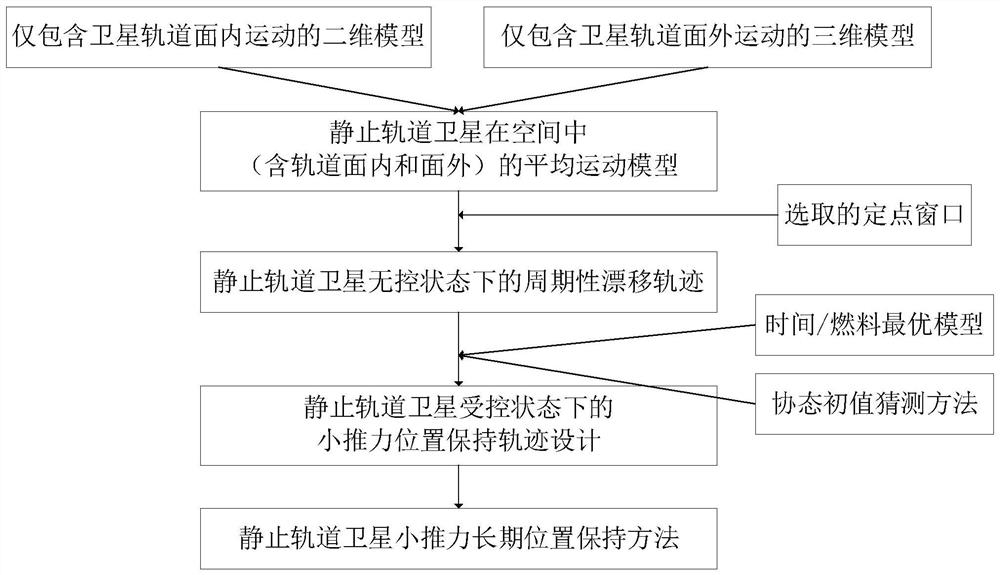
A low-thrust long-term position keeping method for geostationary satellites
A static orbit, low-thrust technology, applied in the direction of aerospace vehicle guidance devices, instruments, aerospace vehicles, etc., can solve the problem of lack of co-state initial value guessing method, position maintenance optimization algorithm convergence stability and convergence speed, underutilization Problems such as the long-term characteristics of satellite perturbation motion can solve the problem of small thrust position maintenance, reduce labor costs and equipment loss, and reduce fuel consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment discloses a method for maintaining a low-thrust long-term position of a geostationary orbit satellite. In order to verify the method, first, a satellite operating in a geostationary orbit is selected as the main research object. The basic parameters of the satellite are shown in the table below.
[0124] Table 1 Satellite parameters
[0125]
[0126]
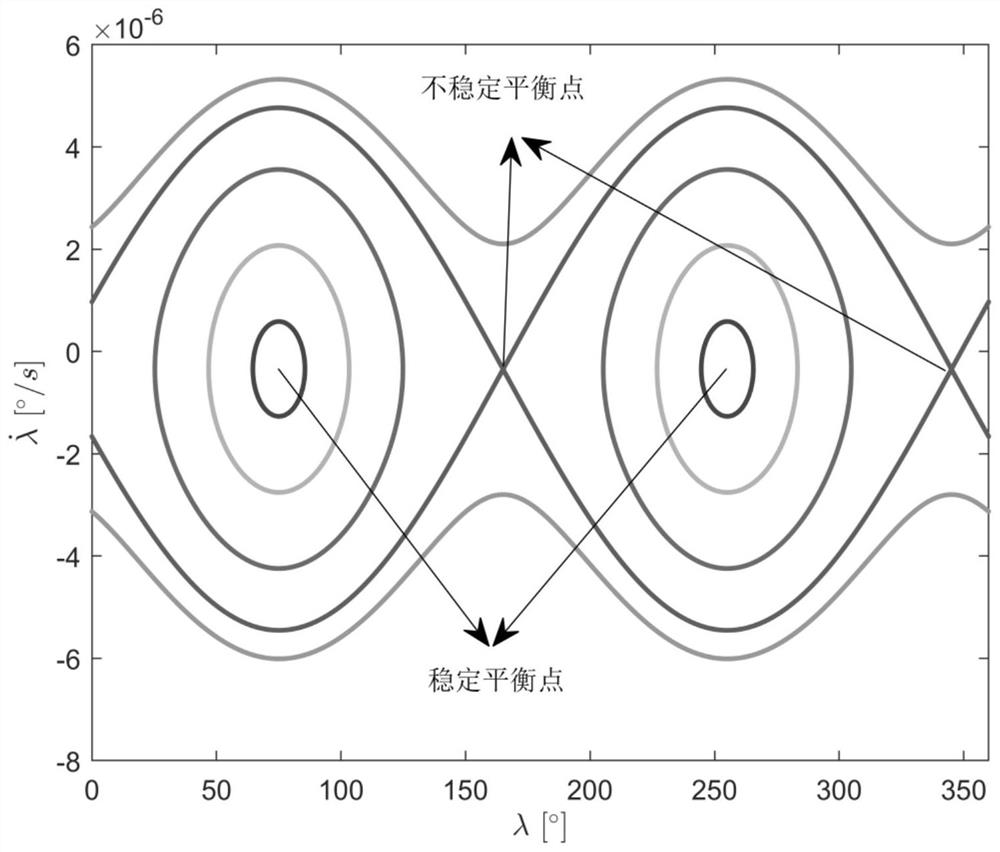
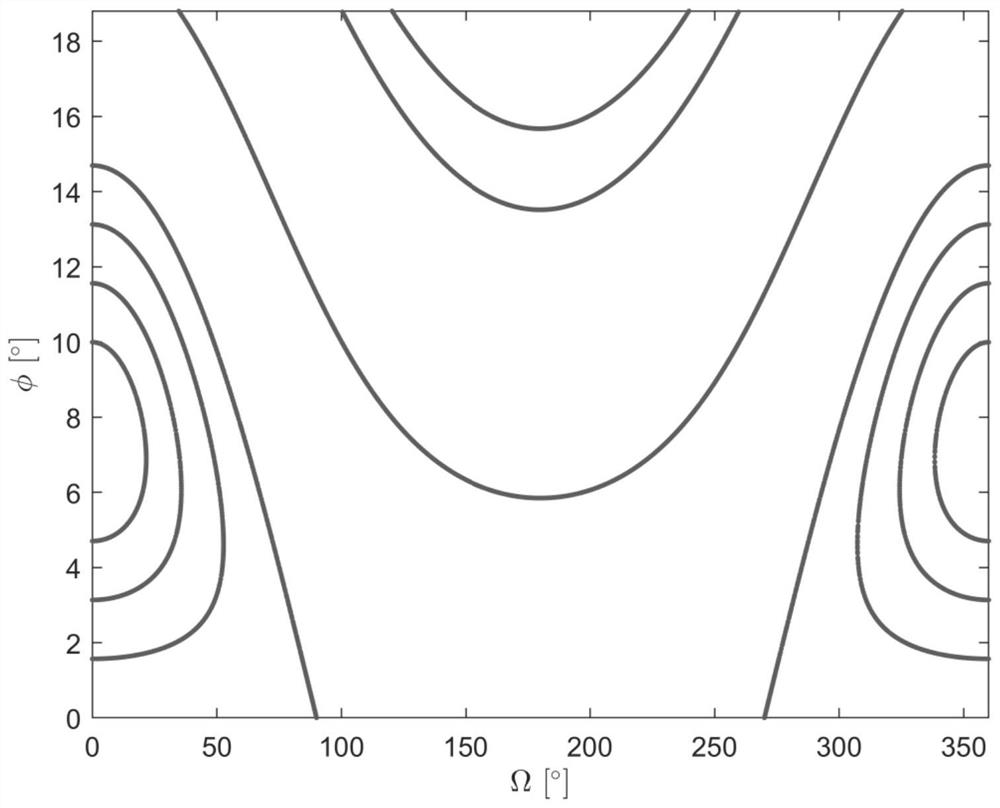
[0127] Step 1: Establish the motion model of the geostationary orbit satellite in the space including the orbital plane and the outer plane under the action of the environment perturbation through spherical coordinates, and analyze the periodic motion law of the geostationary orbit satellite;
[0128] The band harmonic term and field harmonic term coefficients used to calculate the aspherical perturbation of the earth are shown in the following table:
[0129] Table 2 The main term coefficients of the Earth's gravitational field
[0130]
[0131] Bringing the parameters ...
Embodiment 2
[0155] The first four steps of Example 2 are the same as the first four steps of Example 1.
[0156] Step 5: Solve the two-point boundary value problem described in step 4 through the co-state initial value guessing method, and bring the result into step 4 to obtain the time-optimal and fuel-optimal control laws for maintaining the low-thrust position:
[0157] Step 5.1: Calculate the pulse thrust ΔV required to maintain the position through the deviation of the number of orbital elements at the beginning and end * =5.987m / s and the action position of the pulse thrust
[0158] Step 5.2: Search for longitudes containing pulse thrust effects of continuous thrust arcs, enabling the satellite to complete the thrust with the applied pulse ΔV * = After 5.987m / s, the position with the same effect is maintained, and the right ascension of the startup and shutdown of the continuous thrust arc is recorded. and the total boot time Δt * =47649s; using continuous thrust F const = 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com