A method and apparatus for decoding information delivered by a light source
A technology of light source and image sensor, applied in the field of optical information, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory stability and reliability, small delay, affecting the shooting effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below through specific embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
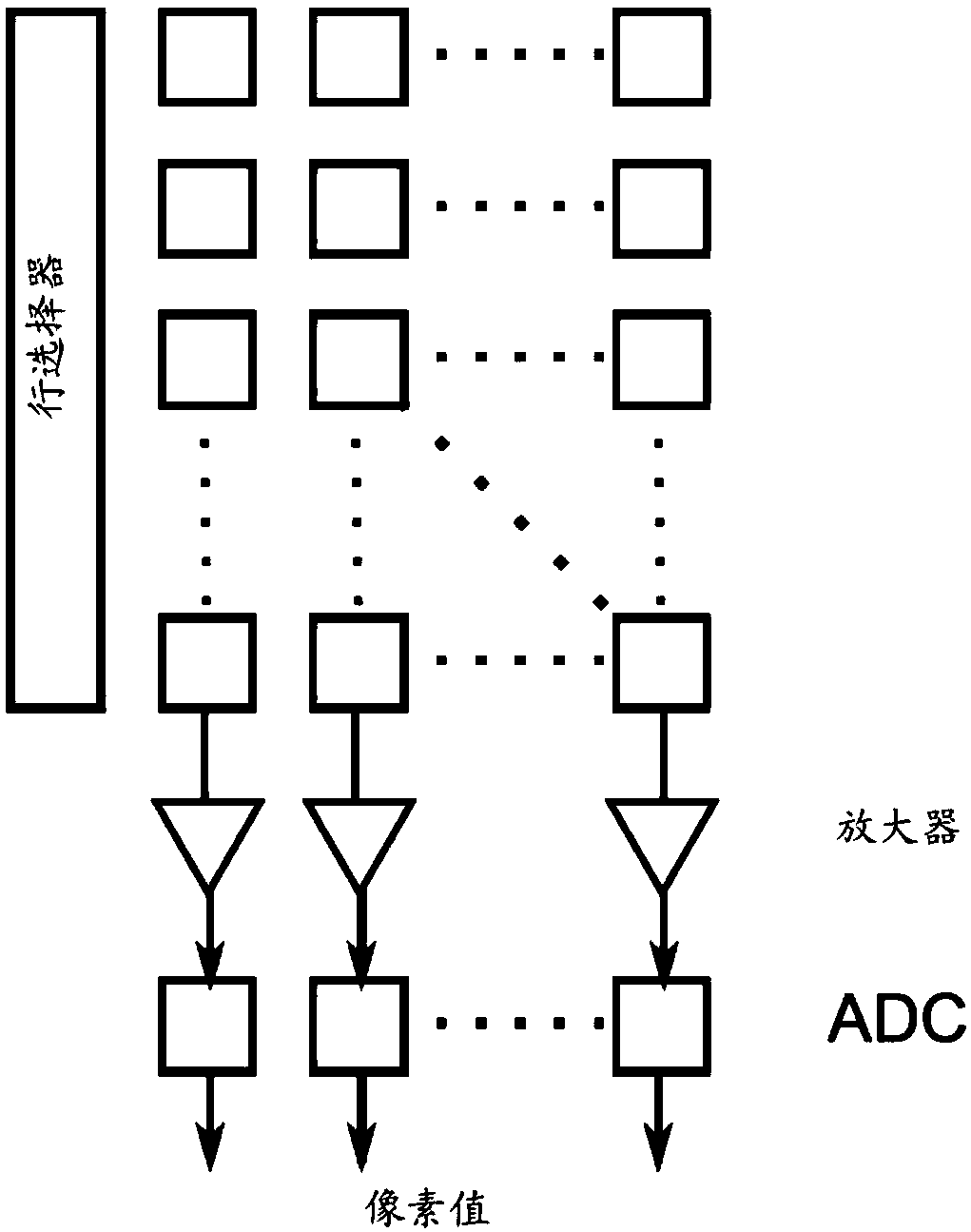
[0050]One embodiment of the present invention relates to an optical communication device capable of transmitting different information by emitting different lights. The optical communication device is also referred to herein as an "optical tag", and the two may be used interchangeably throughout this application. The optical communication device includes a light source and a controller, the controller is configured to control the light source to work in two or more modes, the two or more modes include a first mode and a second mode, wherein, in In the first mode, the property of the light emitted by the light source changes at a first frequency to convey the first information; in the second mode, the property of the light emitted by th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com