Data storage method and device, data reading method and device and electronic equipment
A technology for data storage and data reading, which is applied in memory systems, electrical digital data processing, memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., and can solve the problems of solid-state hard drive system design difficulties, write amplification, and large storage space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
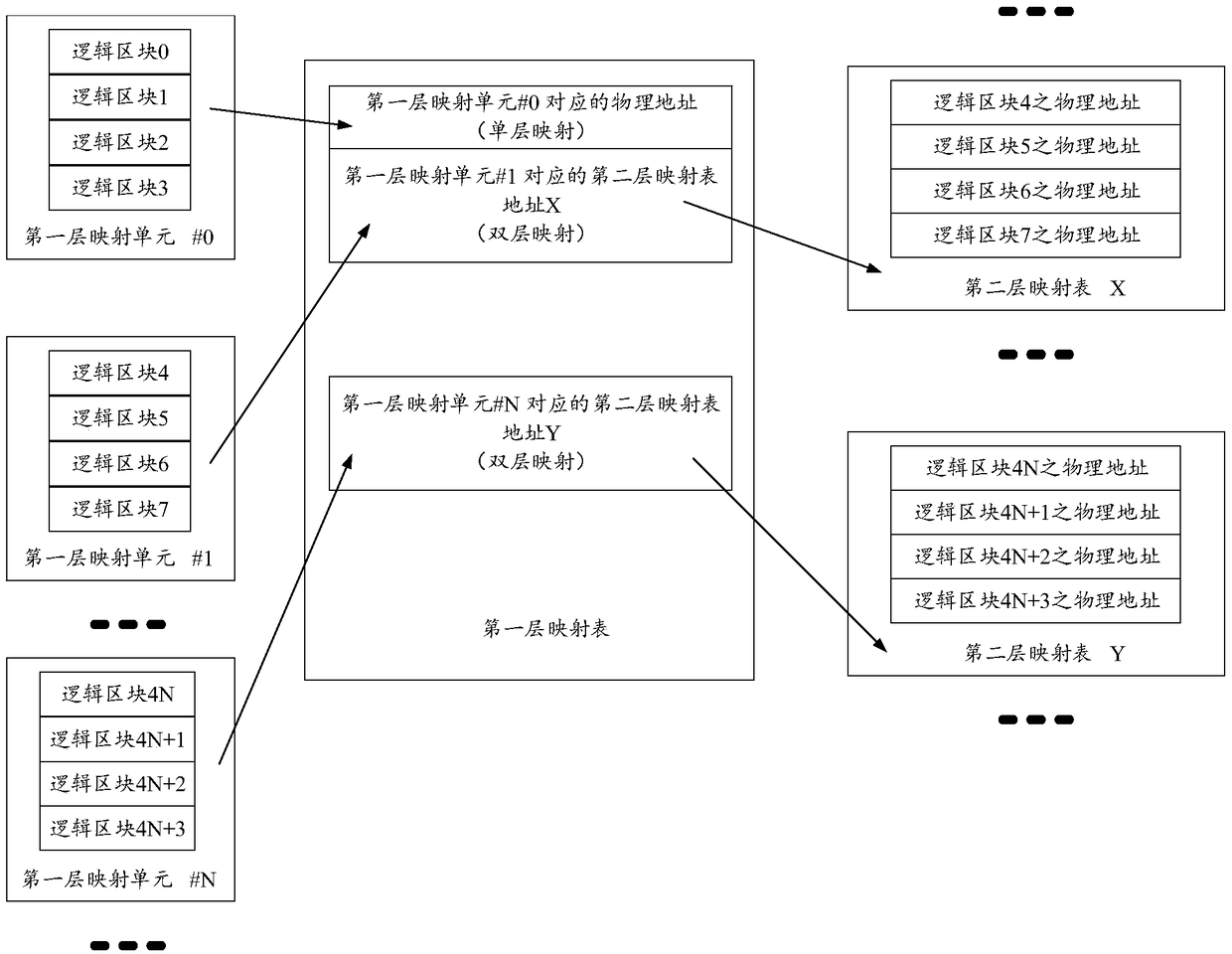
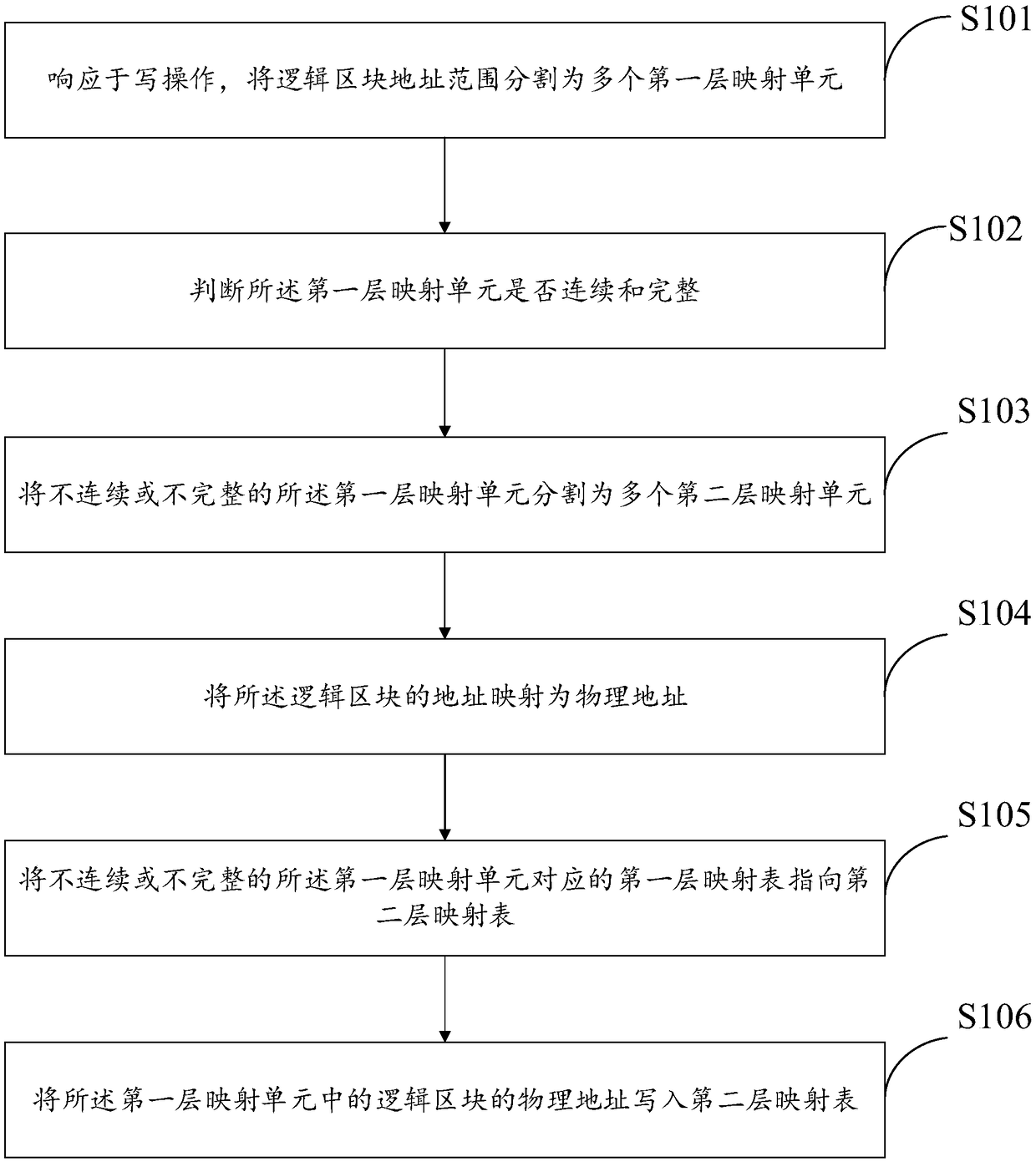
[0070] Such as figure 1 As shown, a data storage method includes:
[0071] Step S101: In response to the write operation, divide the logical block address range into multiple first-layer mapping units;
[0072] The logical block address range includes multiple logical blocks, and the logical address range is the capacity of the solid state disk. For the division into multiple first-layer mapping units, multiple include one or more, and if there is not enough one, it is divided into one.
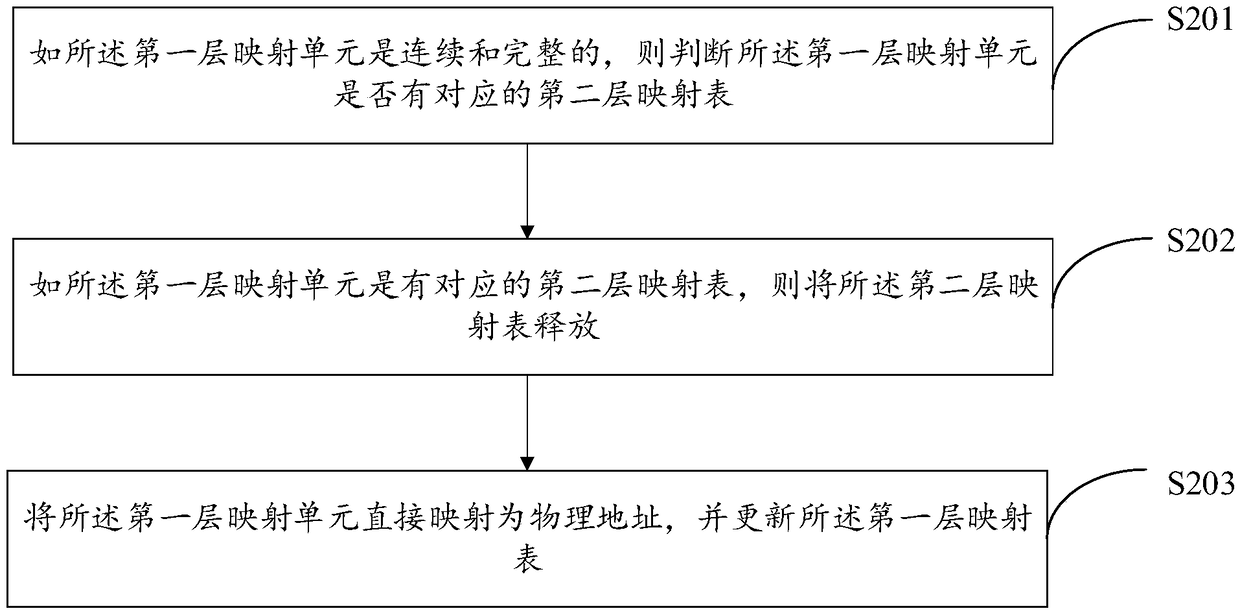
[0073] Step S102: Determine whether the first-layer mapping unit is continuous and complete; continuous refers to whether the logical addresses of the written data are continuous. When the host writes data, it may be written at random addresses, or multiple logical addresses may be written consecutively. When a block is written at a random address, it will cause the first-level mapping unit to be discontinuous. For completeness, if the data written by the host cannot make up a first-level m...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Corresponding to the data storage method in Embodiment 1, the present invention also provides a data reading method, including:
[0140] In response to a read operation, dividing the logical block address range into first-level mapping units;
[0141] Querying the first-layer mapping table corresponding to the first-layer mapping unit;
[0142] If the physical address corresponding to the logical block is found in the first-level mapping table, the physical address is directly read from the first-level mapping table, and then the physical address in the first-level mapping table is passed to Address read data;
[0143] If the physical address corresponding to the logical block is not found in the first-level mapping table, read the address of the second-level mapping table from the first-level mapping table, and then read the address of the second-level mapping table from the second-level mapping table read out the physical address; then read data through the physical...
Embodiment 3
[0146] The present invention also provides a data storage device using the data storage method of Embodiment 1;
[0147] and / or
[0148] Implement the second data reading method.
[0149] For example, a solid-state disk, or other data storage devices based on a solid-state disk, or a data storage device with the same storage principle as a solid-state disk, such as an existing data storage device of a mobile phone or a tablet computer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com