MRI method for t1 mapping of the heart using a maximum likelihood reconstruction in k-space
A maximum likelihood, cardiac technique, applied in the field of magnetic resonance data acquisition, which can solve problems such as effective local magnetic field disturbance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0094] In the figures, like numbered elements are equivalent elements or perform the same function. Elements that have been discussed previously will not necessarily be discussed in subsequent figures if the function is equivalent.
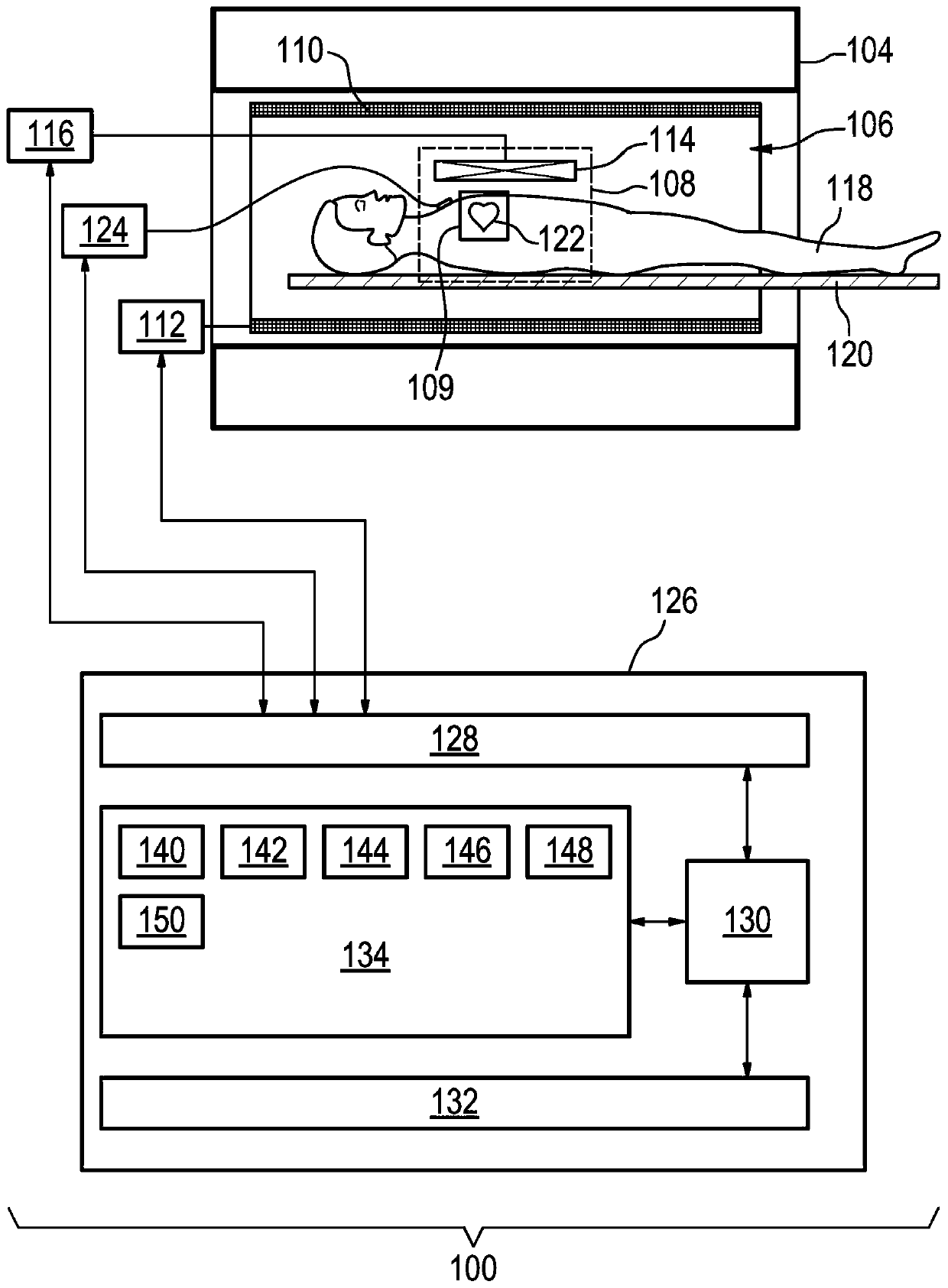
[0095] figure 1 An example of a magnetic resonance imaging system 100 with a magnet 104 is shown. Magnet 104 is a superconducting cylindrical magnet having a bore 106 therethrough. It is also possible to use different types of magnets; for example split cylindrical magnets and so-called open magnets can also be used. A split cylindrical magnet is similar to a standard cylindrical magnet, except that the cryostat has been split into two parts to allow access to the isoplane of the magnet so that the magnet can be used, for example, in conjunction with charged particle beam therapy. An open magnet has two magnet parts, one above the other, with a space in between large enough to accommodate the object: the arrangement of the two part areas is sim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com