Block chain-based blacklist sharing method, arbitration method and device
An arbitration method and blacklist technology, applied in the field of blockchain-based blacklist sharing methods, arbitration methods and devices, can solve problems such as complex procedures, multi-party collaboration, and easy tampering, and achieve the effect of solving complex procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
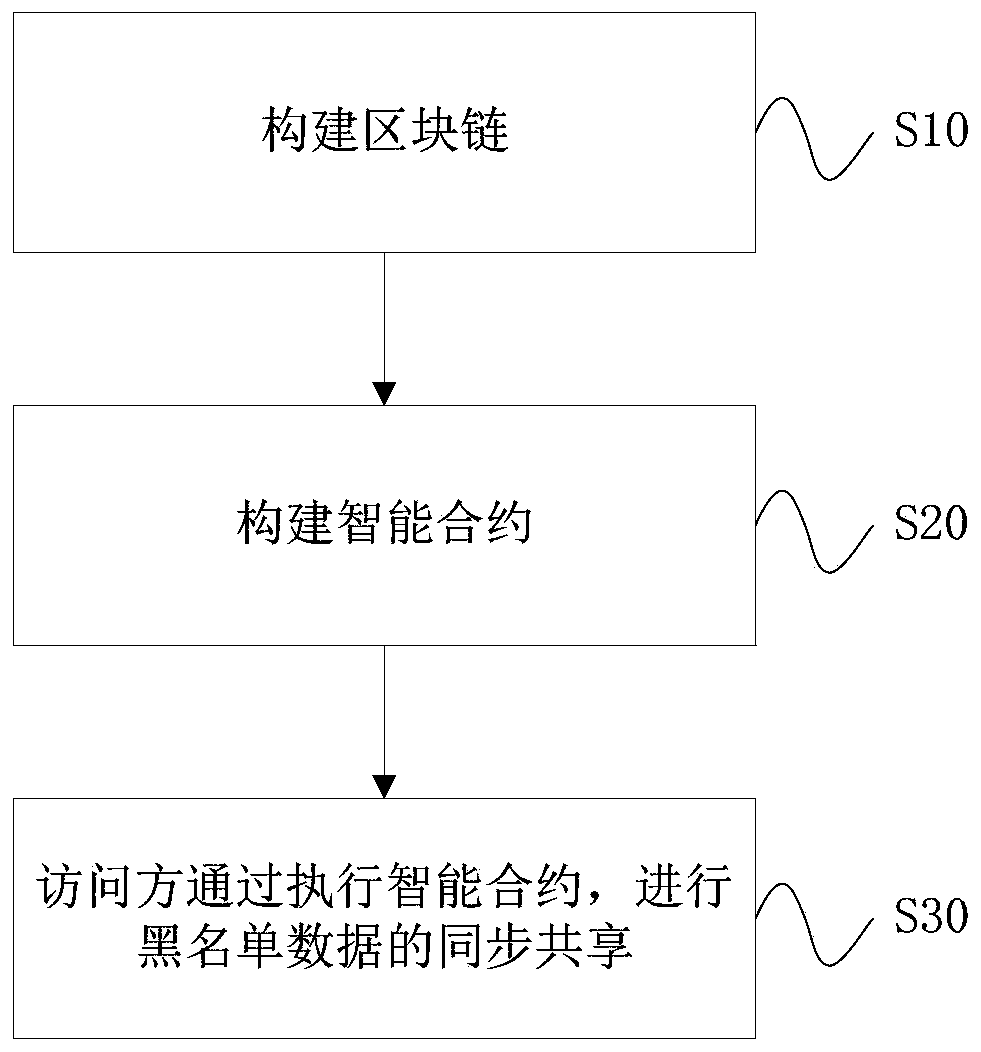
[0045] This embodiment provides a block chain-based blacklist sharing method, such as figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0046] S10: Build a block chain, the block chain includes several blocks;
[0047] S20: Build a smart contract, the smart contract stores blacklist data for the read and write logic of the blacklist, and the smart contract also exchanges data with the block chain;
[0048] S30: The accessing party performs synchronous sharing of blacklist data by executing the smart contract.
[0049] In the step S10, the block chain is used to store the maintenance process of all access parties to the blacklist, including adding data to the blacklist.
[0050] The smart contract’s logic of reading and writing to the blacklist includes sharing permissions. The smart contract is a group of functions that can realize active or passive processing of data, accept, store and send value, and control and manage various types of data on the chain. Programmatic rules and ...
Embodiment 2
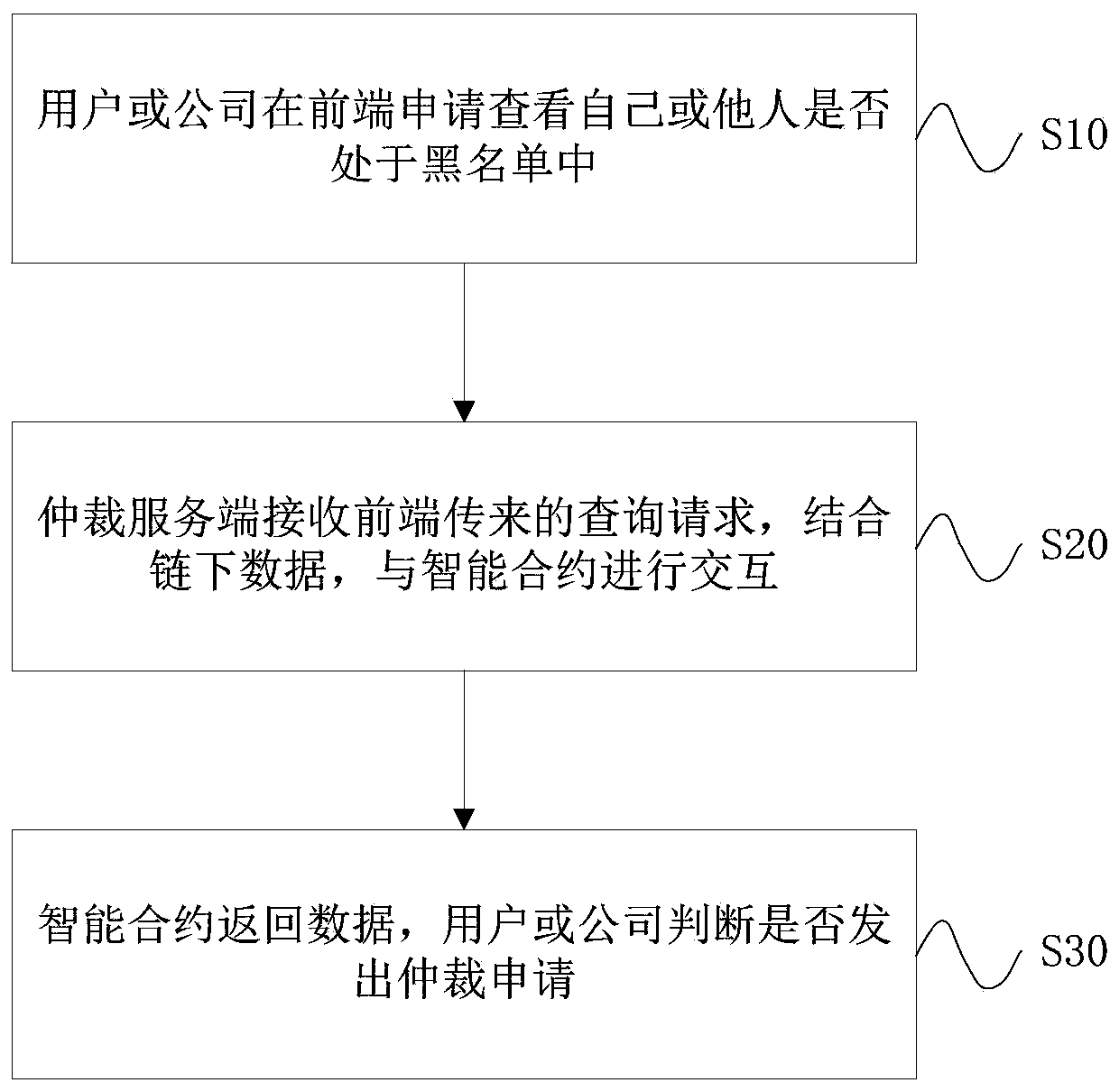
[0056] This embodiment provides a blockchain-based blacklist arbitration method, such as figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0057] S01: Users or companies apply on the front end to check whether they or others are in the blacklist
[0058] S02: The arbitration server receives the query request from the front end, combines the off-chain data, and interacts with the smart contract;
[0059] S03: The smart contract returns the data, and the user or company decides whether to issue an arbitration application.
[0060] The smart contract contains the following functions:
[0061] a: smart contract query: traversal query on the underlying storage;
[0062] b: Permission and blacklist storage: store the write permission of the company and the arbitrator in the address variable, and store the IDs of the blacklist and arbitration list in the uint array;
[0063] c: Initialization permissions: When the smart contract is deployed for the first time, determine the read and wri...
Embodiment 3
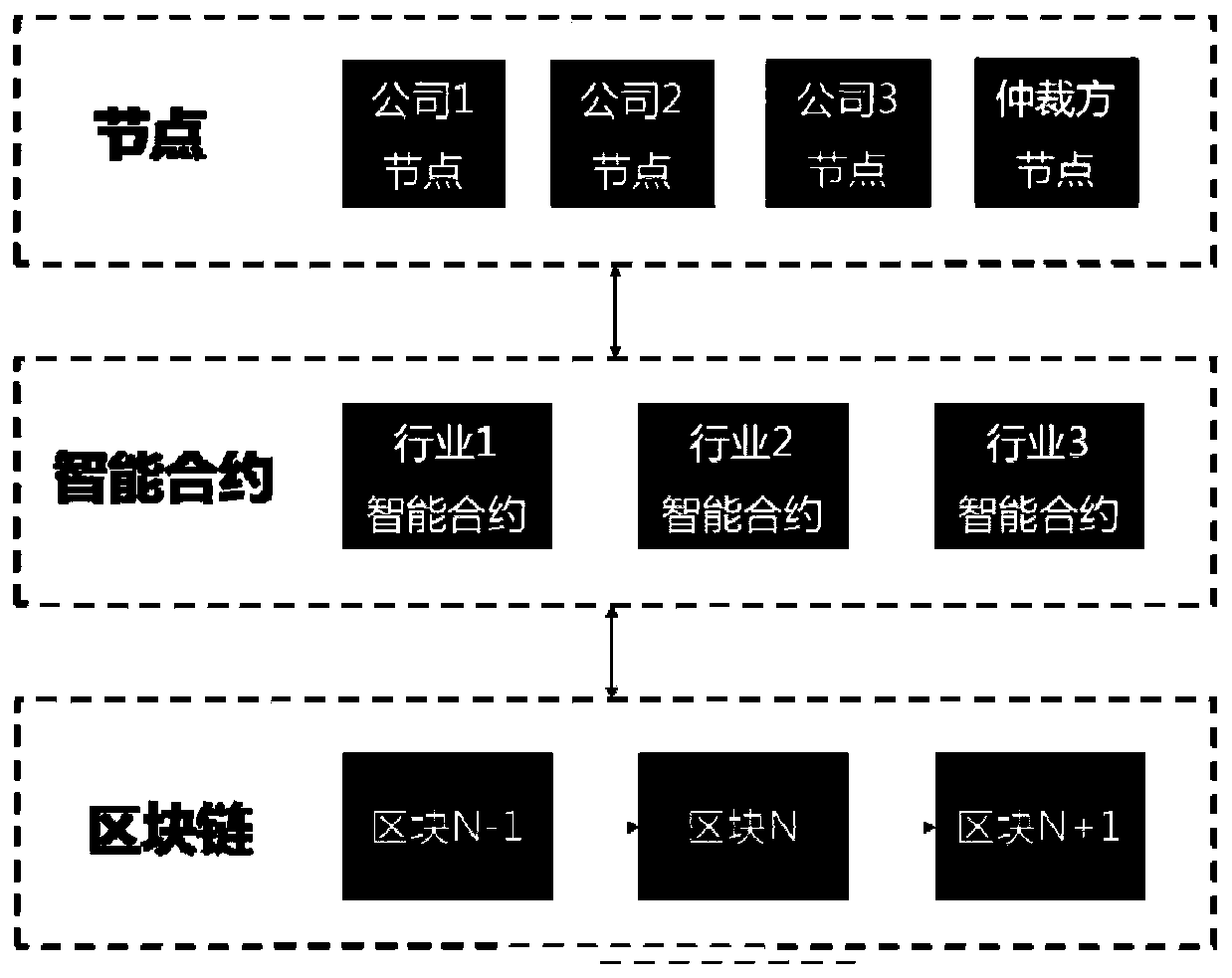
[0068] This embodiment provides a block chain-based blacklist sharing and arbitration device, including a data processing unit, which completes the block chain-based blacklist sharing method described in Embodiment 1 and the block-based method described in Embodiment 2. Chain blacklist arbitration method.
[0069] The same or similar reference numerals correspond to the same or similar components;
[0070] The terms describing the positional relationship in the drawings are only for illustrative purposes and cannot be interpreted as limitations on this patent;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com