A Calculation Method of Supply-production Balance Speed of Electric Submersible Direct Drive Screw Pump Production Well
A calculation method and technology of screw pumps, applied in pumps, production fluids, earthwork drilling and production, etc., can solve the problem that the speed of screw pumps cannot be adjusted according to the formation fluid supply conditions of oil wells, so as to avoid large-scale fluctuations and prolong operation The effect of longevity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
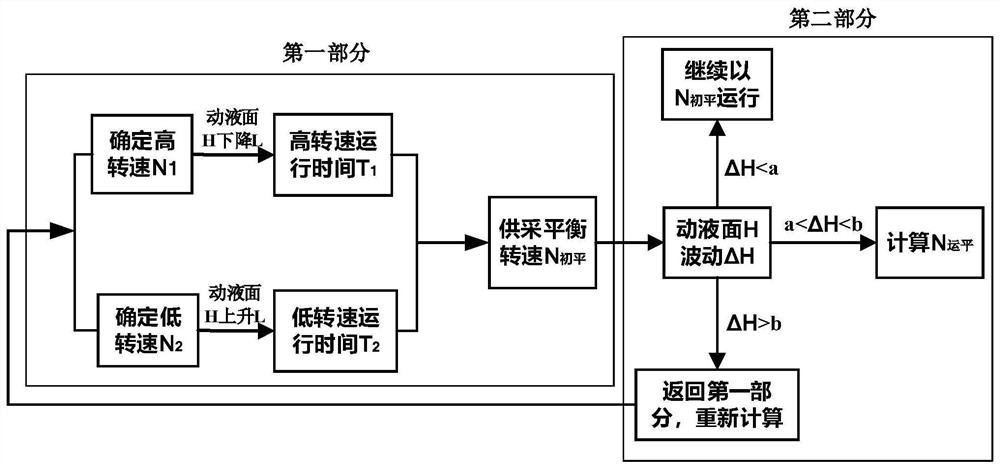
[0043] step1: Set the screw pump to run at the rated speed N, monitor the change of the dynamic liquid level H, if H rises, increase N at a certain rate until the dynamic liquid level H starts to decrease, and the unit starts at the current speed N 1 Run, when H drops to the height of the dynamic fluid level required to maintain a reasonable flow pressure in the oil well, start timing to calculate the time T required for the dynamic fluid level to continue to drop to the height L 1 ;
[0044] step2: Then reduce the speed at a certain rate until it reaches the speed N when the dynamic liquid level H starts to rise 2 , to calculate the time T required for the liquid level to rise to the same height L 2 ;
[0045] step3: Calculate N 初平 , N 初平 =((N 1 ×T 1 )+(N 2 ×T 2 )) / (T 1 +T 2 );
[0046] step4: The unit uses N 初平 Run, monitor the change of ΔH;
[0047] step5: Calculate N based on the change of ΔH 运平 .
Embodiment 2
[0049] Step1: Set the screw pump to run at the rated speed N, and monitor the change of the dynamic fluid level H. If H decreases, the unit will continue to operate at N. When H drops to the height of the dynamic fluid level required to maintain the reasonable flow pressure of the oil well, start timing calculation The time T required for the liquid level to continue to drop to a height L 1 ;
[0050] step2: Then reduce the speed at a certain rate until it reaches the speed N when H starts to rise 2 , to calculate the time T required for the liquid level to rise to the same height L 2 ;
[0051] step3: Calculate N 初平 , N 初平 =((N×T 1 )+(N 2 ×T 2 )) / (T 1 +T 2 );
[0052] step4: The unit uses N 初平 Run, monitor the change of ΔH;
[0053] step5: Calculate N based on the change of ΔH 运平 .
Embodiment 3
[0055] step1: Set the high speed value N that can make the dynamic fluid level H drop according to the well conditions 1 And the low speed value N that can make the dynamic liquid level rise 2 ;
[0056] step2: The computer group starts with N 1 The time T required for the liquid level to drop to height L during operation 1 , and with N 2 The time T required for the dynamic liquid level to rise to the same height L during operation 2 ;
[0057] step3: Calculate N 初平 , N 初平 =((N 1 ×T 1 )+(N 2 ×T 2 )) / (T 1 +T 2 );
[0058] step4: The unit uses N 初平 Run, monitor the change of ΔH;
[0059] step5: Calculate N based on the change of ΔH 运平 .
[0060] The method for calculating the supply-production balance speed of electric submersible direct drive screw pump production wells of the present invention is an adaptive speed intelligent adjustment method, which can automatically and real-time adjust the operating speed of the electric submersible direct drive screw pump ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com