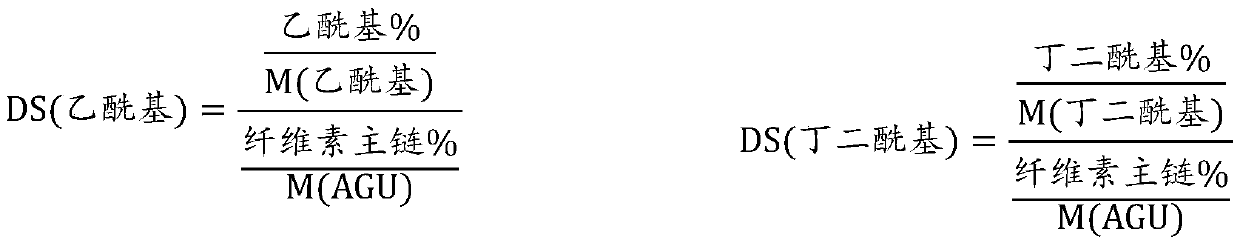Efficient process of preparing an esterified cellulose ether
A technology for esterifying cellulose ether and cellulose ether, which is applied in the field of preparing esterified cellulose ether and can solve the problems of affecting the color of esterified cellulose ether, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0046] All parts and percentages are by weight unless otherwise indicated. In the examples, the following test procedure was used.
[0047] Viscosity of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS)
[0048] A 10 wt% solution of esterified cellulose ether in acetone was determined by first determining the loss on drying of HPMCAS according to "Hypromellose Acetate Succinate USP and National Formulary, NF 29, pp. 1548-1550" preparation. 10.00 g of HPMCAS by dry weight were then mixed with 90.0 g of acetone at room temperature under vigorous stirring. The mixture was rolled on a roller mixer for about 24 hours. The solution was centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 3 minutes using a Megafuge 1.0 centrifuge (available from Heraeus Holding GmbH, Germany), followed by Ubbelohde viscosity measurements according to DIN 51562-1:1999-01 (January 1999). Measurement.
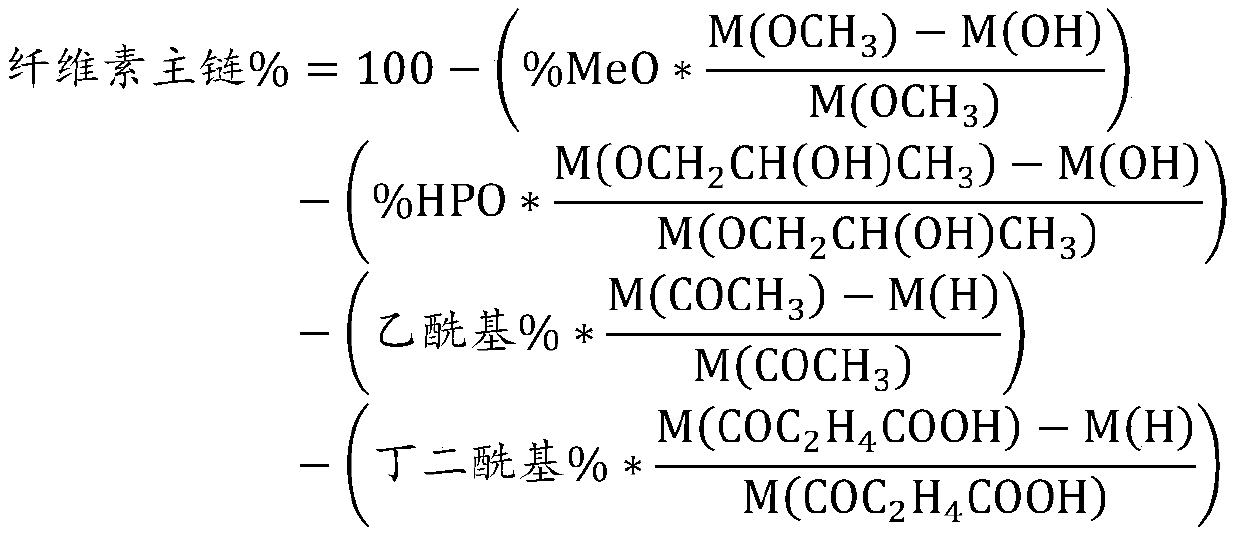
[0049] Ether group and ester group content of HPMCAS
[0050] The content of ether groups in the esterified cel...
example 2
[0076] HPMCAS of Production Example 2
[0077] Example 1 was repeated except that the amounts of HPMC, acetic acid, sodium acetate, acetic anhydride, and succinic anhydride were as listed in Table 1 below.
[0078] HPMCAS of Production Example 3
[0079] Example 1 was repeated except that the amounts of HPMC, acetic acid, sodium acetate, acetic anhydride, and succinic anhydride were as listed in Table 1 below.
[0080] Production of the HPMCAS of Comparative Example B
[0081] The same mixture of HPMC, glacial acetic acid and sodium acetate as in Example 2 was heated to 85°C. Then, succinic anhydride was added to the mixture in the amount listed in Table 1 below, and three minutes later acetic anhydride was added to the mixture. The amounts of succinic anhydride and acetic anhydride were selected to achieve about the same degree of substitution with acetyl groups and about the same degree of substitution with succinyl groups as in Example 2.
[0082] The reaction was...
example 5
[0100] Example 5 demonstrates that even when HPMC with a viscosity of 5.3 mPa·s is used as starting material, a low weight average molecular weight and a rather low viscosity in acetone of HPMCAS is obtained. It is desirable to use this type of HPMC; less severe depolymerization conditions are required than for the production of lower viscosity HPMC. This favorably affects the color of HPMC and the HPMCAS produced therefrom.
[0101] The comparison between Examples 3, 2 and 1 demonstrates that the molar ratio of aliphatic carboxylic acid, such as acetic acid, to anhydroglucose units of cellulose ether can be reduced in the process of the invention without increasing the weight average molecular weight and the HPMCAS produced. Viscosity in acetone.
[0102] In contrast, comparisons between Comparative Examples C and B and between Comparative Examples E and D, respectively, show that the weight average molecular weight and the produced The viscosity of HPMCAS in acetone is sig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com