained; secondly, external refining, wherein the obtained molten steel is subjected to refining; thirdly, vacuum degassing, wherein vacuum air exhaust is carried out, and casting is carried out to obtain a steel ingot; fourthly, forging, wherein program heating is carried out; and fifthly, heat treatment, wherein the forged forge piece is quenched and tempered in sequence, and before quenching, one-time annealing or normalization is carried out. The obtained product is high in yield strength and tensile strength, the mechanical property is good, the elongation is high, the anti-shock effect is better, and the preparing method is easily industrialized, low in cost and better in application prospect.
Owner:福建三宝钢铁有限公司
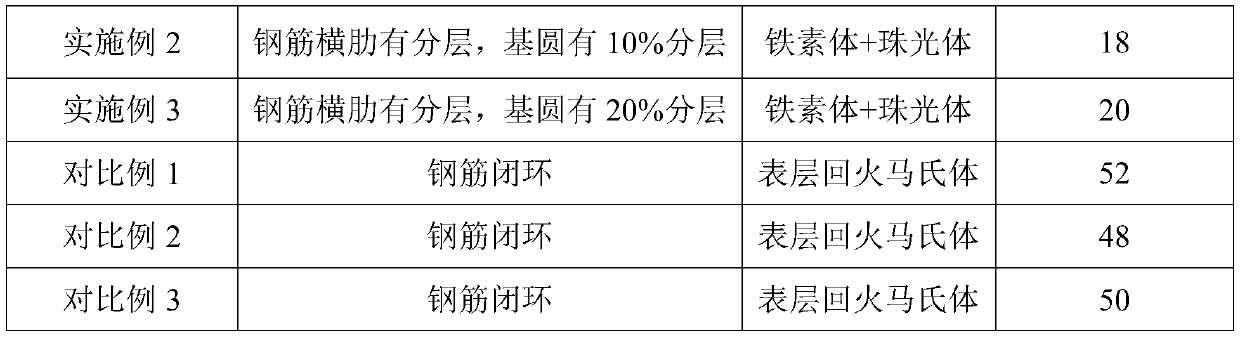
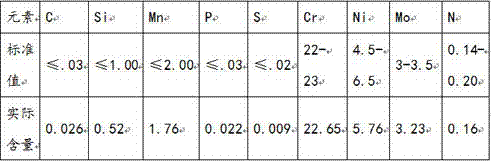
Flange forge piece made of dual-phase steel and production technique of flange forge piece
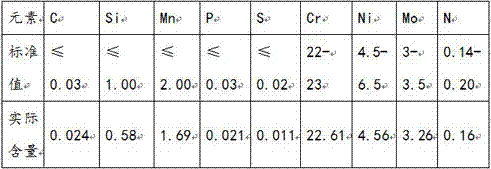
InactiveCN106957998AIncreased nickel contentHigh impact energy at low temperatureChemical compositionDual-phase steel
The invention provides a flange forge piece made of dual-phase steel and a production technique of the flange forge piece. The dual-phase steel comprises 0-0.03% of C, 0-1.00% of Si, 0-2.00% of Mn, 0-0.03% of P, 0-0.02% of S, 22-23% of Cr, 4.5-6.5% of Ni, 3-3.5% of Mo and 0.14-0.20% of N. Production machining is conducted through smelting, forging and heat treatment. In the forging process, the initial forging temperature is 1180+ / -20 DEG C, the final forging temperature is higher than 900 DEG C, and air cooling is conducted after forging. According to the flange forge piece made of the dual-phase steel, the content of nickel in the chemical composition is increased, and accordingly the low-temperature impact work is substantially improved.
Owner:无锡市法兰锻造有限公司
Submerged-arc welding wire for high-rise building structure refractory steel
ActiveCN110280925ASimple ingredientsImprove mechanical propertiesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaChemical elementHigh rise
The invention discloses a submerged-arc welding wire for high-rise building structure refractory steel. The submerged-arc welding wire comprises the following chemical elements of, in percentage by weight, 0.03%-0.16% of C, 0.10%-0.20% of Si, 0.40%-1.00% of Mn, 0.20%-0.50% of Ni, 0.05%-0.20% of Mo, 0.01%-0.05% of Ti, 0.0005%-0.002% of B, 0.01%-0.04% of Nb, 0.01%-0.04% of Al, 0.01%-0.04% of V, 0.001%-0.004% of N, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurity elements. The submerged-arc welding wire is simple in composition, the deposited metal and welded joint formed by welding have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, relatively high high-temperature tensile property and relatively high low-temperature impact power, the cost is low, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Weathering steel flame straightening process
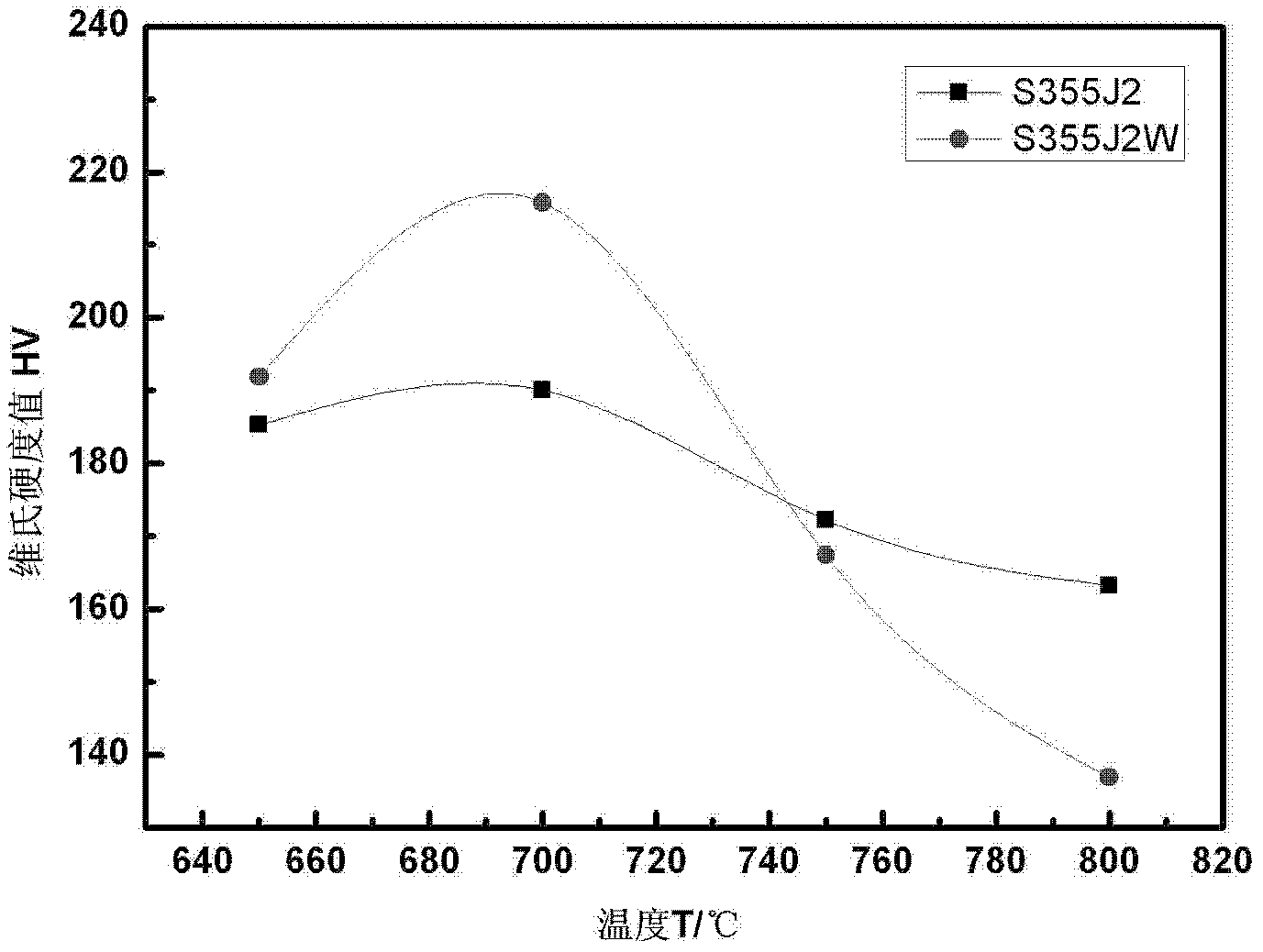
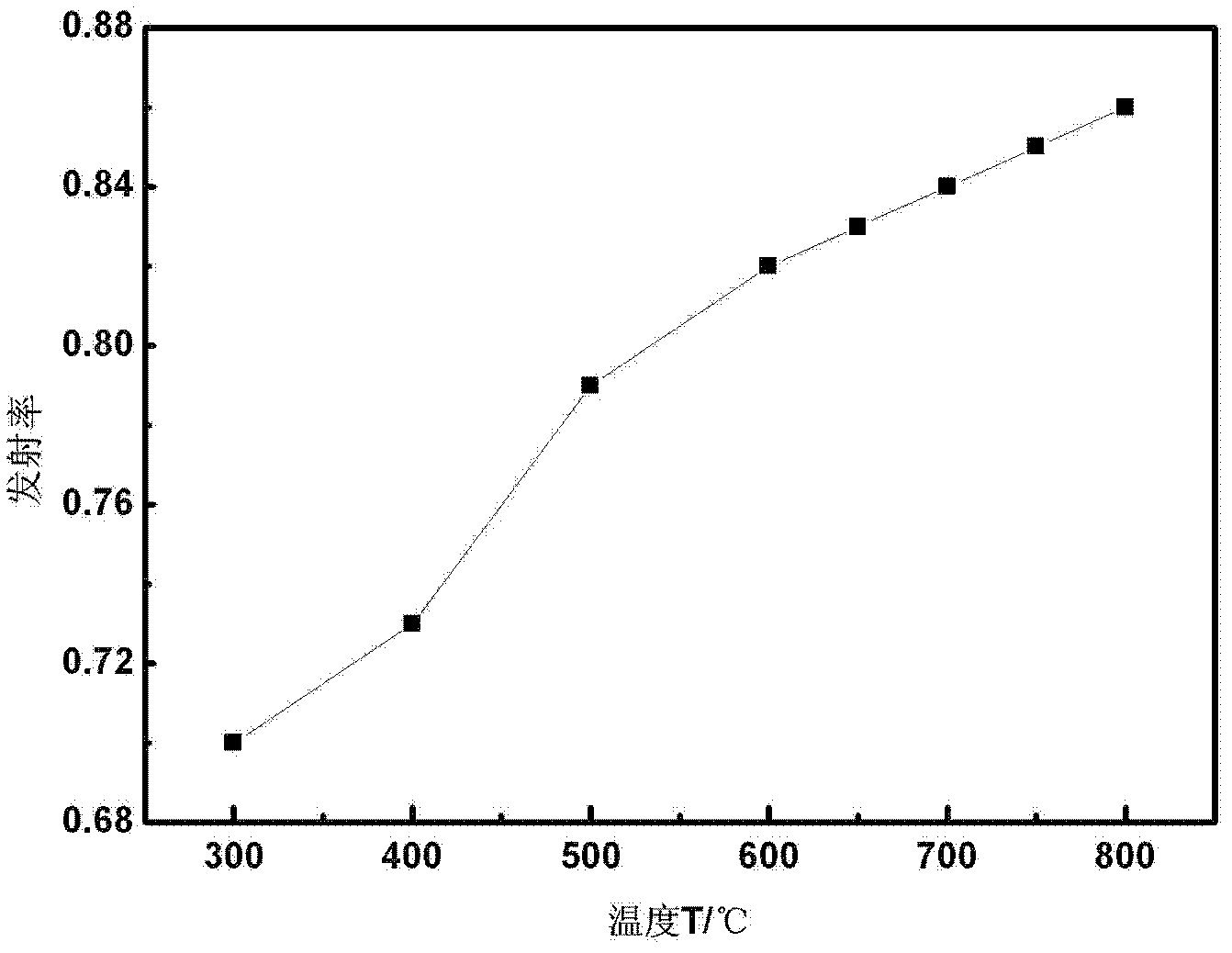
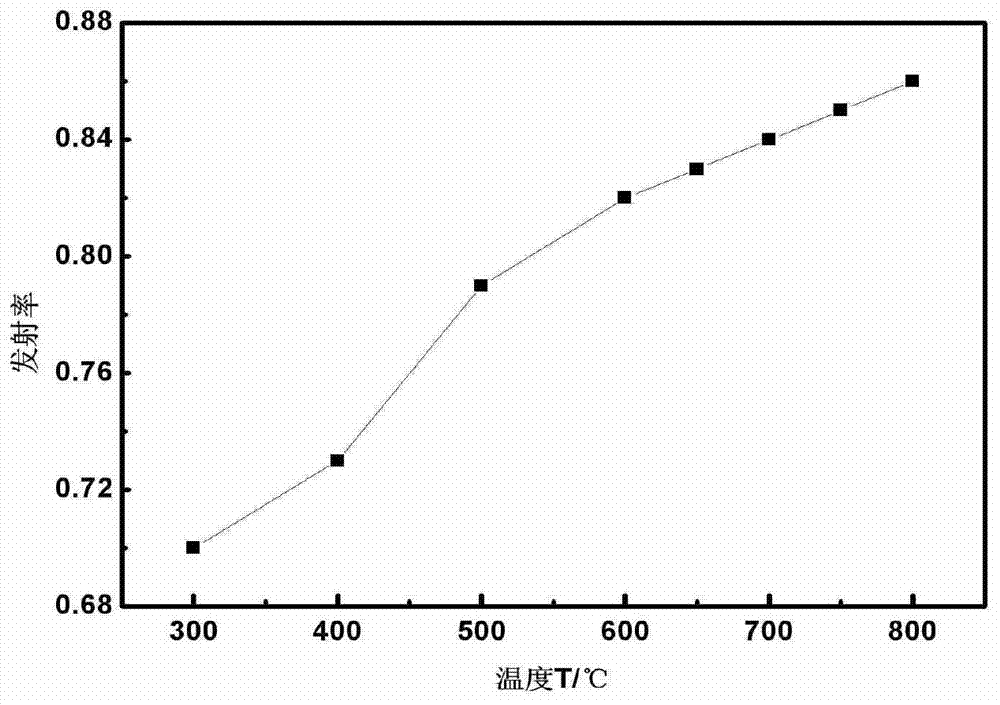
InactiveCN102605148AHigh impact energy at low temperatureHeat treatment process controlEmissivityHardness
The invention relates to a weathering steel flame straightening process, belonging to the technical field of metal material processing. The weathering steel flame straightening process comprises the following steps: calibrating the emissivity of an infrared thermometer according to different materials; determining that the test distance ratio is 30:1; heating a workpiece heating area uniformly by using the neutral oxyacetylene flame, and monitoring the center area of the workpiece heating area in real time by using the infrared thermometer; controlling the highest heating temperature of a flame straightening area on the workpiece at 730-750 DEG C, controlling the emissivity of the infrared thermometer at 0.85, keeping the highest heating temperature of the flame straightening area at 730-750 DEG C for 2 to 3 minutes after the highest heating temperature of the flame straightening area reaches 730-750 DEG C, and cooling the workpiece heating area in air. Due to the adoption of the method, the hardness and the strength of the weathering steel flame straightening area can be close to those of the base material, the metal low-temperature impact energy of the weathering steel flame straightening area can be higher than that of the base material, and at the test temperature of 40 DEG C below zero, the impact energy of the weathering steel flame straightening area of which the highest heating temperature is controlled at 600-650 DEG C can be 2.5 times of that of the workpiece made of the same material.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Low-temperature superhigh-toughness wear-resistant copper alloy and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN106916996APlay a role in solid solution strengtheningImprove mechanical propertiesAviationWear resistant
The invention relates to low-temperature superhigh-toughness wear-resistant copper alloy and a preparing method thereof and belongs to the technical fields of metal materials and preparation. The copper alloy consists of the following components in a percent by mass: 25.0-45.0% of nickel, 2-15% of manganese, 1-8% of zinc, 0.1-5.0% of titanium, 0.5-5% of iron, 0.1-3% of chromium and the balance of copper. The preparing method comprises the following preparing steps: preparing materials, carrying out casting, carrying out hot extrusion, carrying out hot forging and obtaining a finished product. The low-temperature comprehensive mechanical properties and the wear resistance of the alloy are improved by adding the elements, such as the manganese, the zinc, the titanium, the iron and the chromium, and at the same time, the alloy is ensured to have great processability. The impact energy of the prepared copper alloy material at the low temperature of -196 DEG C is larger than 170J and is 3-5 times of other common wear-resistant copper alloy materials. The copper alloy material is particularly suitable for manufacturing wear-resistant parts used in low-temperature environments in the fields of aviation, aerospace and the like.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Steel plate for cryogenic spherical tank container and production method thereof
The invention discloses a steel plate for a low-temperature spherical tank container and a heat treatment production method thereof, which is smelted from the following components by weight percentage: C≤0.12%, Si 0.15%-0.50%, Mn 1.2%-1.6%, Ni 0.3 %~0.8%, P≤0.010%, S≤0.005%, Al 0.020%~0.045%, Nb≤0.040%, the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The chemical composition design of the steel plate of the present invention adopts low-cost carbon and manganese solid solution strengthening, and by adjusting and optimizing the ratio of other elements in the steel plate, it can ensure good mechanical properties of the steel plate under the condition of low carbon equivalent, so that the steel plate has good structure, comprehensive Performance and welding performance, but also reduce costs and enhance market competitiveness. The method obtains a uniform ferrite+tempered sorbite structure through a reasonable heat treatment process, and improves the impact toughness of a large thickness steel plate; 25%, simulating post-weld performance, good welding performance, and good mechanical properties.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL
Economical fabrication method of high-toughness X70 pipeline hot rolled steel plate coil
ActiveCN103045945BReduce inclusionsReduce grain boundary segregationHeat treatment process controlCoiling procedureChemical composition
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Heat treatment process for improving low-temperature impact work of 42CrMo bearing
InactiveCN101705342BHigh impact energy at low temperatureImprove reliabilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesQuenchingHeating temperature
Owner:LUOYANG LYC BEARING
A production method for improving low-temperature toughness of high-strength thick steel plate
ActiveCN104745796BImprove low temperature toughnessImprove performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesFurnace temperatureProcess systems
The invention relates to a production method for improving the low-temperature toughness of high-strength thick steel plates, which belongs to the technical field of thick plate production. The rolled thick steel plate adopts the following heat treatment process: when the surface temperature is higher than Ac3 or reaches the furnace temperature, and the core temperature is at Ac1~Ac3, the steel plate is quenched by a roll quenching machine; or when the surface temperature reaches the furnace temperature , When the core temperature is higher than Ac3 but lower than the furnace temperature, use a roll quenching machine to quench the steel plate. After quenching, the steel plate can be tempered at different temperatures or left untreated. Compared with the steel plate produced by the conventional quenching process, the process can reduce the risk of quenching cracking, and the strength of the steel plate produced by this process can be increased by more than 20MPa, and the low-temperature impact energy can be increased by more than 30%. The production process is simple, the cycle is short, the oxidation degree of the steel plate is low, the energy consumption is low, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
A kind of submerged arc welding wire for high-rise building structure refractory steel
ActiveCN110280925BSimple ingredientsImprove mechanical propertiesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetallurgyHigh heat
The invention discloses a submerged arc welding wire used for fire-resistant steel in high-rise building structures. The chemical element weight percentage content of the submerged arc welding wire is C: 0.03-0.16%; Si: 0.10-0.20%; Mn: 0.40-1.00% ; Ni: 0.20-0.50%; Mo: 0.05-0.20%; Ti: 0.01-0.05%; B: 0.0005-0.002%; Nb: 0.01-0.04%; Al: 0.01-0.04%; N: 0.001-0.004%; the rest is Fe and unavoidable impurity elements. The submerged arc welding wire of the invention has simple components, and the deposited metal and welded joints formed by welding have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, high high-temperature tensile properties, high low-temperature impact energy, low cost, and good application prospects.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method of manufacturing ultralow-temperature steel through low-alloy steel
ActiveCN102965594BIncrease the number ofIncrease grain size gradeChemical compositionSmelting process
The invention relates to a method of manufacturing ultralow-temperature steel through low-alloy steel, which comprises the steps of: setting the chemical ingredients and mass percents of the low-alloy steel as follows: 0.16-0.18% of C, 0.20-0.38% of Si, 1.6-1.8% of Mn, not larger than 0.02% of Al, not larger than 0.01% of Cu, not larger than 0.025% of S, not larger than 0.025% of P, 0.12-0.24% of Re, not larger than 0.01% of Pb and not larger than 0.01% of Sn; smelting the low-alloy steel to reduce the compounds with low smelting points and brittle substance, and entering the reducing period when the phosphor content of the molten steel is not larger than 0.02%, wherein the decarburization quantity is not lower than 0.5% at the smelting oxidization period, no peroxidation occurs to cause successive recarburization; and generating white slag and desulfurizing at the reducing period of the smelting procedure, and discharging and casting the steel when the sulfur content is smaller than 0.025%. During the smelting process, S and P, especially P of the low-alloy steel is controlled to the minimum margin to reduce the compounds with low smelting points and the brittle substance so as to improve the low-temperature impact power.
Owner:SHAOGUAN XINSHIKE SHELL MOLDING
A kind of production method of wear-resistant steel plate
ActiveCN111500918BReduce dosageLow alloy contentFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesTemperingChemical composition
Owner:HEBEI PUYANG IRON & STEEL
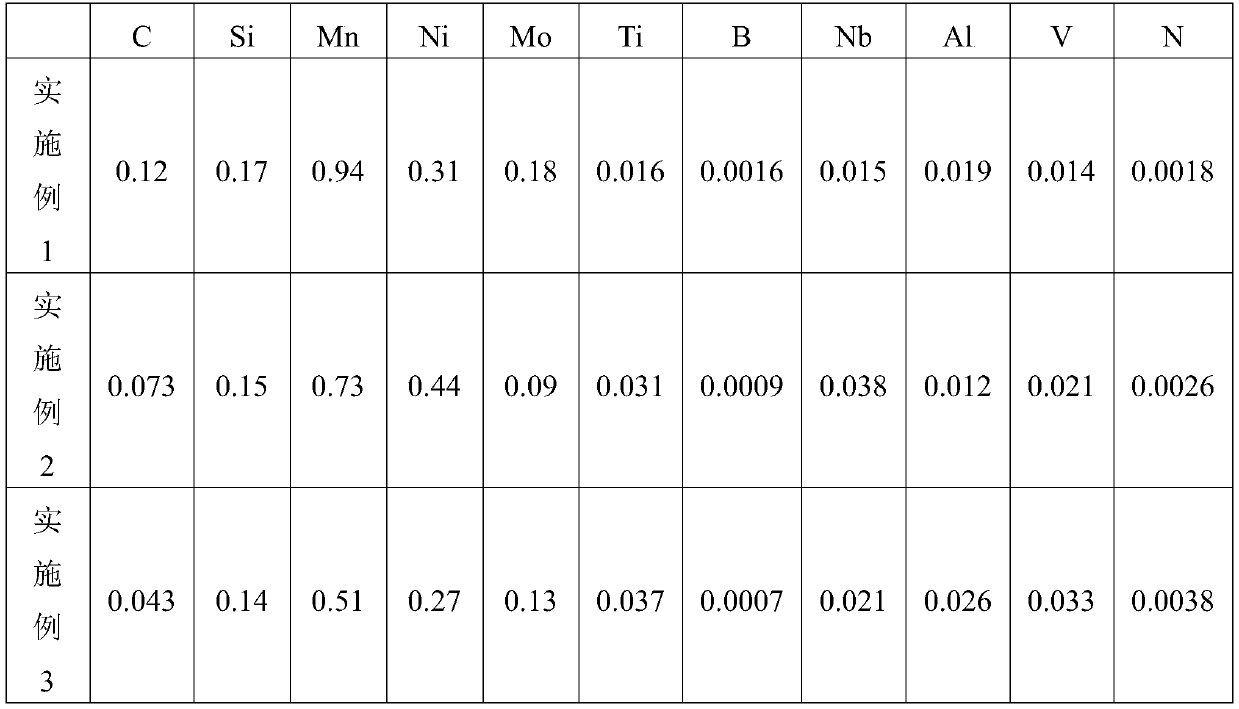
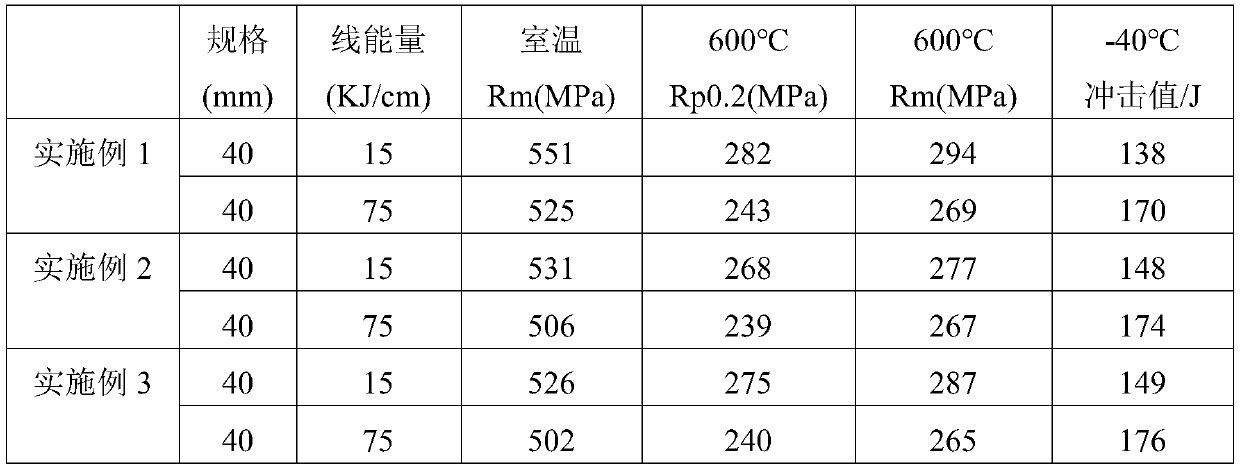
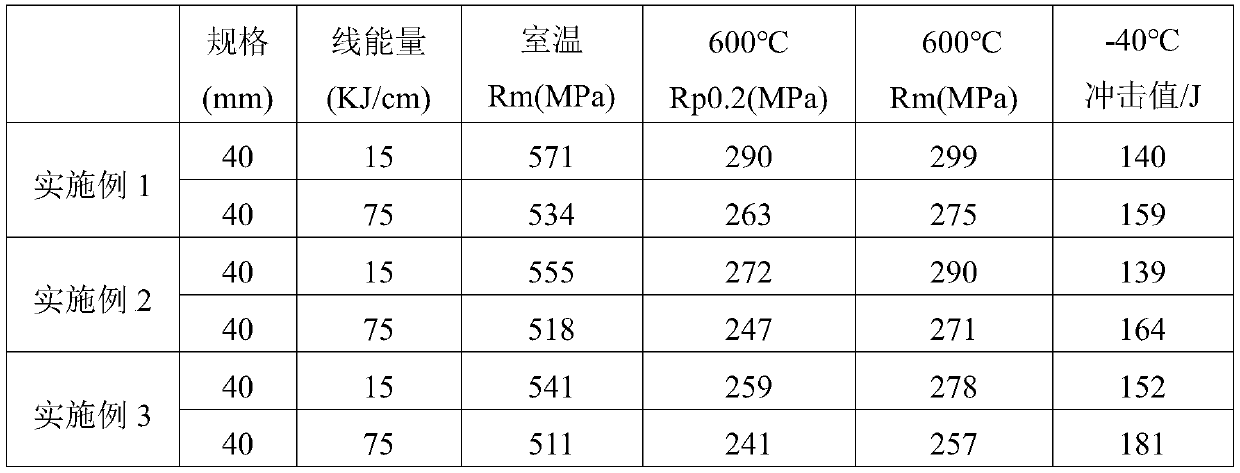
High-performance ocean platform steel and its production method
InactiveCN102732789BImprove mechanical propertiesHigh impact energy at low temperatureProcess optimizationDie casting
The invention provides high-performance ocean platform steel and its production method. When the thickness of a steel plate is 8-40mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.11-0.13% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.45-1.55% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.035-0.045% of V, 0.025-0.030% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities; and when thickness of a steel plate is 40-100mm, the steel plate is composed of the following chemical components, by weight, 0.10-0.12% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 1.50-1.60% of Mn, 0.012% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.070-0.075% of V, 0.030-0.040% of Nb, 0.050% or less of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Al, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method of the steel plate of the invention comprises the steps of electric furnace smelting, LF furnace refining, VD vacuum treatment, continuous casting (or die casting), heating, control rolling, cooling, stacking, and normalizing to prepare the steel plate. Through a reasonable component design and process optimization, the steel plate of the invention has excellent mechanical performances, welding performances and processing performances, and has strong market competitiveness.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
Welding wire and method for welding fire-resistant steel with yield strength of 420MPa grade through welding wire
InactiveCN111360448AReduce manufacturing costImprove mechanical propertiesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaUltimate tensile strengthMechanical property
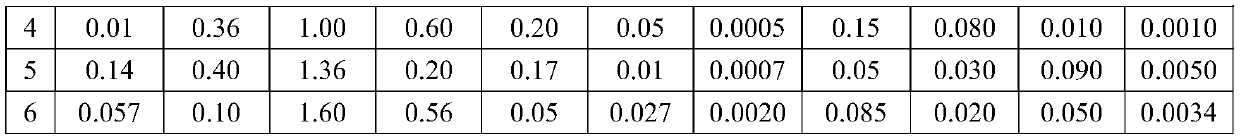
The invention discloses a welding wire and a method for welding fire-resistant steel with the yield strength of 420MPa grade through the welding wire. The welding wire is prepared from, by mass, 0.01-0.14% of C, 0.10-0.40% of Si, 1.00-1.60% of Mn, 0.20-0.60% of Ni, 0.05-0.20% of Mo, 0.01-0.05% of Ti, 0.0005-0.002% of B, 0.05-0.15% of Nb, 0.02-0.08% of Al, 0.01-0.09% of V, 0.001-0.005% of N, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurity elements. After welding is performed, the formed deposited metal and welded joint have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, high high-temperature tensile property and high low-temperature impact energy. The welding wire adopts low-Mo component design, and has lower production cost with the same performance.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A high-strength eh36 steel plate for large heat input welding and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN109161671BHigh impact energy at low temperatureImprove toughnessUltimate tensile strengthToughness
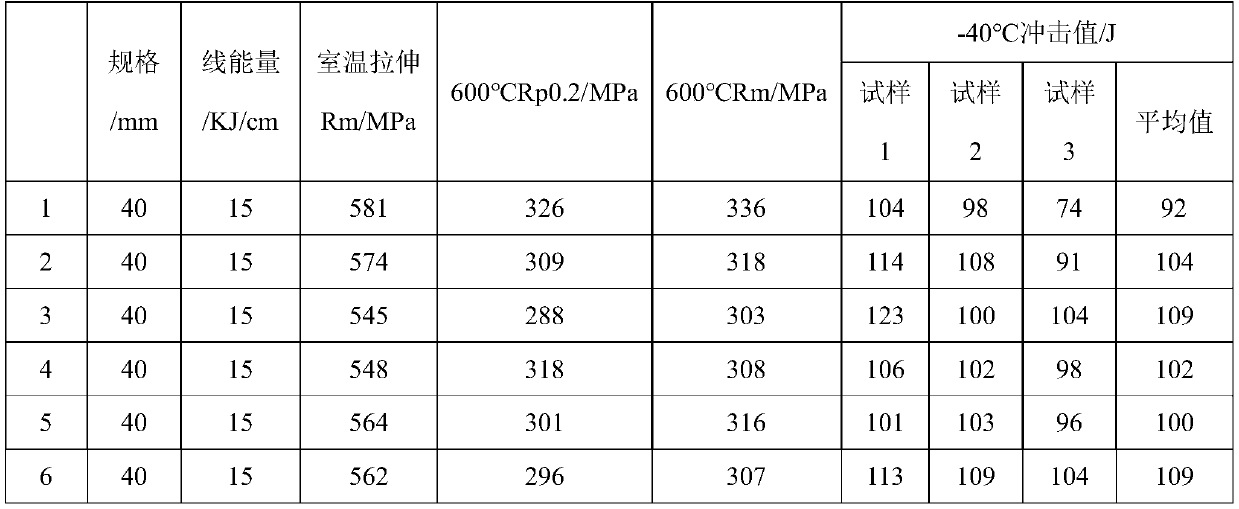
The invention relates to a large heat input energy welding high-strength EH36 steel plate which is made of the following components in percentage by weight through smelting: 0.06-0.18% of C, 0.15-0.50% of Si, 1.10-1.60% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.012% of P, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, 0.10-0.40% of Ni, 0.010-0.030% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.010% of Al, 0.010-0.030% of Ti, 0.001-0.010% of Ca and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The maximum thickness of the steel plate is 100mm, the yield strength of the steel plate is greater than or equal to 355MPa, the tension strength of the steel plate is greater than or equal to 510MPa, and the low-temperature impact absorption energy KV2 of the steel plate at minus 40 DEG C is greater than or equal to 150KJ. A production method of the steel plate comprises the following steps: carrying out smelting, LF / RH (Ladle Furnace / Ruhrstahl Heraeus) refining, continuous casting, heating, rolling, and rapid cooling, thereby obtaining a finished product of the steel plate. The steel plate produced by using the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high purity, high strength, good low-temperature impact resistance, good toughness when the maximum input line energy is 300KJ / CM, and the like, can be widely applied to fields such as shipbuilding, bridges and building structures, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Steel plate for cryogenic container and production method thereof
InactiveCN103540838BImprove mechanical propertiesImprove organizationEconomic benefitsIndustrial engineering
The invention discloses a steel plate for cryogenic containers and a production method, belonging to the technical field of special steel plates and steel plate production methods. This steel plate for cryogenic vessels is smelted from the following components by weight percentage: C≤0.12%, Si0.15-0.50%, Mn1.2-1.6%, Ni0.3-0.8%, P≤0.010%, S≤ 0.005%, Al0.020~0.045%, Nb≤0.040%, the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities. The invention creates a new steel plate for low-temperature containers and its production method, which can ensure good mechanical properties of the steel plate under the condition of less precious alloy usage, make the steel plate have good structure, comprehensive performance and welding performance, and improve the delivery state of the steel plate The low-temperature impact toughness in the die-welded state meets the market's demand for high-quality low-temperature container steel, and makes a positive contribution to the localization of large-scale engineering low-temperature equipment, with significant economic benefits.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL +1
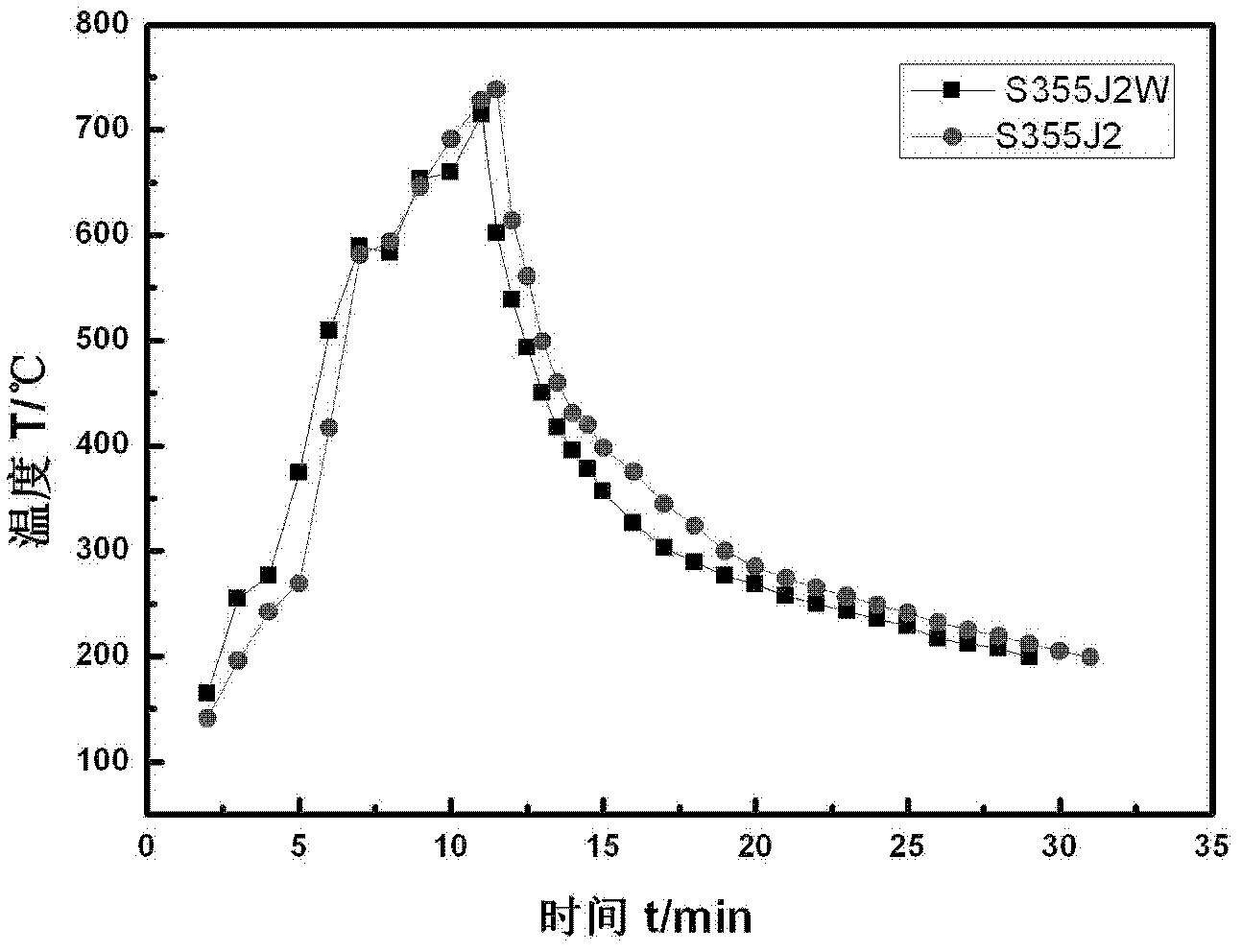
Flame straightening method of bogie frame of high speed train
InactiveCN104498688AHigh impact energy at low temperatureSatisfied with the technical effectFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlHardnessImpact energy
The invention relates to a flame straightening method of a bogie frame of a high speed train. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating an infrared thermometer according to the applied range of flame heating temperature parameters; adjusting the emissivity of the infrared thermometer according to the calibration result; positioning the infrared thermometer above a weathering steel flame straightening area; heating the flame straightening area through neutral flame of oxy-acetylene flame and monitoring the temperature of a central region of a heating area in real time through the infrared thermometer at the same time until the temperature of reaches 730 to 750 DEG C; maintaining for 3 to 5 minutes; and cooling by air. According to the method, the high-weatherability steel is straightened; the hardness and the strength of a base material in the flame straightening area are closest to those of the base material; the low-temperature impact energy of the metal in the straightening area is more than that of the base material, and the impact energy AKV is up to 200J under the test temperature of -40 DEG C, and is 2.5 times that of a test specimen prepared from the same material under the maximum heating temperature controlled to be 600 to 650 DEG C in the straightening area.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Ultra-wide specifications, high-strength and high-toughness marine engineering steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses ultra-wide high-strength high-toughness steel for marine engineering and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises 0.05 to 0.10% of C, 0.10 to 0.50% of Si, 1.2 to 1.5% of Mn, 0.20 to 0.40% of Cu, 0.10 to 0.30% of Ni, no more than 0.01% of P, no more than 0.01% of S, 0.01 to 0.05% of Als, 0.020 to 0.040% of Nb, 0.010 to 0.020% of Ti and 0.040 to 0.070% of V. According to the invention, a heating temperature is 1,150 to 1,200 DEG C, and heat preservation is performed for 30-60 min; in a first stage, rolling temperature is 1,000-1,050 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is no less than 15%; in a second stage, rolling temperature is 850-950 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is no less than 15%; in a third stage, rolling temperatureis 800-830 DEG C, and an average single-pass reduction rate is more than 10%; and an average cooling rate is more than 3 DEG C / s, a self-tempering temperature is 600-650 DEG C, and slow cooling time is no less than 24h. A manufactured steel plate has a width of 3,500 to 4,500 mm and is high in strength and excellent in low-temperature toughness.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
A production method of wear-resistant, low-temperature and atmospheric corrosion-resistant steel
The invention provides a production method for wear-resistant low temperature-resistant weather-resistant steel. Steel with steel coil thickness of 2.5 to 16.0 mm is produced and comprises 0.065 to 0.085% of C, 0.20 to 0.30% of Si, 0.85 to 0.950% of Mn, no more than 0.020% of P, no more than 0.004% of S, 0. 45 to 0.55% of Cr, 0.12 to 0.25% of Ni, 0.25 to 0.35% of Cu, 0.010 to 0.030% of Nb, 0.020 to 0.040% of Al, 0.010 to 0.018% of Ti, 0.0015 to 0.0030% of Ca and no more than 0.0045% of N. During rolling, the furnace box temperature of a heating furnace is set to be 1200 + / - 20 DEG C, the temperature of a slab is maintained for 30 to 40 min, the tapping temperature of the slab is 1200 + / - 20 DEG C, the temperature of an intermediate slab in a finish rolling mill is 900 to 1000 DEG C, the thickness of the intermediate slab in the finish rolling mill is no less than 50 mm, finishing temperature is 860 + / - 10 DEG C, rolling temperature is 600 + / - 10 DEG C, and a laminar cooling speed is 15 + / - 12 DEG C / s.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com