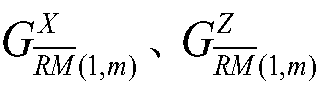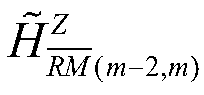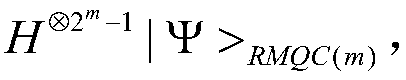Implementation method of a fault-tolerant logic H gate based on an RMQC code
A technology of fault-tolerant logic and implementation method, which is applied in the field of quantum computing and quantum error-correcting codes, and can solve the problems of not considering single qubit, fault-tolerant logic H-gate implementation process, high resource consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] This embodiment is used in the coded state |Ψ> RMQC(4) Fault-tolerant logic H gates are implemented.
[0046] refer to figure 1 , the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0047] Step 1) For the encoded state |Ψ> RMQC(4) Add an H gate for each qubit of :
[0048] pair containing three stable subgroups with The encoded state of |Ψ> RMQC(4) After numbering the 15 qubits in , add the H gate to get the intermediate state where |Ψ> RMQC(4) The number of stabilizers included is 14, which are Contains 4 X stabilizers, 4 Z stabilizers included, and Contains 6 Z stabilizers;
[0049] Step 2) Get three stable subgroups with The symptom value corresponding to each stabilizer in :
[0050] Step 2a) Yes The Z stabilizer in and The X stabilizers in are measured separately to get the symptom value corresponding to each Z stabilizer Symptom value corresponding to each X stabilizer i∈{1,2,...,6}, j∈{1,2,...,4}, get symptom value for:
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0093] This embodiment is the same as step 1) to step 4) and step 7) to step 8) in embodiment 1, only step 5) and step 6) have been modified, for the coded state |Ψ> RMQC(5) Fault-tolerant logic H gates are implemented.
[0094] refer to figure 1 ,
[0095] Step 5) to All Z stabilizers included are grouped:
[0096] In each x-model contained in the 5-model, the two vertices of the inner model and the outer model respectively belong to Z stabilizer Bilaterally stabilized subgroups x∈{4,5}, index∈{1,2,...,(x-1)×2 5-x}, all x-models correspond to two-sided stable subgroups Combined into a set of bilaterally stable subgroups in:
[0097]
[0098]
[0099] in:
[0100]
[0101]
[0102]
[0103]
[0104] Also divide each x-model contained in the 5-model other than Z stabilizer Combined into one-sided stabilized subgroups All x-models correspond to one-sided stable subgroups Combined into a set of one-sided stable subgroups in:
[0105]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com