Collaborative path planning method for kinematic redundant two-arm space robot
A space robot and path planning technology, which is applied to aircraft, manipulators, motor vehicles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
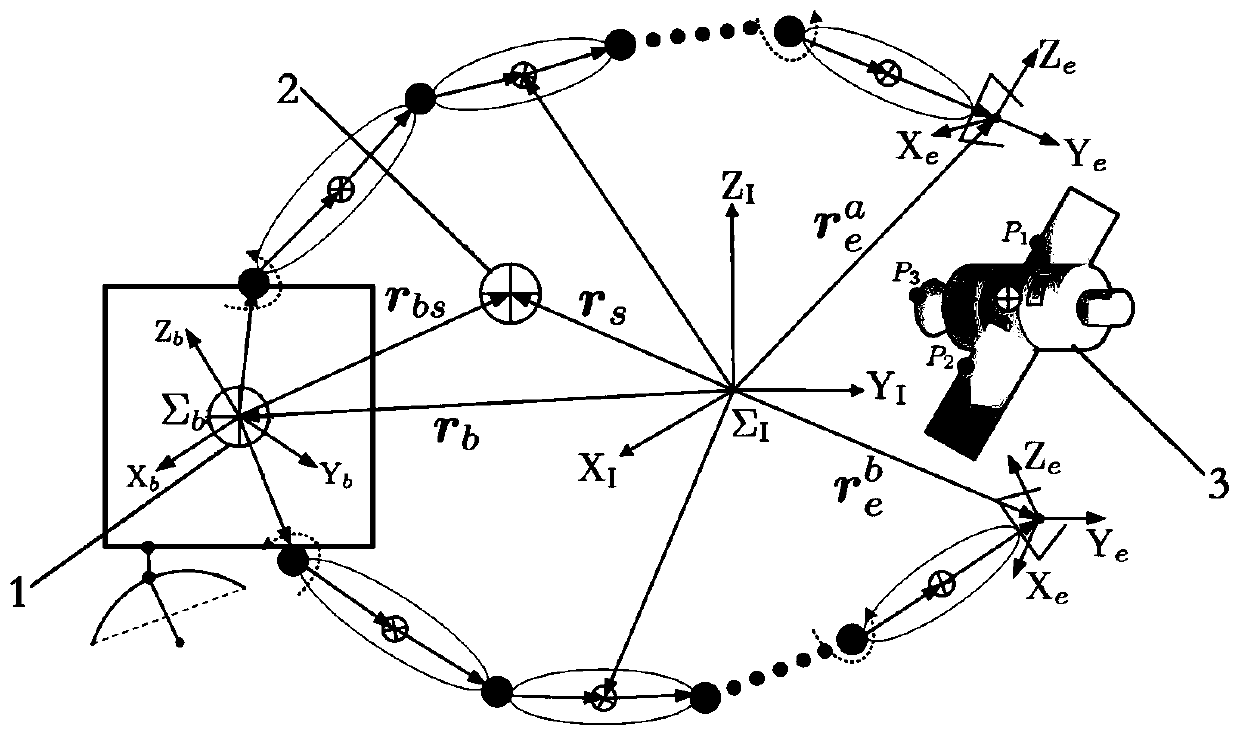
[0146] Only the arms move, and the end effectors a and b arrive at the capture point from the initial position; where the initial position is:
[0147]
[0148]
[0149]
[0150] The terminal locations are:
[0151]
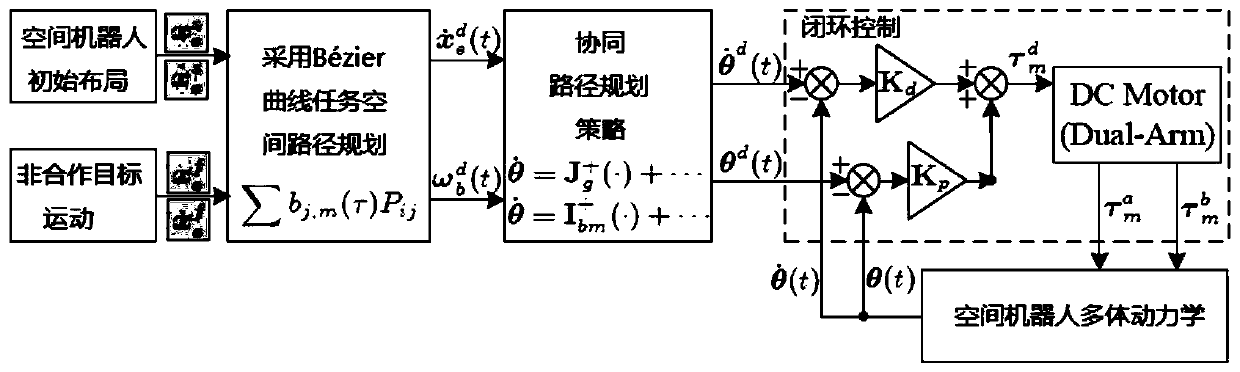
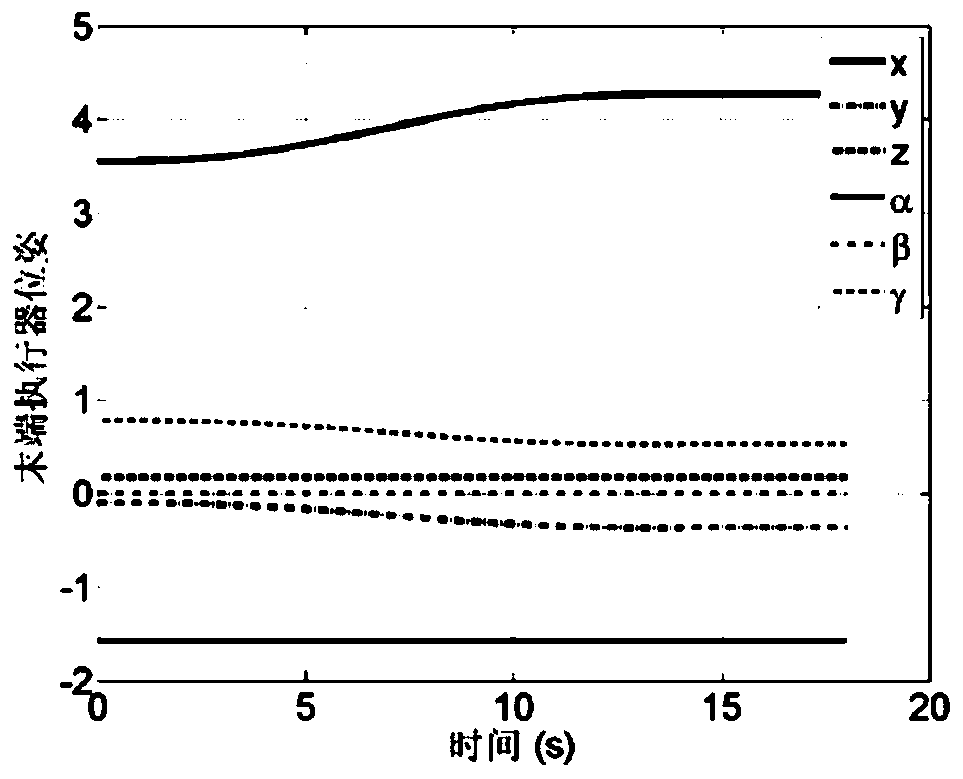
[0152] For simulation results see Figure 3-6 , through the velocity and acceleration boundaries, it can be determined that the execution time is T=14s. It can be seen from the simulation results that the designed end-effector path conforms to the proposed constraints and can complete the proposed capture task. When the cooperative trajectory planning strategy is not considered, see Figure 7-12 , it can be seen that both arms can perform the tracking task regardless of zero-space motion. Pedestal attitude and position are affected. The largest attitude and position perturbations reach 0.34° and 0.63m.
Embodiment 2
[0154] Drive the dual-arm end effector to the target capture point in Example 1 while minimizing the disturbance of the base attitude.
[0155] choose ω b = 0 and As dependent on speed. see Figure 13-18 , showing the trajectory tracking results of a zero-response manipulator. It can be noticed that the attitude disturbance of the base is O(10 -4 ), ensuring the unresponsive manipulator arm of the dual-arm space robot. The orientation deviation of the end effector caused by suppressing the attitude disturbance of the base is less than 0.05°. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the collaborative path planning strategy.
Embodiment 3
[0157] Drive the end effector of both arms to reach the target capture point in Example 1, and adjust the posture position of the base at the same time. In this simulation, the base pose is required to change from the initial reached terminal value degree, the base position is free. For simulation results see Figure 19-24 , it can be seen that the end effector can reach the capture point of the on-orbit target at the required speed. The direction tracking deviation of the end effector is less than 0.3°. The simulation results show that it is feasible and effective to adjust the attitude of the base by using the path coordination of the two arms. From the above three examples, it can be seen that the collaborative path planning method proposed by the present invention can complete the capture task of the end effector while ensuring the minimum attitude disturbance of the base or adjusting the attitude of the base.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com