Methods and kits for reducing the susceptibility of lipoprotein particles to atherogenic aggregation induced by arterial-wall enzymes
A technology for atherosclerosis and lipoprotein particles, applied in peptide/protein components, biological testing, pharmaceutical formulations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
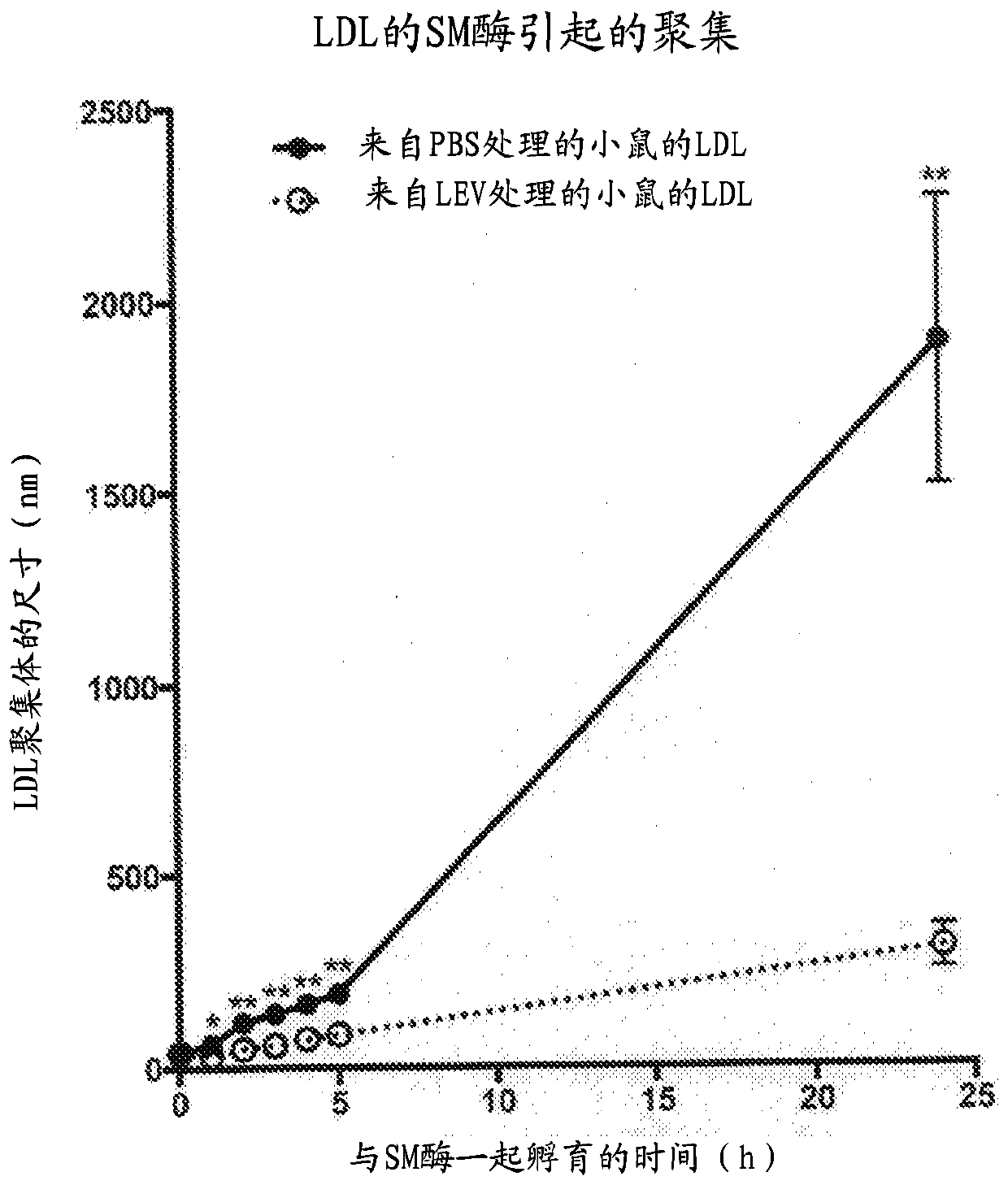
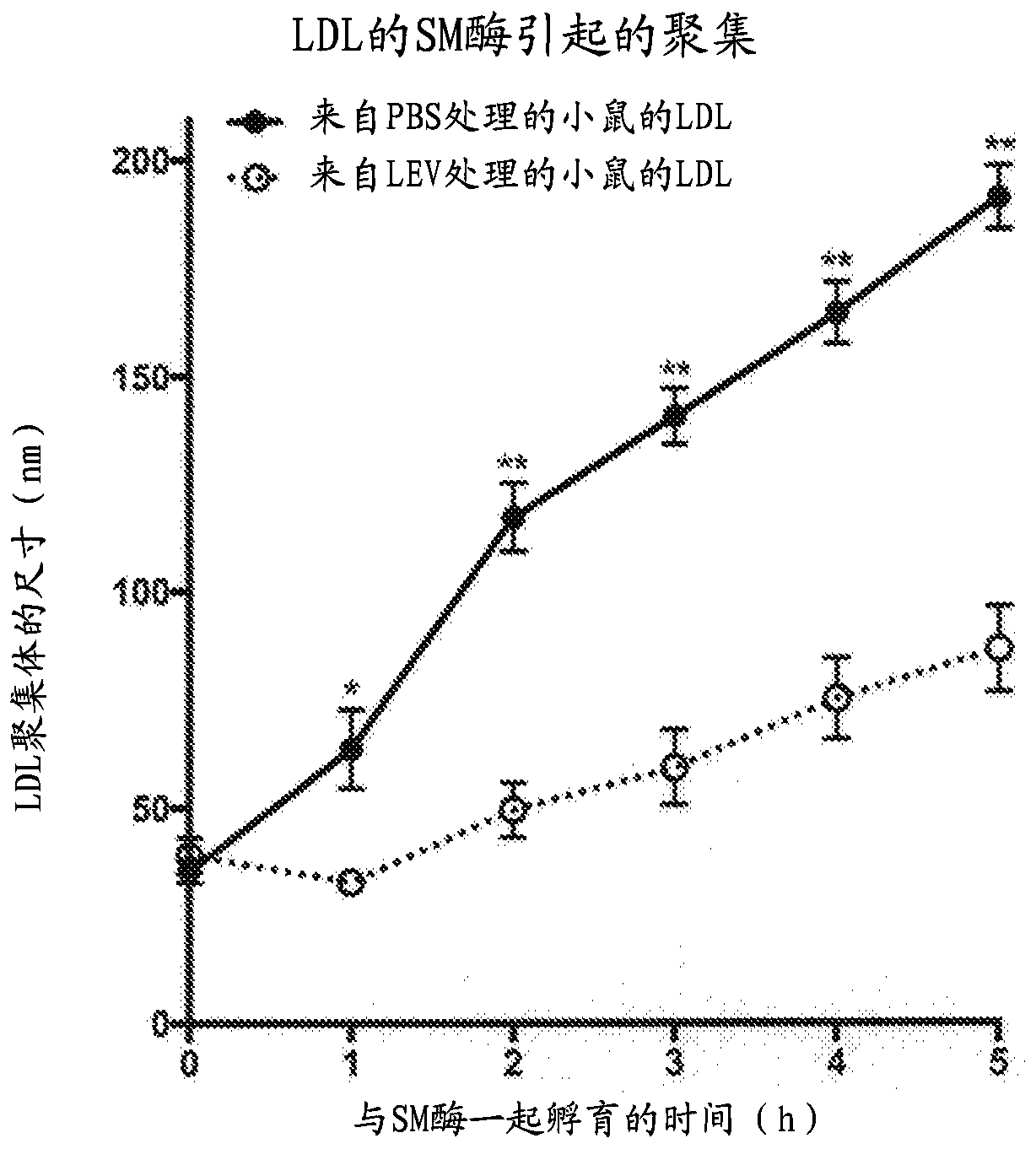
[0139] LDL particles from LEV-treated hypercholesterolemic mice were far less sensitive to SMase-mediated aggregation than LDL particles from PBS-treated hypercholesterolemic mice
[0140] This example was designed to show in an in vitro (test tube) test that LDL from LEV-treated mice was much more resistant to SMase-mediated aggregation than LDL from control (saline-treated) mice. Testing of the sensitivity of LDL to aggregation was performed according to the existing literature (9, 10, 16). This example is important because SMase-mediated accumulation of LDL is expected to be an important contributor to atherosclerotic plaques associated with cardiovascular disease.
[0141] Production of LEVs
[0142] The procedure used in this example to prepare LEVs from POPC is as follows: In a sterile bio-cabinet, the procedure is performed under a decontaminated atmosphere (e.g. HEPA-filtered air), with all surfaces and equipment cleaned and sterilized . Synthetic, pure, dry, gran...
Embodiment 2
[0151] Effect of LEV treatment on LDL composition
[0152] The 16 LDL samples from Example 1 were also subjected to compositional analysis. Lipids were extracted by the Folch procedure under nitrogen in the presence of lipid antioxidants and then subjected to an automated high-throughput tandem mass spectrometry procedure (described in detail previously) (15).
[0153] The results are shown in Figure 4 . exist Figure 4 In , an asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference between the results obtained with LEV-injected mice and PBS-injected mice. Treatment of mice with a single injection of LEV resulted in a decrease in the molar ratio of sphingomyelin to phosphatidylcholine (SM:PC) in the LDL of the mice.
[0154] In LDL samples from LEV-injected mice compared to LDL from PBS-injected mice (controls), there was a statistically significant increase in the overall PC:protein ratio, and in the UC:PC ratio, UC: There was a statistically significant reduction in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com