Tool and method for sleeving rigid thermal protection layer on non-closed equal-diameter revolving body cabin section
A heat protection layer and non-enclosed technology, applied in the direction of connecting components, material gluing, weight reduction, etc., can solve the problems of high profile requirements, difficulty, and low efficiency of the aircraft, so as to avoid interference and damage the cabin and ensure the profile , highly operable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
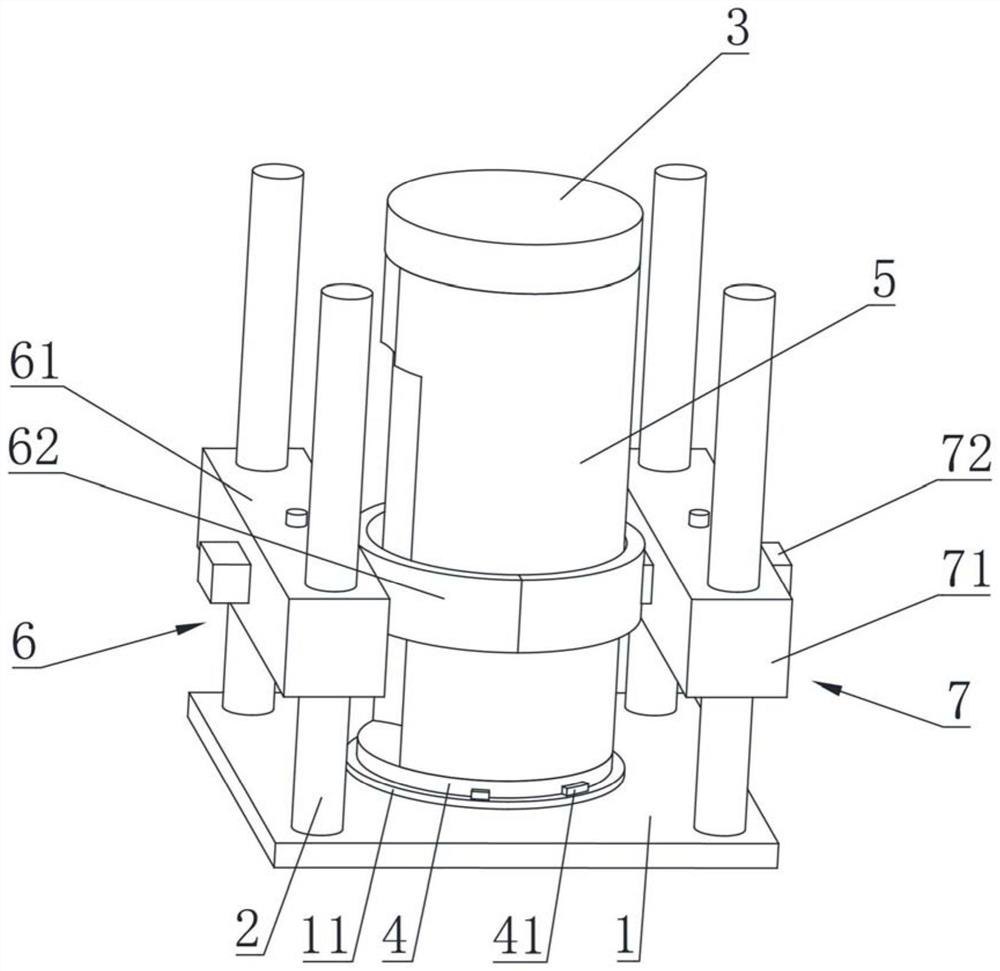
[0064] see figure 1 As shown, the rigid heat protection layer provided by the embodiment of the present invention is sleeved on the non-enclosed isometric rotary body cabin section, including a bottom plate 1, four columns 2, a front extension 3, a rear extension 4 and at least one sliding mold , wherein, one end of the column 2 is vertically connected to the bottom plate 1, the front extension 3 and the rear extension 4 are respectively installed at the front end and the rear end of the cabin section 5, and the axial distance between the front end and the rear end of the cabin section 5 is extended Size, so that the axial margin of the heat protection layer is also better installed and fixed, to ensure the quality of the heat protection layer at the front edge and the rear end edge. The front extension 3 and the rear extension 4 generally adopt a cylindrical structure with the same diameter as the cabin section.
[0065] The sliding mold includes a first side mold 6 and a se...
Embodiment 2
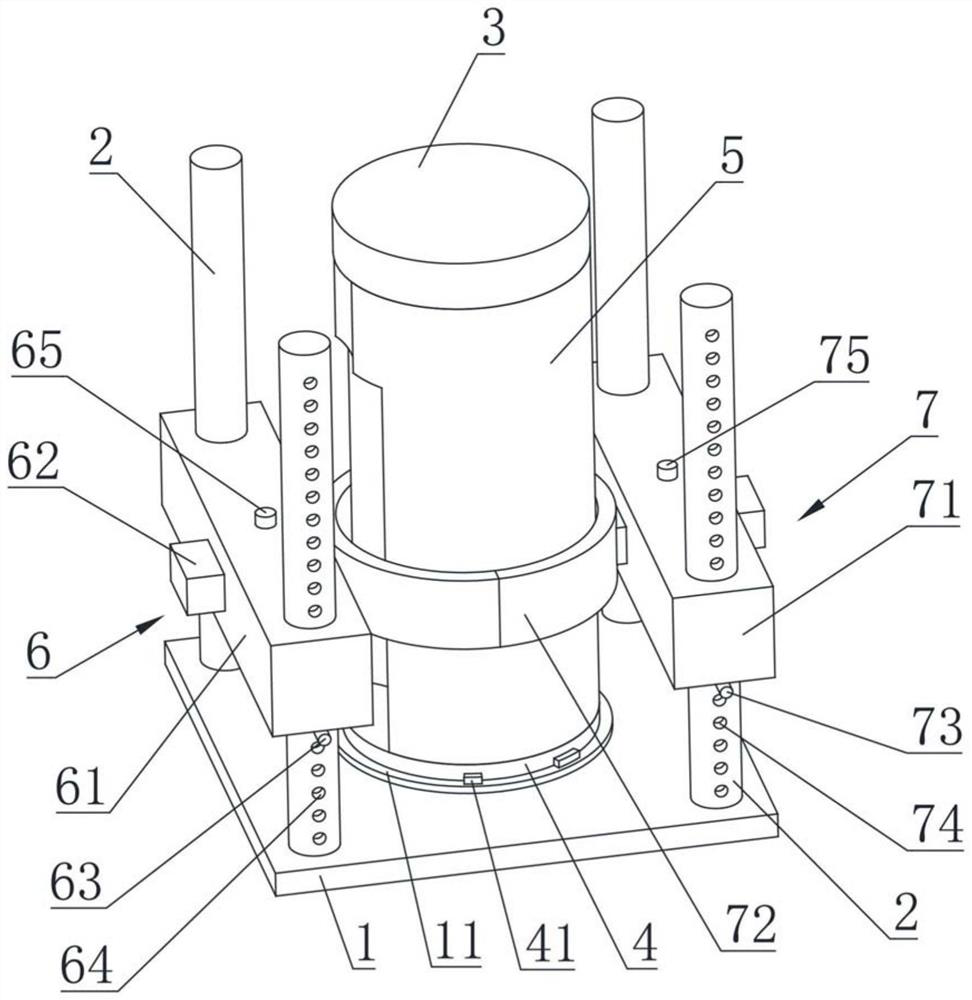
[0076] see figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the second embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the similarities will not be repeated. The difference is that at least one column 2 for installing the first axial sliding part 61 is provided with multiple The first adjustment hole 64, a plurality of the first adjustment holes 64 are arranged at intervals along the axial direction of the column 2, and the first adjustment pin 63 cooperates with the first adjustment hole 64 to fix the first side mold 6 in the The upper position of the column 2 in the axial direction.
[0077] At least one column 2 for installing the second axial sliding part 71 is provided with a plurality of second adjustment holes 74, and the plurality of second adjustment holes 74 are arranged at intervals along the axial direction of the column 2, The position of the second side mold 7 in the axial direction of the column 2 is fixed by the second adjustment pin 73 cooperating with the sec...
Embodiment 3
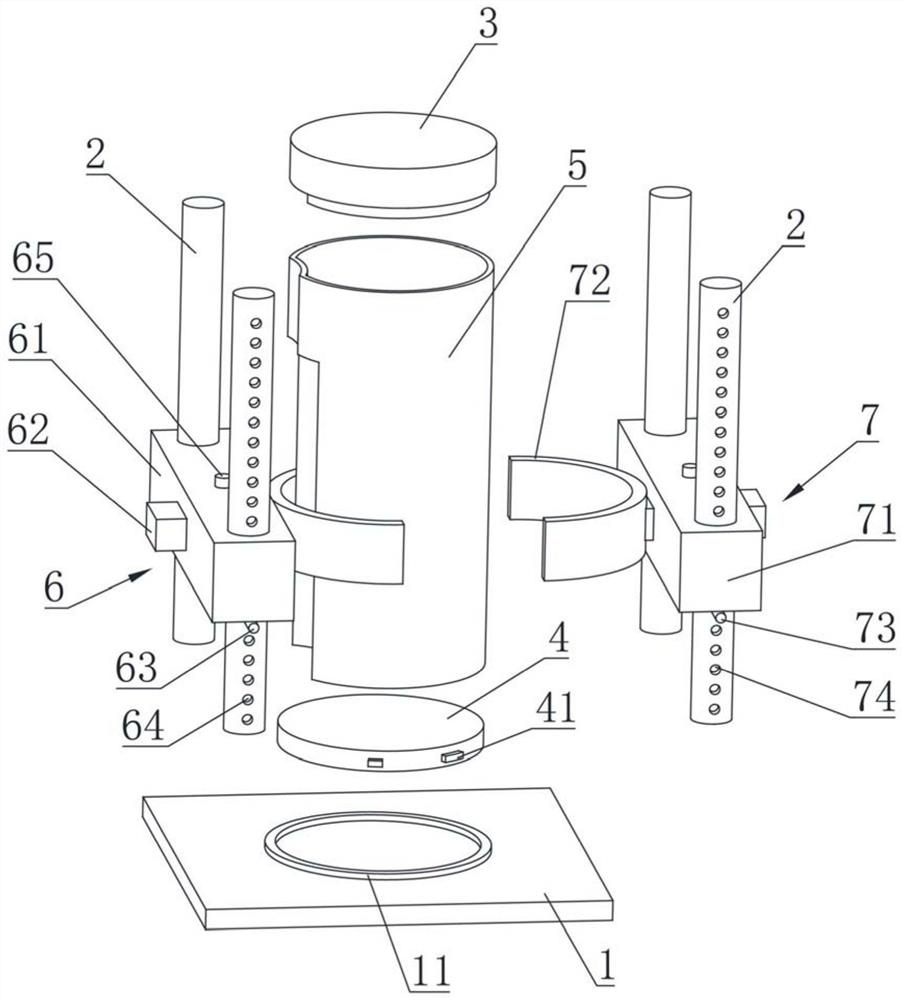
[0081] The third embodiment is an improvement on the basis of any one of the first or second embodiments, and the similarities will not be repeated. The axial direction of the column 2 is installed on the column 2. By adjusting the position of multiple sliding molds, the segmental positioning of the heat protection layer can be realized, which can avoid the interference position, avoid interference and damage the cabin, and maximize the Ensure the contour of the heat protection layer after socketing.
[0082] see Figure 4 As shown, a tooling structure is schematically shown, including two sliding molds. Of course, in some other embodiments, the number of sliding molds can also be adjusted as required, for example, three sliding molds, four sliding molds.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com