Peptides and methods for detecting peanut allergies
A technology of peanut peptides and peanuts, applied in chemical instruments and methods, allergic diseases, peptide sources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0121] Example 1: Analysis of the LEAP cohort using epitope assays
[0122] As background, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) (eg, Learning Early About Peanut allergy (LEAP)) have previously been conducted to determine the best strategies for preventing peanut allergy in young children. The LEAP trial consisted of 640 children between the ages of 4 and 11 months who were identified as being at high risk for peanut allergy. The children were divided into two groups: avoidant and edible (snacks containing peanuts, >3 meals; 6 g peanut protein per week). The results of this trial showed that the proportion of children developing peanut allergy at 5 years of age was 4- to 6-fold higher in the avoidance group compared with the eating group, as measured by the oral food challenge (OFC). The results of the LEAP trial are published eg in Toit et al., N. Engl. J. Med., 2015, 372, 803-813. As a result, the trial led to changes in U.S. guidelines for peanut allergy prevention.
[012...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Example 2: Evaluation of an epitope classifier for predicting peanut allergy
[0150] To assess the diagnostic suitability of IgE and IgG4 epitope reactivity using this same (LEAP) cohort, patients whose final diagnosis was confirmed by OFC were selected to develop algorithms and identify classifiers for predicting allergy.
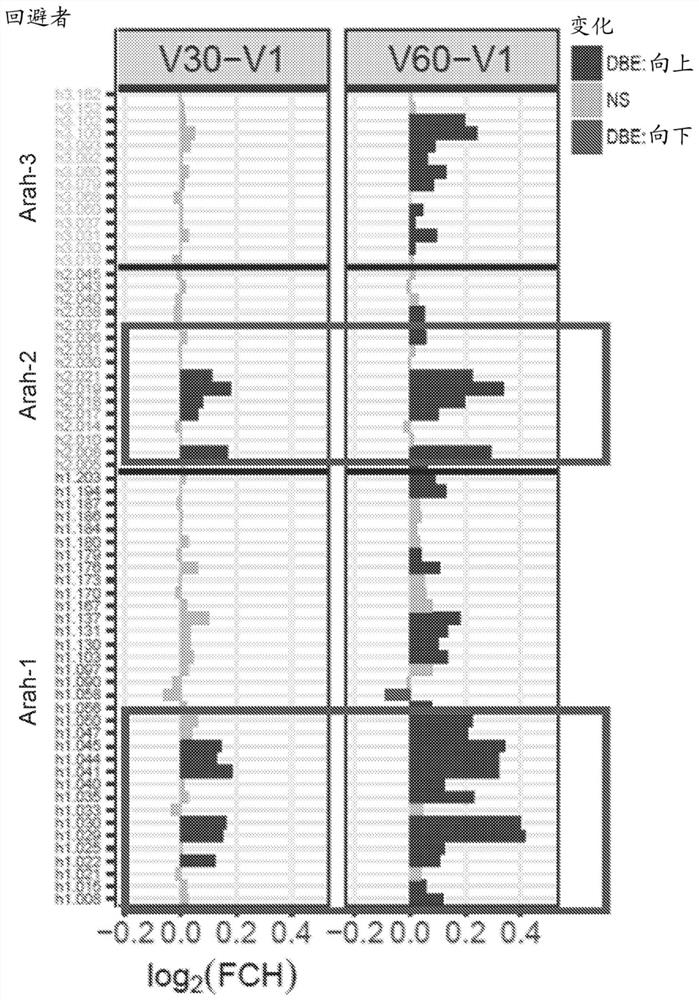
[0151] IgE / IgG4 epitope-specific binding was assessed over 5 years using samples from 341 children at high risk of peanut allergy recruited in the LEAP trial ( Figure 7 ). IgE epitope-specific antibodies were developed in patients in the avoidance group and were specific for patients with peanut allergy at 5 years of age mainly in two regions (see Figure 7 , green arrow, left). IgG4 epitope-specific antibodies were increased in all patients, suggesting that peanut exposure occurred through a non-oral route in peanut avoiders. In particular, peanut eaters produced IgG4 early (see Figure 7 , right panel), particularly in the region of interest...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Embodiment 3: test
[0166] Based on the robust data presented here, the binding patterns of IgE / IgG4 to peanut epitopes are expected to be informative and useful for characterizing the severity of allergic disease in patients, assessing patients longitudinally to guide initial and inter-study dosing, during the study Tracking or predicting adverse events (to improve safety), confirming patients' allergic status at clinical endpoints of treatment, and monitoring patients after treatment to determine if / when additional therapy is needed to maintain treatment responsiveness.
[0167] Subgroups of patient samples will be identified. At a minimum, samples will include Ar101-treated and placebo groups that include patients who: 1) remain in the study until the clinical endpoint; 2) continue to be monitored after the clinical endpoint to assess ongoing non-responsiveness; 3) due to 4) withdraw from the study without adverse reactions; 5) have available serum composition and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com