Electric vehicle and power supply control method
An electric vehicle and front-end technology, applied in electric vehicle charging technology, electric vehicle, battery/battery traction, etc., can solve the problems of heavy weight, need to recharge, short driving distance, etc. The effect of charging costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
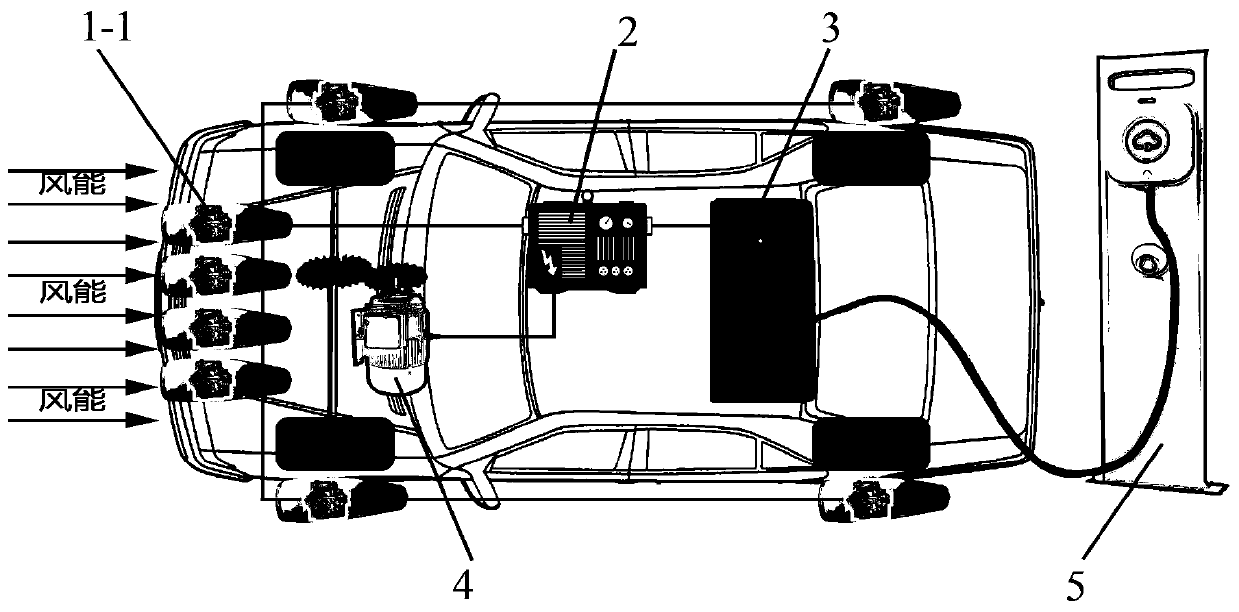
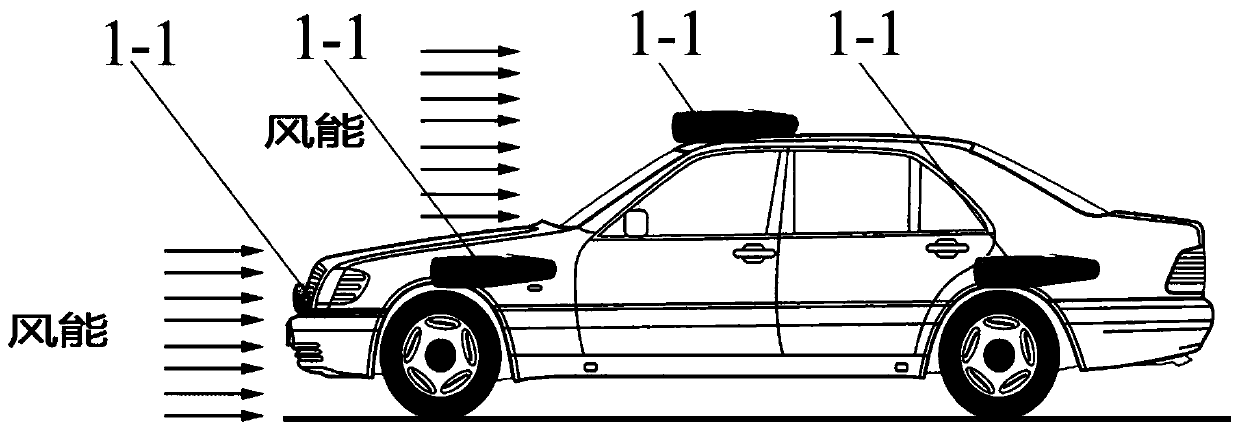
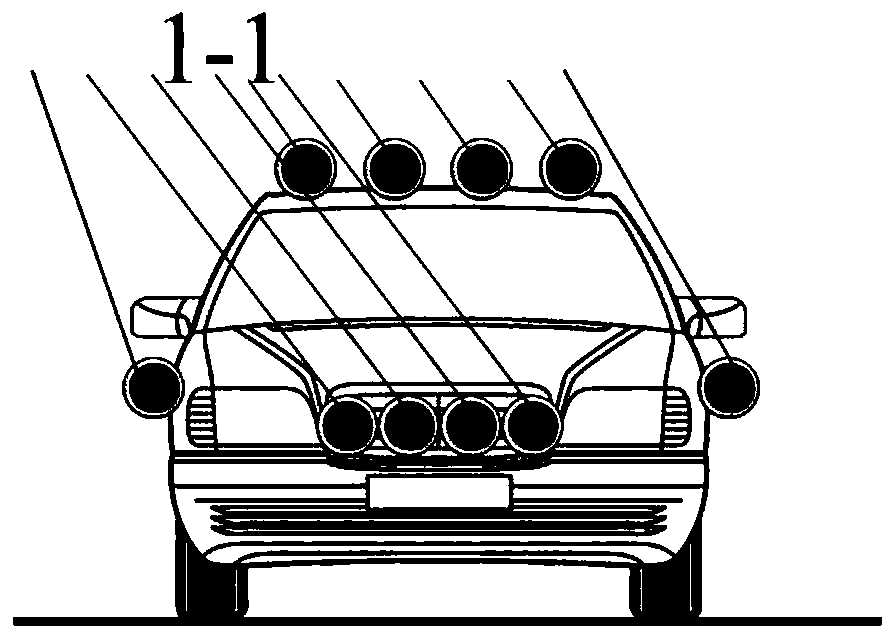
[0039] The auxiliary power generation equipment in this embodiment is a wind power generator. figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of Embodiment 1 of the electric vehicle of the present invention, figure 2 It is a side view of Embodiment 1 of the electric vehicle of the present invention, image 3 It is the front view of Embodiment 1 of the electric vehicle of the present invention. combine Figure 1-Figure 3 As shown, in the present embodiment, a plurality of wind generators 1-1 are installed on the front end of the electric vehicle, the top of the vehicle body, and the side of the vehicle body, and the wind kinetic energy generated in the running of the electric vehicle converts wind energy into The electric energy is transmitted to the motor 4 through the inverter 2, and the electric motor 4 converts the electric energy into kinetic energy to drive the electric vehicle; at the same time, the excess electricity generated by the wind generator 1-1 can also be conv...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the auxiliary power generation equipment in this embodiment is a fuel generator. Figure 4 It is a structural schematic diagram of electric vehicle embodiment 2 of the present invention, as Figure 4 As shown, in the present embodiment, a fuel generator 1-2 is installed in the hood of the electric vehicle. During the running of the electric vehicle, the fuel generator 1-2 converts energy into electrical energy, and then through the inverter 2 The electric energy is delivered to the motor 4, and the electric motor 4 converts the electric energy into kinetic energy to drive the electric vehicle; the excess electricity generated by the fuel generator 1-2 can also be stored in the storage battery 3, which is used for the electric vehicle and other accessories . The engine of the fuel generator 1-2 in this embodiment is a coolant-cooled engine or an air-cooled engine. Fuel generators 1-2 include: gasoline generators, diesel generato...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the auxiliary power generation equipment in this embodiment is a combination of one fuel generator and multiple wind power generators. Figure 7 It is a structural schematic diagram of the electric vehicle embodiment 3 of the present invention, as Figure 7 As shown, the present embodiment at first installs a fuel generator 1-2 in the hood of the electric vehicle, and the fuel generator 1-2 is the same as the fuel generator 1-2 in embodiment 2. During the process, the fuel generator 1-2 converts energy into electric energy, and then transmits the electric energy to the motor 4 through the inverter 2, and the electric motor 4 converts the electric energy into kinetic energy to drive the electric vehicle; secondly, it is installed at the front end of the electric vehicle A plurality of wind power generators 1-1, the wind power generators 1-1 are the same as the wind power generators 1-1 in Embodiment 1, convert wind energy into ele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com