Railway vehicle axle temperature monitoring method and system
A technology for railway vehicles and monitoring systems, applied in railway vehicle shape measuring instruments, railway car body components, railway auxiliary equipment, etc., can solve the problems of transmission, short time, and long time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
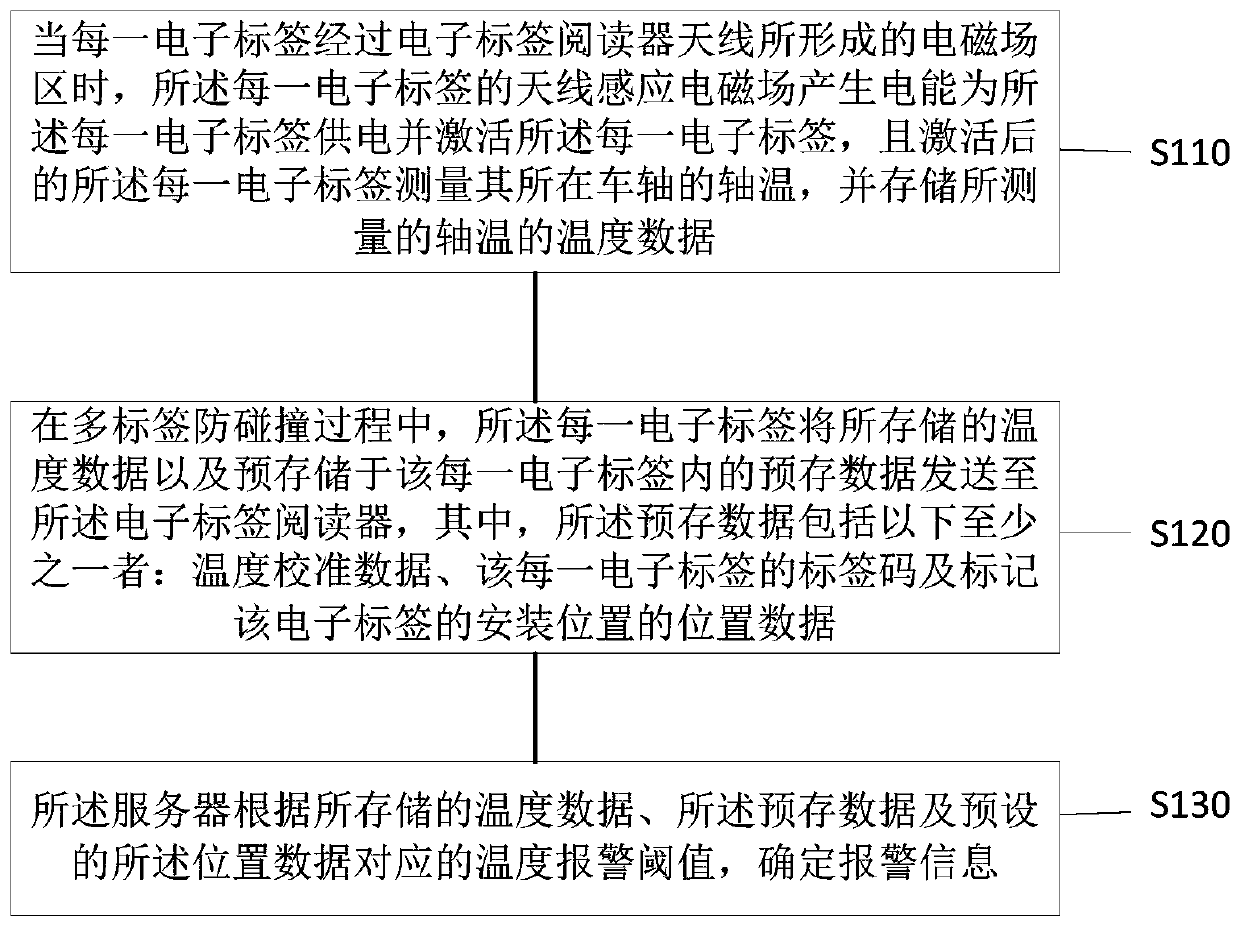
[0036] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the specific method of Embodiment 1. In the first embodiment, electronic tags capable of measuring axle temperature are arranged on the axles of each railway vehicle, and each electronic tag is configured to obtain electric energy in the magnetic field of a suitable electronic tag reader antenna installed on the ground.
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the axle temperature monitoring method may include:
[0038] S110, when each electronic tag passes through the electromagnetic field area formed by the antenna of the electronic tag reader, the antenna of each electronic tag induces an electromagnetic field to generate electric energy to supply power to each electronic tag and activate each electronic tag, and Each activated electronic tag measures the axle temperature of the axle where it is located, and stores the temperature data of the measured axle temperature.
[0039] Wherein, the antenna of each electronic tag induces an electr...
Embodiment 2
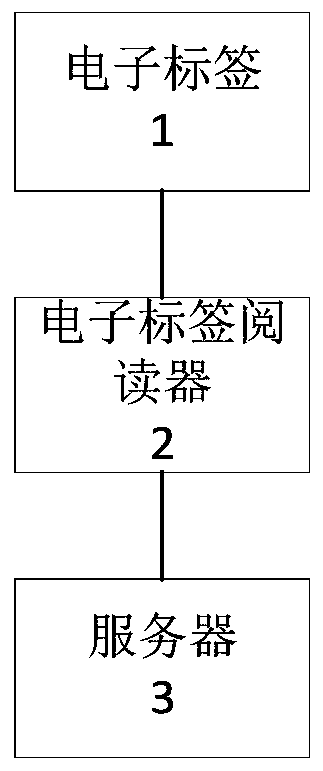
[0055] figure 2 It is a module connection block diagram of an axle temperature monitoring system of a railway vehicle.
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, the second embodiment provides an axle temperature monitoring system of a railway vehicle. The axle temperature monitoring system includes: each electronic tag 1 is arranged on the axle of each railway vehicle, and is used to measure the axle temperature and store the measured temperature. The temperature data of the shaft temperature and the pre-stored data are used to obtain electric energy in the electromagnetic field of the compatible electronic tag reader 2 antenna, wherein each electronic tag 1 is also used for when it passes through the electronic tag reader 2 antenna When the electromagnetic field is formed, the antenna induction electromagnetic field of each electronic tag 1 generates electric energy to power each electronic tag 1 and activate each electronic tag 1, and each electronic tag 1 after activation Mea...
Embodiment 3
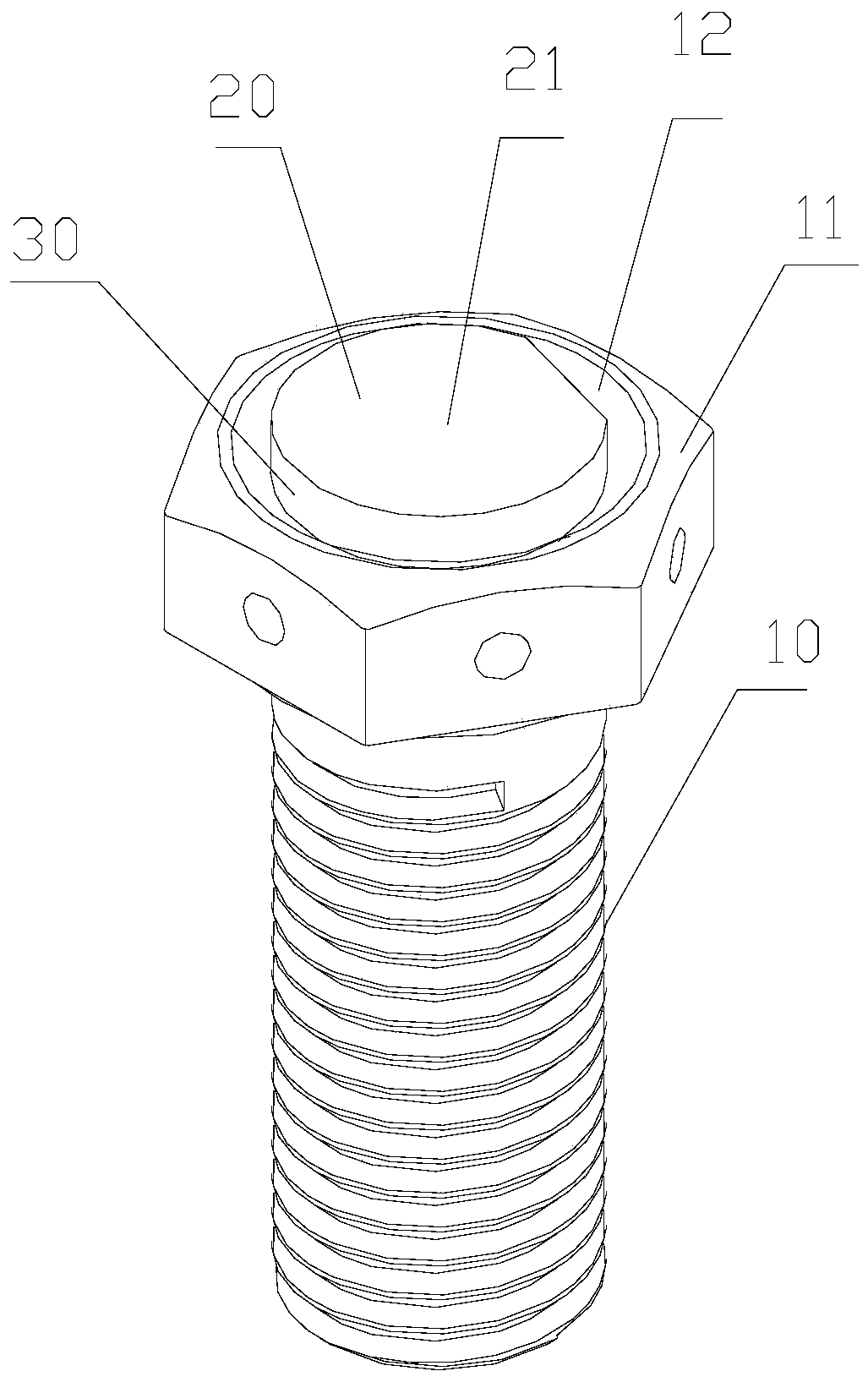
[0062] Before describing the third embodiment in detail, the structure of the existing electronic tag will be briefly introduced. In the existing electronic tags, a structure in which a rigid antenna, a bolt and a temperature sensing module cooperate is adopted, and the whole temperature sensing module and the rigid antenna are mainly designed inside the bolt. Due to the nature of the rigid antenna itself (large volume, not easy to fix), it can only be designed inside the bolt, and the design inside the bolt will affect the efficiency of data transmission, which will not affect the original slow-speed railway vehicles. However, when used on high-speed railway vehicles at the present stage, the transmission efficiency of the existing electronic tags cannot meet the requirements, and in severe cases, the temperature data cannot be transmitted.
[0063] image 3 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the electronic tag; Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the structure of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com