A development method and well type selection method for a multi-layer superimposed tight gas reservoir
A technology for tight gas and gas reservoirs, applied in the direction of production fluid, earthwork drilling and production, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve problems such as shortage, systematic evaluation of horizontal well development effects, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing production and recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
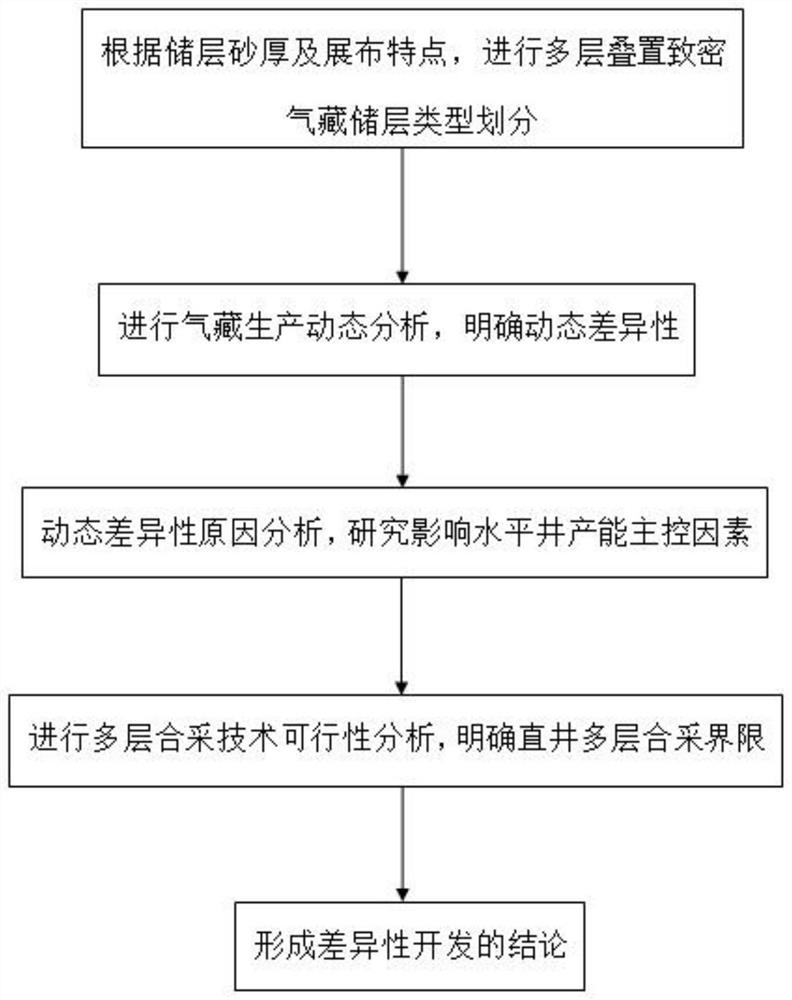
[0059] In this example, the development effect of the middle-shallow multilayer superimposed tight gas reservoir in a certain area is analyzed, such as figure 1 As shown, the method for developing a multilayer stacked tight gas reservoir in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0060] A. According to the sand thickness and distribution characteristics of the reservoir, classify the reservoir types of the multi-layered tight gas reservoirs;
[0061] B. Carry out dynamic analysis of gas reservoir production, compare the dynamic indicators of vertical wells and horizontal wells in gas reservoirs, and clarify dynamic differences;
[0062] C. Analyze the reasons for dynamic differences and study the main control factors affecting the productivity of horizontal wells;
[0063] D. Carry out the feasibility analysis of multi-layer commingled production technology, and clarify the multi-layer commingled production boundary of vertical wells;
[0064] E. Forming the conclusi...
Embodiment 2
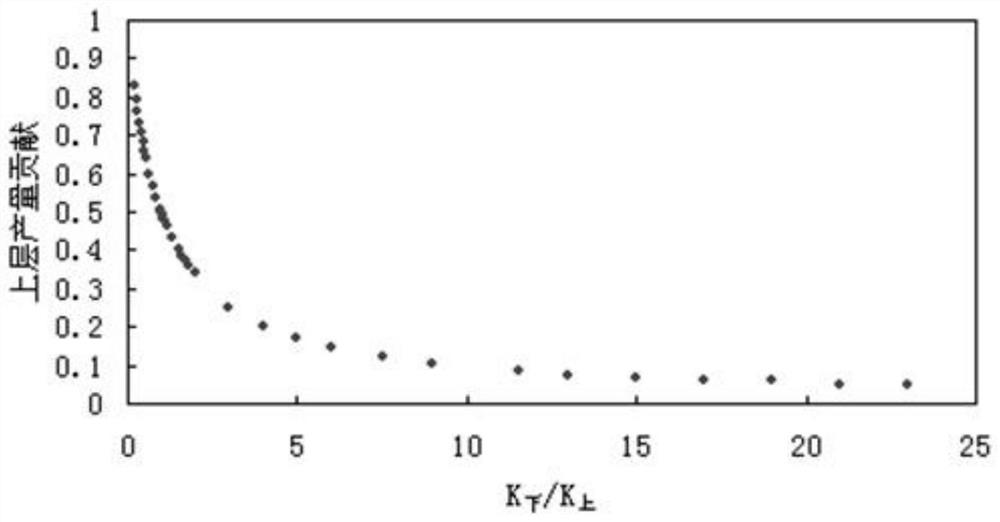
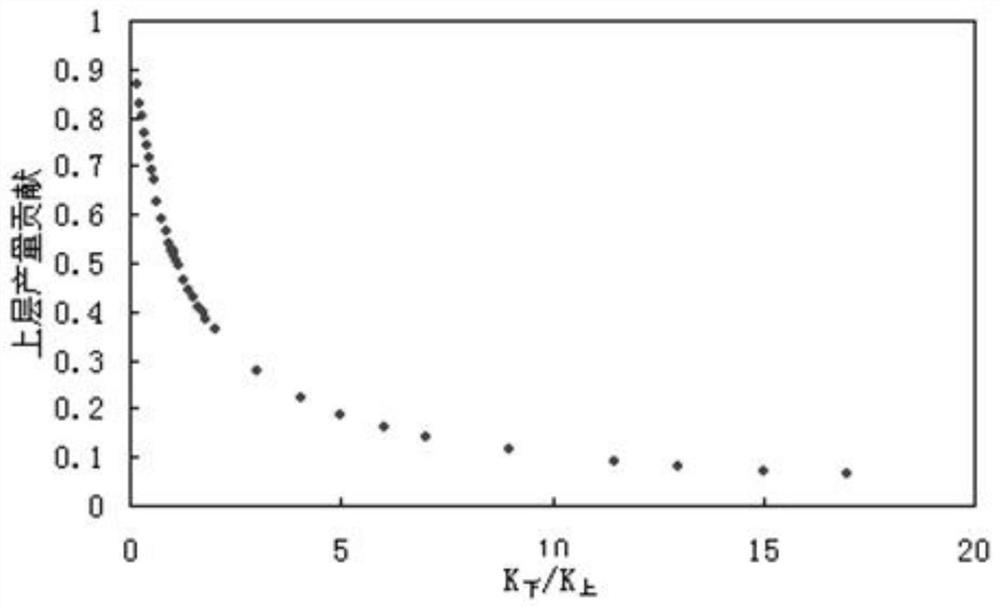
[0097] like Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, according to the method for developing a multi-layered tight gas reservoir described in Embodiment 1, in this embodiment, a vertical well multi-layered commingled production limit analysis is carried out in step D, and a dual-layer commingled production is established by numerical simulation technology according to the gas reservoir physical properties, temperature and pressure systems. A homogeneous gas reservoir model with no channeling in layers, the burial depth is 2300m at the base of the model, the porosity is 0.1076, and the permeability is 0.19×10 -3 μm 2 , the vertical permeability is zero, the effective thickness of the reservoir is 10 meters, the original formation pressure is 42.3MPa, and the numerical calculation grid is 30×30×3. In the model, only the upper and lower layers are the target layers, and the middle is the impermeable barrier. layer, the total model reserves are 1.43×10 8 m 3, given that the combined prod...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Based on the development methods for multi-layer stacked tight gas reservoirs described in Embodiments 1 and 2, this embodiment provides a well type selection method. Based on the development effects of horizontal wells in different reservoirs, the well type adaptability evaluation is carried out, and then the The suitable well types for three types of reservoirs are selected:
[0112] Type I reservoir: both horizontal wells and vertical wells are suitable, but vertical wells are more economical; H≥23m, K≥0.11m, S w ≤50%;
[0113] Type II reservoir: some suitable for vertical wells, some suitable for horizontal wells; H: 16-20m, K≥0.15mD, S w ≤54%, horizontal well should be used; H: 20-23m, K≥0.17mD, S w ≤54%, using vertical wells;
[0114] Type III reservoir: horizontal wells can be used for development in a few areas; H: 10-16m, K≥0.2mD, S w ≤58%, using horizontal well development;
[0115] Among them, H is the effective thickness, K is the permeability, S w is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com