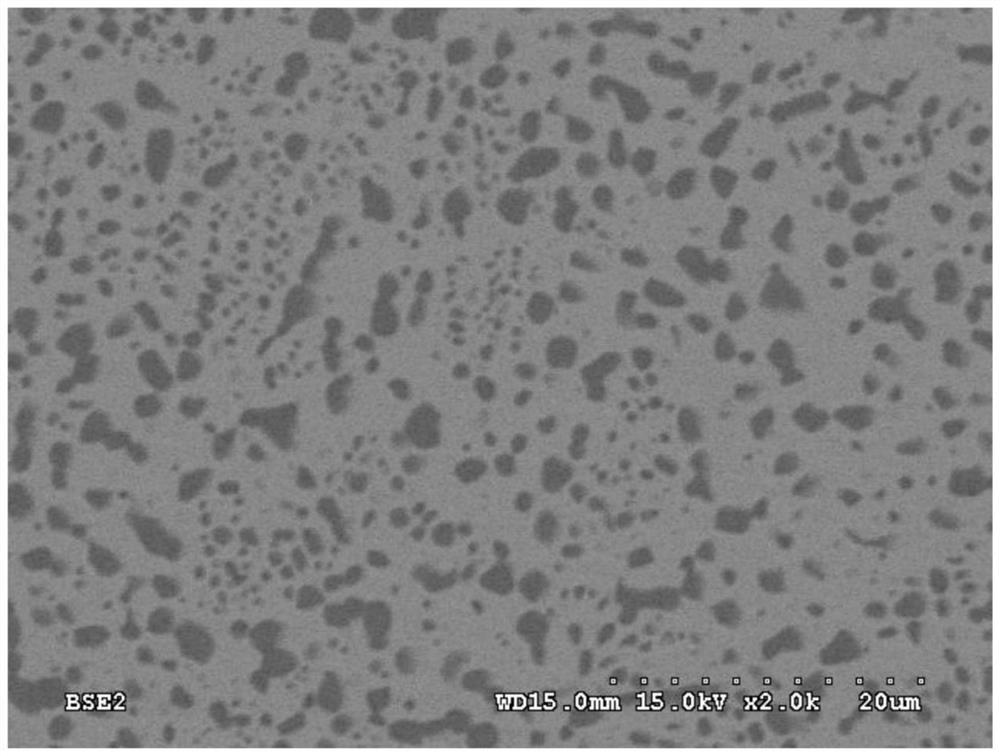
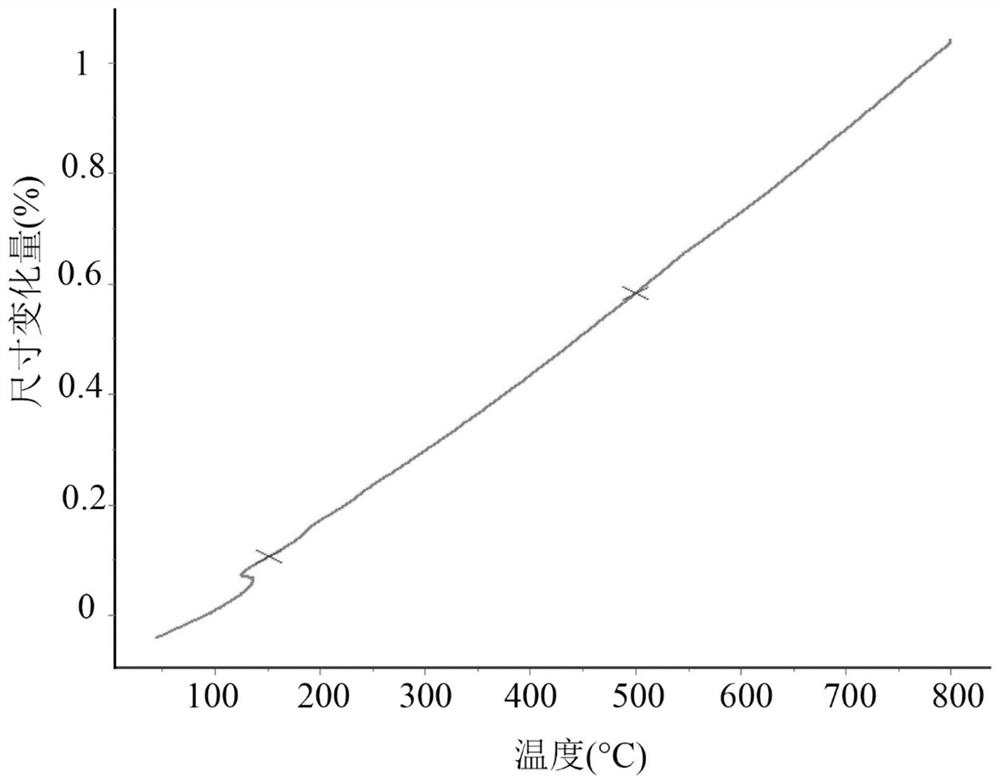
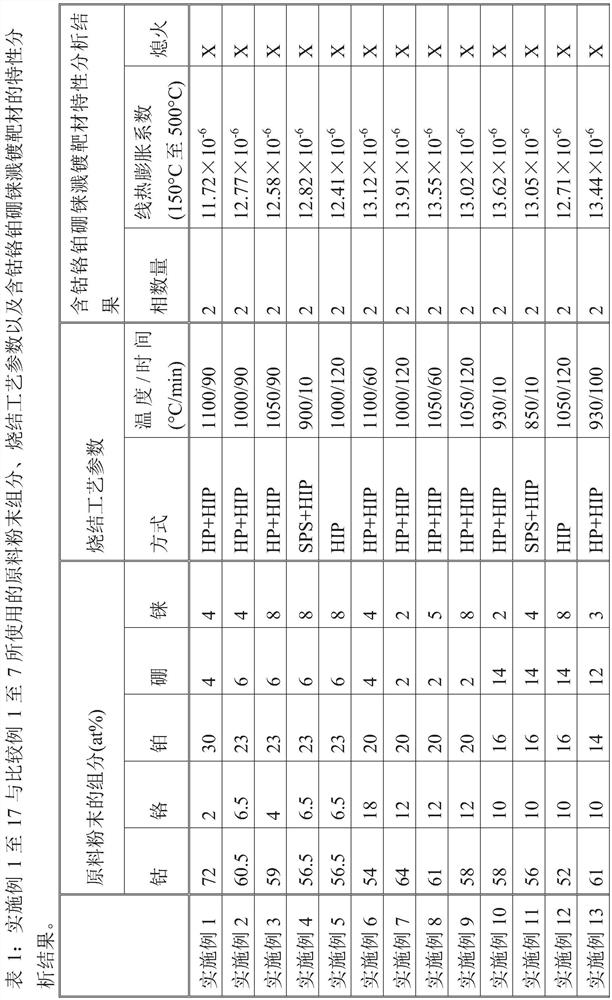
Cobalt-chromium-containing platinum-boron-rhenium sputtering target material, cobalt-chromium-containing platinum-boron-rhenium layer and its preparation method
A sputtering target, cobalt-chromium technology, applied in the field of cobalt-chromium-platinum-boron-rhenium sputtering target material, can solve the problems of increasing the probability of sputtering flameout and poor heat conduction effect, so as to increase sputtering stability, low line Effect of thermal expansion coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 17
[0034] Examples 1 to 17: Preparation of cobalt-chromium-containing platinum-boron-rhenium sputtering target
[0035] Examples 1 to 17 prepared sputtering targets containing cobalt, chromium, platinum, boron, and rhenium in a similar manner, and the differences among the examples lie in the raw material components, sintering methods and sintering parameters.
[0036] First, raw materials such as cobalt, chromium, platinum, boron, and rhenium were weighed according to the composition ratio shown in Table 1, and then the raw material powder was made into raw material powder through pre-alloy melting and atomization steps. Specifically, the raw material powder is a single pre-alloyed powder containing cobalt, chromium, platinum, boron and rhenium.
[0037] Next, the raw material powder is sintered by means of hot pressing forming method, hot isostatic pressing forming method, plasma sintering forming method or a combination thereof, so as to prepare each cobalt-chromium-containing...
Embodiment 18 to 20
[0047] Examples 18 to 20: Preparation of cobalt-chromium-containing platinum-boron-rhenium sputtering targets
[0048] Examples 18 to 20 prepare cobalt-chromium-containing platinum-boron-rhenium sputtering targets in a manner similar to that of Examples 1 to 3, 6 to 10, 13, 15 and 16, the difference being that in the raw material powders of Examples 18 to 20 It also includes an added element, the added element is hafnium, palladium, yttrium, neodymium, terbium, tantalum or a combination thereof, based on the total number of atoms of the raw material powder, the content of the added element is greater than 0 at% and less than or equal to 5 at%. The components, sintering methods and sintering parameters of the raw material powders used in Examples 18 to 20 are listed in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com