A method for constructing a linear model of heat exchange between rivers, lakes, and atmosphere during glacial periods
A linearization and atmospheric technique, applied in design optimization/simulation, instrumentation, calculation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
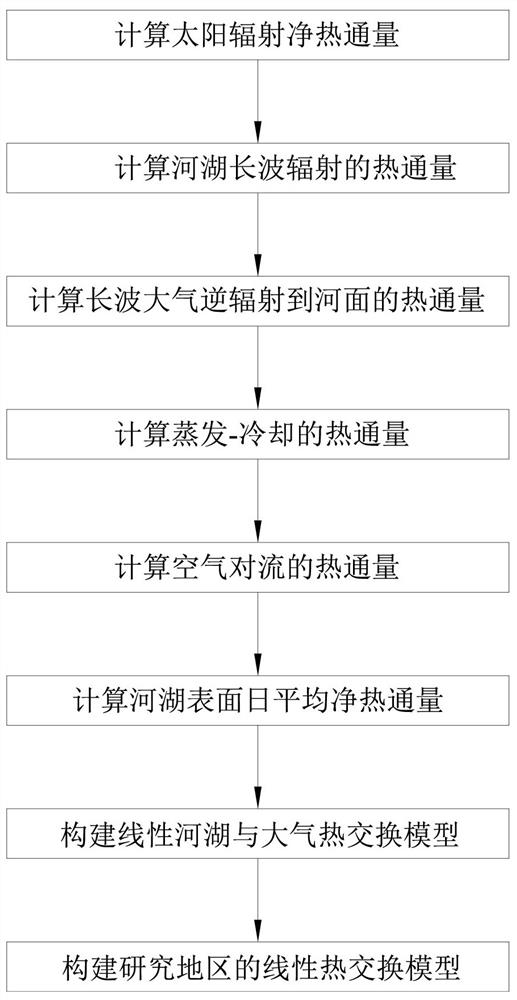
[0074] This embodiment is a method for constructing a linearized model of heat exchange between rivers, lakes and the atmosphere during glacial periods. The method described is based on the research results of solar energy utilization, climatology, hydrology, water resources and other disciplines. First, a nonlinear heat exchange model suitable for frozen rivers, lakes and the atmosphere is established, including solar radiation, long-wave radiation, evaporation-cooling and convection. . on the basis of:
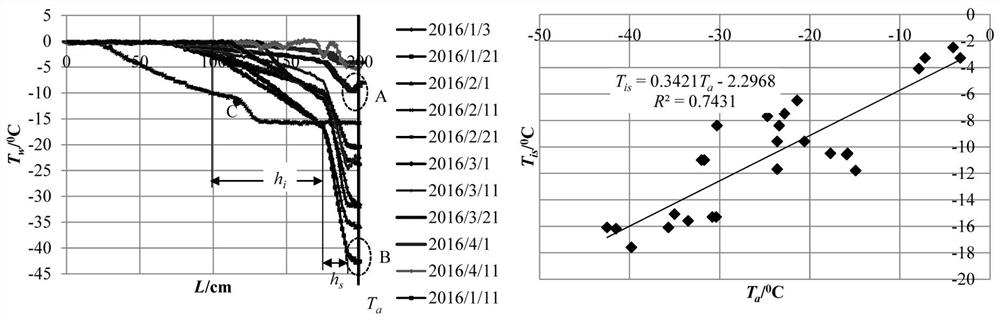
[0075] 1) Based on the prototype observation, it is found that the surface temperature T of frozen rivers and lakes s close to T a , including snow cover and exposed ice surface, at T s =T a A method for linearizing a nonlinear heat transfer model between rivers, lakes and the atmosphere.
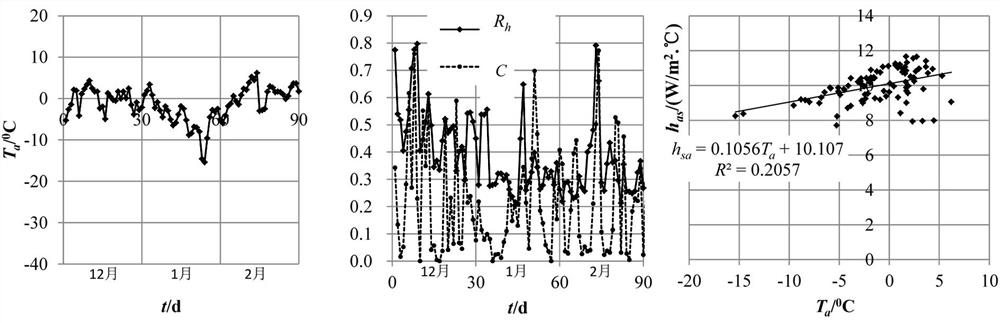
[0076] 2) A linear regression method is proposed to determine the heat exchange coefficient h based on the historical daily average weather data of the weather station sa and meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com