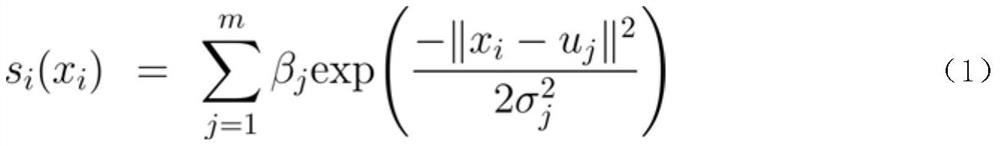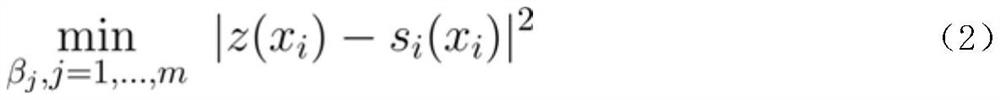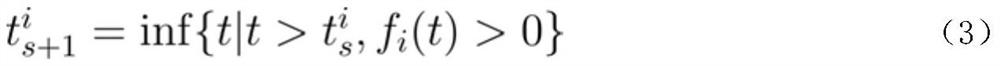A distributed optimization method for multi-robot event-driven communication
An event-driven, multi-robot technology, applied in the field of automation, can solve the problems of robot electromagnetic source positioning accuracy, large amount of calculation, multi-communication bandwidth, etc., to achieve the effect of improving resource utilization efficiency, reducing burden, and optimizing network communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] Take the field search for electromagnetic signal nodes in infinite sensor networks as an example. The search environment is 200 meters long and 200 meters wide, and a coordinate system is established, which can be expressed as [-100, 100]×[-100, 100]. Four robots (n=4) were employed.
[0026] The specific implementation steps for the i-th robot in the robot group are as follows:
[0027] The first step: calculate the relevant parameters of the robot, the specific steps are as follows:
[0028] a. Establish the communication matrix A of the robot group A=[a ij ]. Such as:
[0029]
[0030] b. Initialize the parameters of the electromagnetic signal intensity distribution model, including: the number m of radial basis functions is 20; the center of radial basis functions u j (j=1, 2,..., m) are uniformly distributed in [-100, 100]×[-100, 100]; radial basis function width σ j uniformly distributed within [80, 130]; the initial weight β of the radial basis function ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com