A Fluorescein-Based Flow Cytometry Method for Identification of Rifampicin Heterogeneous Drug Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
A technology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and flow cytometry, which is applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microorganism measurement/inspection, and can solve mutations, affect detection accuracy, and fail to identify drug-resistant genes, etc. problems, to achieve high accuracy and avoid the accumulation of experimental errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 The method for identifying heterogeneous drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by flow cytometry based on fluorescein of the present invention
[0043] 1.1 Equipment and materials
[0044] The flow cytometer FACSAriaTM Ⅱ was produced by BD Company in the United States, and the bacterial ultrasonic disperser BACspreaderTM1100 was produced by Guangdong Tibikang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; the 300-mesh stainless steel cell filter was purchased from Xiangbo Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Middlebrook 7H10 solid medium and Middlebrook 7H9 Liquid medium was purchased from BD Company in the United States, fluorescein diacetate was purchased from LIFE Company in the United States, and PBS (pH 7.4±0.1) was purchased from Hangzhou Gino Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd.
[0045] 1.2 Identification method
[0046] S1. Preparation of working solution:
[0047] Fluorescein diacetate fluorescent dye: take out the stock solution of fluorescein diacetate fluorescent dye, thaw it...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Using the method of the present invention to detect Rifampicin heterogeneously resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
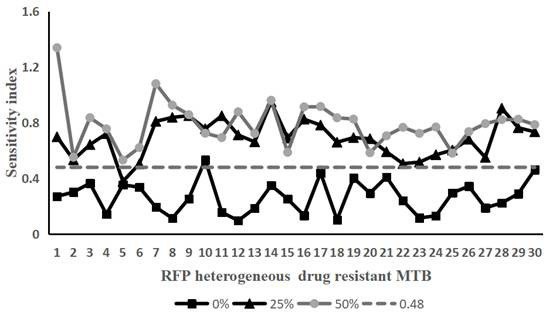
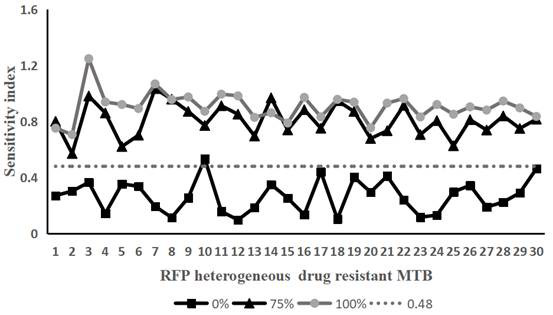
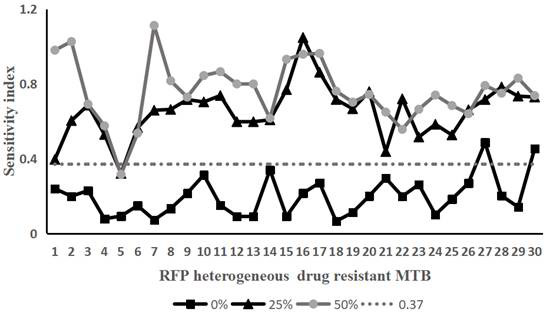
[0058] Take 30 strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that have been determined to be heterogeneously resistant to rifampicin and Mycobacterium tuberculosis that are sensitive to rifampicin. Containing rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis accounted for 0% (that is, containing 100% of sensitive bacteria), 25% (that is, containing 75% of sensitive bacteria), 50% (that is, containing 50% of sensitive bacteria), 75% % (that is, containing 25% of sensitive bacteria) and 100% (that is, containing 0% of sensitive bacteria) bacterial liquid samples.
[0059] According to the operation method of Example 1, the above-mentioned 150 samples of the prepared bacterial liquid were tested according to the method of Example 1. On the 10th and 14th day of treatment with the drug (rifampicin final concentration was 50 μg / mL), the Sampling, staining, te...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap