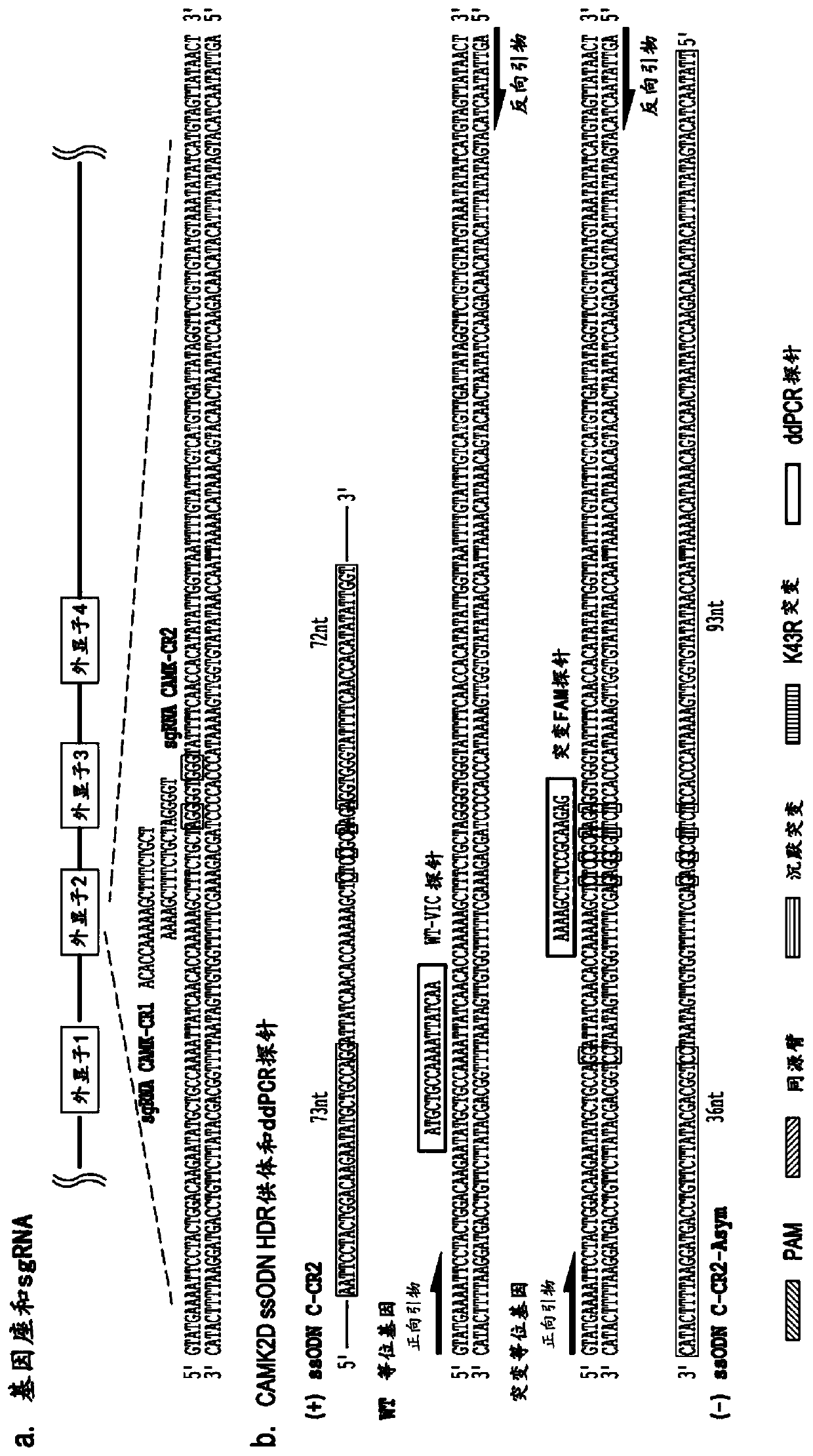
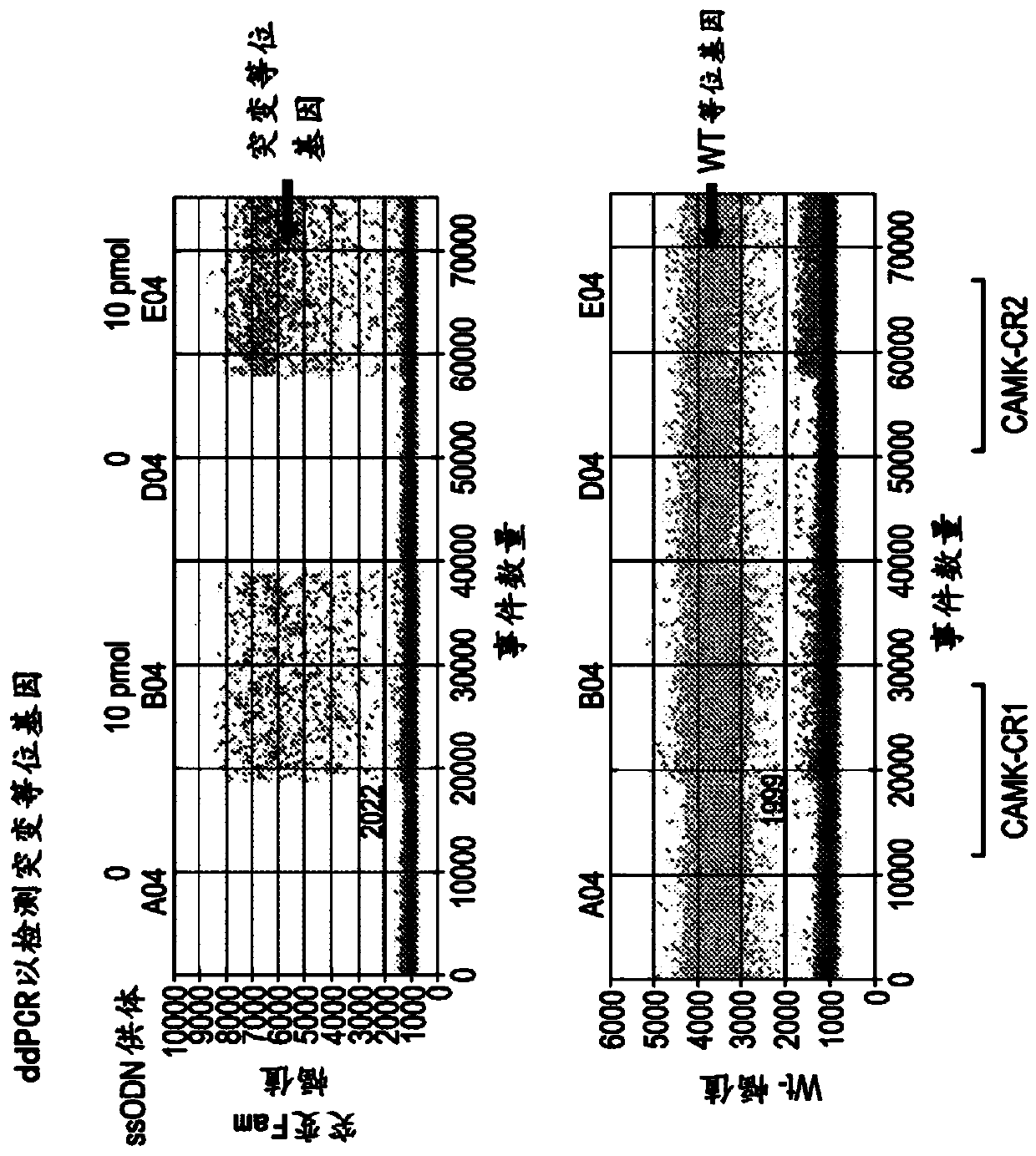
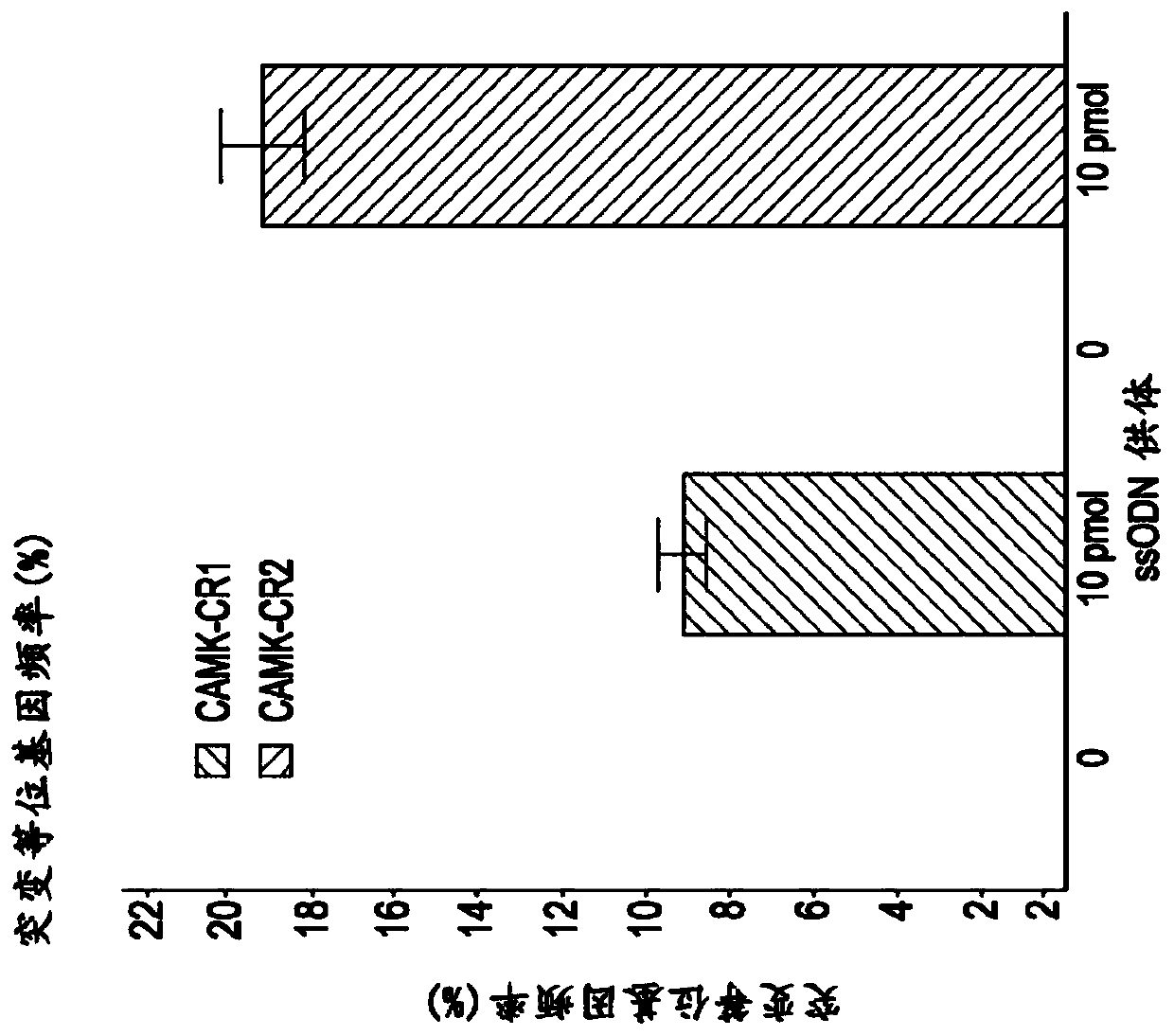
Methods for increasing the efficiency of homology directed repair (HDR) in the cellular genome
A genome and genome sequence technology, applied in the field of improving the efficiency of homology-directed repair (HDR) in the cell genome, can solve the problem of low efficiency of genome modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Cold shock increases the frequency of homology-directed repair for gene editing in induced pluripotent stem cells
[0075] introduction
[0076] One of the most promising applications of clustered regularly spaced palindromic repeat (CRISPR) technology is its use to create genetic models of human disease. CRISPR technology can be used on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) isolated from normal individuals to study disease phenotypes, or on IPSCs derived from disease patients to revert putative disease-causing mutations back to wild type (1,2). The relative robustness of the CRISPR pathway compared with zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) and transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) allows for the comparison of protein-coding mutations as well as empirical data generated by genome-wide association studies and other non-coding mutations. Testing becomes possible (3,4). Despite many successes, gene editing in iPSCs is challenged by the fact that homology-di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com