Patents
Literature
112 results about "Ice sheet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than 50,000 km² (19,000 sq mi). The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the last glacial period at Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America.
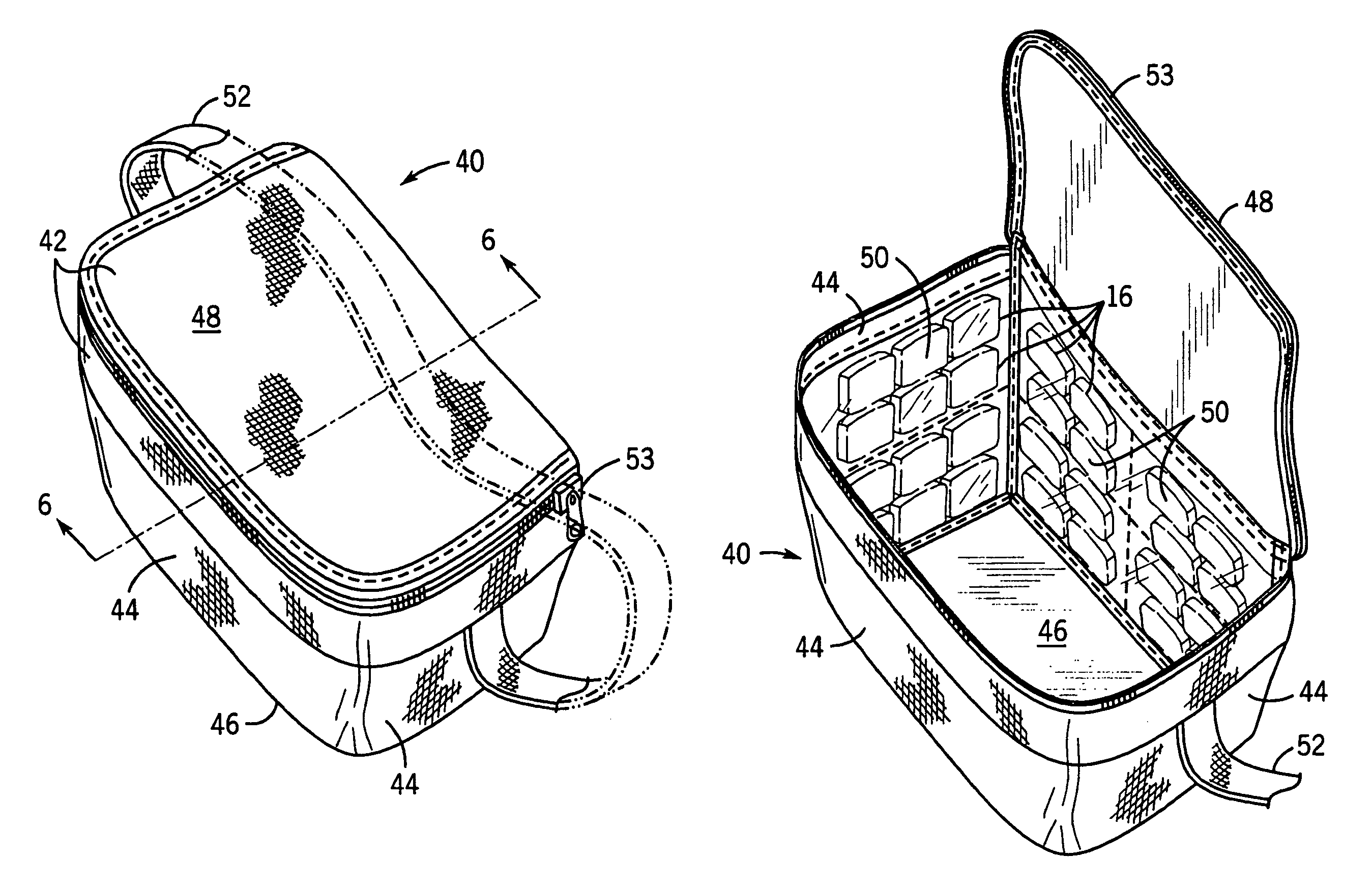
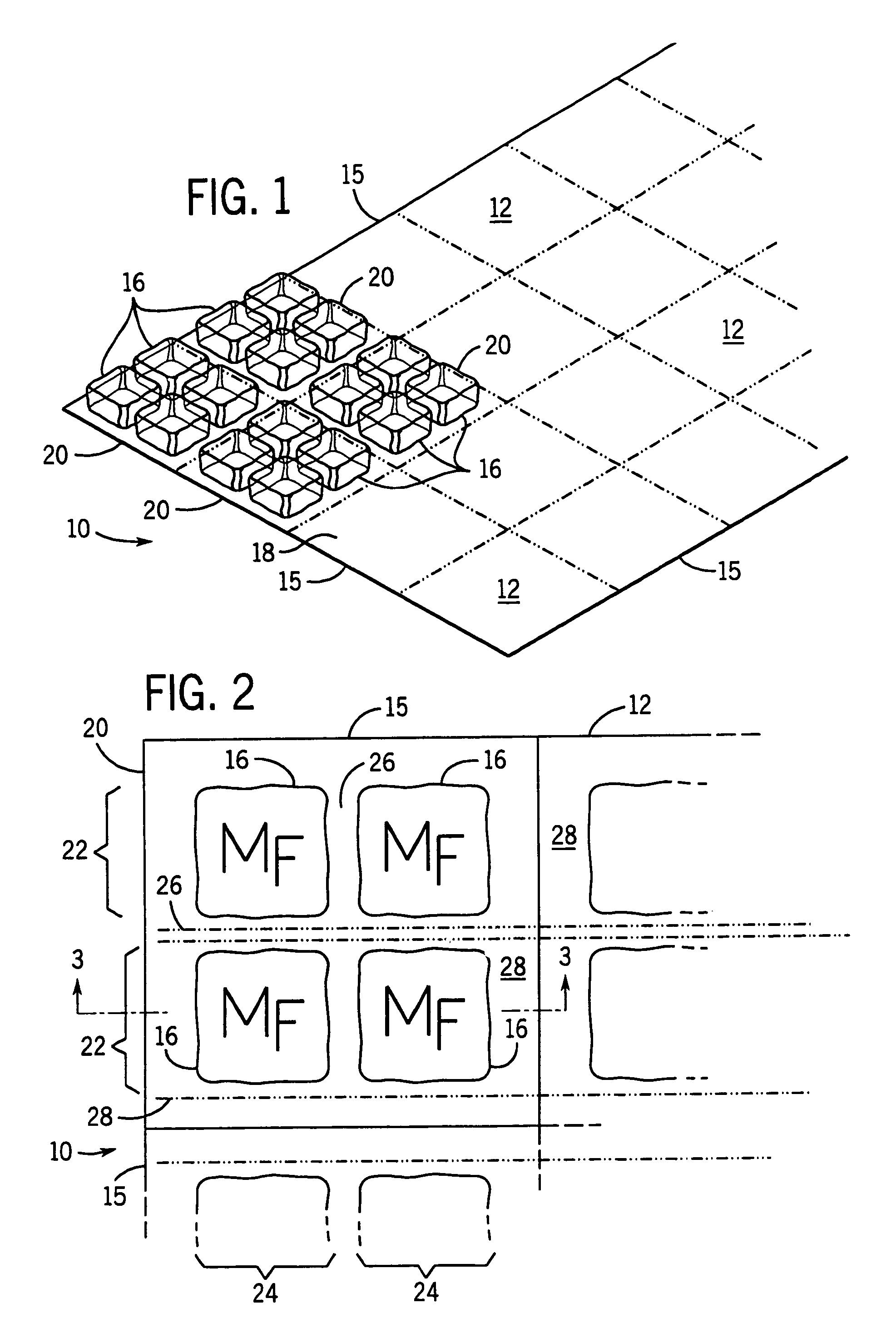
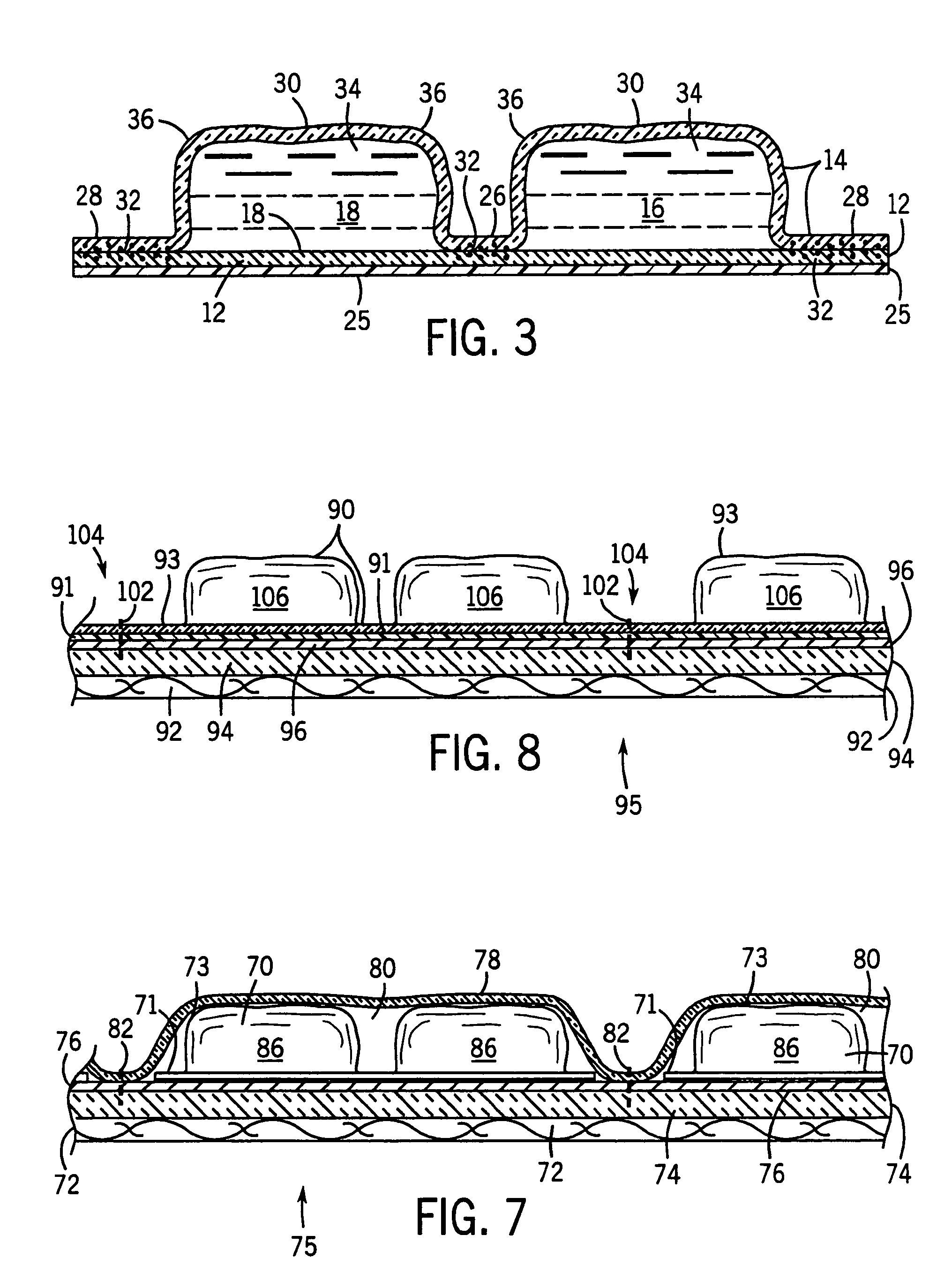
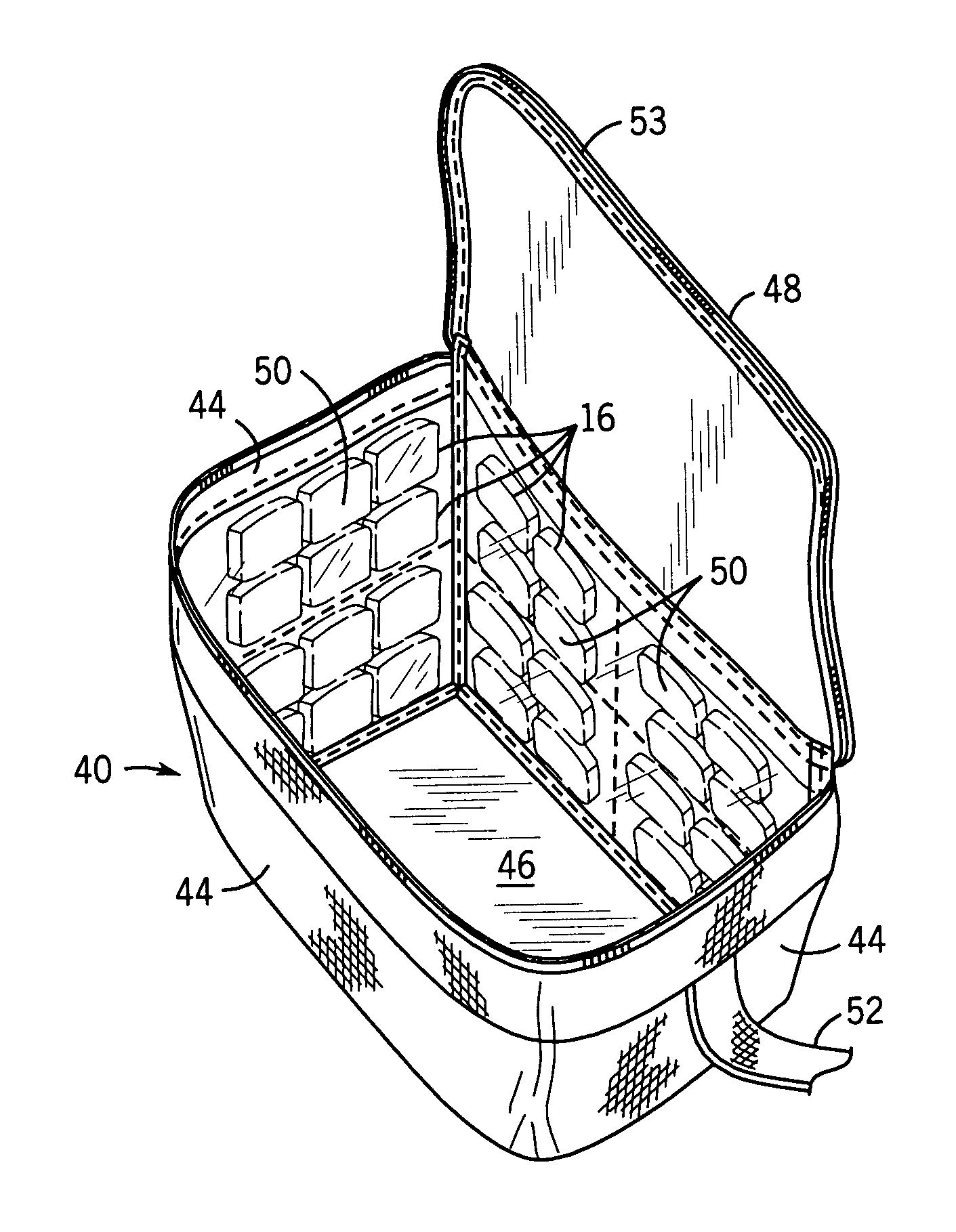
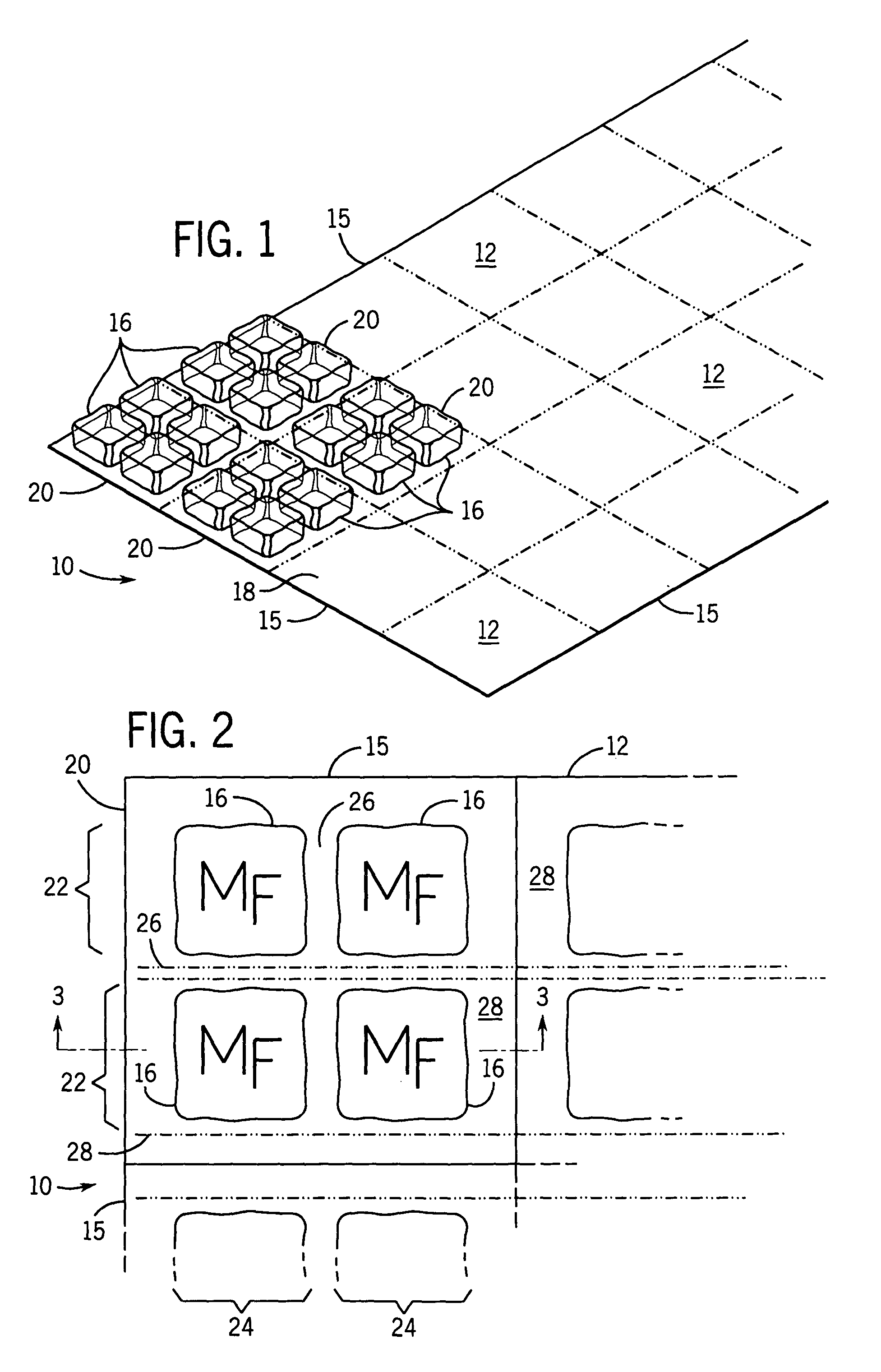
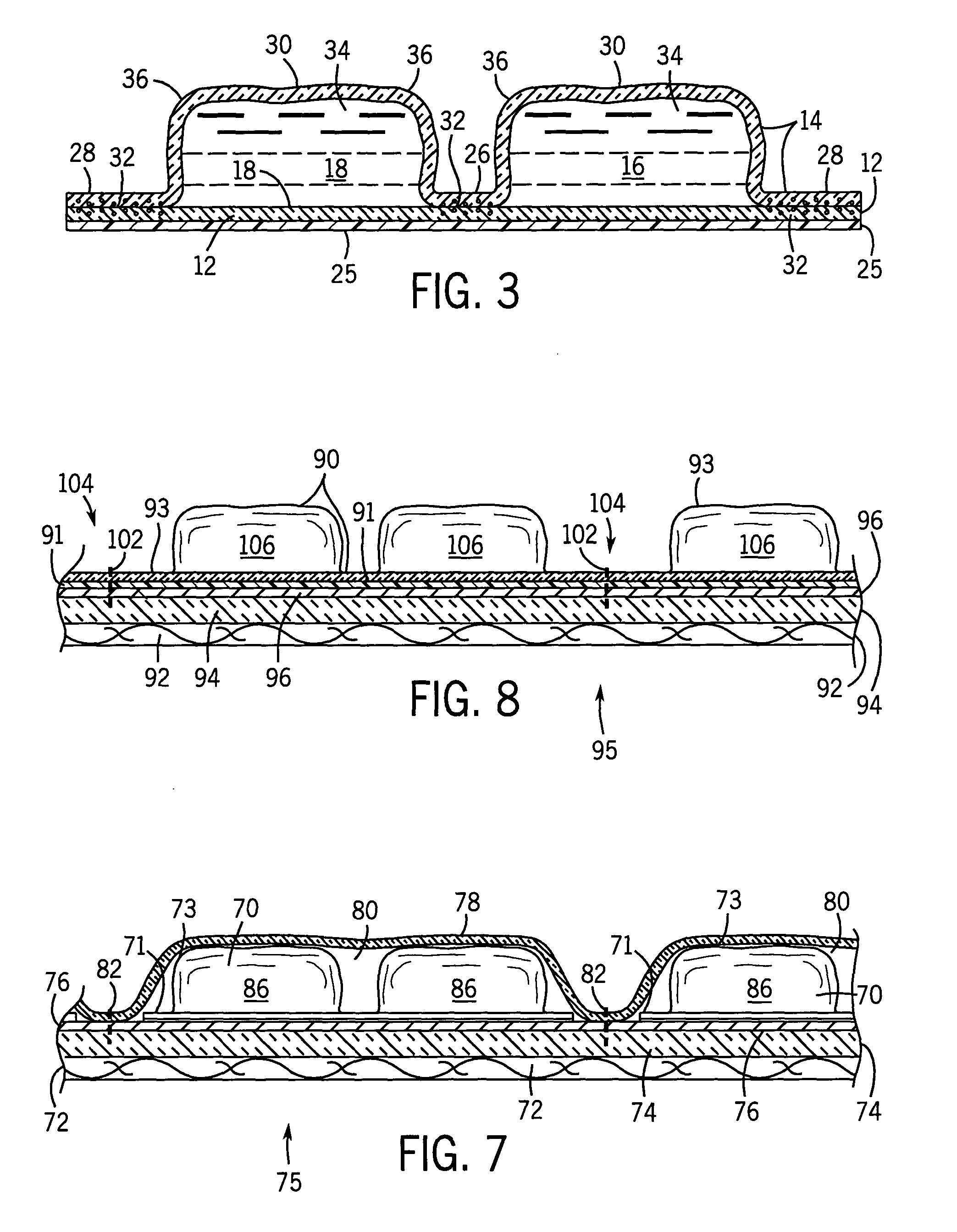
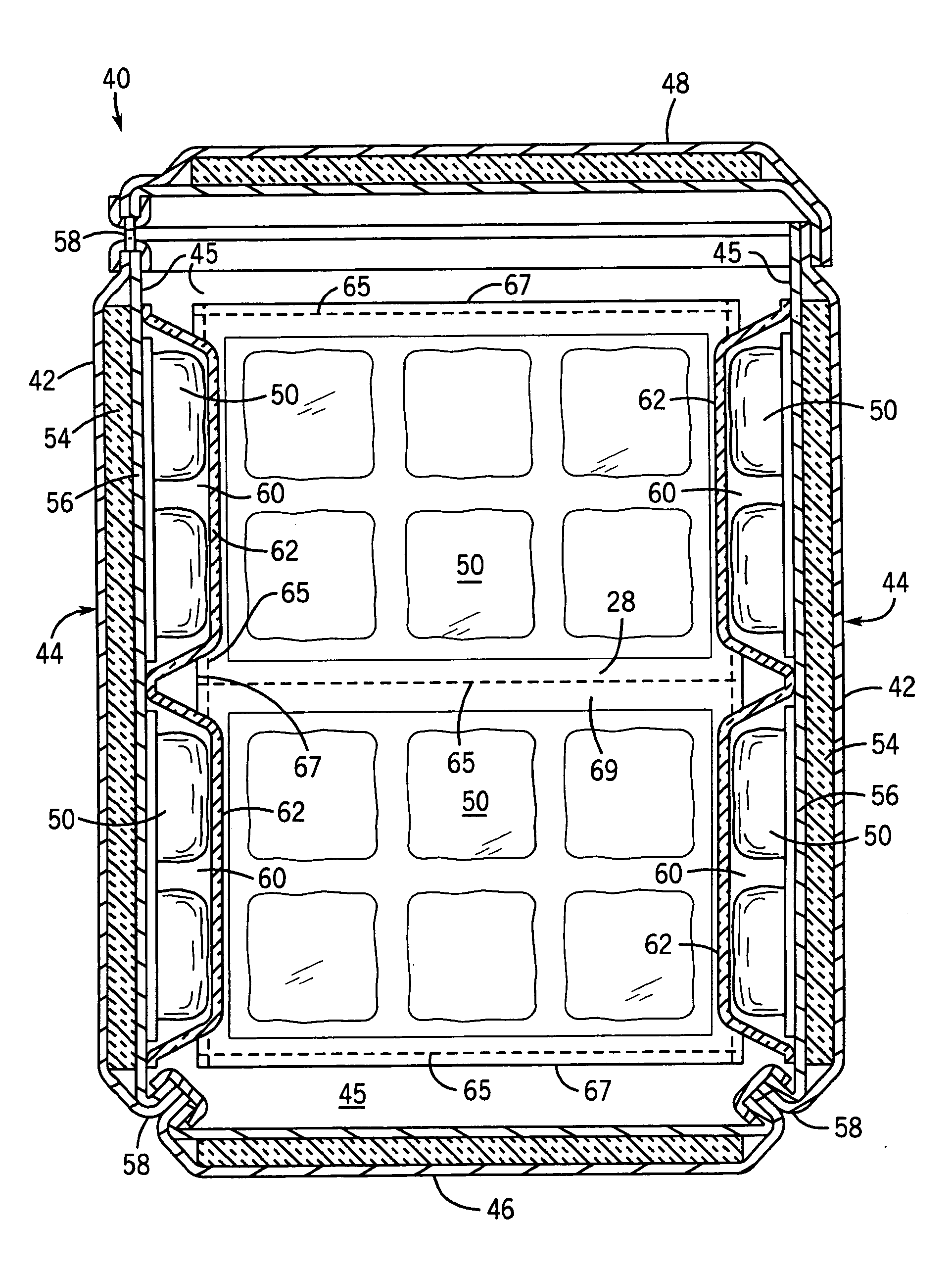
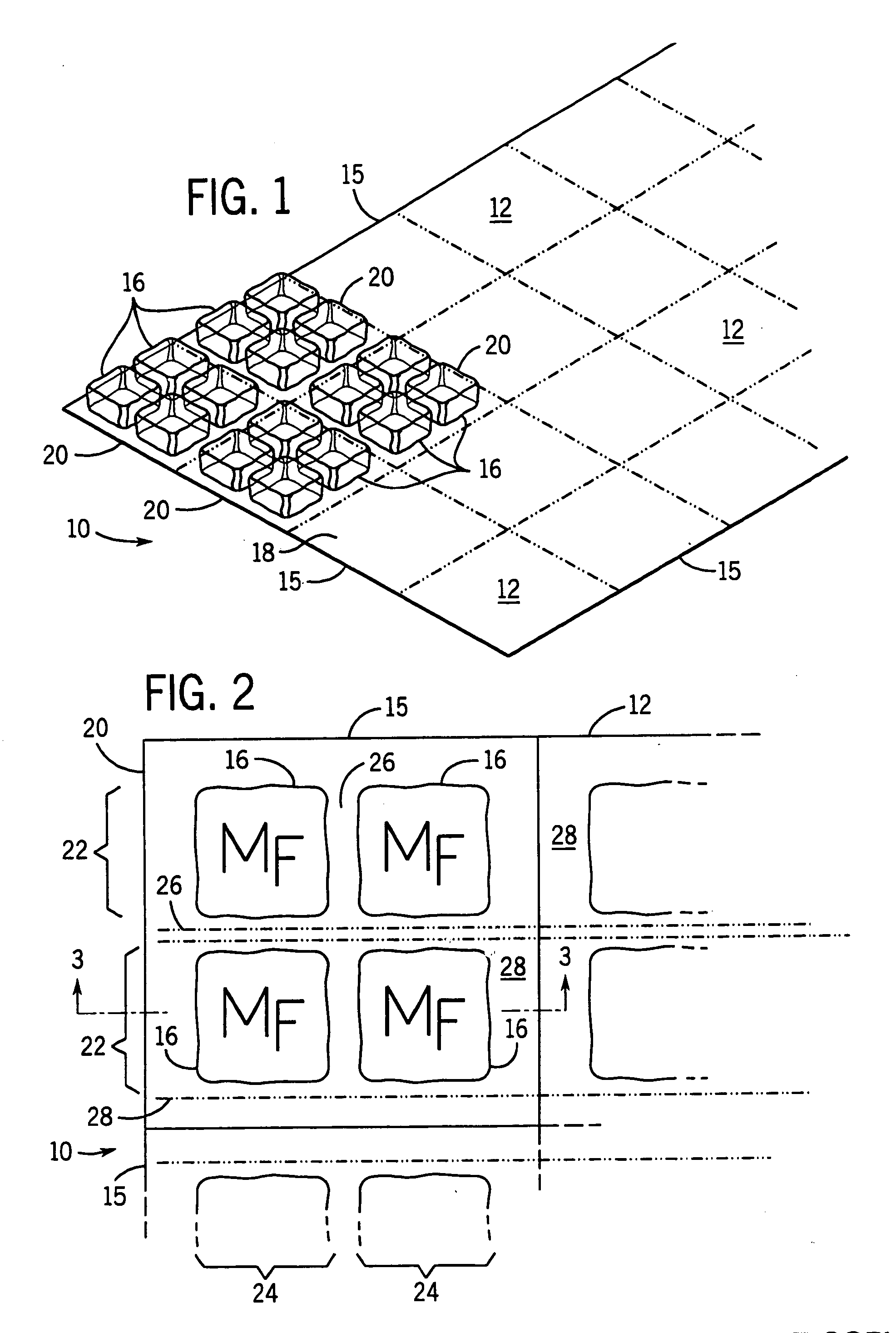
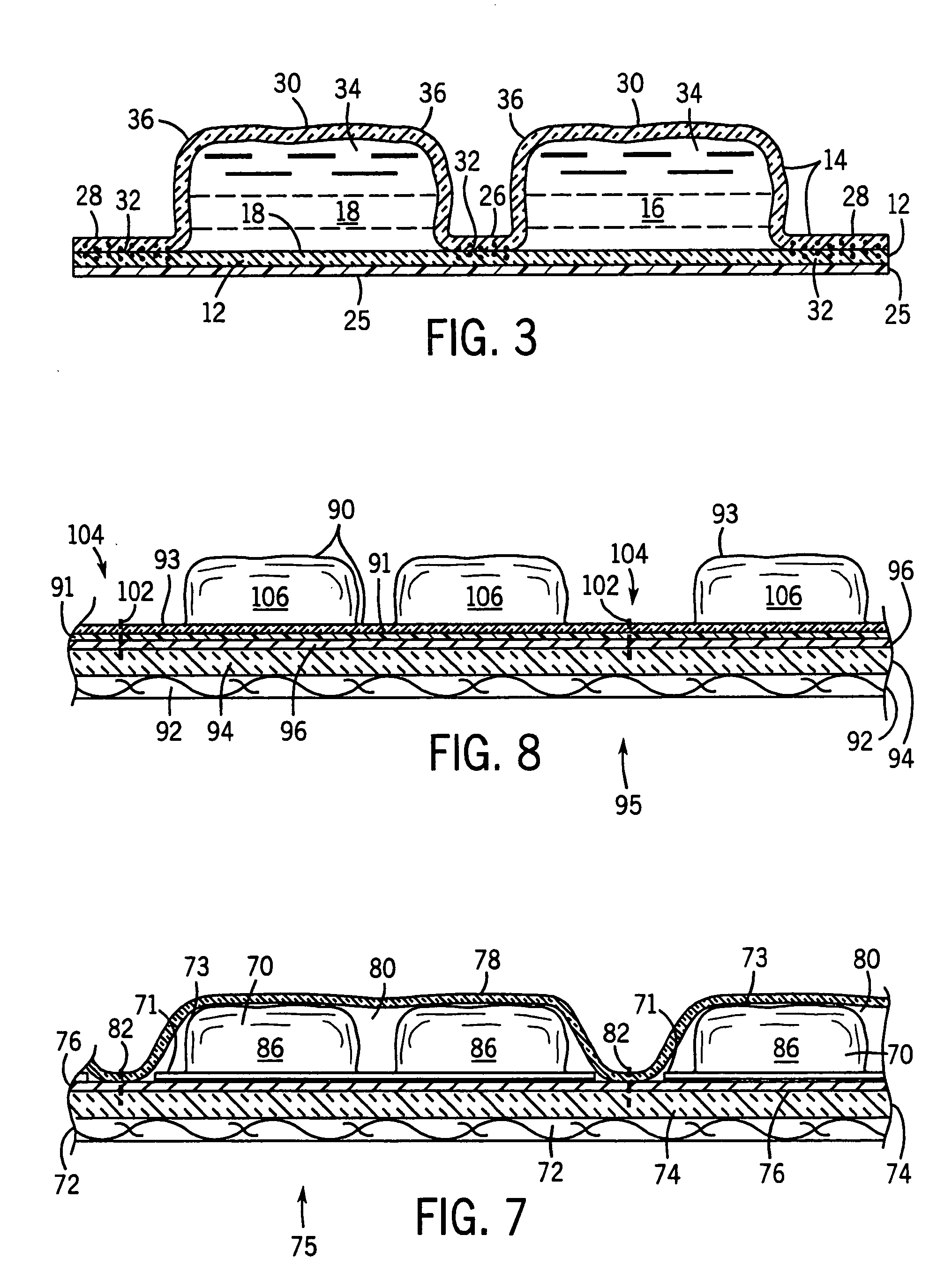
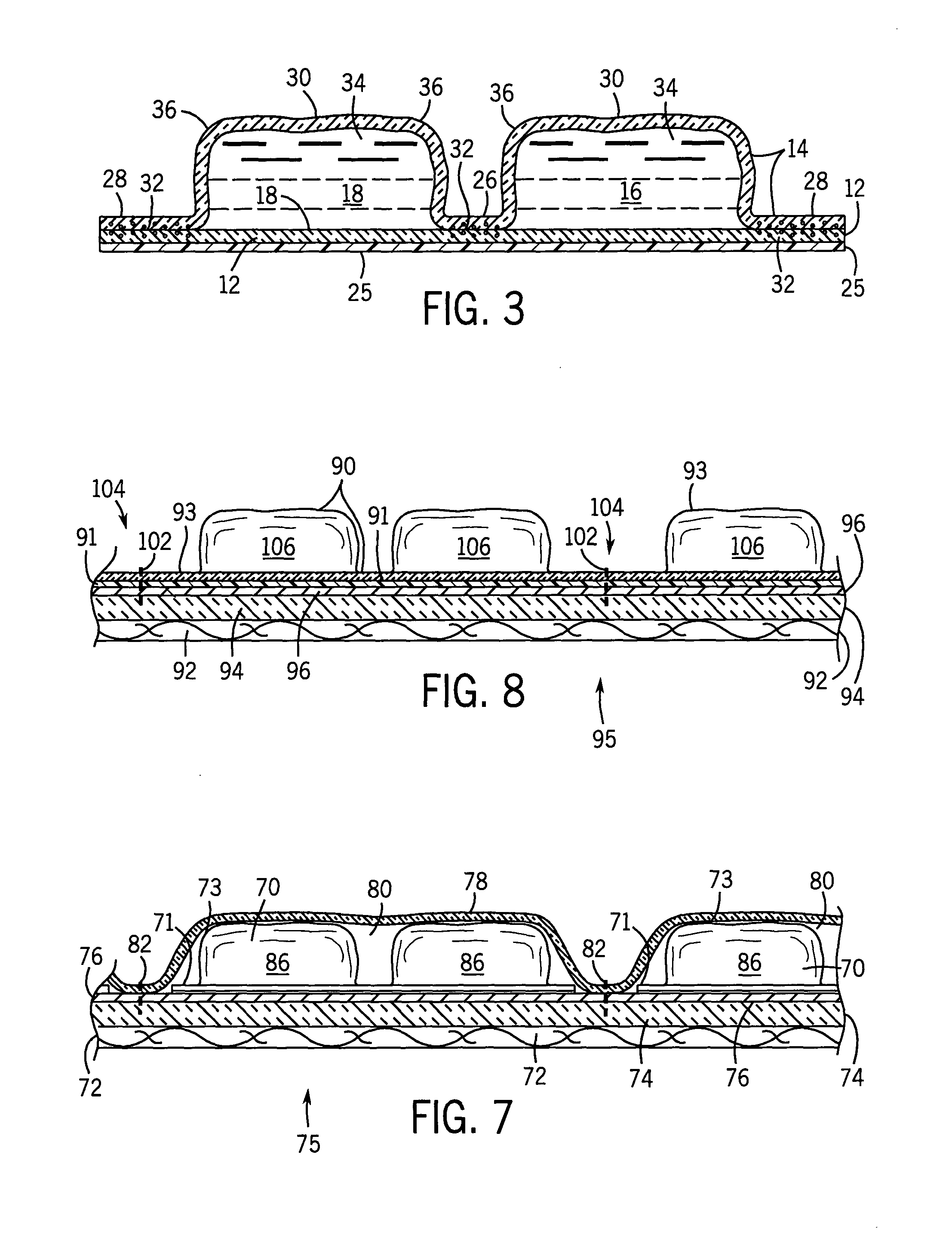
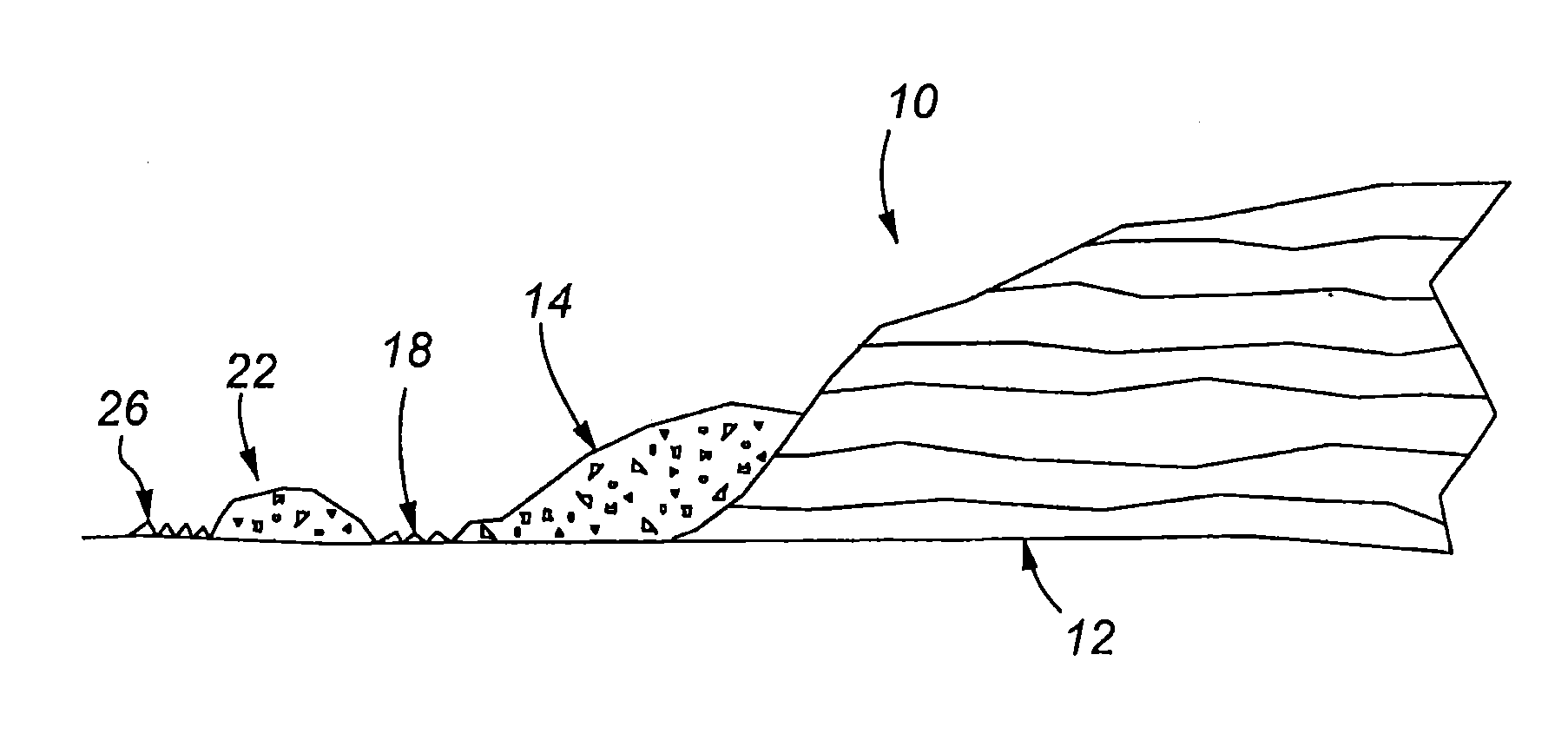
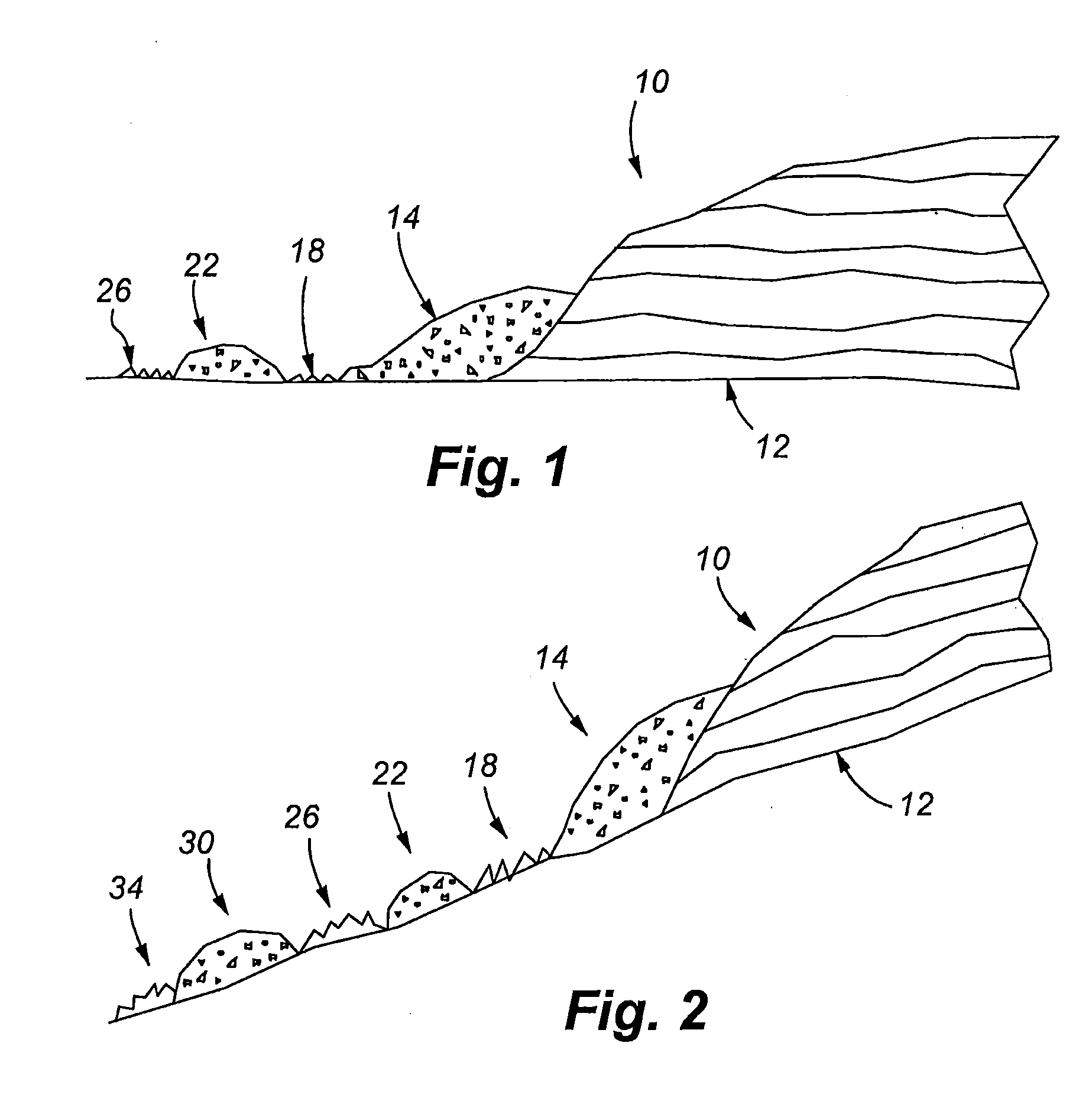
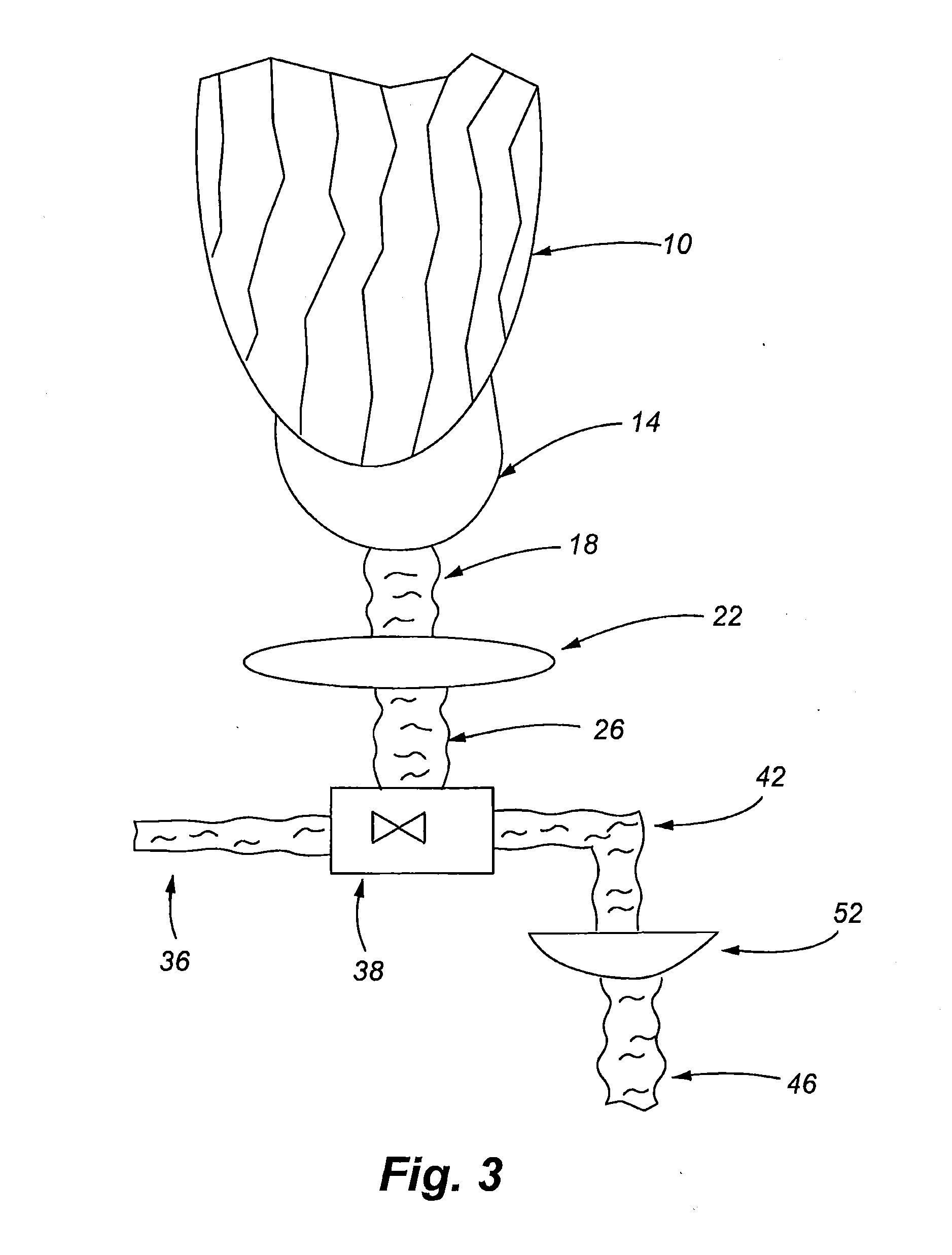
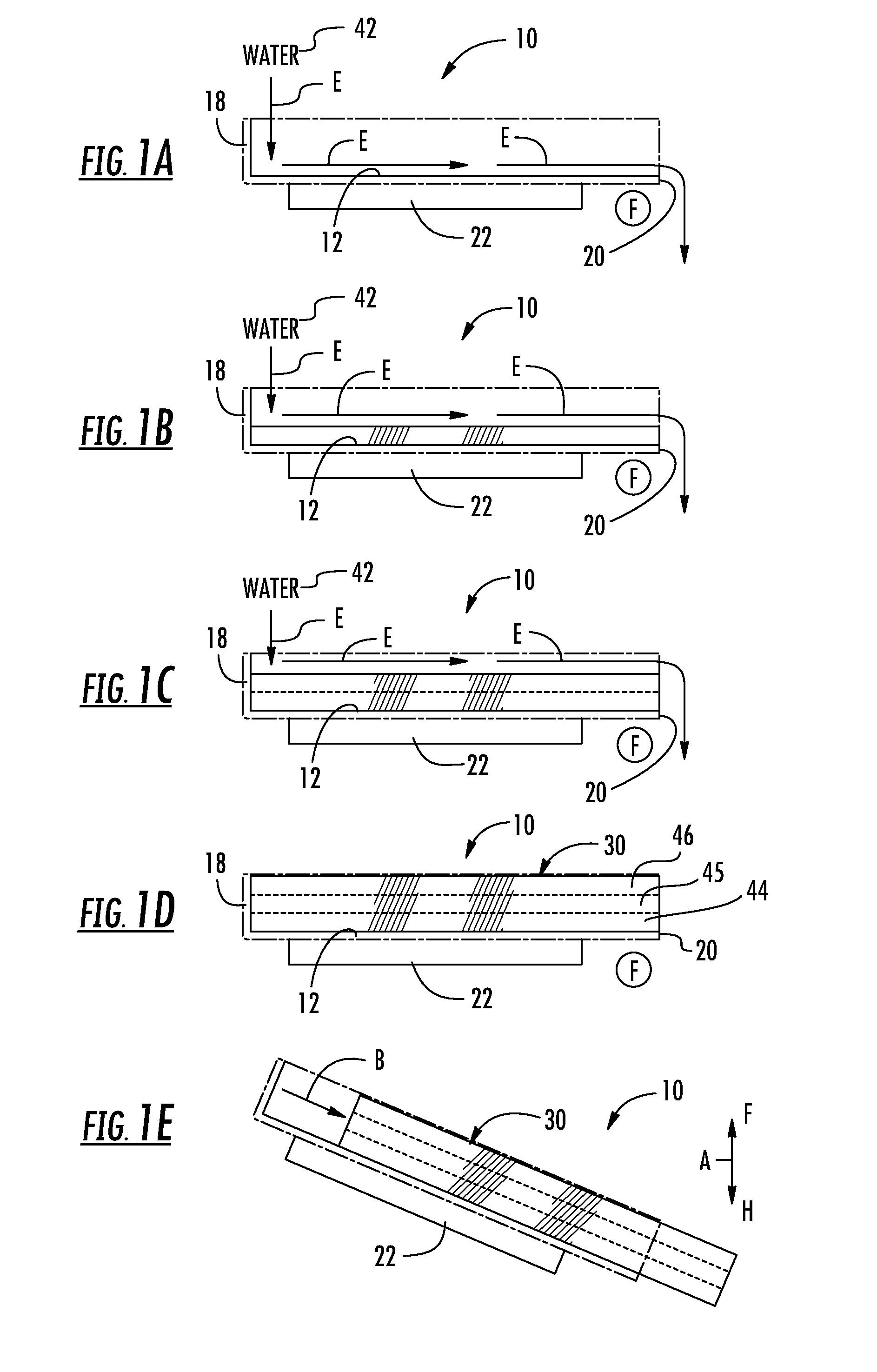
Portable cooler with built-in refrigerant cubes
ActiveUS7730739B2Effective mergerEasy to storeLighting and heating apparatusIce productionThermal insulationCooling effect
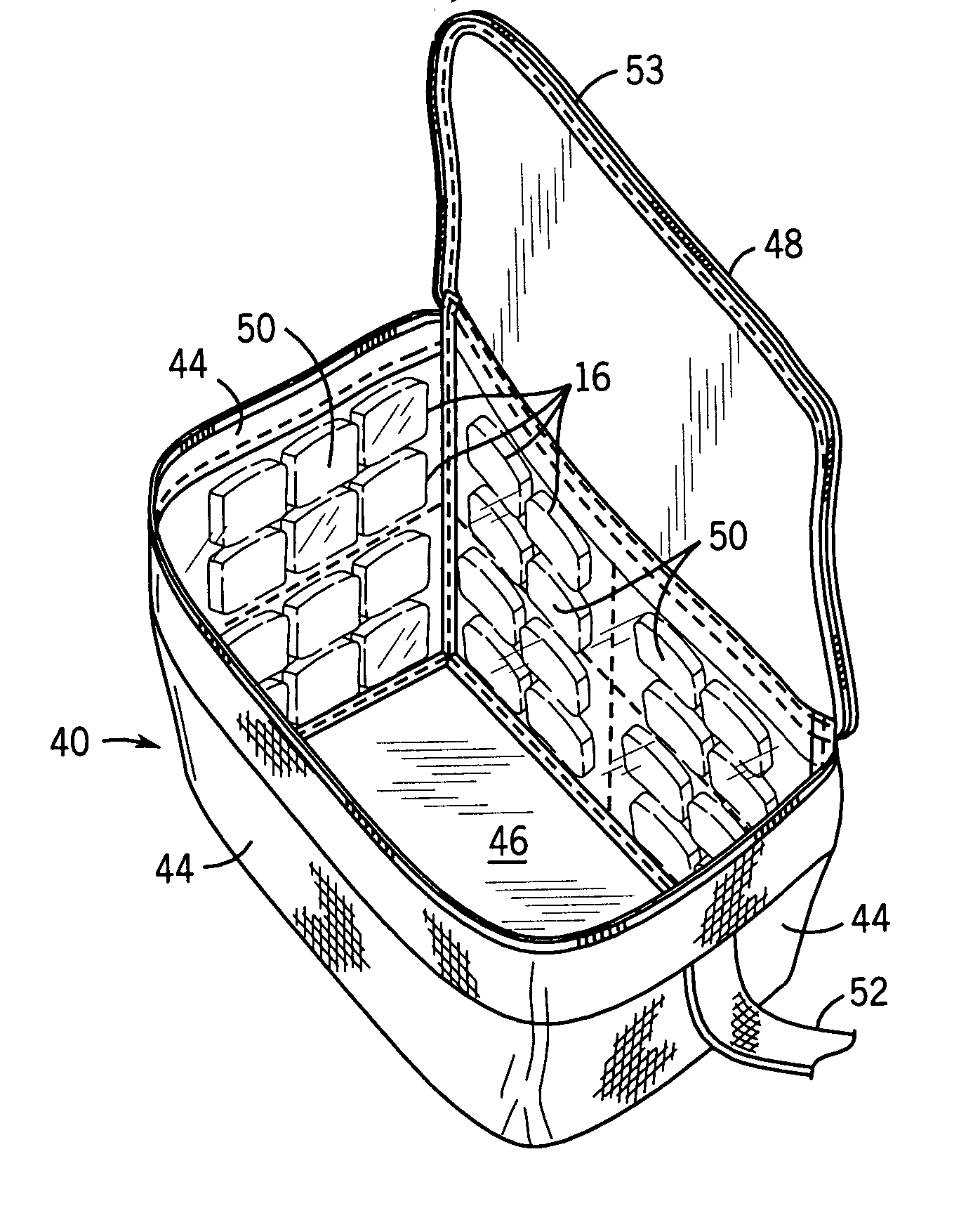
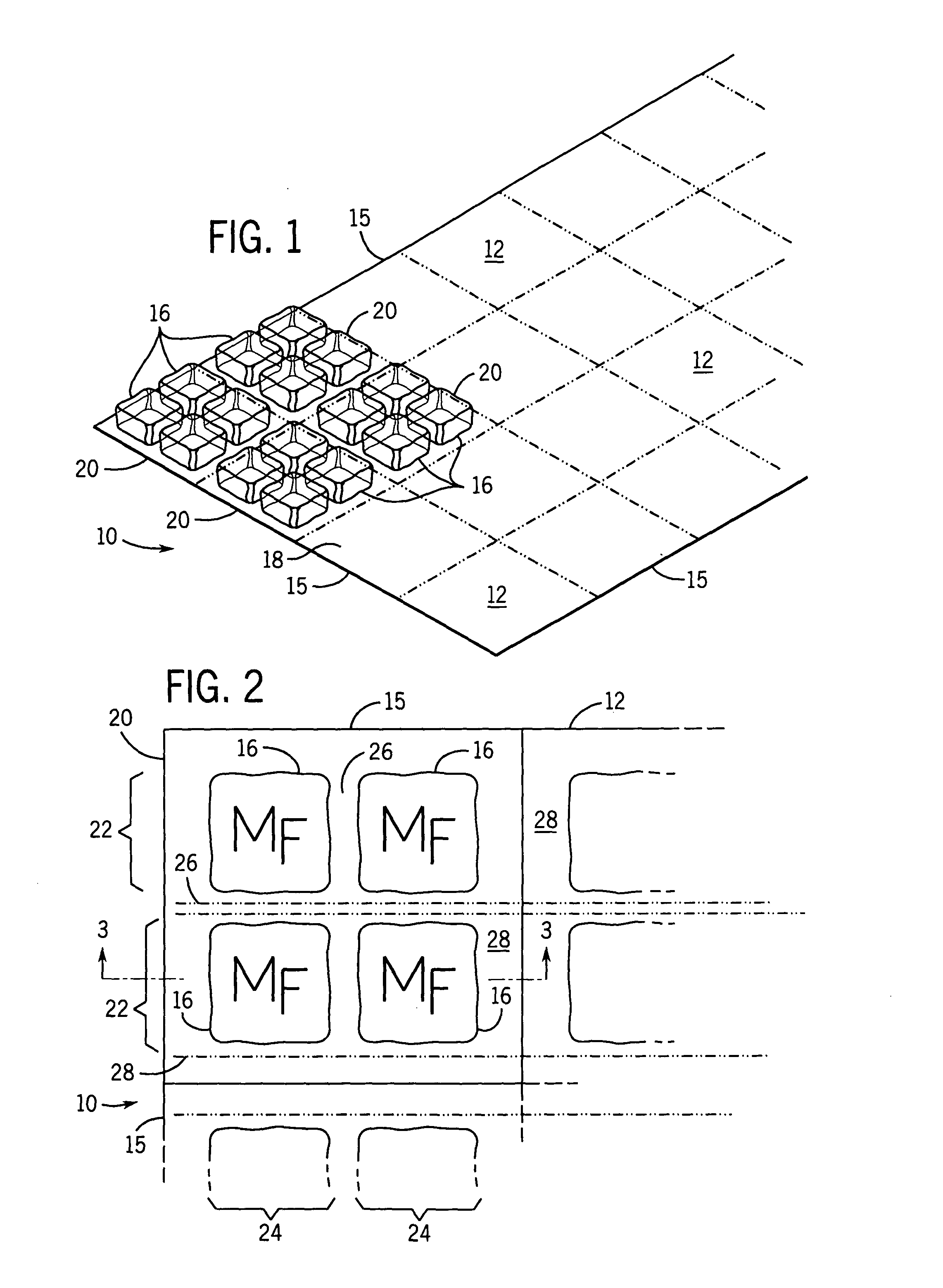
A portable cooler having one or more ice sheets including built-in refrigerant cubes. The cooler comprises an outer fabric shell and one or more sets of spaced apart refrigerant cubes encapsulated in plastic to form ice sheets that are attached to the interior walls of the cooler. The walls of the cooler may also include one or more layers of thermal insulation. The ice sheets provide a visually pleasing appearance to the inside of the cooler suggestive of cooling effects. The ice sheets may be retained along the walls of the cooler by seams sewn along the lanes passing between the refrigerant cubes, by being retained in pockets formed by sidewall liners or by being secured into chambers defined by the cooler's outer walls and a plastic insert fitted into the cooler. The cooler may include a hinged top and bottom that can be folded flat for allowing the cooler to assume a compact configuration during storage or freezing of the refrigerant cubes.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
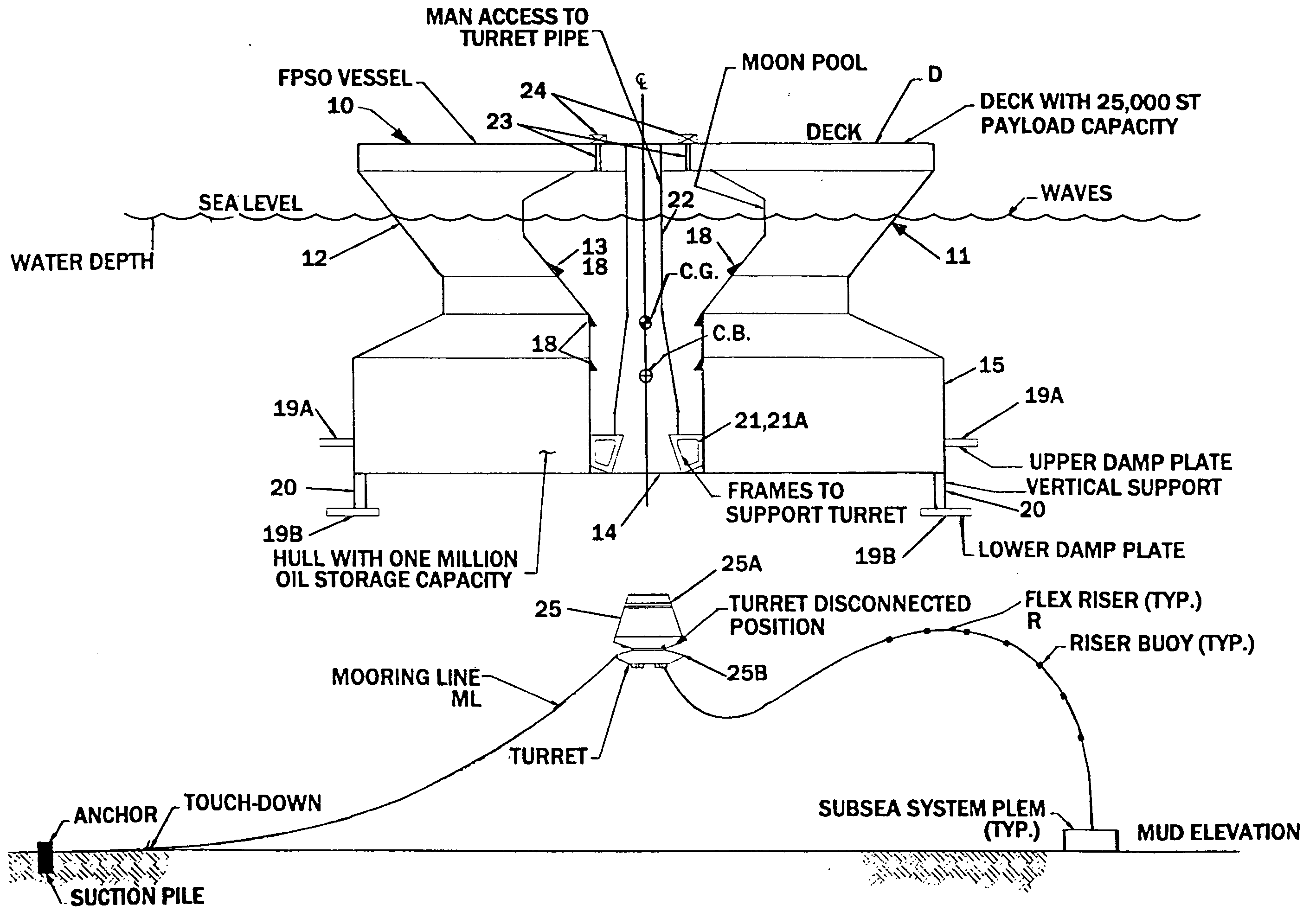
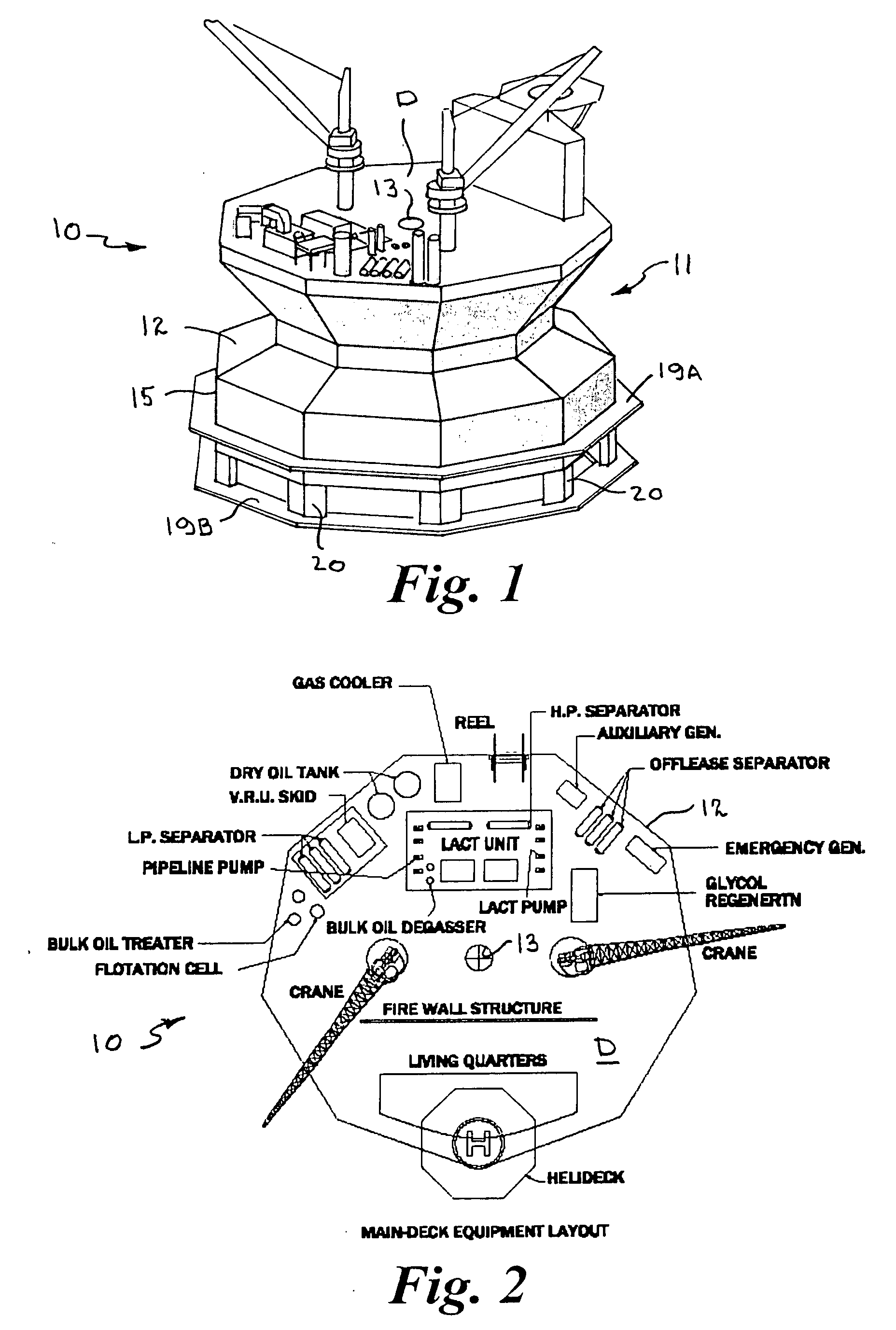
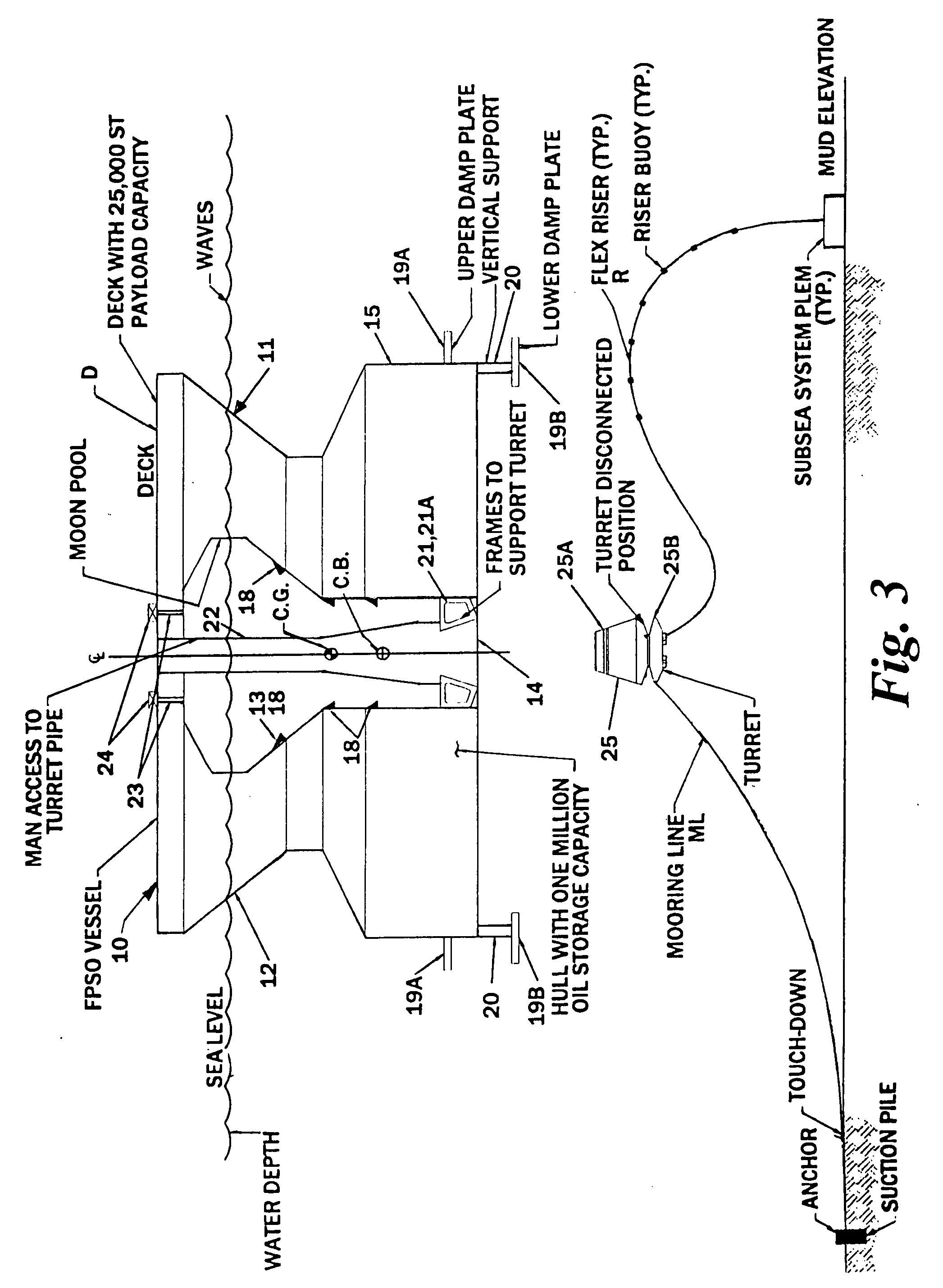
Offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel for use in ice-covered and clear water applications
InactiveUS20090126616A1Reduces dynamic amplificationReduce resonanceProtective foundationMovement controllersResonanceBuoy
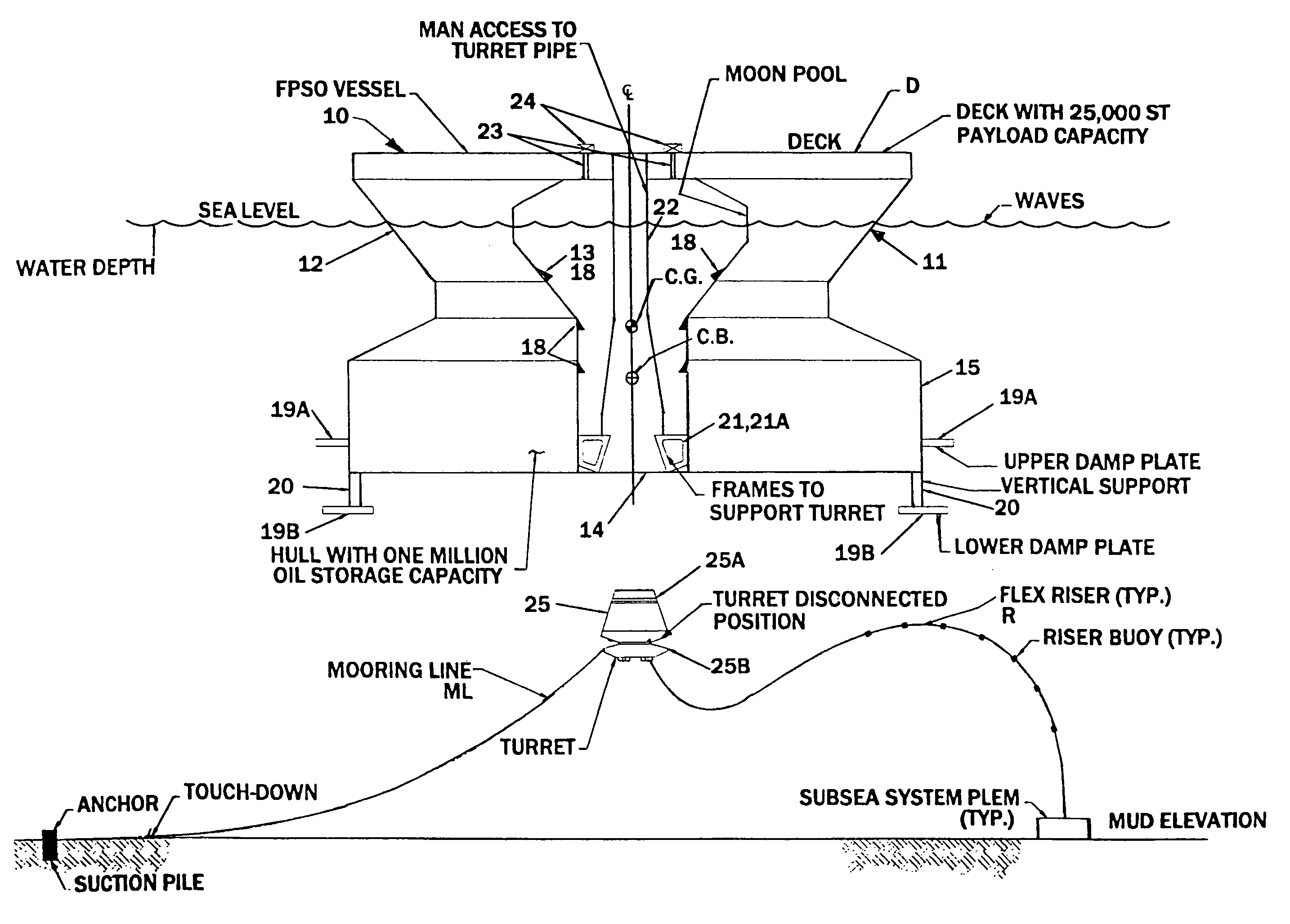
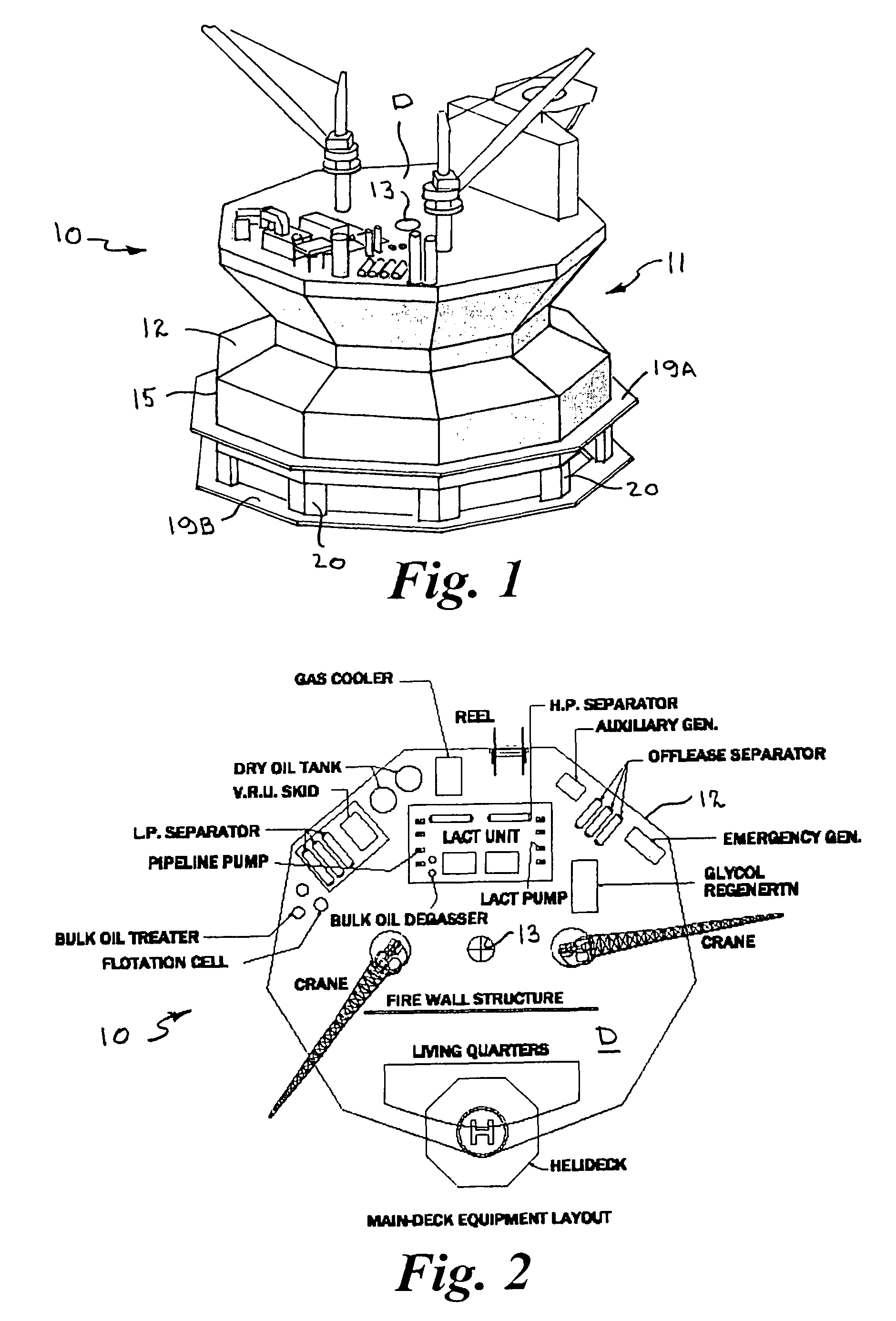
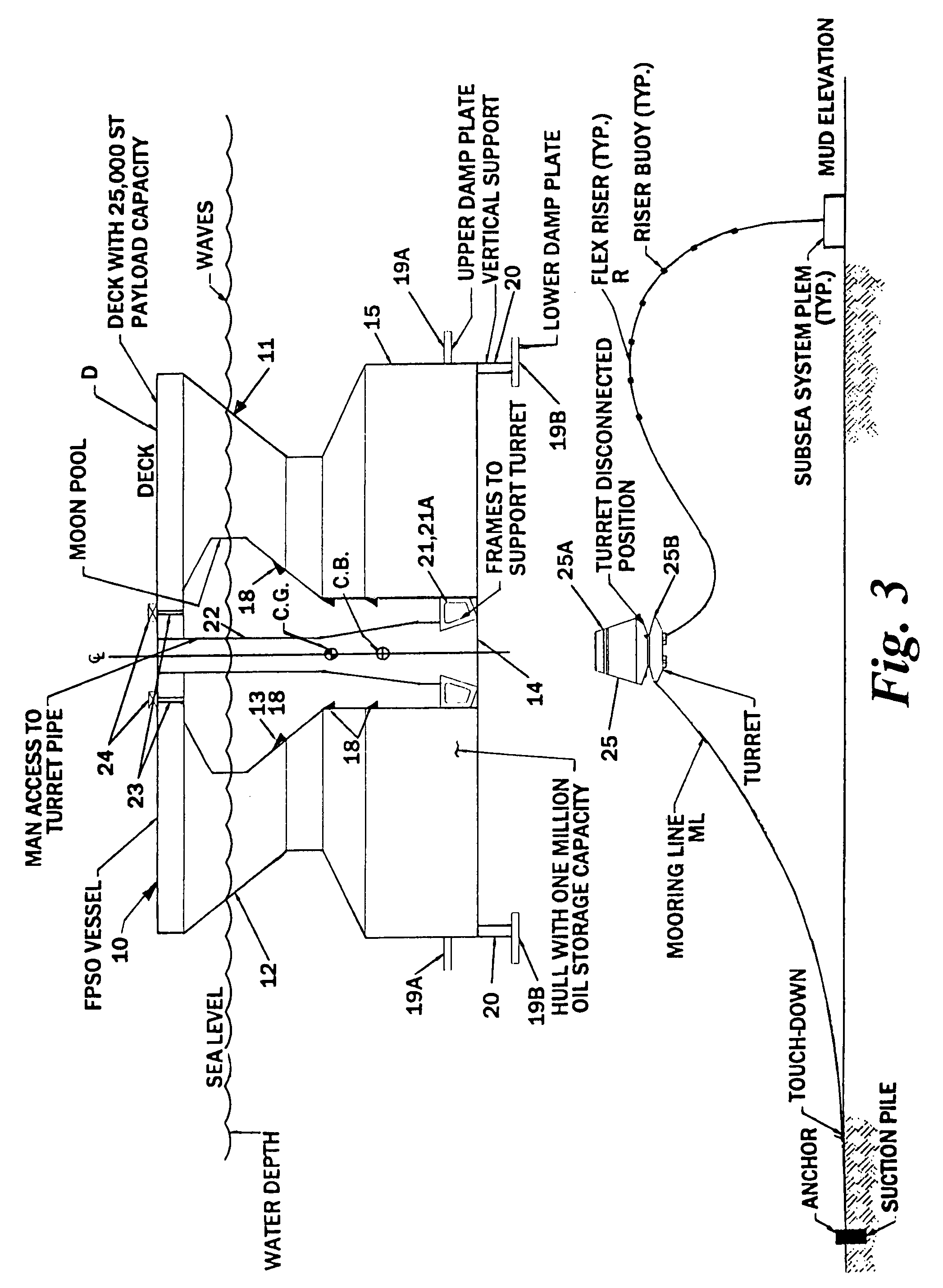
An offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel has a monolithic non ship-shaped hull of polygonal configuration surrounding a central double tapered conical moon pool and contains water ballast and oil storage compartments. The exterior side walls of the hull have flat surfaces and sharp corners to cut ice sheets, resist and break ice, and move ice pressure ridges away from the structure. An adjustable water ballast system induces heave, roll, pitch and surge motions of the vessel to dynamically position and maneuver the vessel to accomplish ice cutting, breaking and moving operations. The moon pool shape and other devices on the vessel provide added virtual mass capable of increasing the natural period of the roll and heave modes, reducing dynamic amplification and resonance due to waves and vessel motion, and facilitate maneuvering the vessel. The vessel may be moored by a disconnectable turret buoy received in a support frame at the bottom of the moon pool and to which flexible well risers and mooring lines are connected.
Owner:SRINIVASAN NAGAN
Portable cooler including ice sheet having refrigerant cubes
InactiveUS6925834B2Effective mergerLighting and heating apparatusIce productionThermal insulationEngineering
A portable cooler having one or more ice sheets including built-in refrigerant cubes. The cooler comprises an outer fabric shell and one or more sets of spaced apart refrigerant cubes encapsulated in plastic to form ice sheets that are attached to the interior walls of the cooler. The walls of the cooler may also include one or more layers of thermal insulation. The ice sheets provide a visually pleasing appearance to the inside of the cooler suggestive of cooling effects. The ice sheets may be retained along the walls of the cooler by seams sewn along the lanes passing between the refrigerant cubes, by being retained in pockets formed by sidewall liners or be being secured into chambers defined by the cooler's outer walls and a plastic insert fitted into the cooler.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
Portable cooler with built-in refrigerant cubes
ActiveUS20050183446A1Easy to storeSpace minimizationLighting and heating apparatusIce productionThermal insulationCooling effect
A portable cooler having one or more ice sheets including built-in refrigerant cubes. The cooler comprises an outer fabric shell and one or more sets of spaced apart refrigerant cubes encapsulated in plastic to form ice sheets that are attached to the interior walls of the cooler. The walls of the cooler may also include one or more layers of thermal insulation. The ice sheets provide a visually pleasing appearance to the inside of the cooler suggestive of cooling effects. The ice sheets may be retained along the walls of the cooler by seams sewn along the lanes passing between the refrigerant cubes, by being retained in pockets formed by sidewall liners or by being secured into chambers defined by the cooler's outer walls and a plastic insert fitted into the cooler. The cooler may include a hinged top and bottom that can be folded flat for allowing the cooler to assume a compact configuration during storage or freezing of the refrigerant cubes.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
Offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel for use in ice-covered and clear water applications
InactiveUS7958835B2High strengthProtective foundationMovement controllersClassical mechanicsPressure ridge
An offshore floating production, storage, and off-loading vessel has a hull of generally cylindrical or polygonal configuration surrounding a central double tapered conical moon pool and contains water ballast and oil and / or liquefied gas storage compartments. The exterior side walls of the polygonal hull have flat surfaces and sharp corners to cut ice sheets, resist and break ice, and move ice pressure ridges away from the structure. An adjustable water ballast system induces heave, roll, pitch and surge motions of the vessel to dynamically position and maneuver the vessel to accomplish ice cutting, breaking and moving operations. The moon pool shape and other devices on the vessel provide added virtual mass for increasing the natural period of the roll and heave modes, reducing dynamic amplification and resonance due to waves and vessel motion, and facilitate maneuvering the vessel. A disconnectable turret buoy at the bottom of the moon pool connects risers and mooring lines.
Owner:SRINIVASAN NAGAN
Fluid property regulator
InactiveUS20080277492A1Low average atmospheric temperatureReduce greenhouse gasFog dispersionMachines/enginesAtmospheric airVolumetric Mass Density
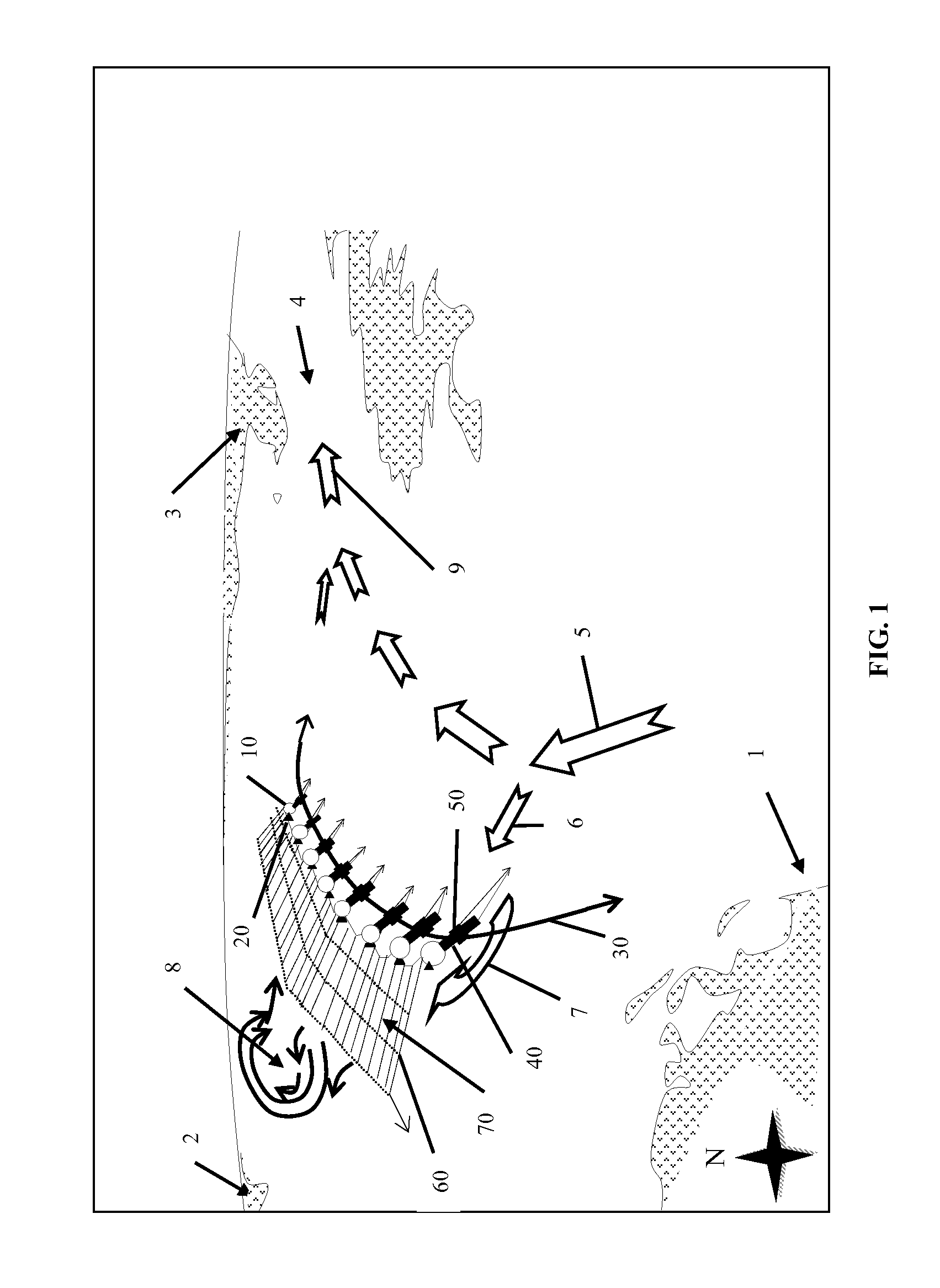
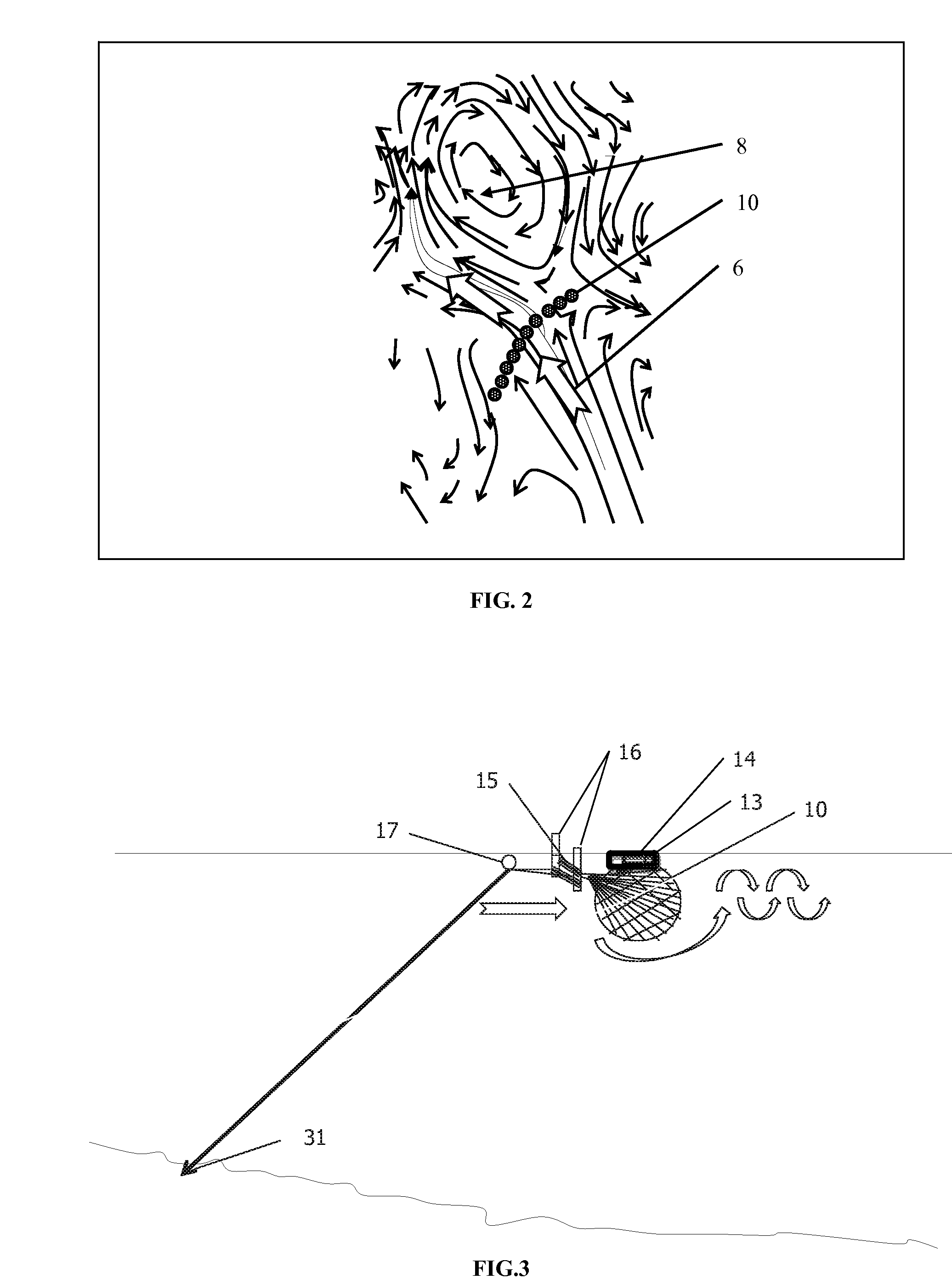
A self-sufficient material property profile regulation method and system, for adjusting fluid property profiles such as in an ocean of multiple property layers, is described. Using this Fluid Property Regulator, the property profiles of a non-enclosed material, including property profiles related to material density, chemical characteristics and space-time position, are affected due to motion of the material relative to a body in the flow stream. The state of other matter with which the initial material then makes direct or indirect contact is also affected. For example, in the case of a liquid such as an ocean current, the temperature, salinity, nutrient content and other properties may be destratified (i.e. layers being combined) as the system lifts large quantities of deep water and combines this material with surface water in the downstream far-field region of the system. The resulting regulation of such ocean water property profiles may then also indirectly affect the properties of the atmosphere above the ocean so that the system can be said to affect planetary properties both oceanic and atmospheric. Rather than merely discharging a pumped material, such as cold water that might quickly re-submerge, the system regulates lasting property profiles. The new Fluid Property Regulator system described in this invention regulates material properties to produce desired outcomes such as increased food and energy production as well as to prevent undesirable outcomes such as hurricanes, elevated planetary temperatures, decreased planetary ice sheet size, raised sea level and glacial freshwater incursions that can halt important major currents.
Owner:CANNON DAVID J
Portable cooler including ice sheet having refrigerant cubes
InactiveUS20050056048A1Effective mergerLighting and heating apparatusIce productionThermal insulationCooling effect
A portable cooler having one or more ice sheets including built-in refrigerant cubes. The cooler comprises an outer fabric shell and one or more sets of spaced apart refrigerant cubes encapsulated in plastic to form ice sheets that are attached to the interior walls of the cooler. The walls of the cooler may also include one or more layers of thermal insulation. The ice sheets provide a visually pleasing appearance to the inside of the cooler suggestive of cooling effects. The ice sheets may be retained along the walls of the cooler by seams sewn along the lanes passing between the refrigerant cubes, by being retained in pockets formed by sidewall liners or be being secured into chambers defined by the cooler's outer walls and a plastic insert fitted into the cooler.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
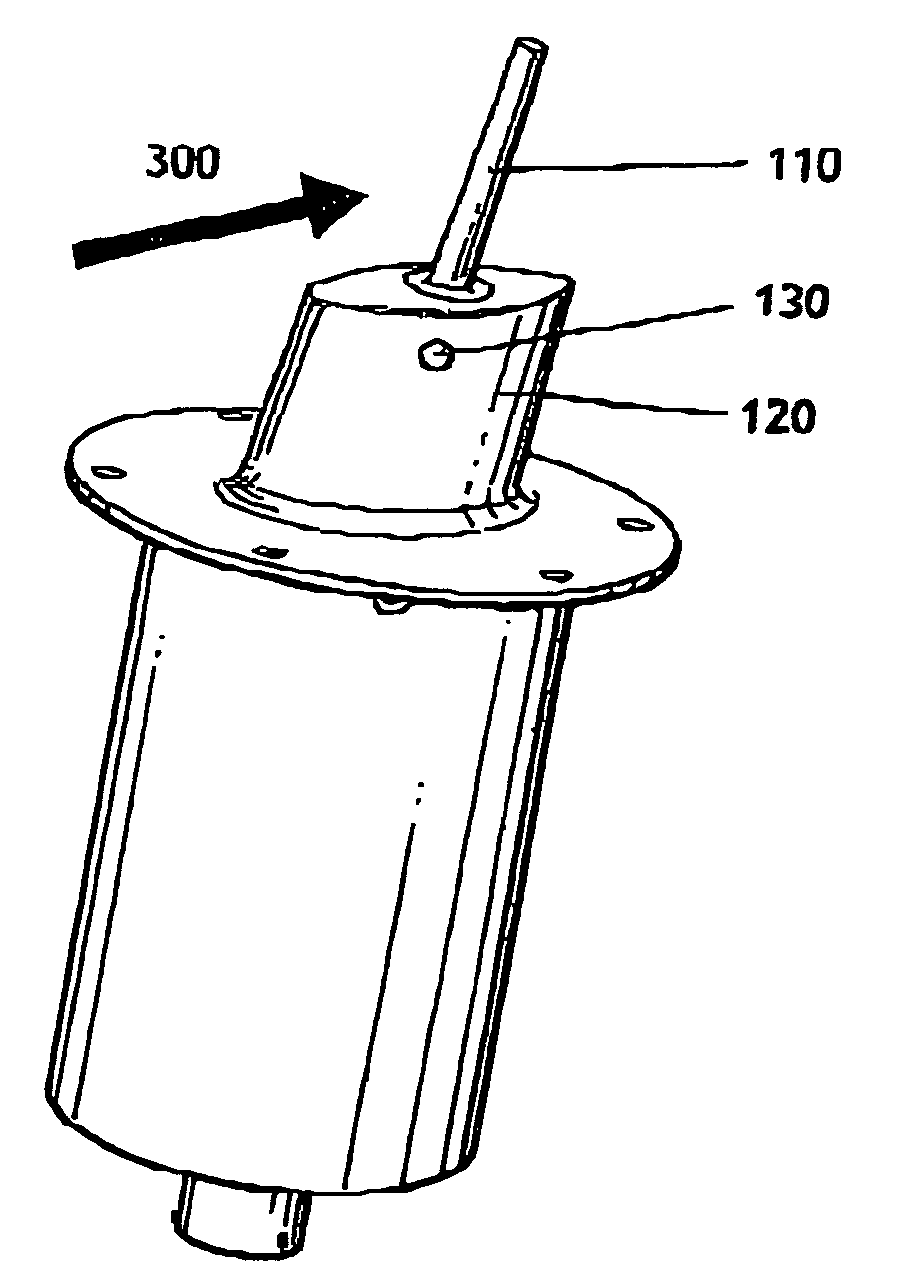
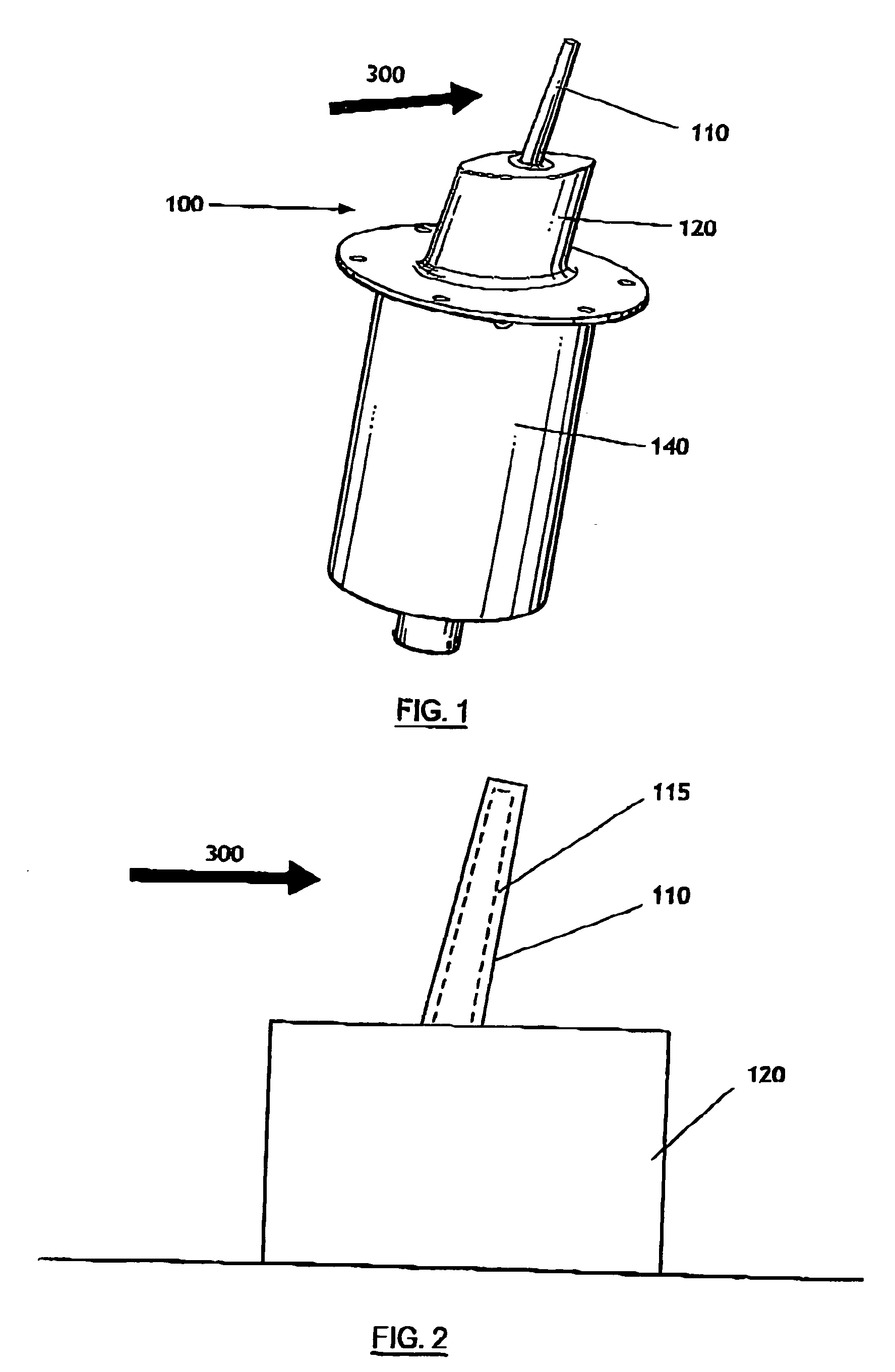
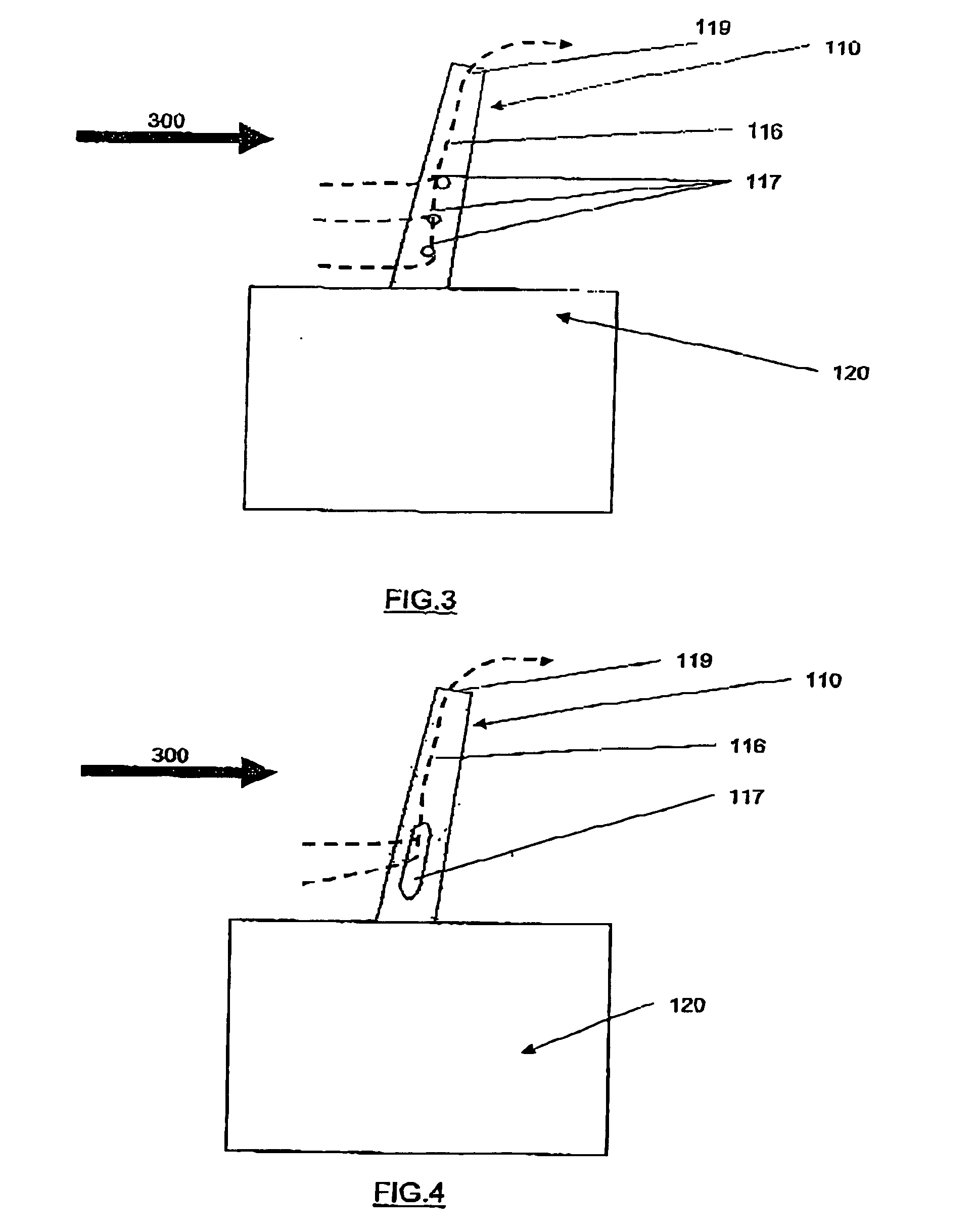
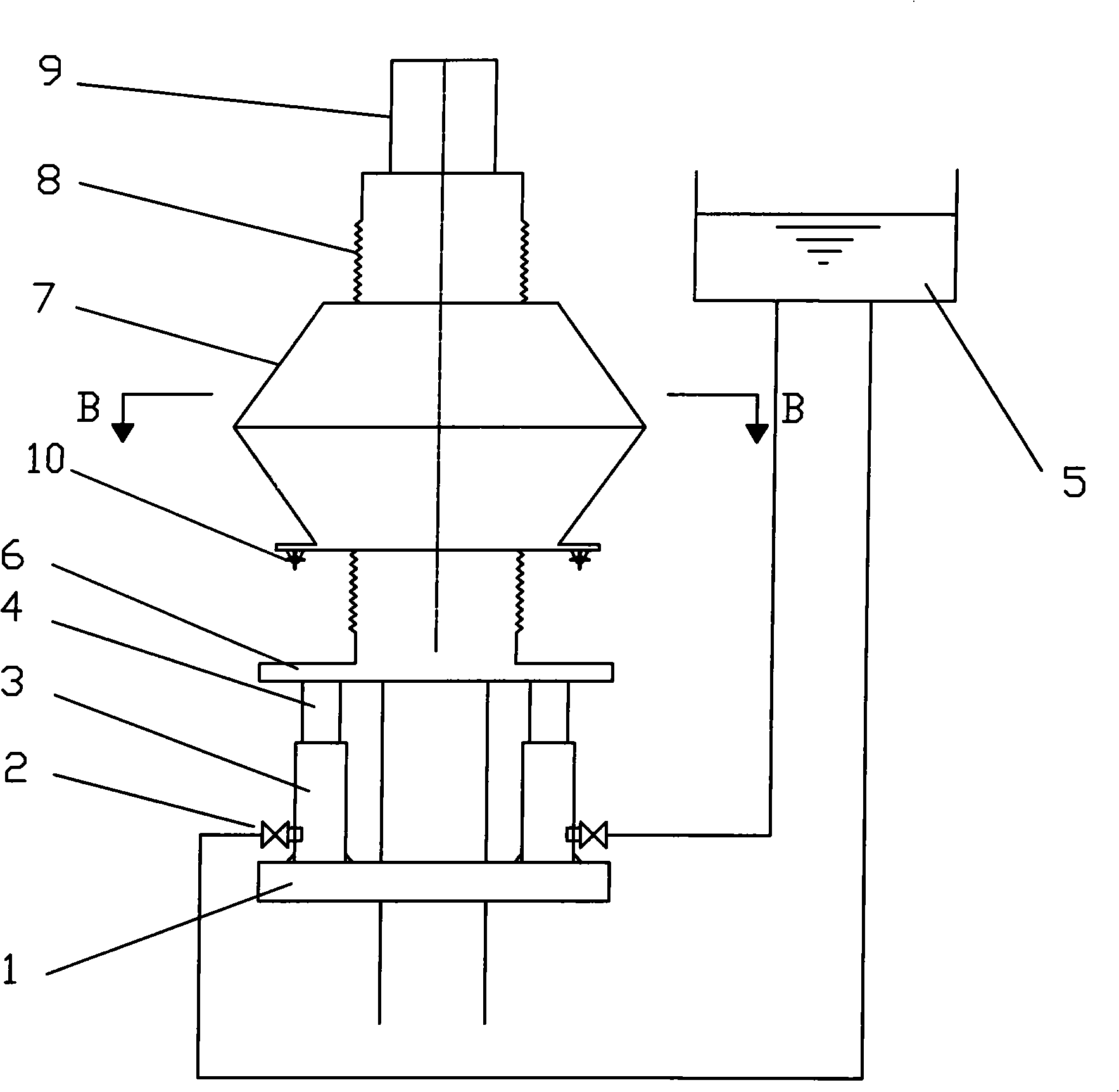
Ice detection assembly installed on an aircraft
InactiveUS20050103927A1Finish quicklyDe-icing is done more quicklyThermometer detailsDe-icing equipmentsEngineeringIce sheet
Ice detection assembly (100) designed for installation on an aircraft, comprising a vibrating finger (110) and a mast (120), the vibrating finger (110) extending into the air from the mast (120) and capable of being vibrated by vibration means at a resonant frequency that is sensitive to an ice deposit on its surface, characterised in that it comprises a cooling system capable of cooling at least part of the detection assembly (100).
Owner:AUXITROL
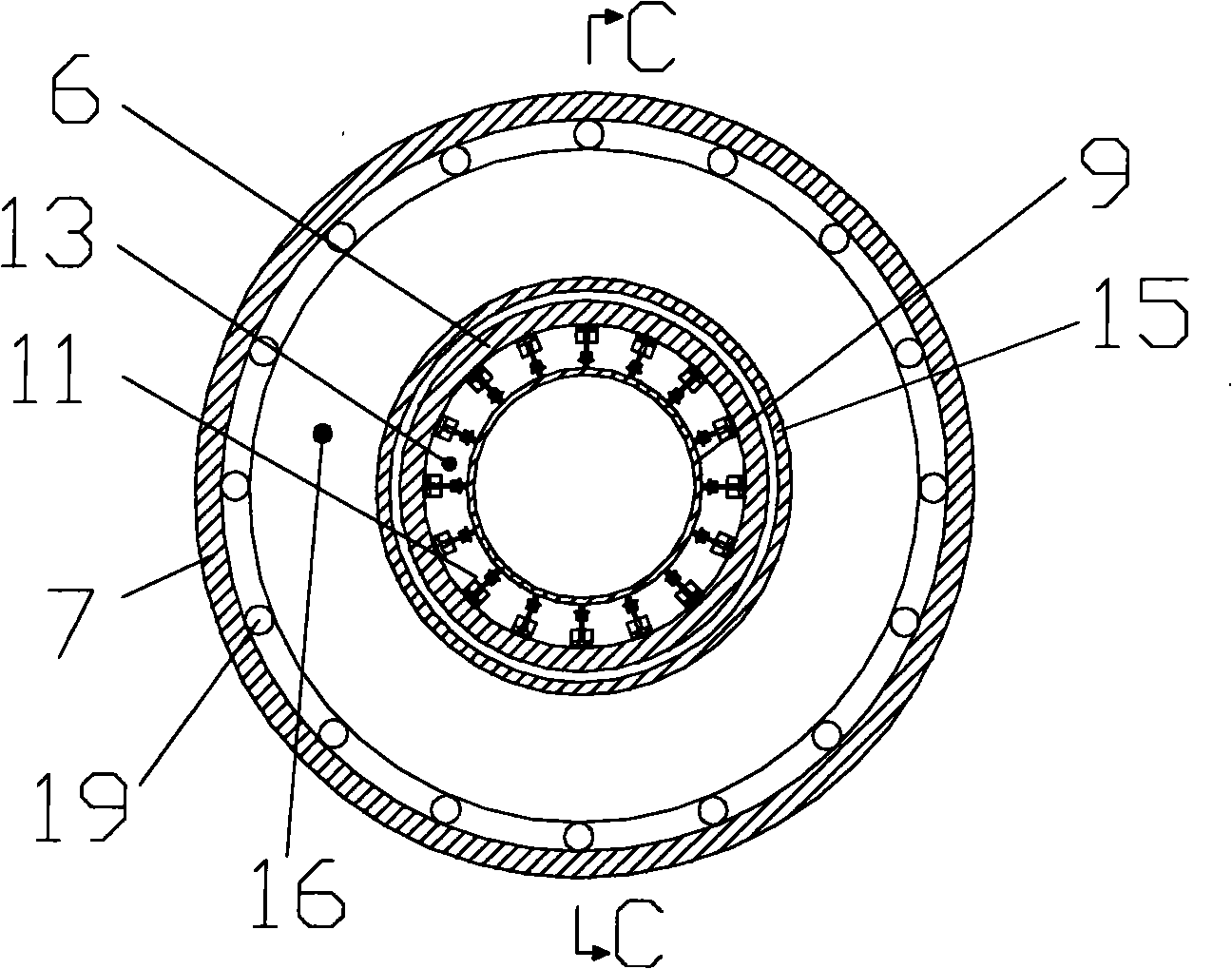
Auto spiral lifting active ice resistant device
InactiveCN101289846AReduce climbingReduce accumulationArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresIcing conditionsPropeller
The invention discloses an automatic spiral elevating active ice-resisting device, comprising a fixed support which is arranged around and fixed with the outside of a leg of a protected object, a hydraulic self-elevating system fixed with the fixed support, a cylinder-type movable support which is fixed with a plunger of the hydraulic self-elevating system and is arranged around the outside of the leg of the protected object, and an ice-resisting cone which is arranged around and connected with the outside of the cylinder-type movable support. The ice-resisting cone is a combined body of a positive cone and an inverted cone; the inner surface of the combined of the positive cone and the inverted cone is in threaded connection with the outer surface of the cylinder-type part of the cylinder-type movable support; a propeller is arranged on the lower end face of the combined of the positive cone and the inverted cone. The device can automatically adapt to tidal range changes, can realize the functions of breaking ice actively, operating fully automatically, reducing the threat to a platform from the accumulation and climbing phenomena of ice sheets, is especially suitable for the sea areas under serious ice conditions, and can effectively protect ocean engineering structures in iced sea areas.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
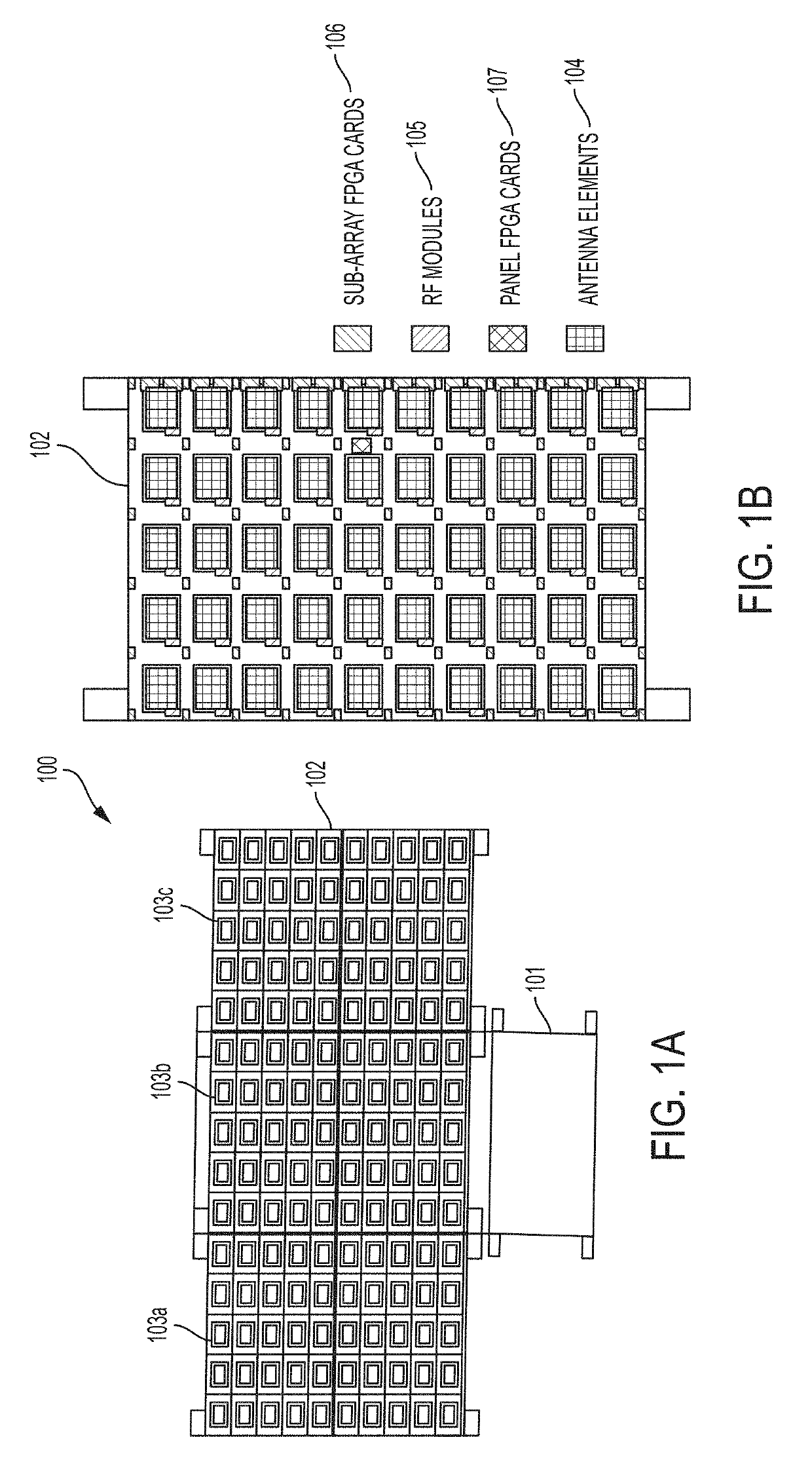
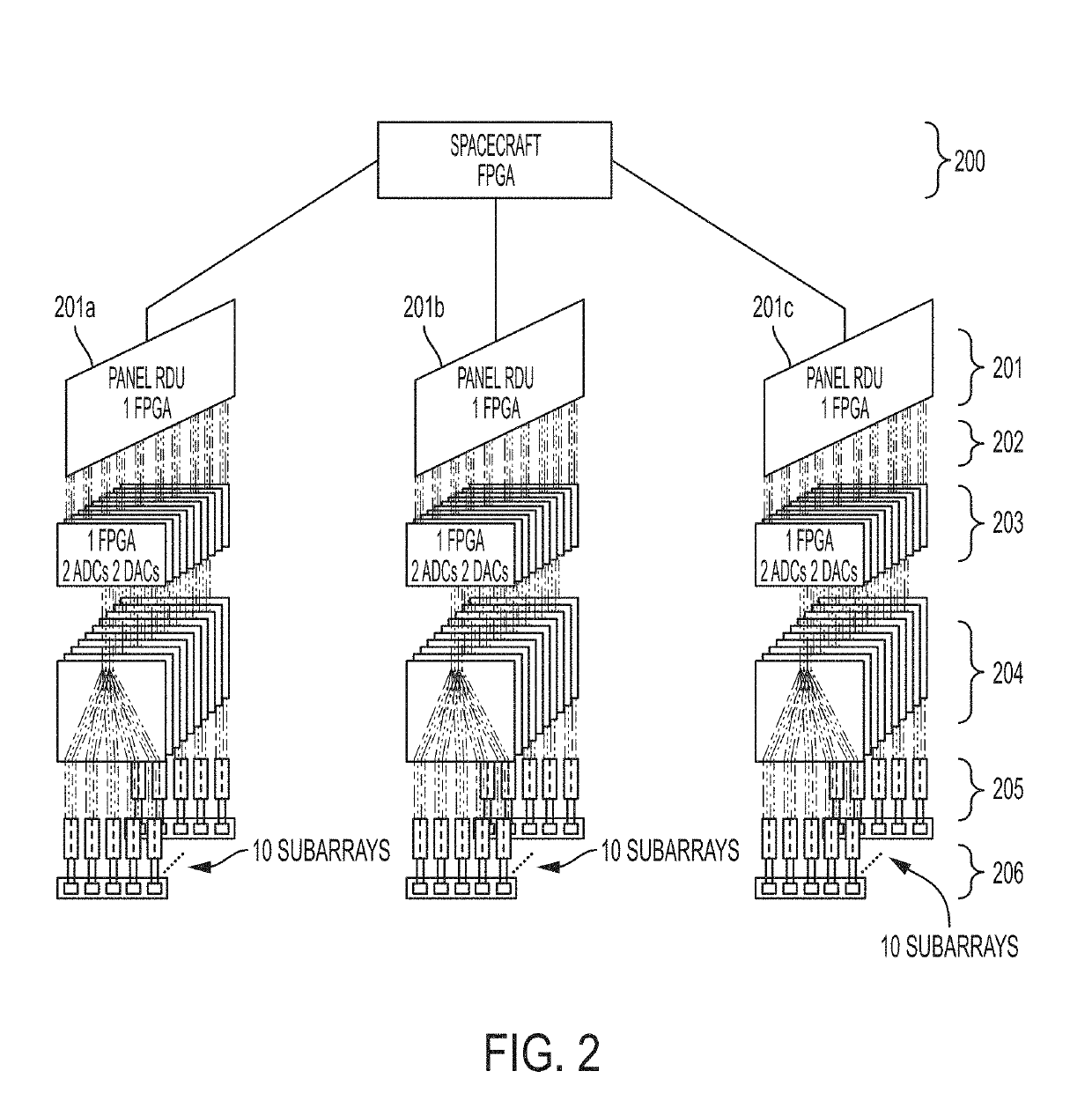
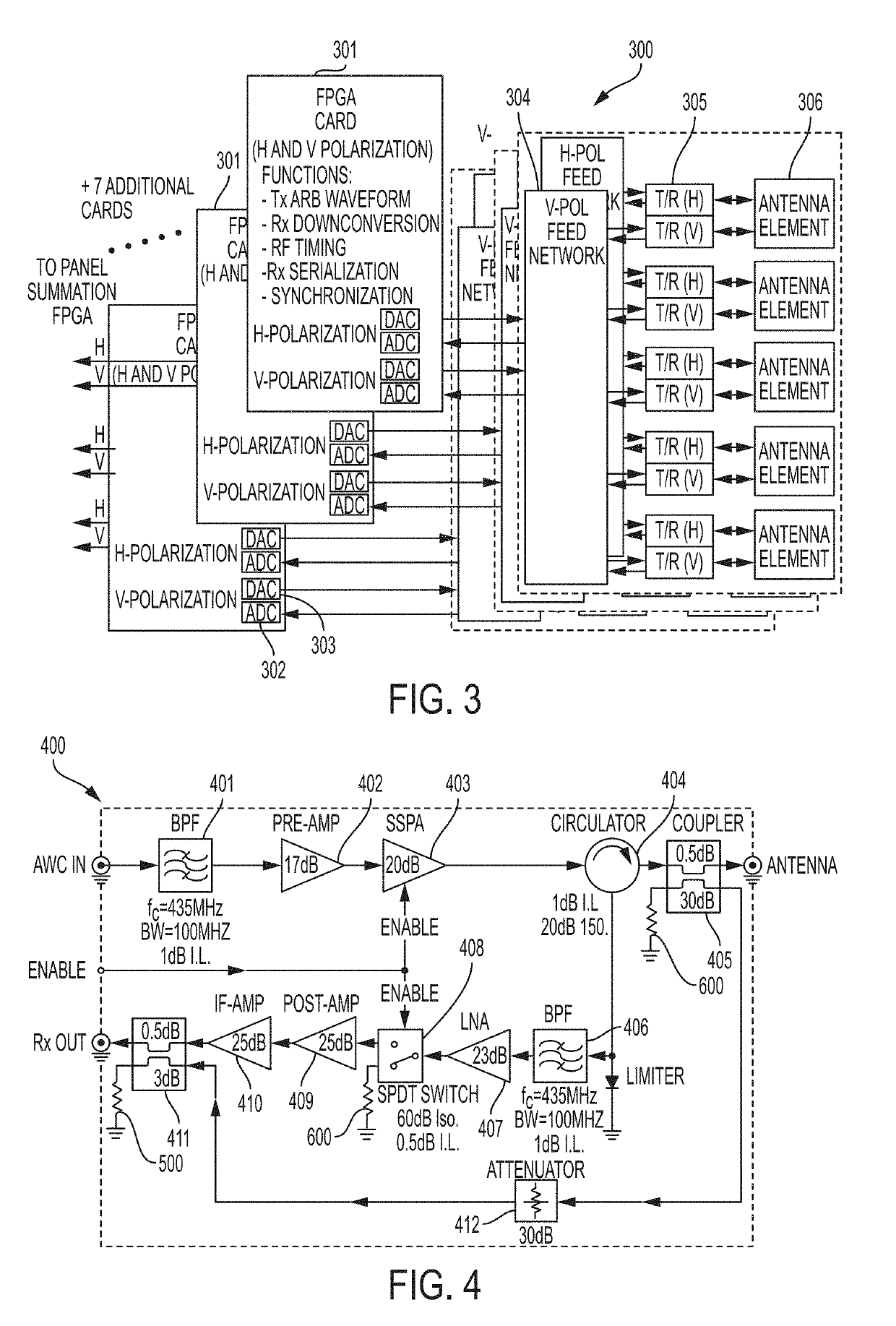
Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar system and method
ActiveUS20190101639A1High resolution measurementReduce development costsModular arraysElectrically short antennasFreeze thawingSynthetic aperture sonar
The present invention relates to an advanced spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system and method that can provide high resolution measurements of the Earth or planetary surface, overcoming limitations in conventional SAR systems, and reduce development costs. The present invention utilizes advanced and innovative techniques, such as software defined waveforms, digital beamforming (DBF) and reconfigurable hardware, to provide radar capabilities not possible with conventional radar instruments, while reducing the radar development cost. The SAR system architecture employs a modular, low power, lightweight design approach to meet stringent spaceborne radar instrument requirements. Thus, the present invention can enable feasible Earth and planetary missions that address a vast number survey goals, including the measurement of ecosystem structure and extent, surface and sub-surface topography, subsurface stratigraphy, soil freeze-thaw, ice sheet composition and extent, glacier depth, and surface water, among many others.
Owner:NASA
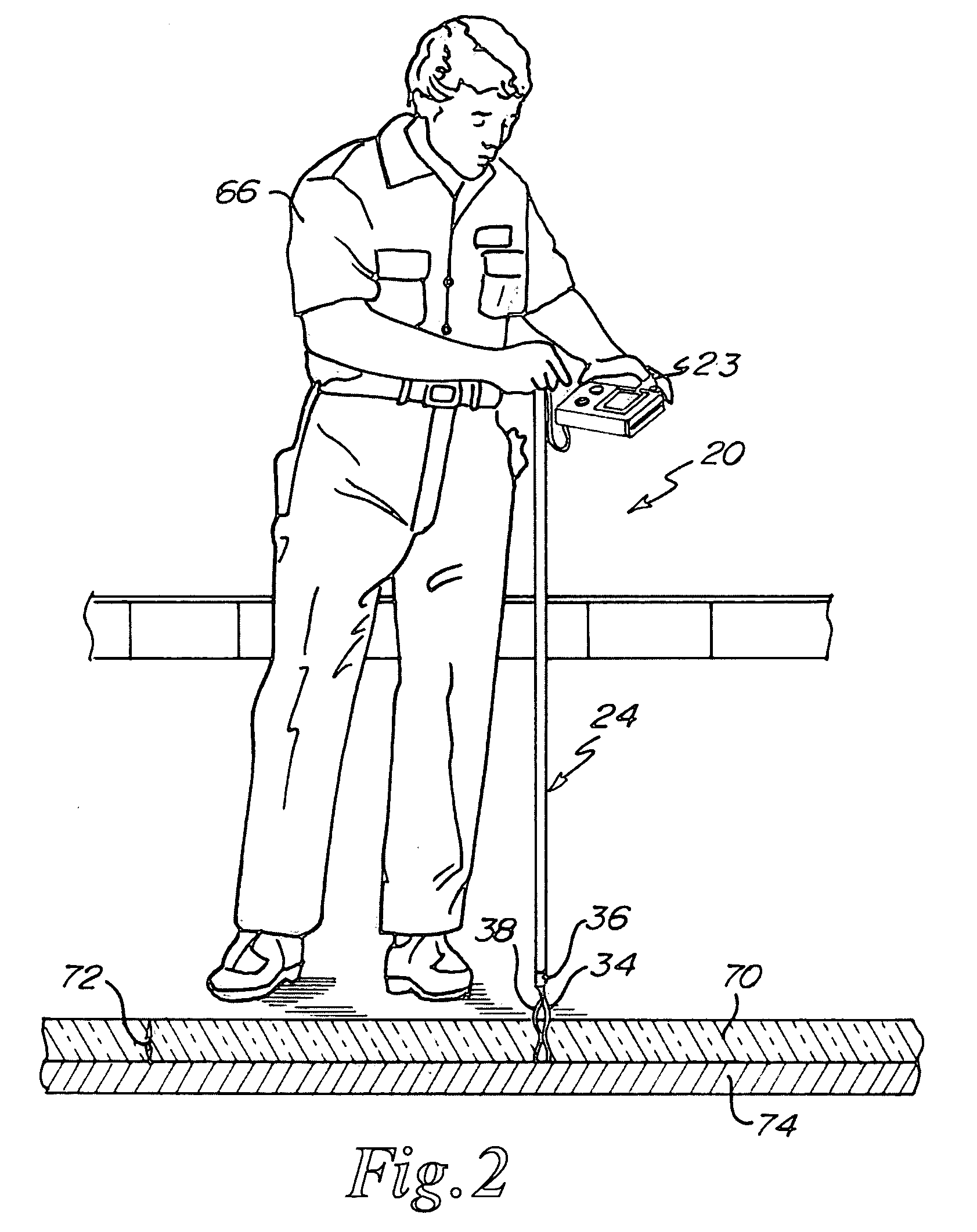
Ice thickness measuring system
InactiveUS20080295599A1Increase speedImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidGraphicsGraphical user interface
An ice thickness measurement system for determining thicknesses of an ice sheet such as an ice rink that is positioned on a solid or granular substrate. The system determines the thickness of the ice sheet using an acoustic technique, is portable, and may include a display graphic or graphical user interface on the portable unit to direct operators of the unit where to conduct an array of measurements on the ice sheet. The system may also be compatible with a computer for downloading of data and uploading of graphical displays.
Owner:PRECICE TECH
Method and system for processing glacial water
ActiveUS20120284210A1Preserve integrityInduced currentTreatment involving filtrationEnergy based wastewater treatmentEngineeringIce sheet
Methods and systems for recovering, processing, containing, and transporting water obtained from an ice source, i.e., a glacier, ice sheet, ice cap, etc., are described herein. The ice obtained from the ice source holds unique properties and is processed as a beverage for consumption having unique properties. Further, the resulting product is produced and transported with minimal human alteration and reduced energy input as compared to conventional methods for packaging water.
Owner:WORLDS FRESH WATERS
Method and system for processing glacial water
Methods and systems for recovering, and processing ice obtained from an ice source, i.e., a glacier, ice sheet, ice cap, etc., are described herein. In particular, the ice obtained from the ice source holds unique properties and is processed as a beverage for consumption having unique properties. Further, the resulting product is produced with minimal human alteration and reduced energy input as compared to conventional methods for packaging water.
Owner:SZYDLOWSKI ALLEN
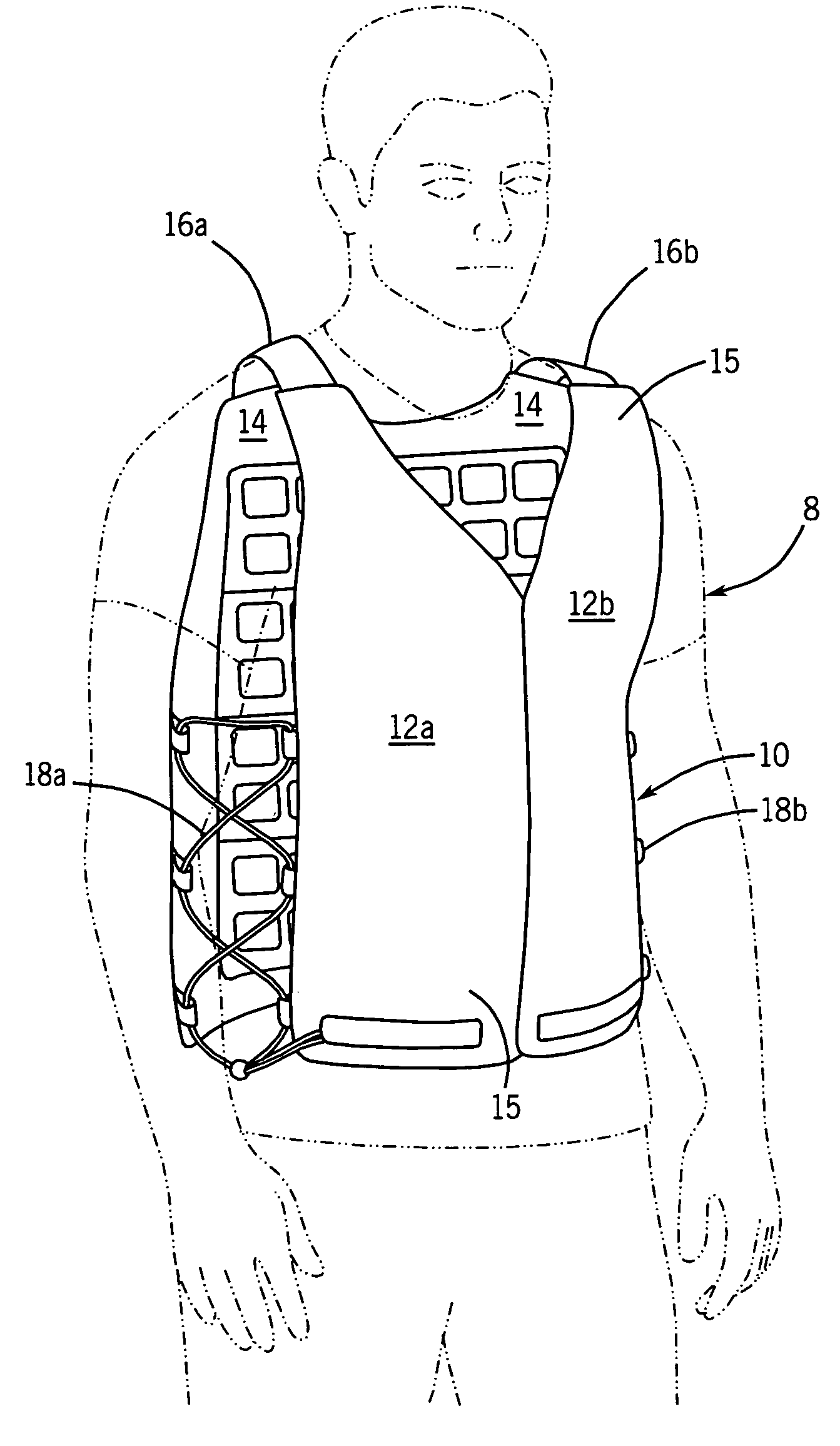
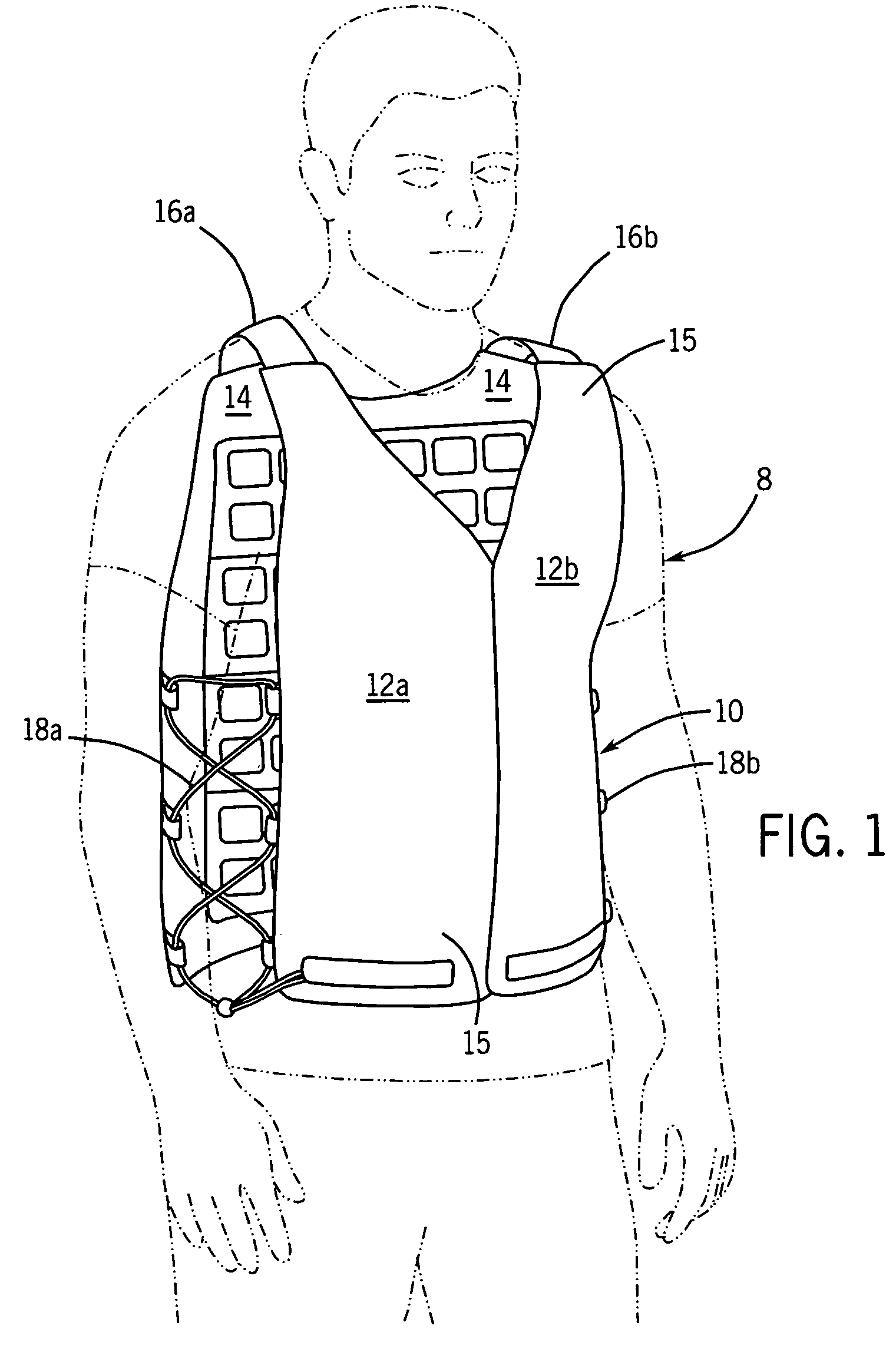
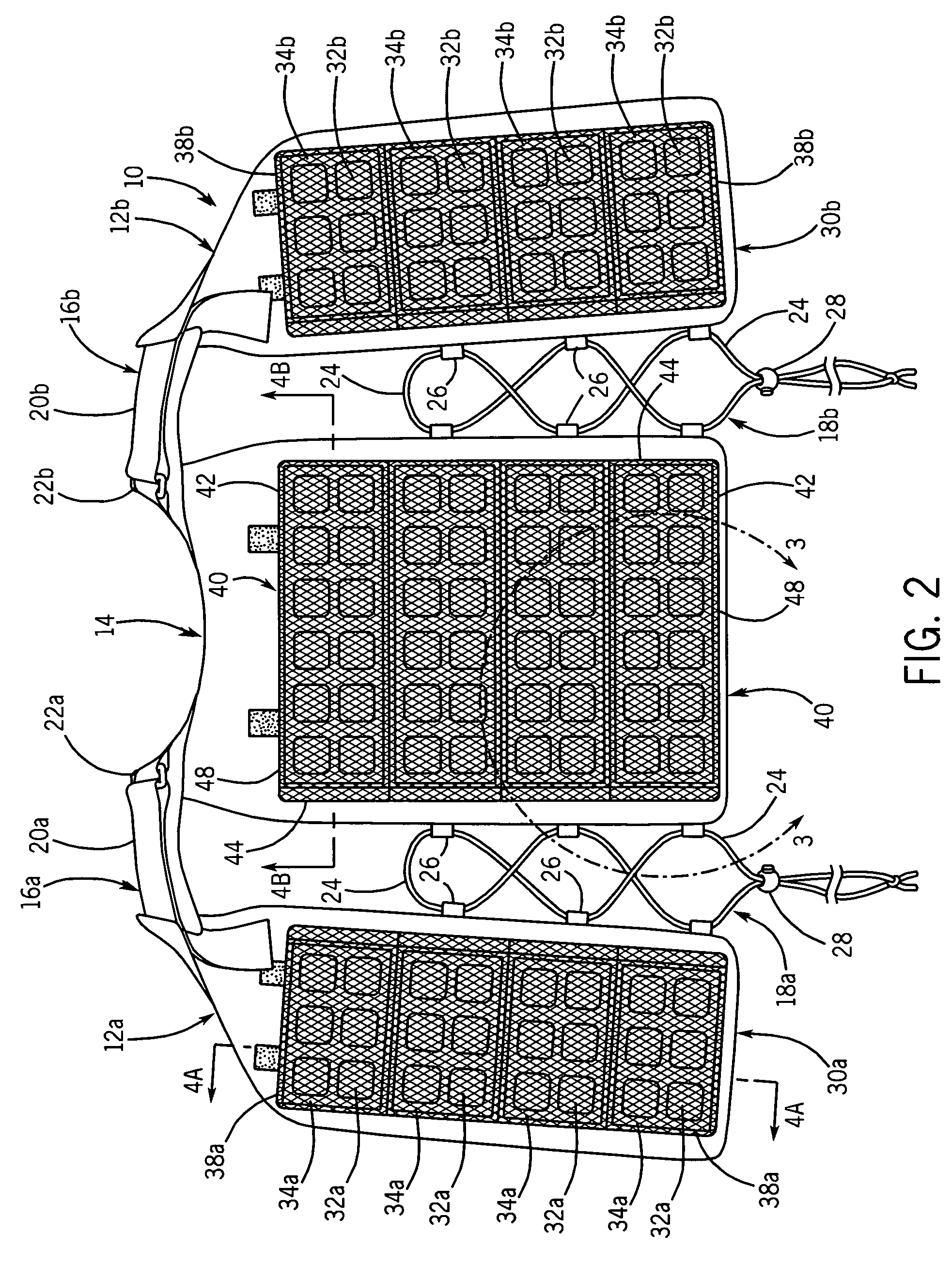
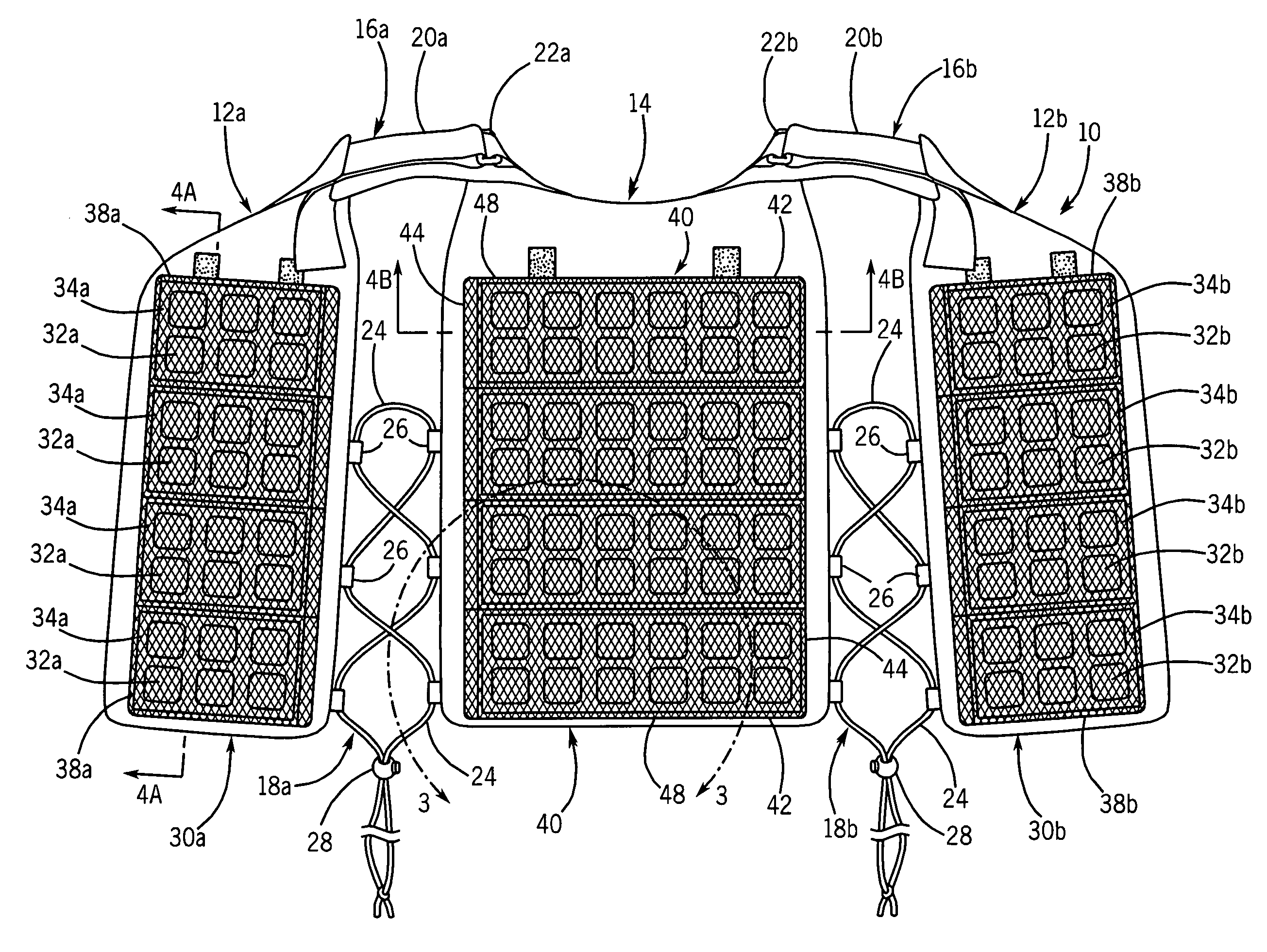
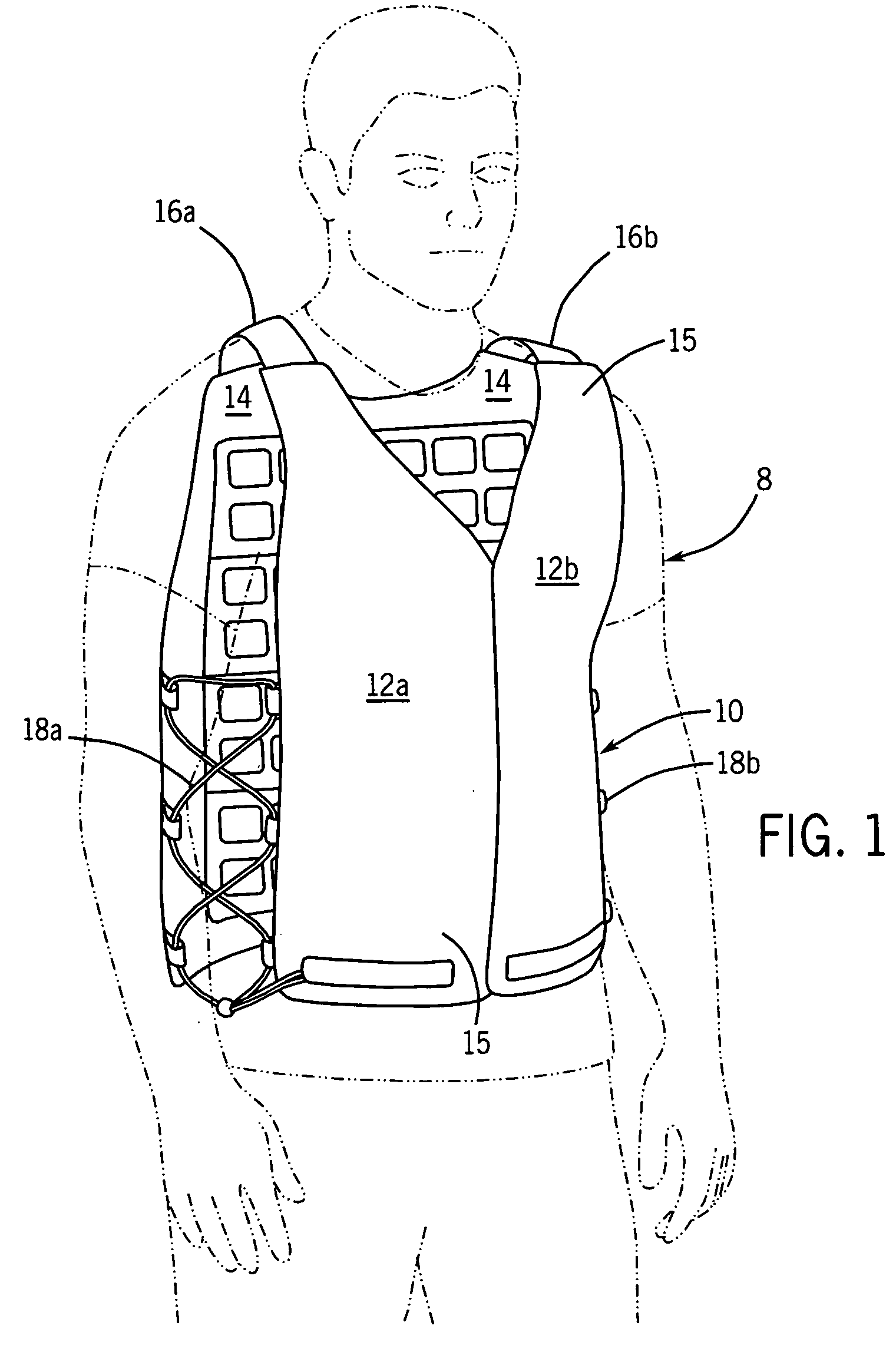
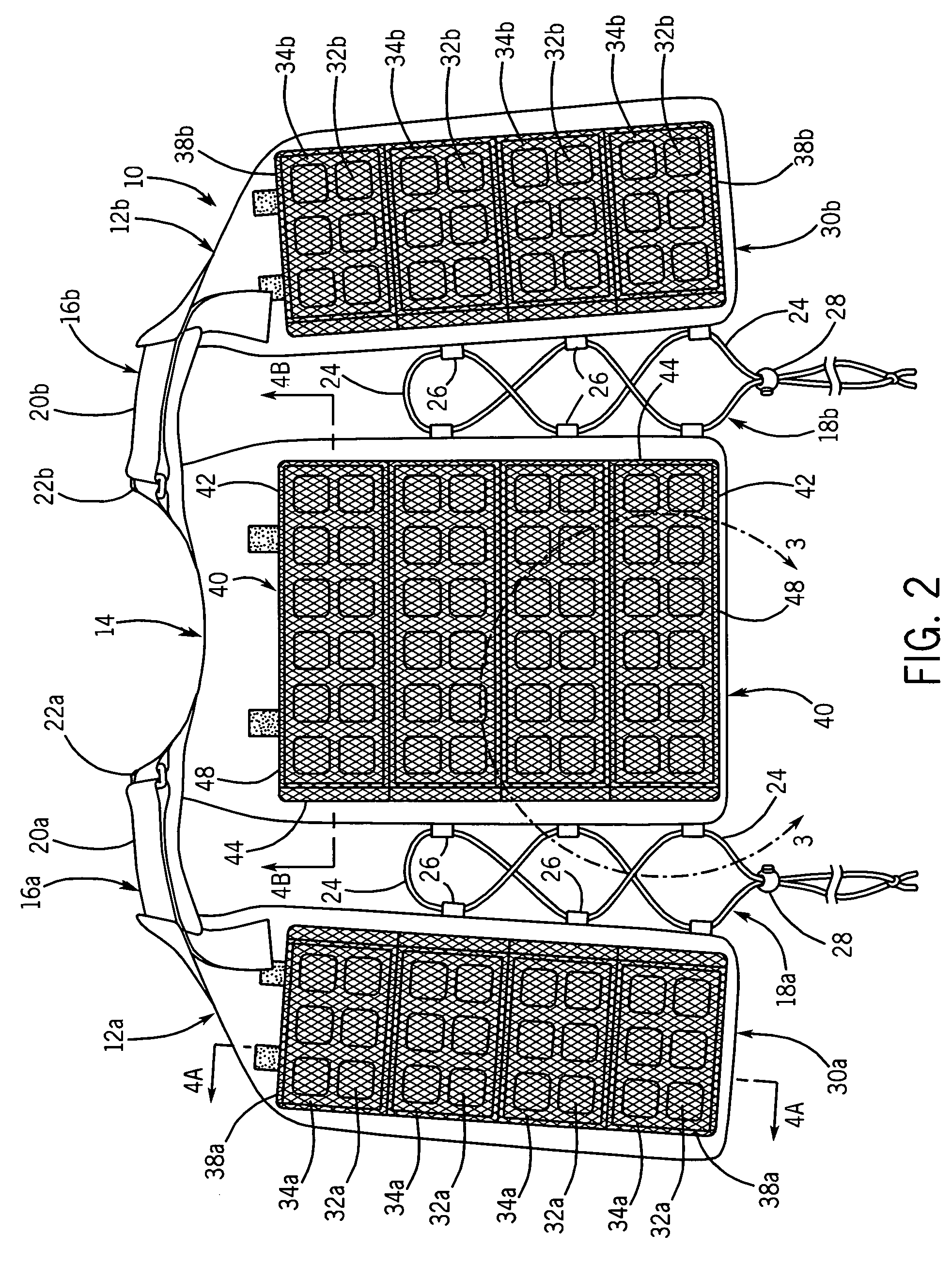
Temperature control vest having visible ice sheets composed of refrigerant cubes
ActiveUS7762096B2Quickly removed and replacedSimple but effective designChemical protectionHeat protectionTemperature controlWorking environment
A temperature control vest for use in providing cooling for workers subject to extreme temperature work environments. The temperature control vest includes chest-covering pieces and a back-covering piece that are connected by adjustable straps that run over the shoulders of the user and lacing assemblies that pass around the sides of the user. The chest covering and back covering pieces each have one or more detachable panels mounted on their interior surfaces that include compartments holding built-in ice sheets composed of refrigerant cubes for providing cooling to the user. The panels are releasably attached to the chest-covering pieces and back-covering piece so that the panels and the ice sheets can be quickly removed and replaced when the ice becomes melted. The compartments in the panels include fabric mesh layers along their inside surfaces for holding the replaceable ice sheets in contact with the user for cooling and heating purposes while providing a pleasing visual appearance. The compartments and mesh also allow the ice sheets to be inspected to assess the extent to which the refrigerant cubes remain frozen and to detect any damage to the ice sheets indicating that the ice sheets should be removed from the compartments and replaced.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
Floating ice sheet based renewable thermal energy harvesting system
InactiveUS8393553B2Reduced extinction threatCost-effectiveRecreational ice productionDomestic cooling apparatusLiquid waterEngineering
The invention provides a floating ice sheet based renewable thermal energy harvesting system, that can harvest energy from naturally occurring temperature differential between liquid water below a floating ice sheet that is substantially at the freezing temperature of water (0 degrees C. or slightly lower for salt water), and colder air above the floating ice sheet. For example, this is a naturally occurring phenomenon in Arctic and Antarctic region sea ice or ice shelf regions, where the air temperature above the floating ice may range from −5 degrees C. down to winter extreme cold temperatures of around −50 degrees C. In addition to the inventive application of thermodynamic cycle engines to harvest renewable energy from this naturally occurring temperature differential, variant embodiments also combine wind energy and / or solar energy subsystems to provide synergistic further benefits and greater quantities of renewable energy harvestable from devices of this class.
Owner:RIC ENTERPRISES
Method and device for simulating variable roughness factor ice cover in ice water dynamic test
The invention relates to a method and device for simulating a variable roughness factor ice cover in an ice water dynamic test. The device comprises a simulated ice cover plate which is matched with a simulated river course is width, the simulated ice cover plate is made of polyethylene boards, multiple fixing holes are formed in the simulated ice cover plate uniformly, rough blocks for simulating the roughness factor are fixed in the fixing holes correspondingly according to test requirements, and the rough blocks are made of polyethylene bars. According to the method and device, the ubiquitous material, namely the polyethylene, serves as the material for simulating the ice cover, the ice cover plane is simulated by boards, the long-strip-shaped polyethylene materials are erected on the board for simulating the rough surface of the ice cover, and simulated ice covers of different roughness factors are formed. Due to the fact that the long-strip-shaped materials which are different in length and density can be replaced in various simple ways, the ice covers of different roughness factors can be simulated, the test can be accelerated, and the test cost can be reduced greatly.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Temperature control vest having visible ice sheets composed of refrigerant cubes
ActiveUS20080141696A1Simple but effective designQuick connectionChemical protectionHeat protectionTemperature controlWorking environment
A temperature control vest for use in providing cooling for workers subject to extreme temperature work environments. The temperature control vest includes chest-covering pieces and a back-covering piece that are connected by adjustable straps that run over the shoulders of the user and lacing assemblies that pass around the sides of the user. The chest covering and back covering pieces each have one or more detachable panels mounted on their interior surfaces that include compartments holding built-in ice sheets composed of refrigerant cubes for providing cooling to the user. The panels are releasably attached to the chest-covering pieces and back-covering piece so that the panels and the ice sheets can be quickly removed and replaced when the ice becomes melted. The compartments in the panels include fabric mesh layers along their inside surfaces for holding the replaceable ice sheets in contact with the user for cooling and heating purposes while providing a pleasing visual appearance. The compartments and mesh also allow the ice sheets to be inspected to assess the extent to which the refrigerant cubes remain frozen and to detect any damage to the ice sheets indicating that the ice sheets should be removed from the compartments and replaced.
Owner:FUCHS MARK D
Polar ice cap melting detecting method
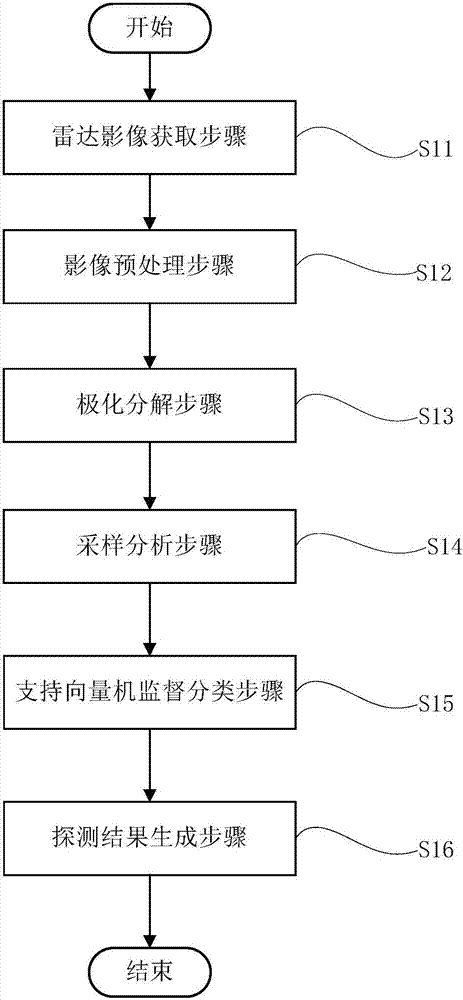
ActiveCN107103280AHigh resolutionHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPolar capDecomposition
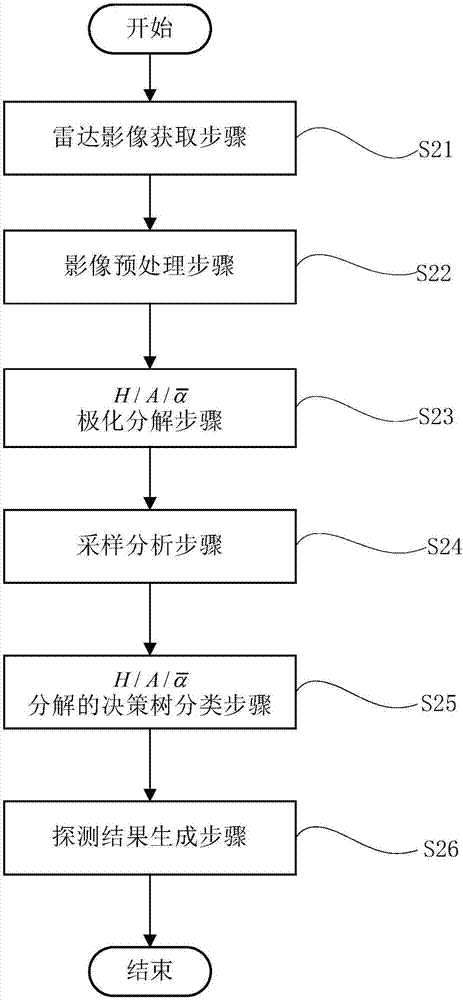
The invention discloses a polar ice cap melting detecting method which comprises the following steps of a radar image acquiring step, namely acquiring a polar image through a satellite-borne polarized synthetic aperture radar; an image preprocessing step, namely performing noise reduction processing on the acquired polarized image of the satellite-borne polarized synthetic aperture radar, thereby suppressing speckle noise; a polarization decomposition step, namely performing non-coherent polarization decomposition on the polarized image, and obtaining each decomposition parameter; a sampling analyzing step, namely selecting a glacial zone with a typical characteristic from the polarized image for performing sample analysis; a classifying step, namely establishing and correcting a classifier, classifying the glacial zone, and obtaining a glacial zone distribution result; and a detecting result generating step, namely performing reprojection and geographical coordinate correction on the glacial zone distribution result, and performing mapping for generating a polar ice cap melting detecting result. The polar ice cap melting detecting method overcomes a defect of overhigh dependence on auxiliary information and area restriction in previous polar ice cap melting detecting method through the satellite-borne polarized synthetic aperture radar and furthermore improves classification precision.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and system for recovering and preparing glacial water
Methods and systems for grouping, recovering, and processing ice obtained from an ice source, i.e., a glacier, ice sheet, ice cap, etc., are described herein. In particular, the ice obtained from the ice source is separated and grouped according to common unique properties and processed as a beverage for consumption having the same unique properties.
Owner:SZYDLOWSKI JUAN CARLOS
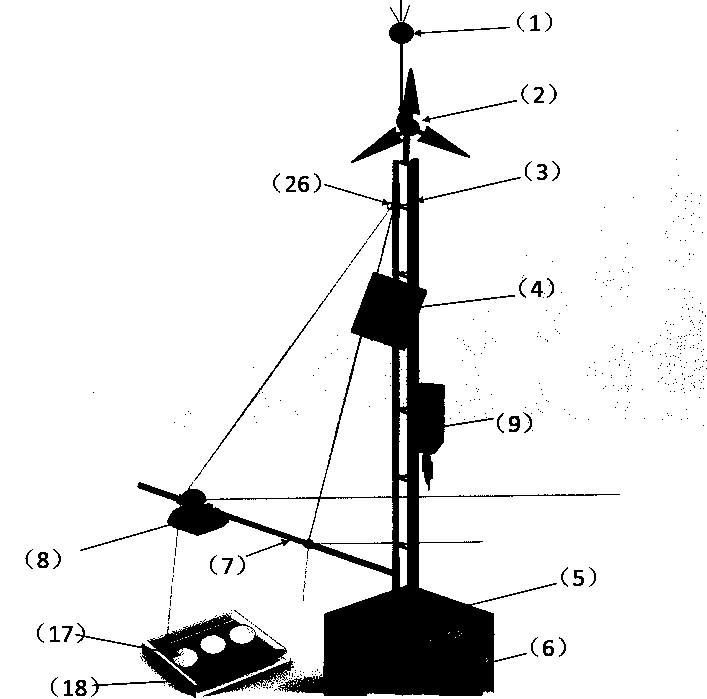
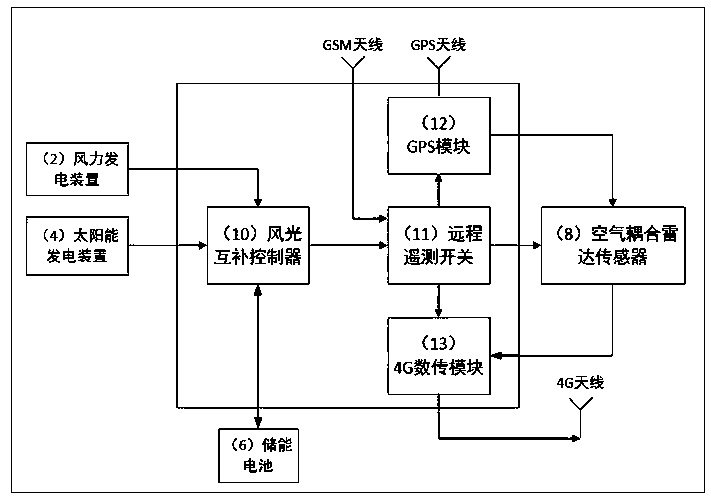
Fixed-point suspended ice thickness and water level integrated continuous monitoring device
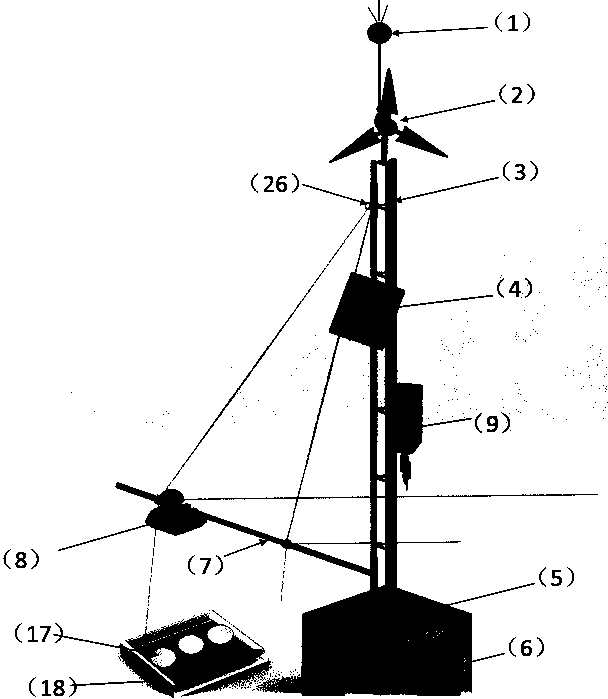
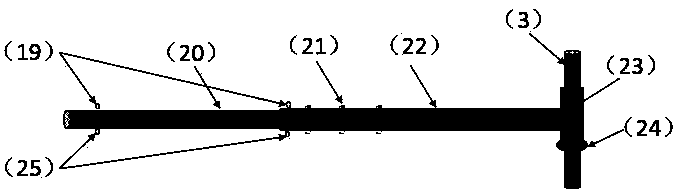
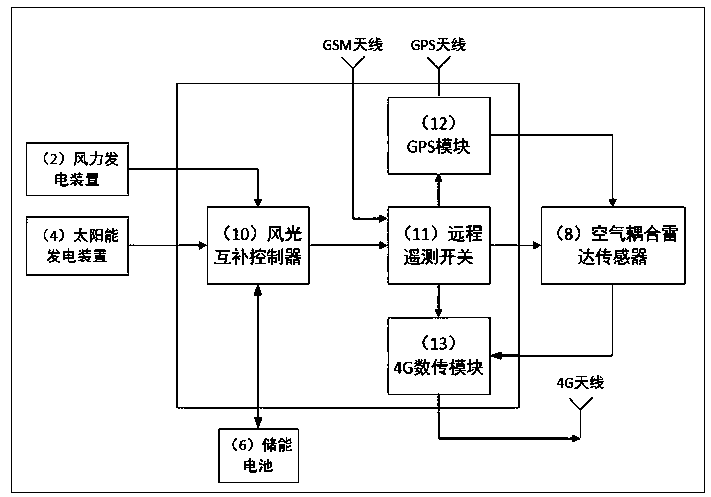
PendingCN109883479AReduce risk of monitoring on iceEasy to installMeasurement devicesEngineeringSolar power
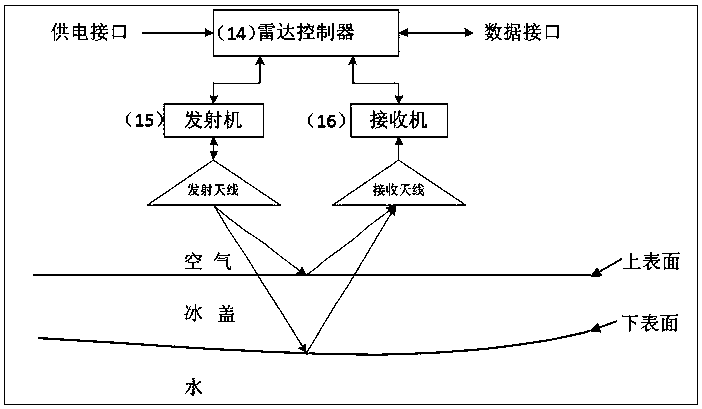
The invention relates to an ice thickness and water level integrated continuous monitoring device, and belongs to the technical field of hydrological monitoring. The monitoring device is composed of alightning arrester, a wind power generation device, a triangular steel tower, a solar power generation device, a mounting base, an energy storage battery, a rotary arm, an air coupling radar sensor (internally comprising a transmitter, a receiver and the like), an integrated control box (internally comprising a wind-solar complementary controller, a remote telemetering switch, a GPS module and a4G data transmission module) and the like. After installation and connection are completed, a remote computer starts each control module through GSM; relevant parameters are sent to the radar sensor through the 4G module; meanwhile, a radar graph with a GPS time label is received on the basis of the 4G module; and according to two-way time t1, in air and two-way time delta t, in an ice cover, of radar waves, recorded by the radar graph, the elevation H1 of the upper surface or the free water surface of the ice cover and the elevation H2 of the lower surface of the ice cover are automatically calculated by using formulae (5) and (6).
Owner:YELLOW RIVER INST OF HYDRAULIC RES YELLOW RIVER CONSERVANCY COMMISSION
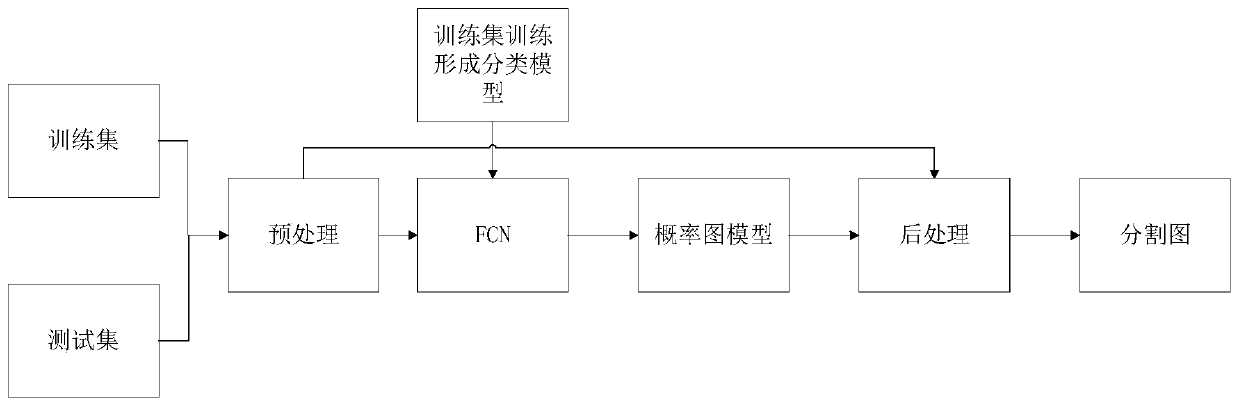
An ice cover radar image ice layer fine segmentation method based on an FCN-ASPP network
ActiveCN109741340AFast convergenceQuick extractionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRadarNetwork on
The invention discloses an ice cover radar image ice layer fine segmentation method based on an FCN-ASPP network, and relates to the field of computer vision and mode recognition. According to the invention, the radar amplitude image is used as a training sample of a network, corresponding data amplification is carried out for the problem of less ice layer image data, and the wide applicability ofthe method is expanded. Lee filtering is carried out on the ice cover image. In order to save edge information as much as possible, a threshold judgment process is added to a filtering process. FCN-is constructed, and FCN-is constructed; according to the ASPP ice layer segmentation deep network, the ASPP layer is improved, so that the extraction capability of the network on small-scale characteristics is enhanced. The preliminary classification result is further processed through CRF, and the segmentation result is further refined on the basis of achieving end-to-end pixel level segmentation.In addition, the network greatly realizes the autonomous learning process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
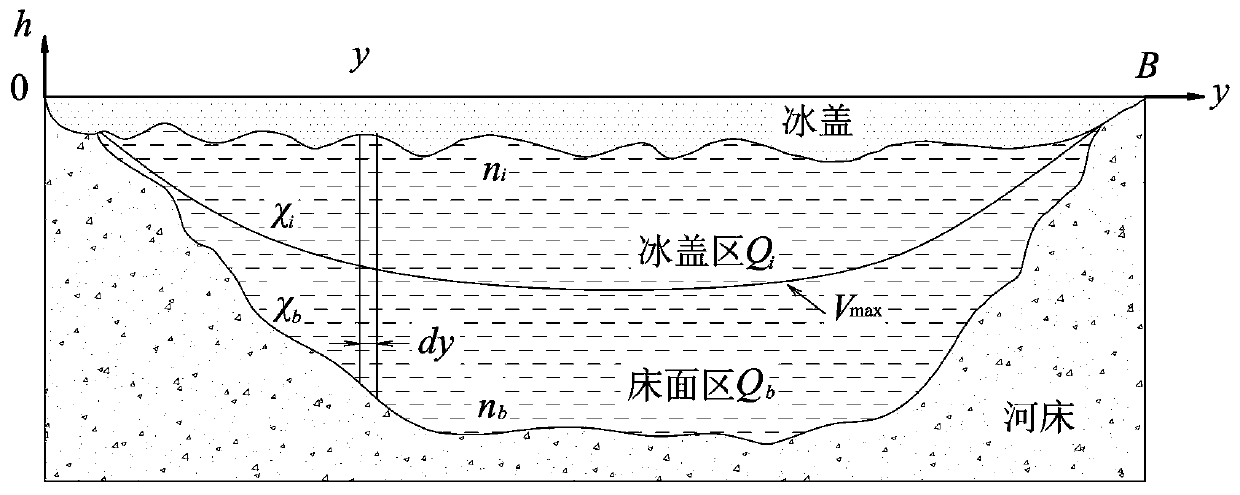
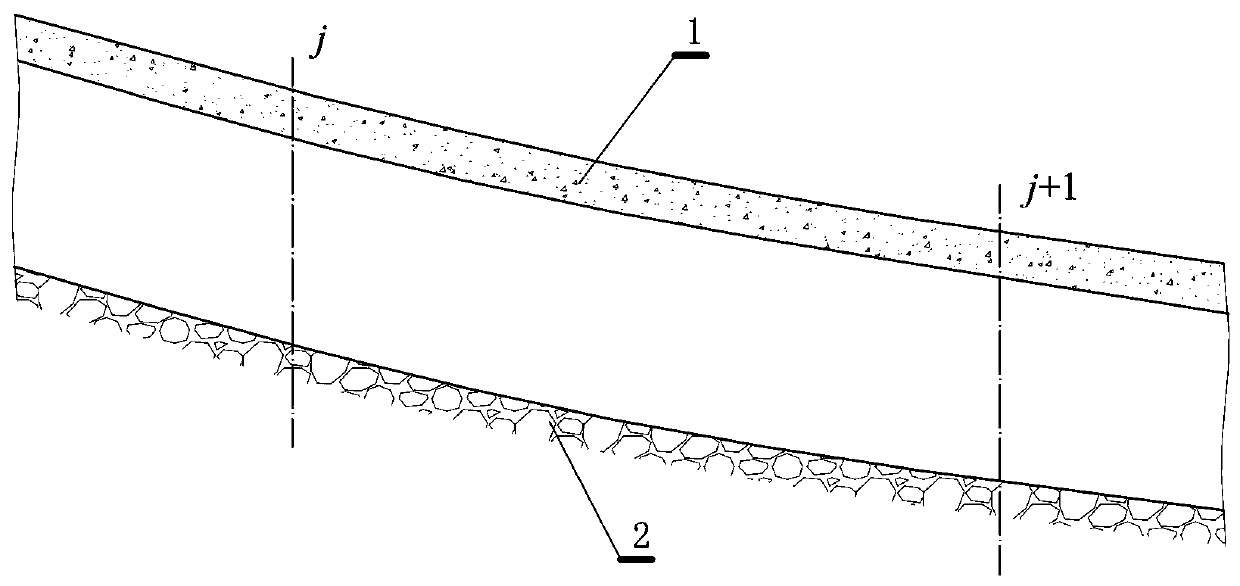
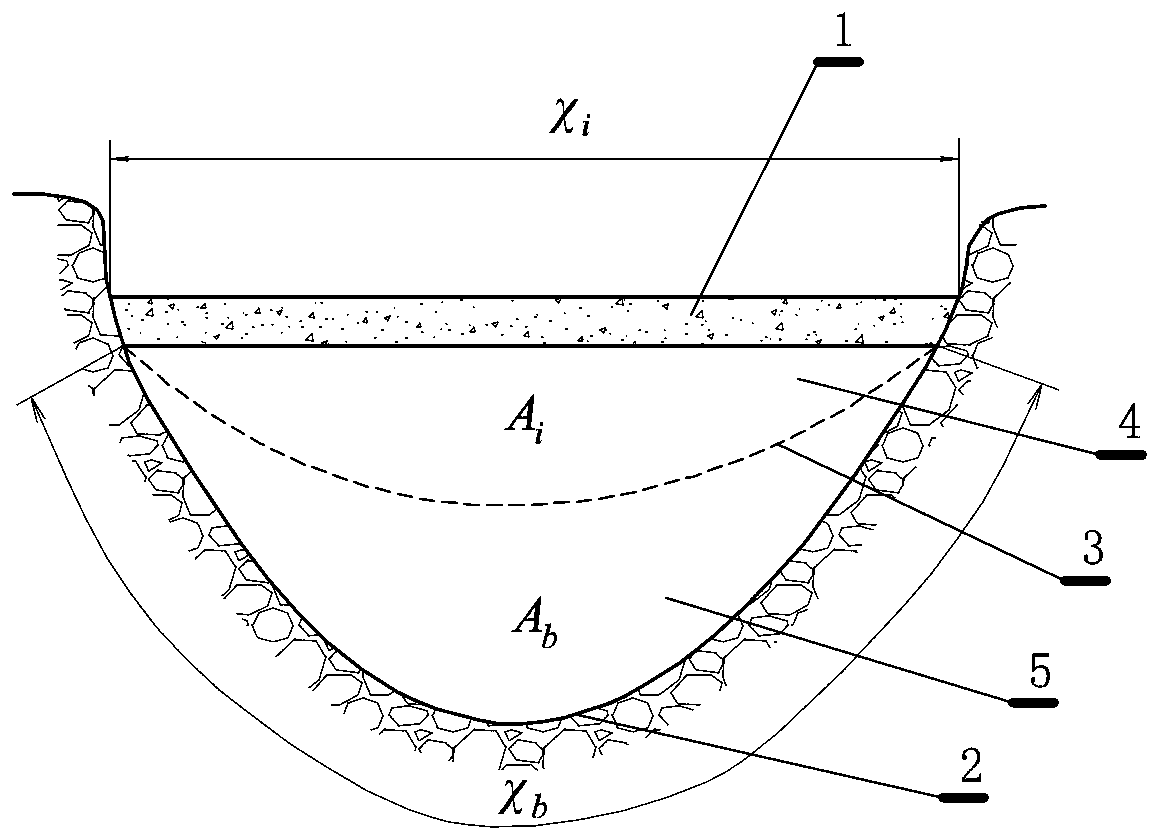
Cold region canal ice period flow test method
ActiveCN110672163AReduce workloadImprove test efficiencyVolume/mass flow measurementComplex mathematical operationsStream flowEngineering
The invention relates to a cold region canal ice period flow test method. The method comprises the steps of measuring a transverse section, calculating a unit width area, calculating an accumulated area, performing flow parameter derivation, drawing a q<->y-y / B relation curve, performing flow measurement, and calculating a total flow. According to the invention, by utilizing the characteristics that an ice cover obviously influences the vertical flow velocity distribution of a certain point of a river section and basically has no influence on the transverse distribution of the average flow velocity of the water depth of the section, the flow under the ice cover in an ice period of a canal is accurately deduced by utilizing an analytical formula of the average flow velocity of the water depth under the ice cover of the canal along the transverse distribution. Compared with a standard or traditional method, the method has the advantages that the total flow under the ice cover can be solved only by acquiring a section form and measuring the flow velocity distribution at any single point position on the section, the workload of flow velocity observation of all measuring lines is greatly reduced, and the testing efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
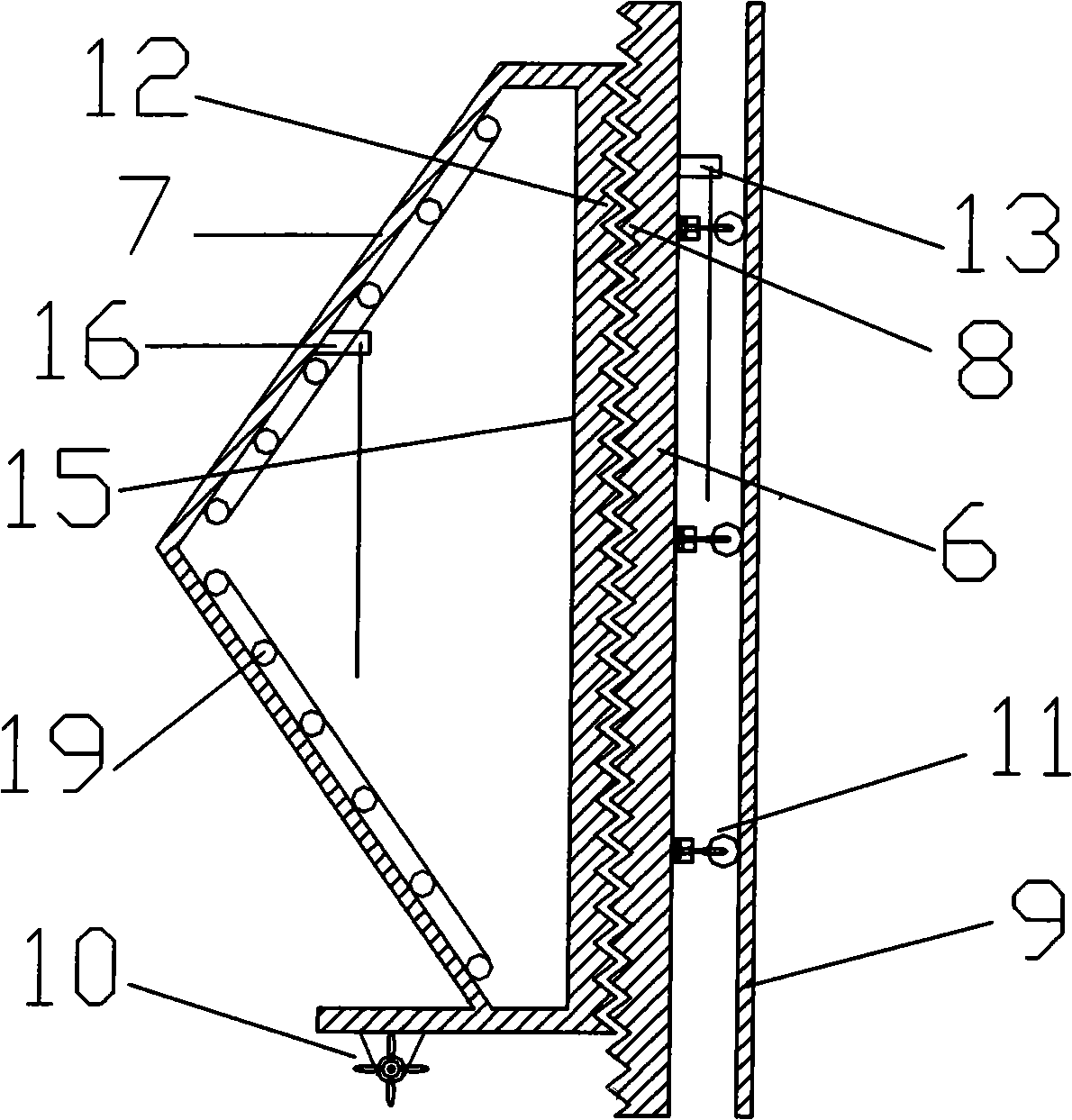
Vibration damping and vibration isolation ice resistant device for self-adapting change of tidal range
InactiveCN101289847AReduce accumulationReduce hill climbingArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresEngineeringSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a vibration decreasing-isolating ice-resisting device with automatic adaptation to tidal range changes, comprising a fixed support which is arranged around and fixed with the outside of a leg of a protected object, a hydraulic self-elevating system fixed with the fixed support, a cylinder-type movable support which is fixed with a plunger of the hydraulic self-elevating system and is arranged around the outside of the leg of the protected object, and an ice-resisting cone which is arranged around and connected with the outside of the cylinder-type movable support. A plurality of horizontal spring vibration isolators are connected between the inner surface of the ice-resisting cone and the outer surface of the cylinder-type part of the cylinder-type movable support; a plurality of vertical spring vibration isolators are connected between the lower part of the ice-resisting cone and the upper surface of a base part of the cylinder-type movable support. The device does not need to be operated manually, automatically adjusts the position of the ice-resisting cone along with tidal range changes, can keep the stability of the ice-resisting cone when ice sheets act on the ice-resisting cone, is especially suitable for the sea areas with large tidal range change range and high change speed, and reduces the adverse effect of ice-induced vibration phenomena on a platform to the utmost extent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
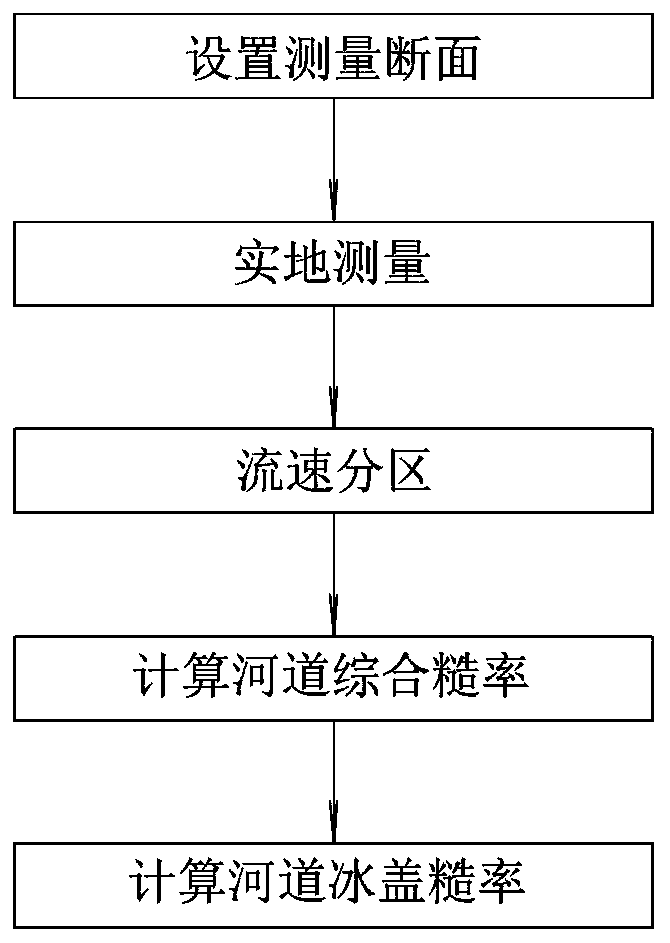
Method for calculating ice cover roughness of canal
ActiveCN110704793AAchieve correct calculationRealize evaluationComplex mathematical operationsHydrometryIce water
The invention relates to a method for calculating ice cover roughness of a canal. The method comprises the following steps: setting a measurement section; performing measurement; partitioning; calculating the comprehensive roughness of the riverway; and calculating the ice cover roughness of the riverway. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, accurately measuring each parameter of a frozen canal by adopting technologies such as river ice water mechanics and hydrological survey; the comprehensive roughness of the canal is calculated through the parameters, the ice cover roughness is deduced through the comprehensive roughness, correct calculation and evaluation of the ice cover roughness of the canal are achieved, and bases and references are provided for safe operation scheduling of the canal under the freezing condition in winter, correct evaluation of the water delivery flow, scientific response to accidents such as ice disasters and the like.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method and system for processing glacial water
ActiveUS8924311B2Preserve integrityInduced currentTreatment involving filtrationEnergy based wastewater treatmentEngineeringIce sheet
Methods and systems for recovering, processing, containing, and transporting water obtained from an ice source, i.e., a glacier, ice sheet, ice cap, etc., are described herein. The ice obtained from the ice source holds unique properties and is processed as a beverage for consumption having unique properties. Further, the resulting product is produced and transported with minimal human alteration and reduced energy input as compared to conventional methods for packaging water.
Owner:WORLDS FRESH WATERS
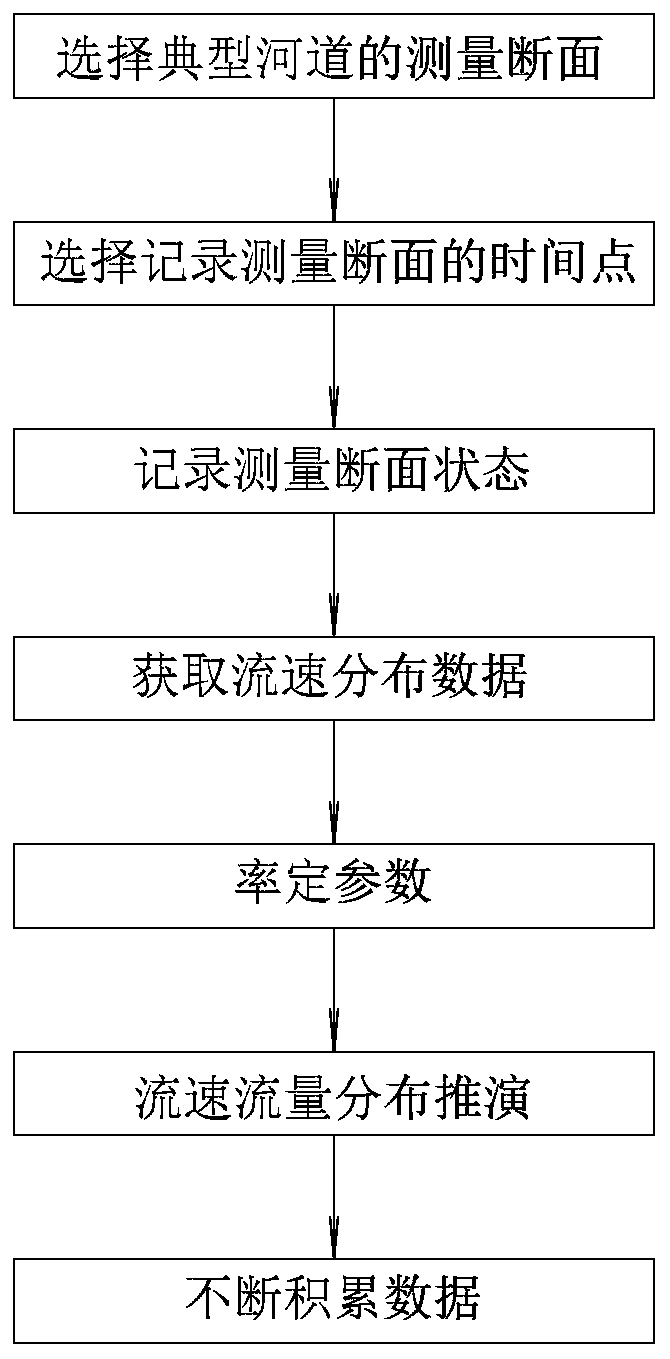
Method for deducing flow velocity distribution under ice sheet
ActiveCN110702079AReduce work intensitySolve complexityHydrodynamic testingMeasuring open water movementRiver routingStream flow
The invention relates to a method for deducing the flow velocity distribution under an ice sheet. The method for deducing the flow velocity distribution under the ice sheet comprises the following steps: selecting a measurement section of a typical river channel; selecting time points for recording the measurement section; recording a measurement section status; obtaining flow velocity distribution data; calibrating parameters: taking the flow velocity of each measurement period into the formula; deducing the flow velocity and flow distribution; and accumulating data constantly. According to the method for deducing the flow velocity distribution under the ice sheet, a comprehensive measurement is performed by combining climatic conditions, ice sheet characteristics, and ice freezing stateon a typical river channel, and a number of parameters required for calculations related to the conditions are calibrated through a flow velocity expression. In the freezing period of each subsequentyear, only the climatic conditions, the ice sheet characteristics and the ice freezing state need to be compared to find the corresponding calculation parameters, so that the same flow velocity expression can be used for obtaining the velocity distribution under the ice sheet, and the digging of the ice surface is not required; therefore, the situation that the flow velocity is not consistent withactual flow conditions caused by artificially dividing the sub-ice flow velocity into the ice sheet area and the river bed area is solved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Multi-sheet spherical ice making
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
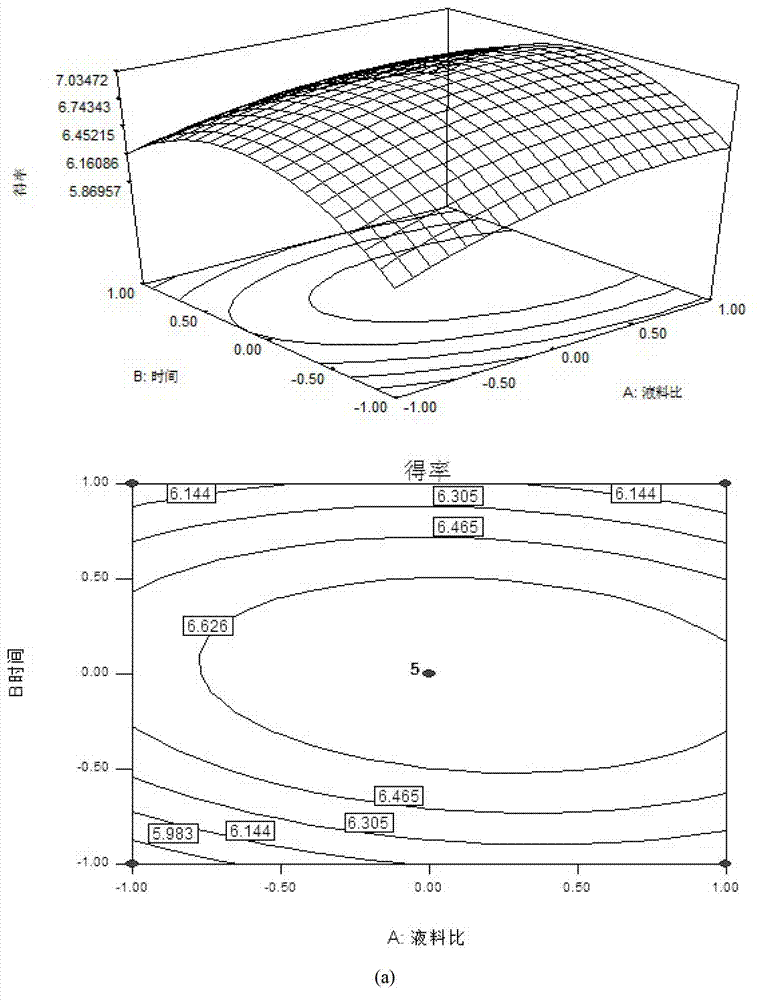
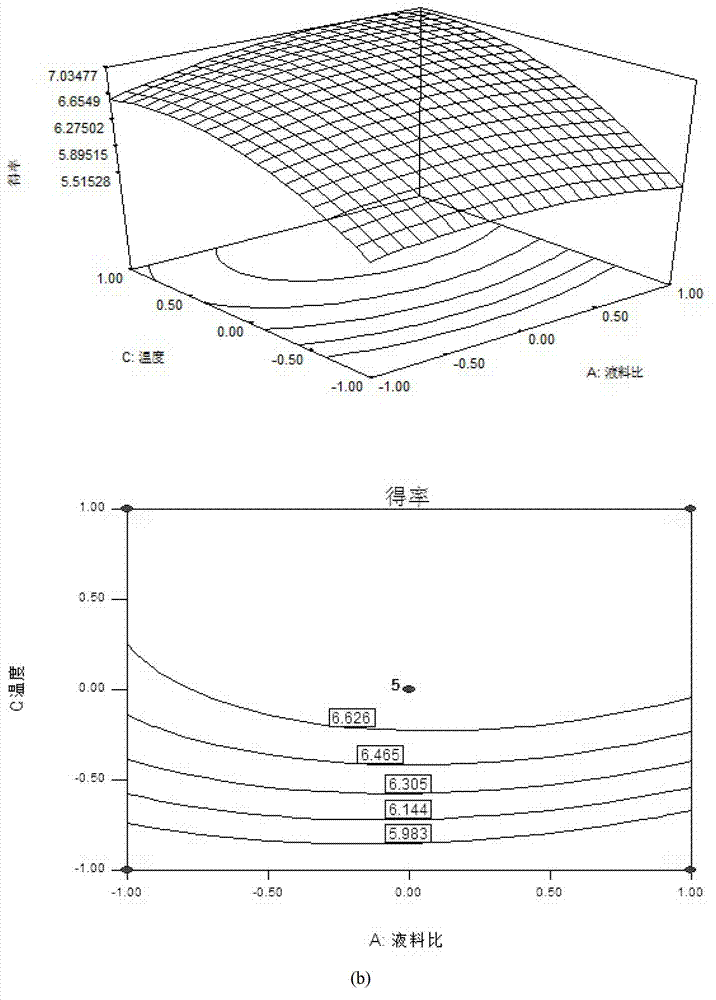
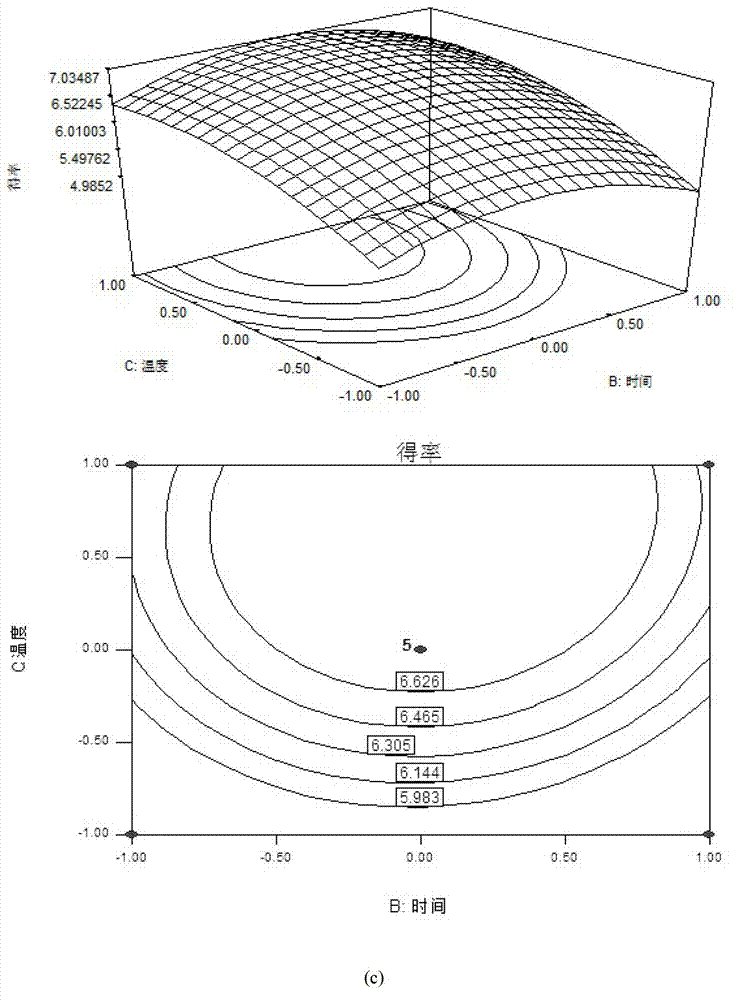
Method for extracting borneol camphor tree leaf crude extract and applied response surface methodology
InactiveCN103083939AHigh extraction rateHigh puritySolid solvent extractionDesign–ExpertLiquid ratio
The invention discloses a method for extracting a borneol camphor tree leaf crude extract. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing borneol camphor tree leaves and petroleum ether according to a material to liquid ratio of the petroleum ether to the borneol camphor tree leaves of 34-36 ml / g, and extracting at the temperature of 48-49 DEG C for 2 to 2.1 hours; and evaporating the obtained extract as the petroleum ether serving as a solvent, thus obtaining the borneol camphor tree leaf crude extract. The invention also provides a method for optimizing the borneol camphor tree leaf crude extract extraction method by response surface methodology. The following three variables are provided, namely the liquid to material ratio of the borneol camphor tree leaves to the petroleum ether, the extraction temperature and the extraction time; and optimization is executed according to Box-Behnken design by using design expert software. By the extraction method, the extraction rate of ice sheets can be increased, and consumption of solvents and resources is reduced, and production and emission of pollutants during production are reduced.
Owner:浙江桐庐百草园中药材开发有限公司
Fixed-point ice thickness and water level integrated and continuous monitoring method
InactiveCN109916449AMonitoring the up and down processReduce risk of monitoring on iceMeasurement devicesEngineeringSolar power
The invention relates to an ice thickness and water level integrated and continuous monitoring method, which belongs to the technical field of hydrological monitoring. The monitoring device is composed of a lightning arrester, a wind power generation device, a triangular steel tower, a solar power generation device, a mounting base, an energy storage battery, a swiveling arm, an air coupled radarsensor (internally provided with a transmitter, a receiver and the like) and an integrated control box (internally provided with a wind-solar hybrid controller, a remote telemetry switch, a GPS module, and a 4G digital transmission module). When mounting and connection are completed, a remote computer opens each control module through GSM, relevant parameters are transmitted to the radar sensor through the 4G module, a radar map with GPS time annotation is received based on the 4G module, according to the two-way time of radar waves in the air and the two-way time deltat in an ice cover recorded by the radar map, the distance between the radar and the upper surface of the ice cover and the ice cover thickness deltah are calculated automatically by using formulas (3) and (4), and by using formulas (5) and (6), an ice cover upper surface or free water surface height H1 and an ice cover lower surface height H2 are calculated automatically.
Owner:YELLOW RIVER INST OF HYDRAULIC RES YELLOW RIVER CONSERVANCY COMMISSION
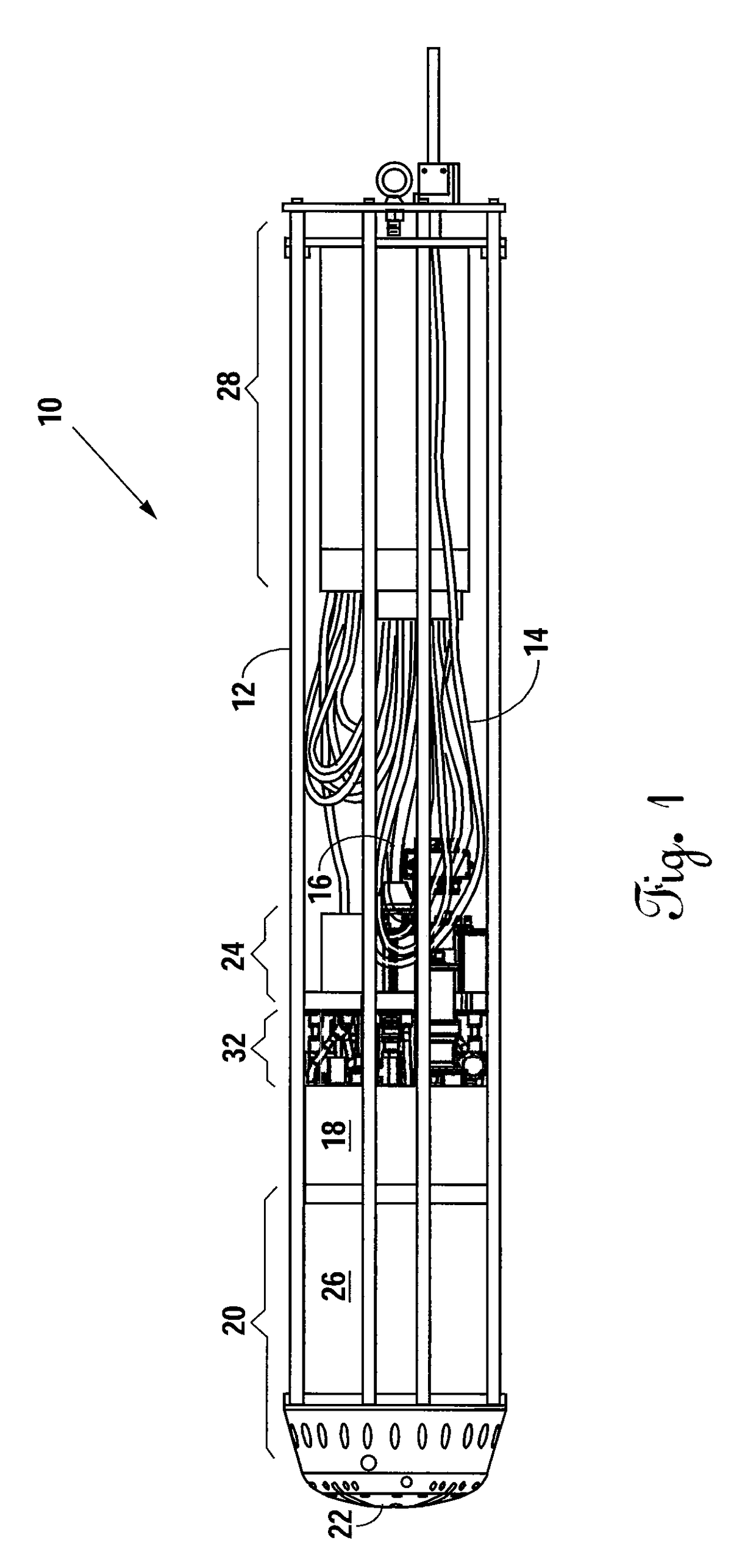
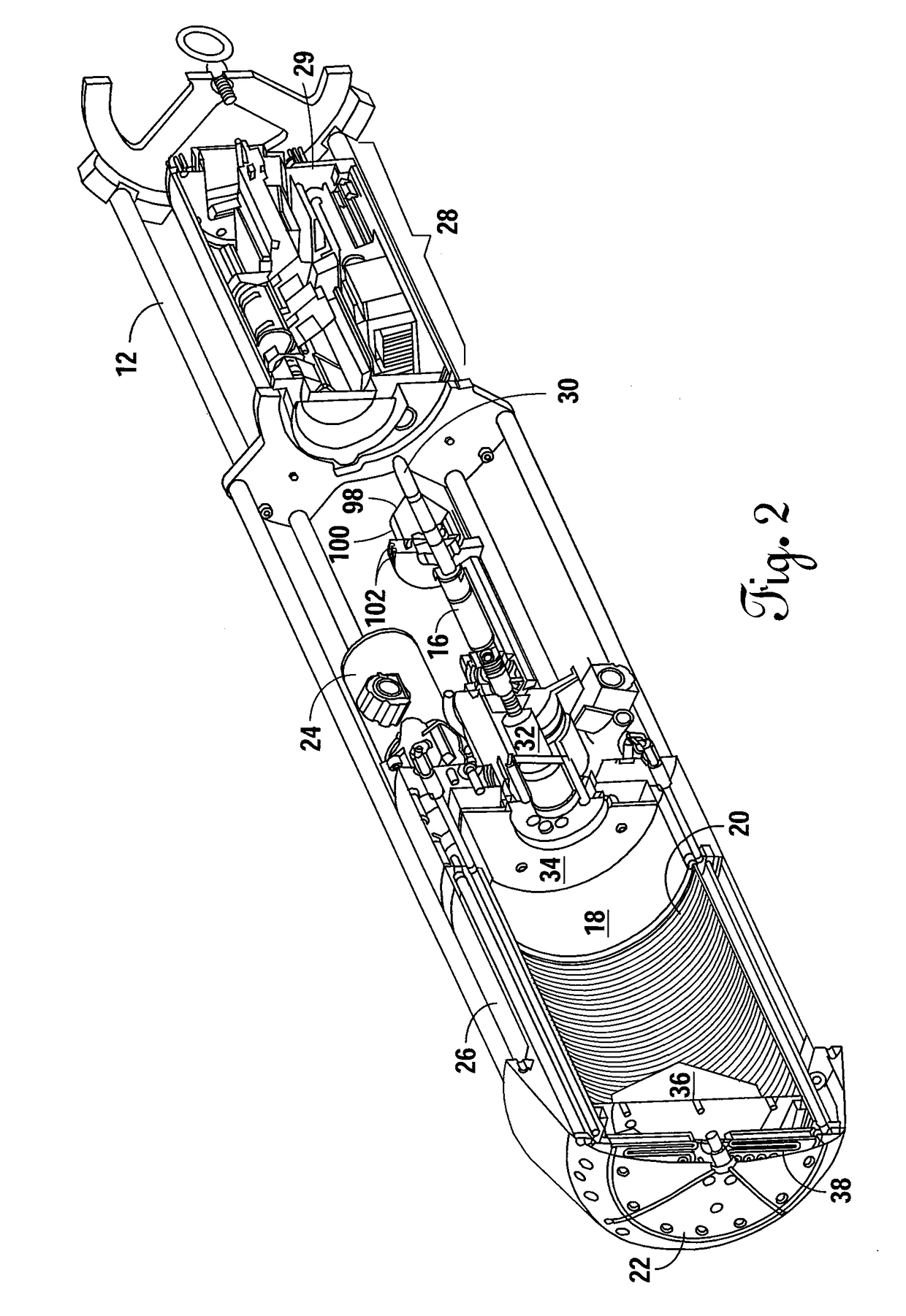
Autonomous Laser-Powered Vehicle
An autonomous laser-powered vehicle designed to autonomously penetrate through ice caps of substantial (e.g., kilometers) thickness by melting a path ahead of the vehicle as it descends. A high powered laser beam is transmitted to the vehicle via an onboard bare fiber spooler. After the beam enters through the dispersion optics, the beam expands into a cavity. A radiation shield limits backscatter radiation from heating the optics. The expanded beam enters the heat exchanger and is reflected by a dispersion mirror. Forward-facing beveled circular grooves absorb the reflected radiant energy preventing the energy from being reflected back towards the optics. Microchannels along the inner circumference of the beam dump heat exchanger maximize heat transfer. Sufficient amount of fiber is wound on the fiber spooler to permit not only a descent but also to permit a sample return mission by inverting the vehicle and melting its way back to the surface.
Owner:STONE AEROSPACE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com