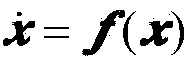Patents
Literature
57 results about "Planetary surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
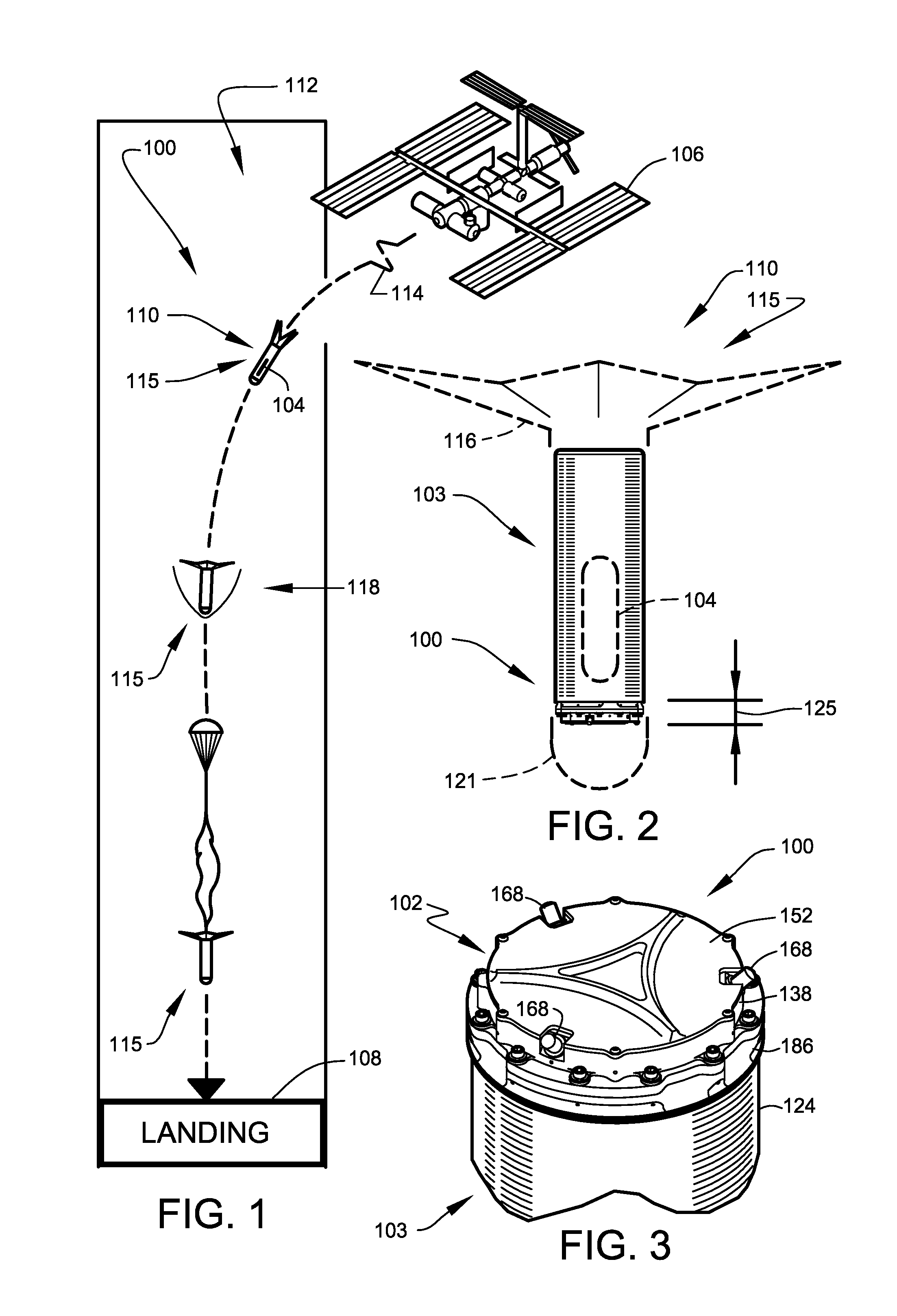
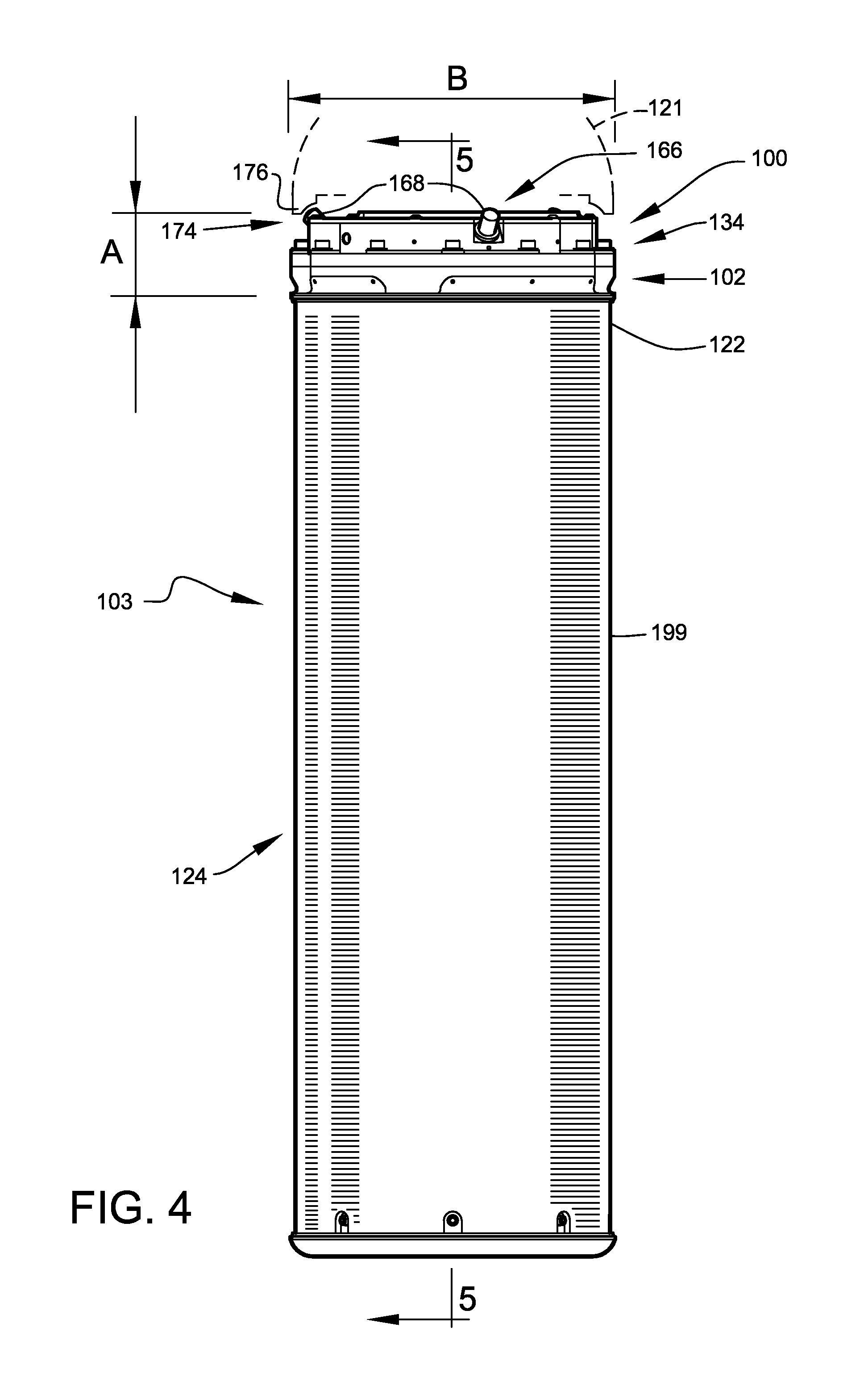
A planetary surface is where the solid (or liquid) material of the outer crust on certain types of astronomical objects contacts the atmosphere or outer space. Planetary surfaces are found on solid objects of planetary mass, including terrestrial planets (including Earth), dwarf planets, natural satellites, planetesimals and many other small Solar System bodies (SSSBs). The study of planetary surfaces is a field of planetary geology known as surface geology, but also a focus of a number of fields including planetary cartography, topography, geomorphology, atmospheric sciences, and astronomy. Land (or ground) is the term given to non-liquid planetary surfaces. The term landing is used to describe the collision of an object with a planetary surface and is usually at a velocity in which the object can remain intact and remain attached.
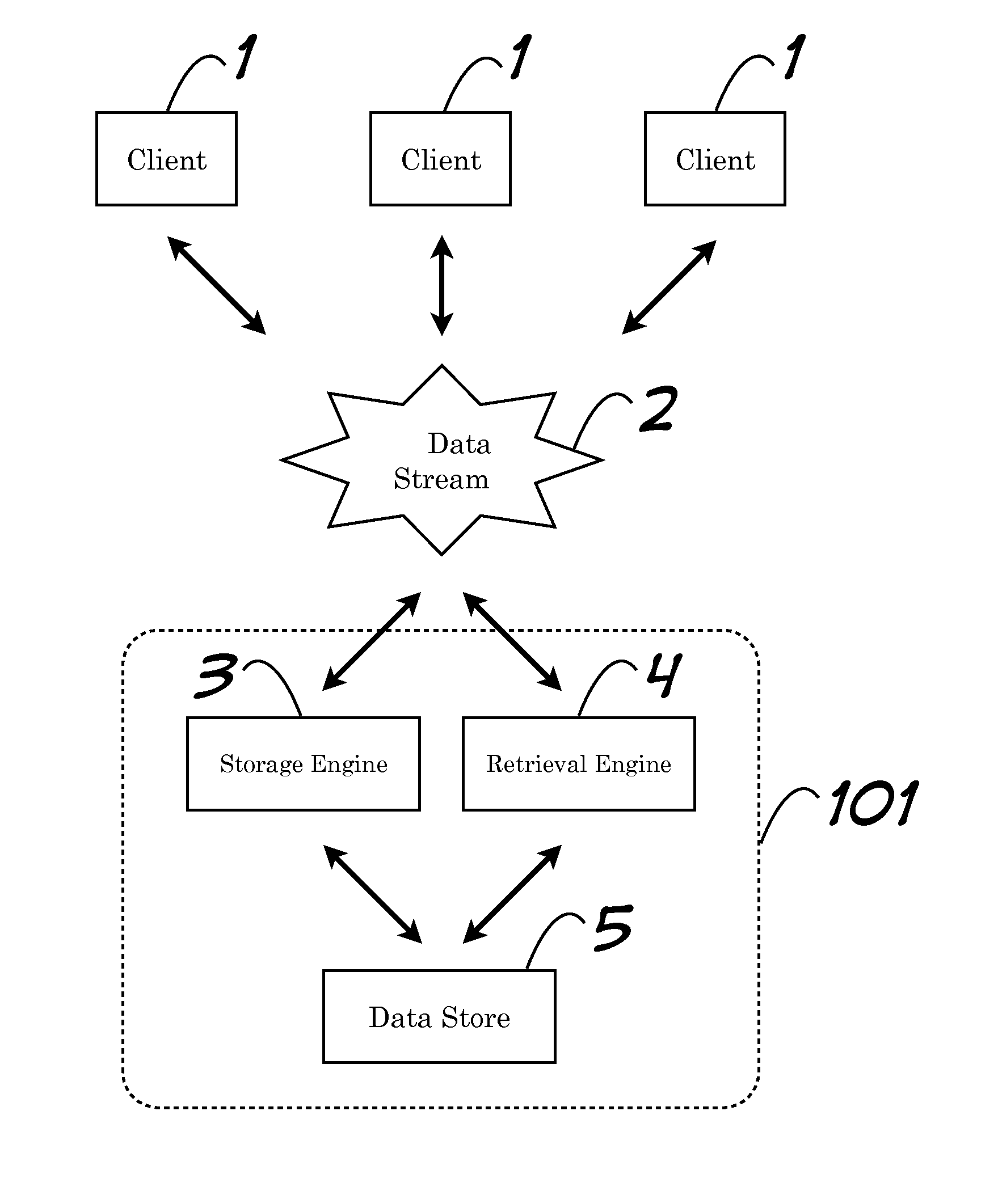
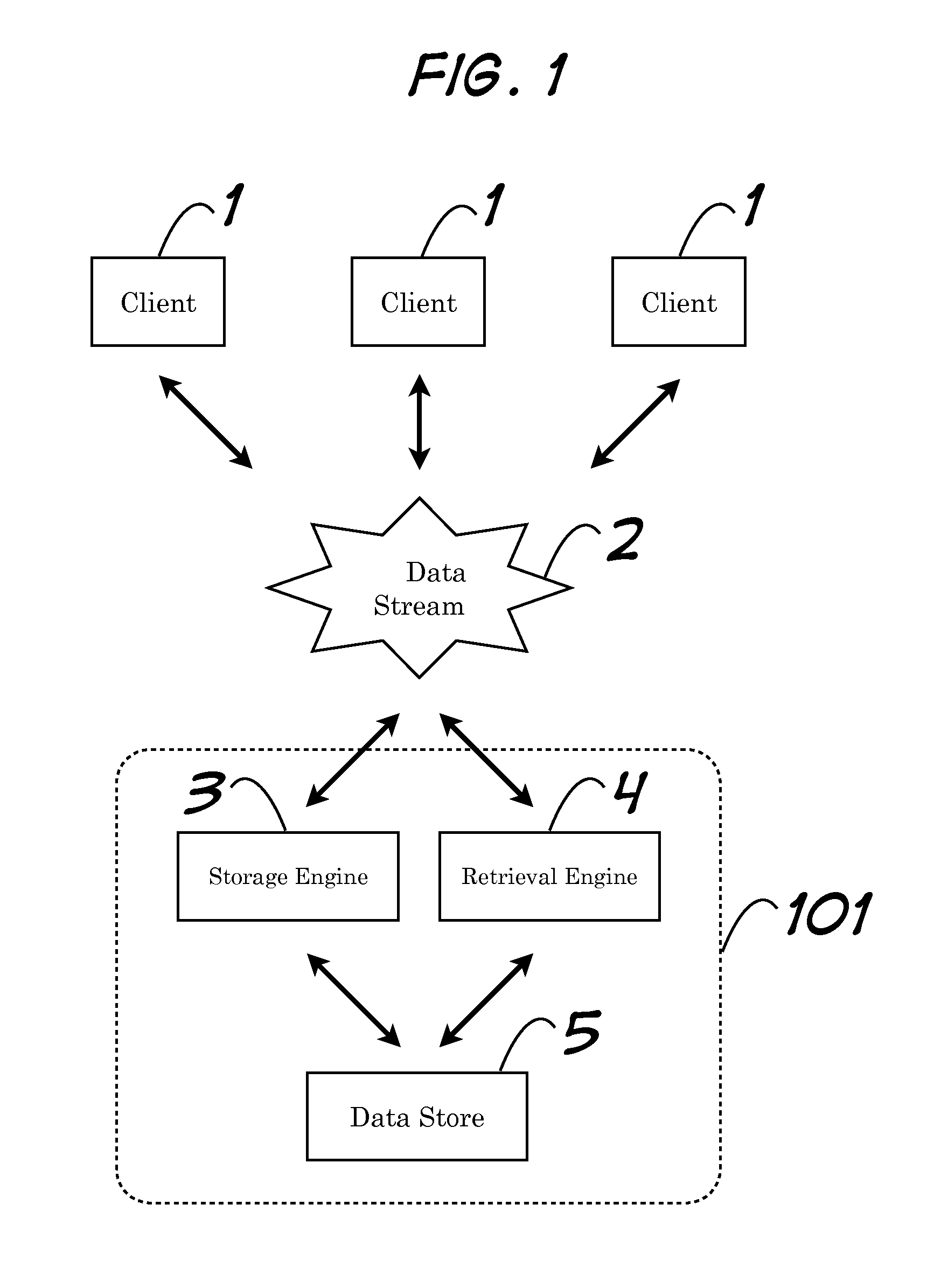
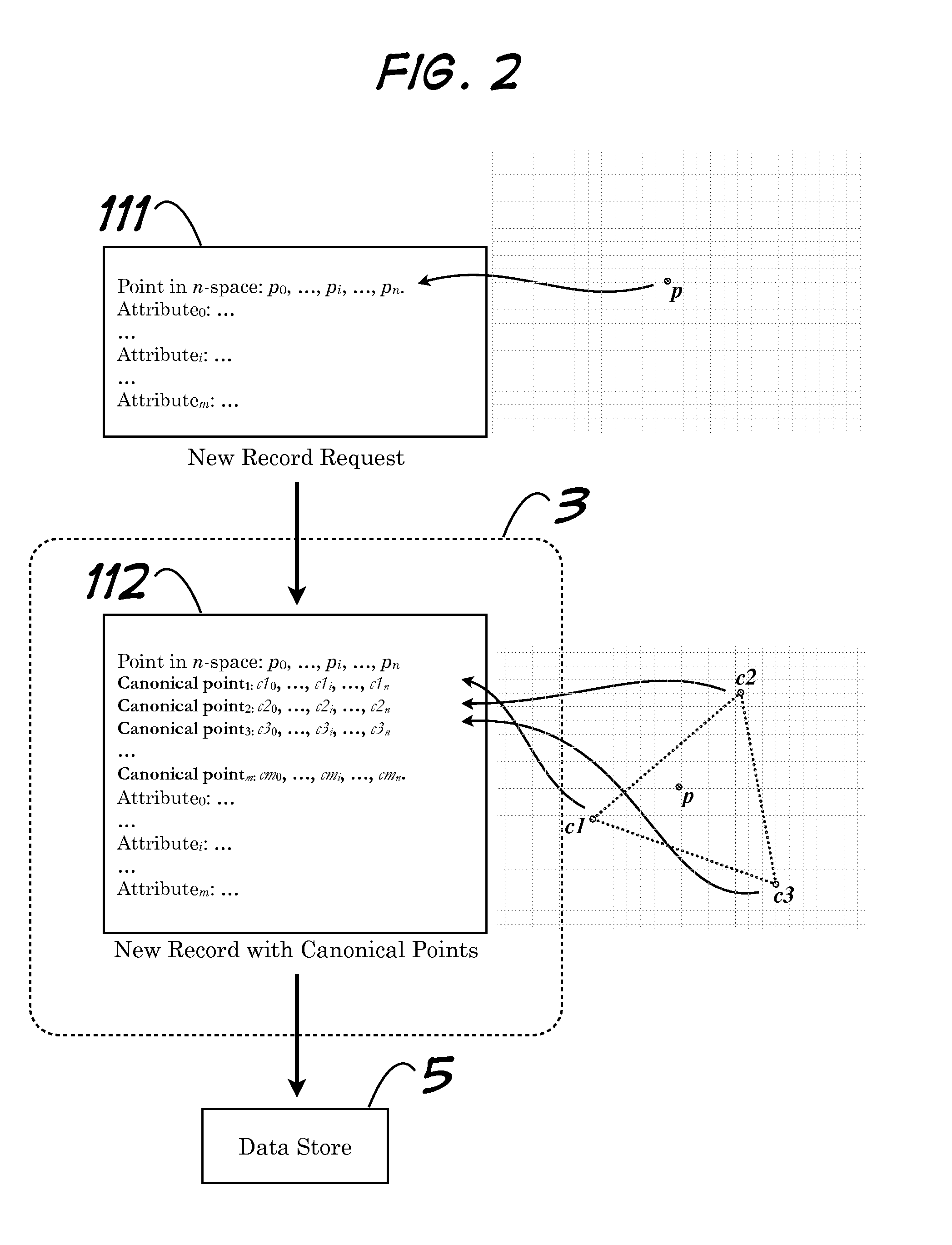
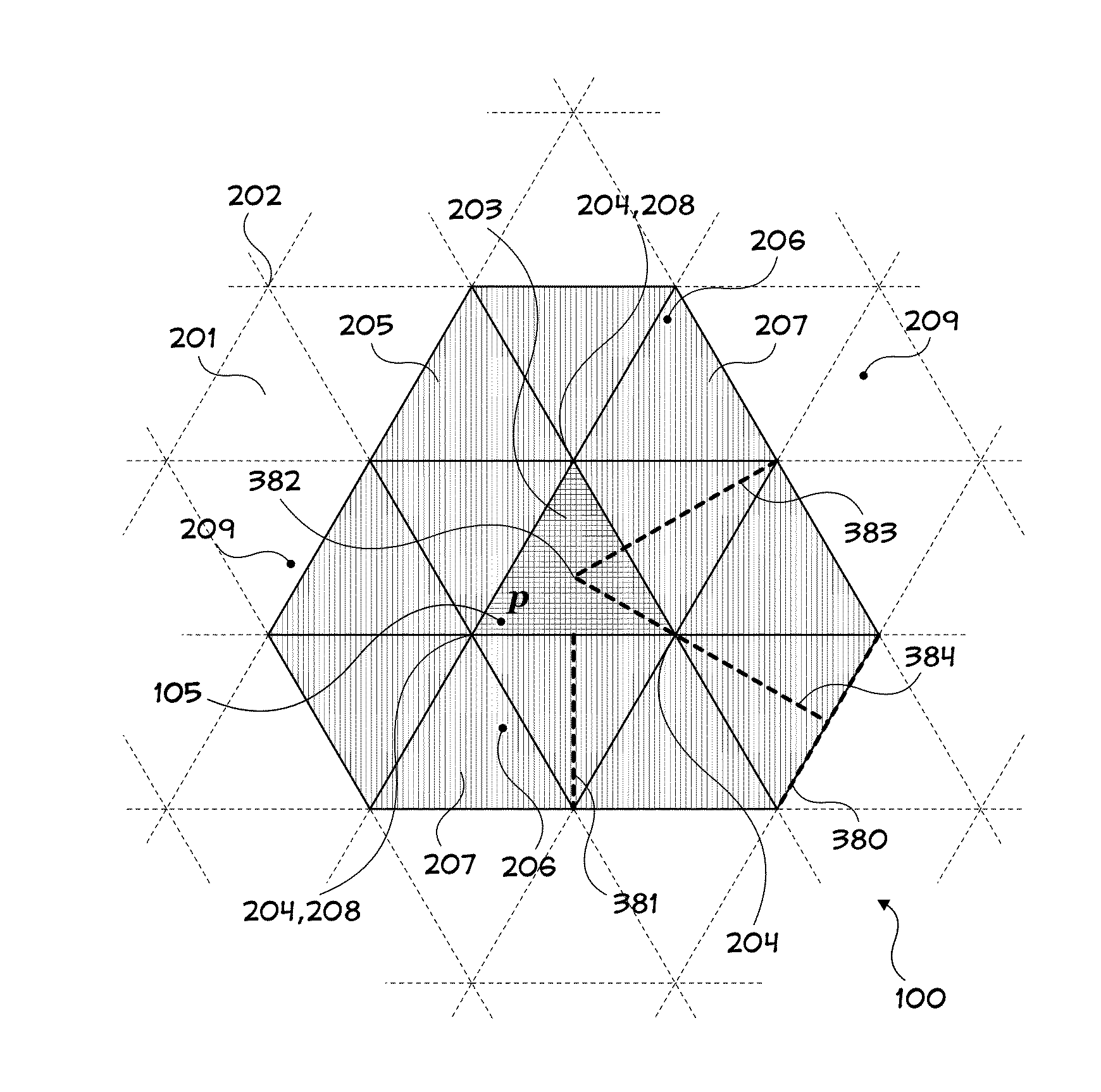
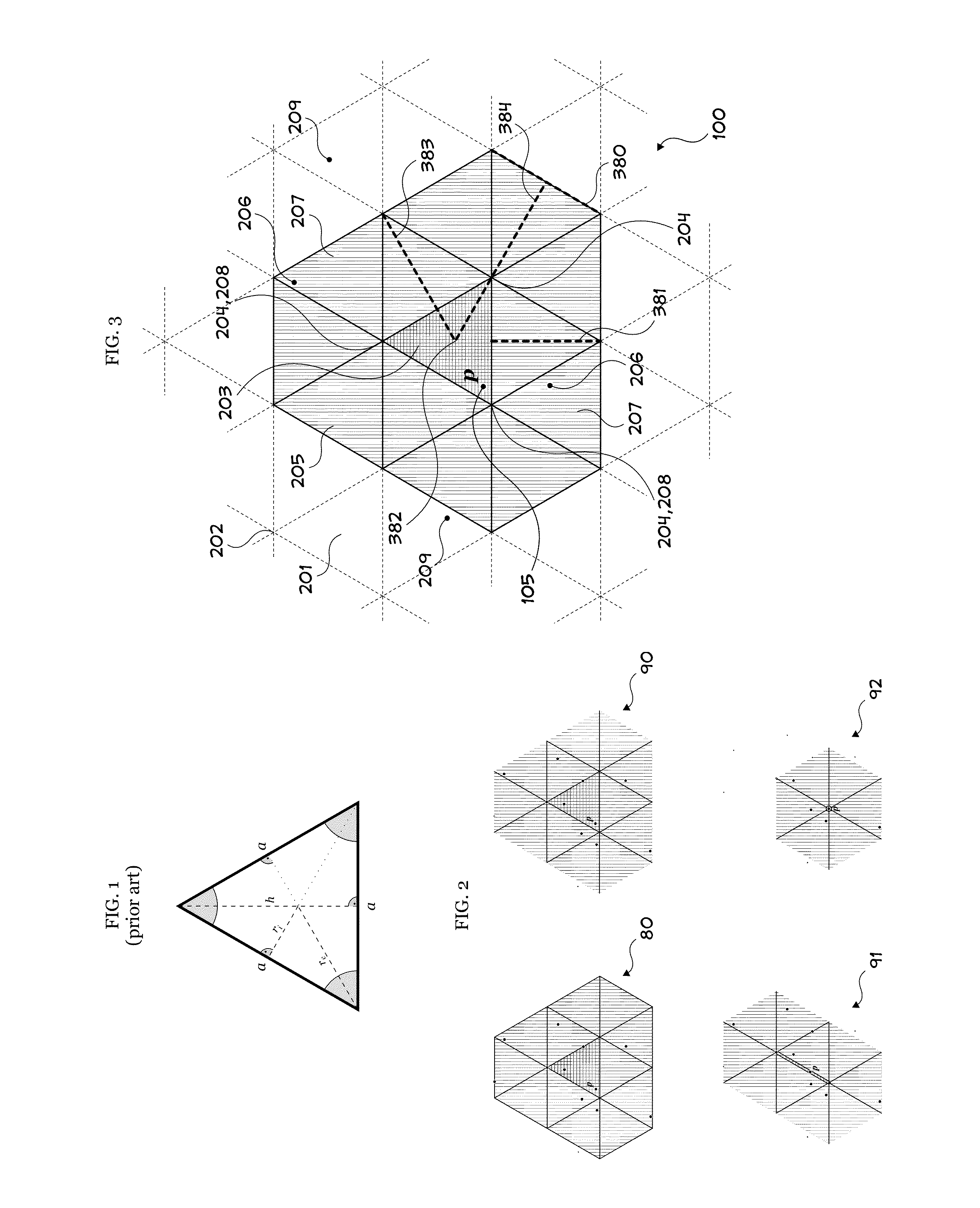
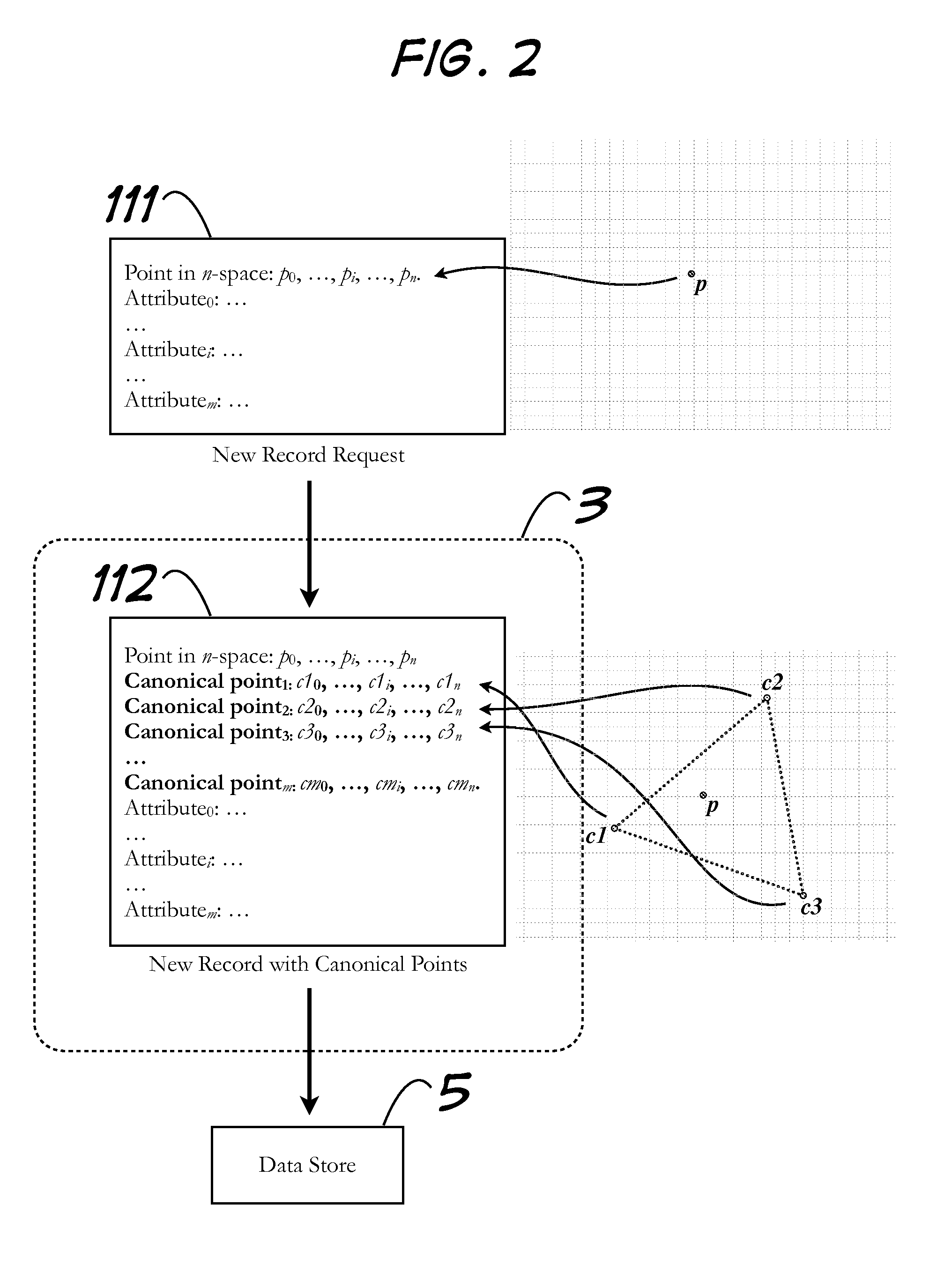
Storage of Arbitrary Points in N-Space and Retrieval of Subset Thereof Based on Criteria Including Maximum Distance to an Arbitrary Reference Point
InactiveUS20130339411A1Effective meanAffect efficiencyDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProximity measureComputer science
Systems and methods pertaining to nearness calculations of points in n-space. Among the embodiments is associating points of interest with point records in a data store, and efficient retrieval of subsets of those point records which meet arbitrary criteria. Criteria can limit retrieval to neighbors of a reference point (i.e., point records associated with points of interest whose home cells that share at least one interface with another designated home cell. Computationally expensive, at-retrieval range calculations are avoided by performing complimentary calculations at-storage and saving them with related records. The invention is appropriate for use with data storage mechanisms which limit inequality or range operations, or for which such operations result in inefficiencies. When used to model neighboring points on a planetary surface in 3-space, the invention does not suffer from polar distortion (where spherical coordinate systems have difficulty).
Owner:BOGOSIAN MATTHEW THOMAS
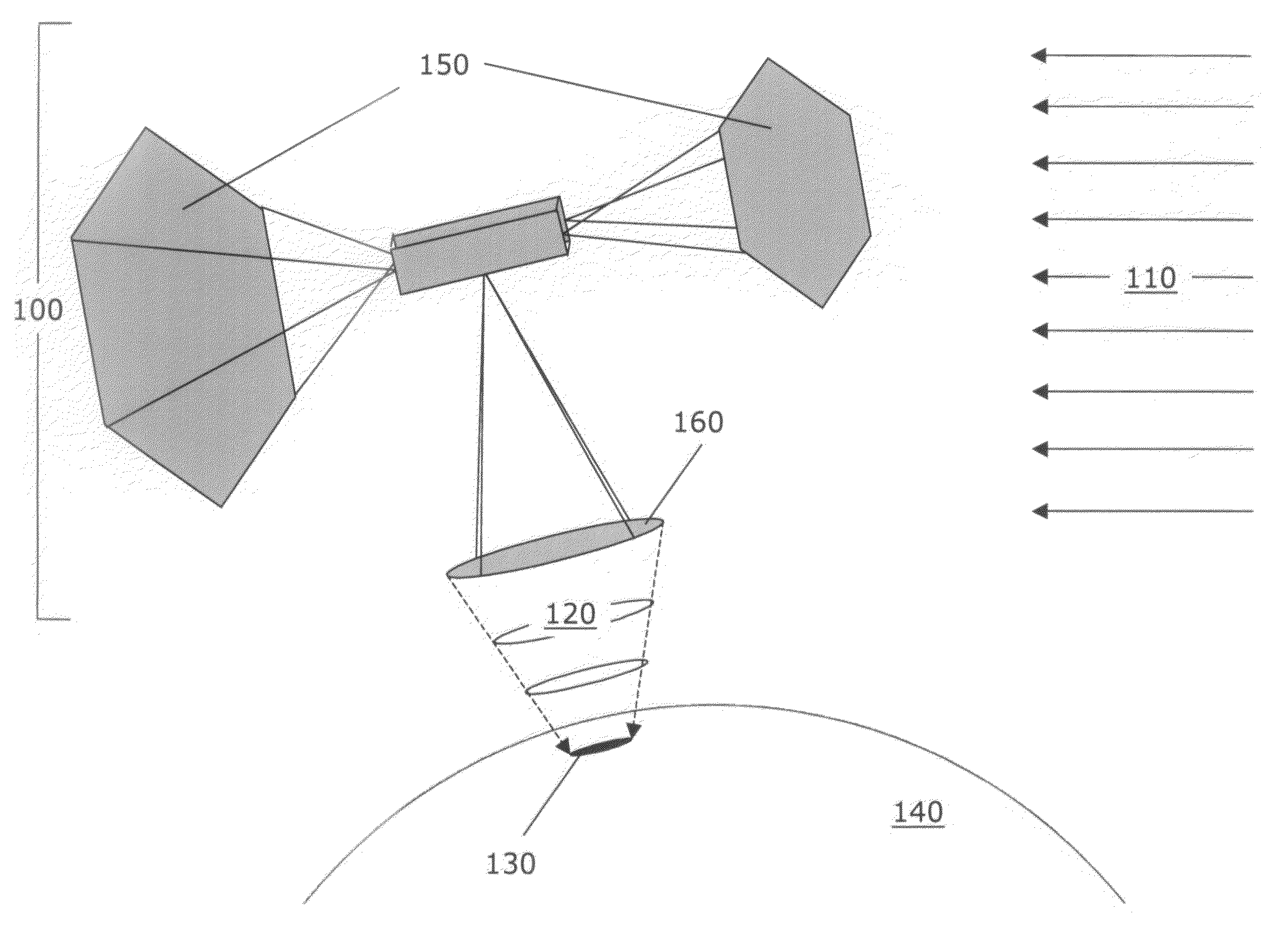
Space solar power system for thermochemical processing and electricity production
InactiveUS20080283109A1Promote absorptionImprove abilitiesSolar heating energyThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentProcess systemsElectricity
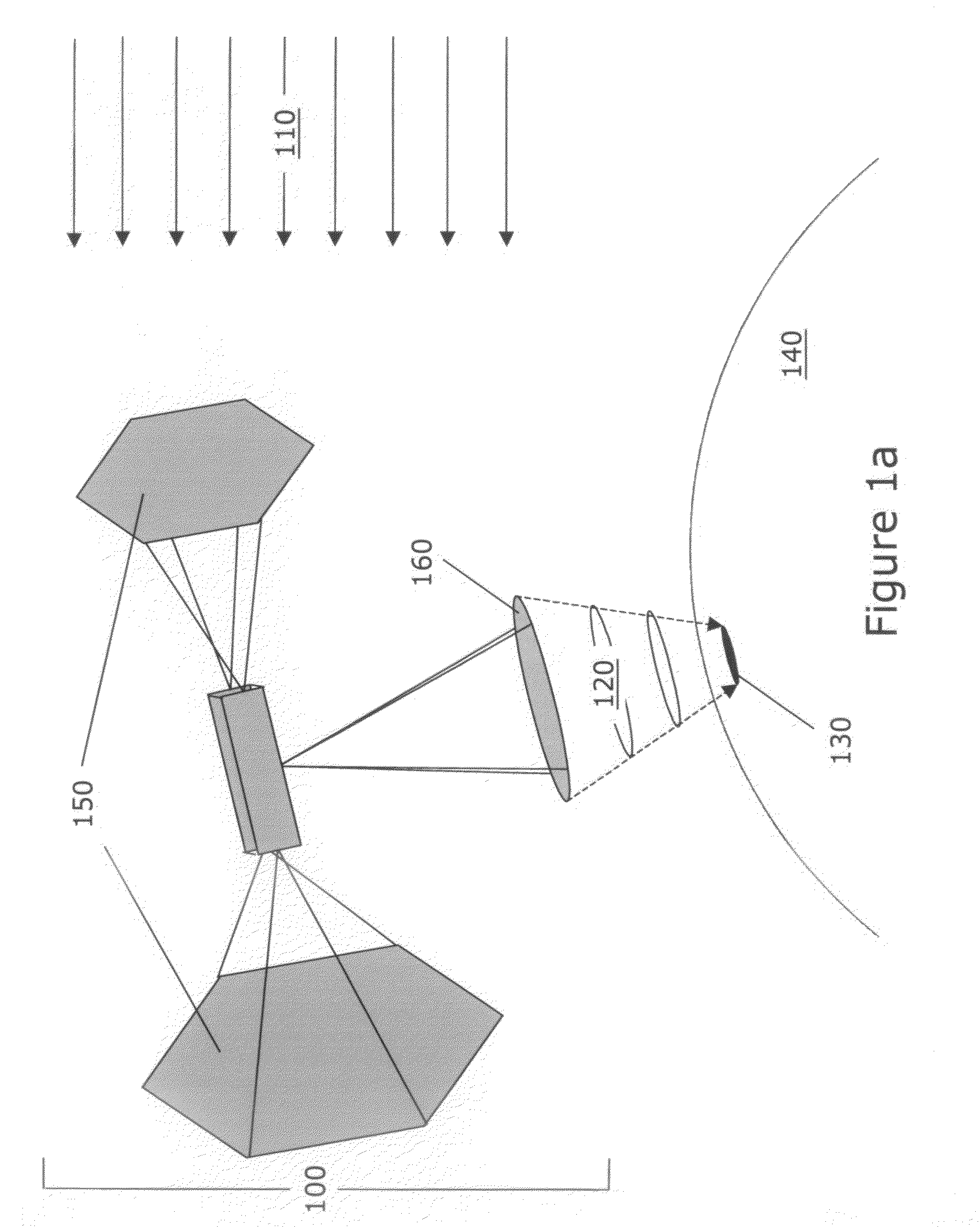
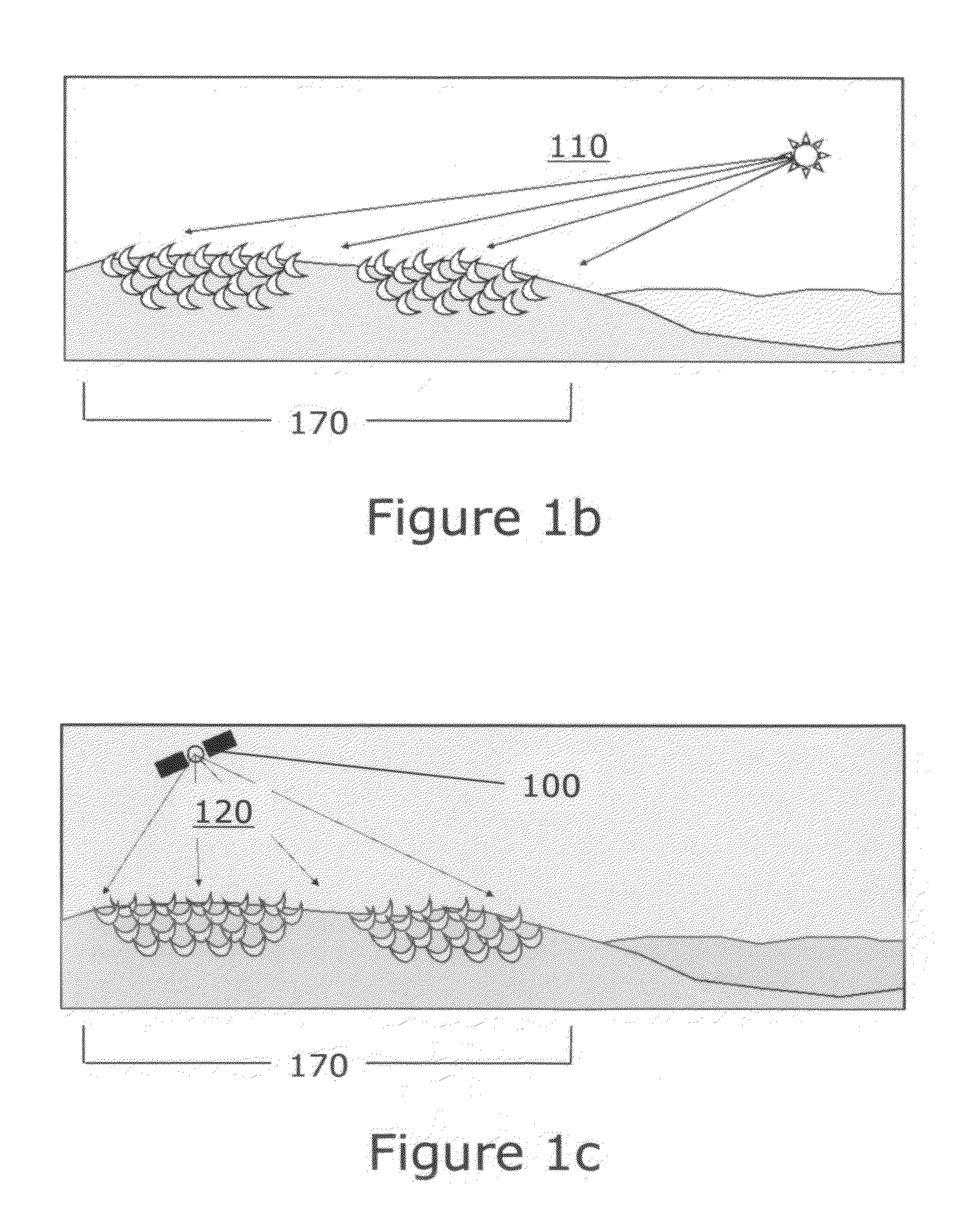
Thermochemical processing systems for the production of electricity and chemicals using energy from an orbiting space solar power satellite (100). Methods of producing electricity and chemicals using the powerbeam (120). Systems and applications include the orbiting satellite, which intercepts solar energy (110) and directs a powerbeam to a lunar or planetary surface or a receiving system in space; rectennas (220) for the production of electricity; and concentrators (300), receivers (310) and thermochemical process systems for the production of fuels and other chemicals. Efforts are made to optimize the operation of the system through the utilization of solar energy, when available, plus the powerbeam from the satellite.
Owner:MANKINS JOHN CARLTON +1
Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar system and method
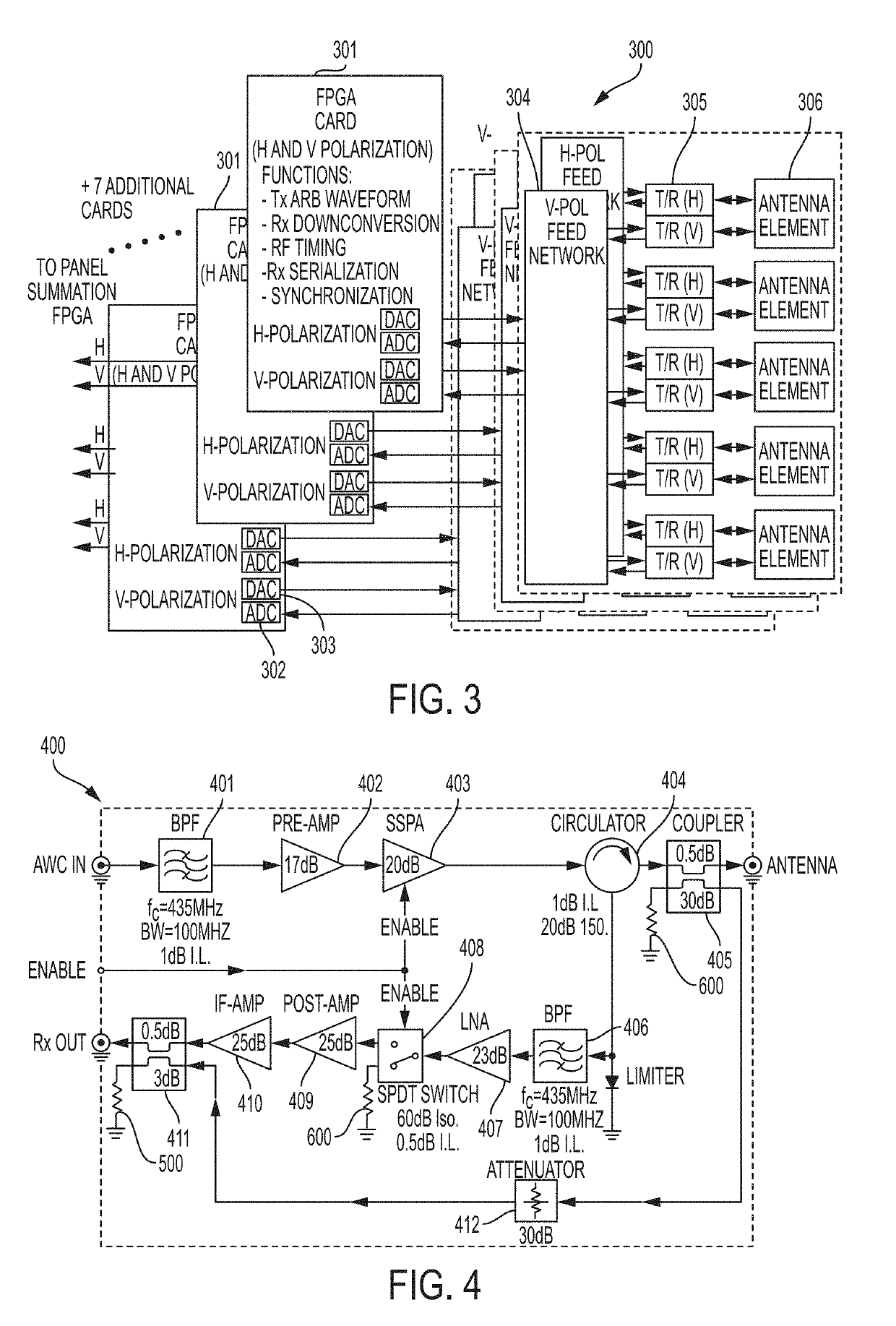
ActiveUS20190101639A1High resolution measurementReduce development costsModular arraysElectrically short antennasFreeze thawingSynthetic aperture sonar
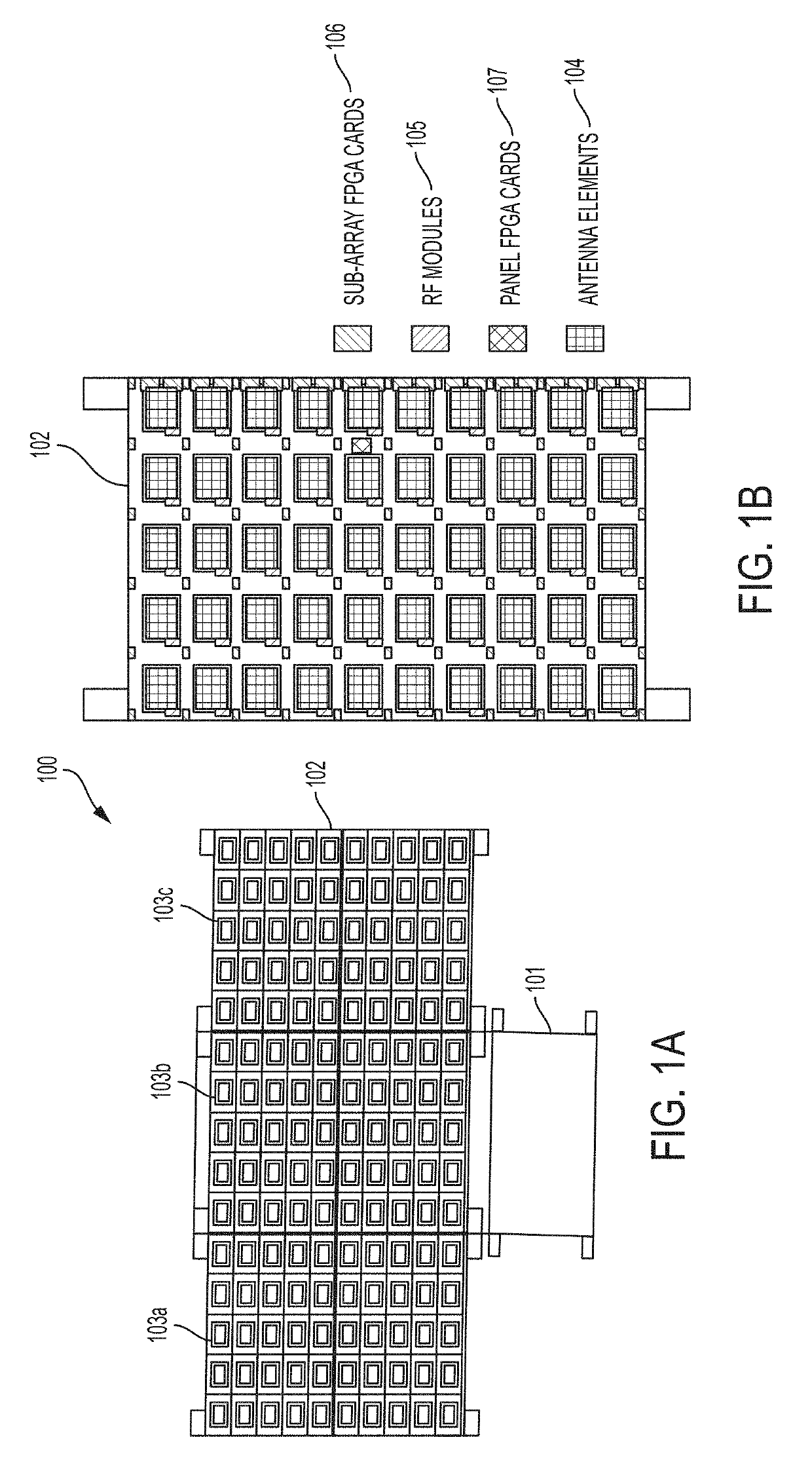
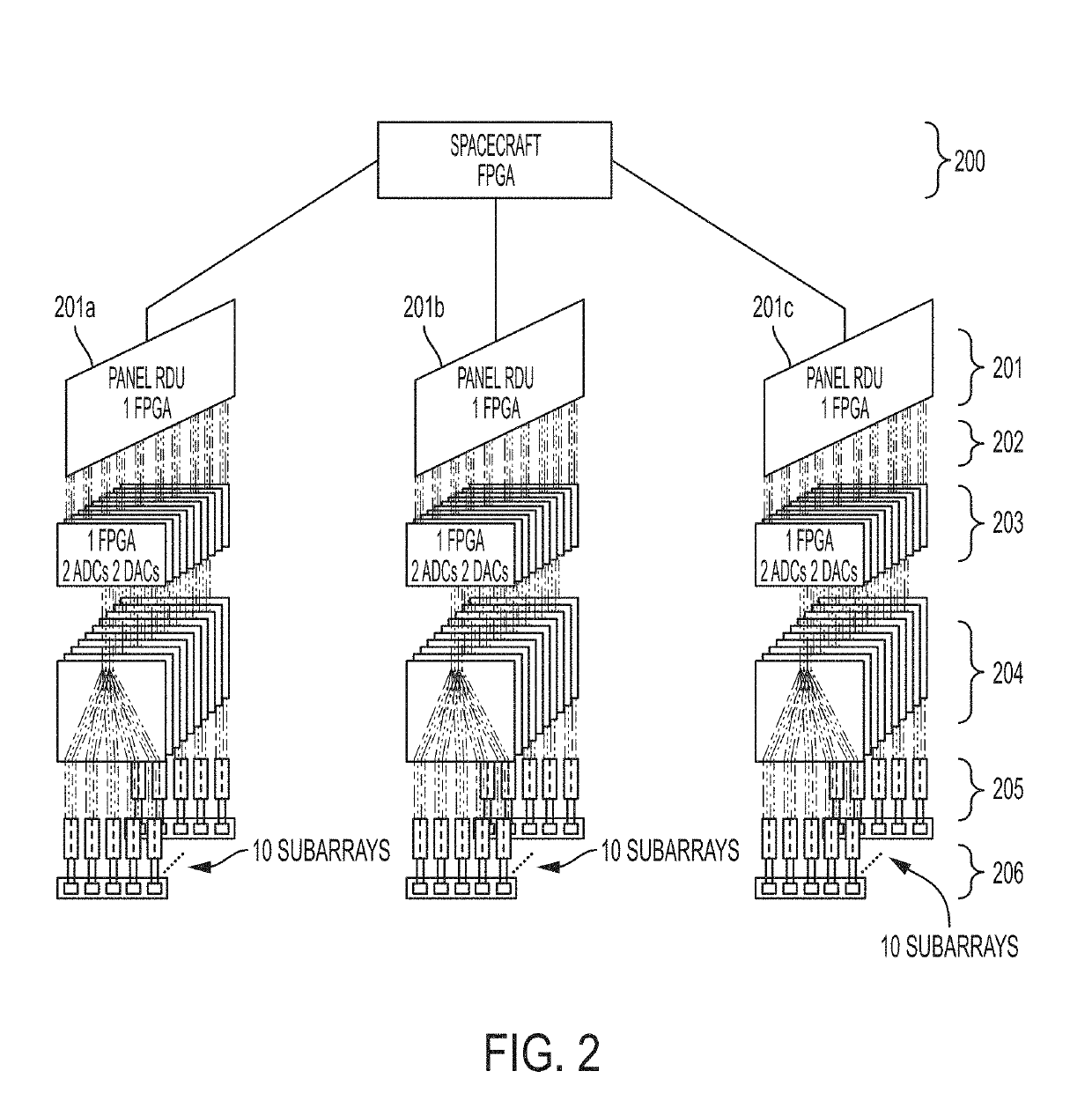
The present invention relates to an advanced spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system and method that can provide high resolution measurements of the Earth or planetary surface, overcoming limitations in conventional SAR systems, and reduce development costs. The present invention utilizes advanced and innovative techniques, such as software defined waveforms, digital beamforming (DBF) and reconfigurable hardware, to provide radar capabilities not possible with conventional radar instruments, while reducing the radar development cost. The SAR system architecture employs a modular, low power, lightweight design approach to meet stringent spaceborne radar instrument requirements. Thus, the present invention can enable feasible Earth and planetary missions that address a vast number survey goals, including the measurement of ecosystem structure and extent, surface and sub-surface topography, subsurface stratigraphy, soil freeze-thaw, ice sheet composition and extent, glacier depth, and surface water, among many others.
Owner:NASA
A power system for a rocket-powered Mars transport aircraft
InactiveCN109018444ASimple structureWith posture adjustment functionCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusAttitude controlGas cylinder
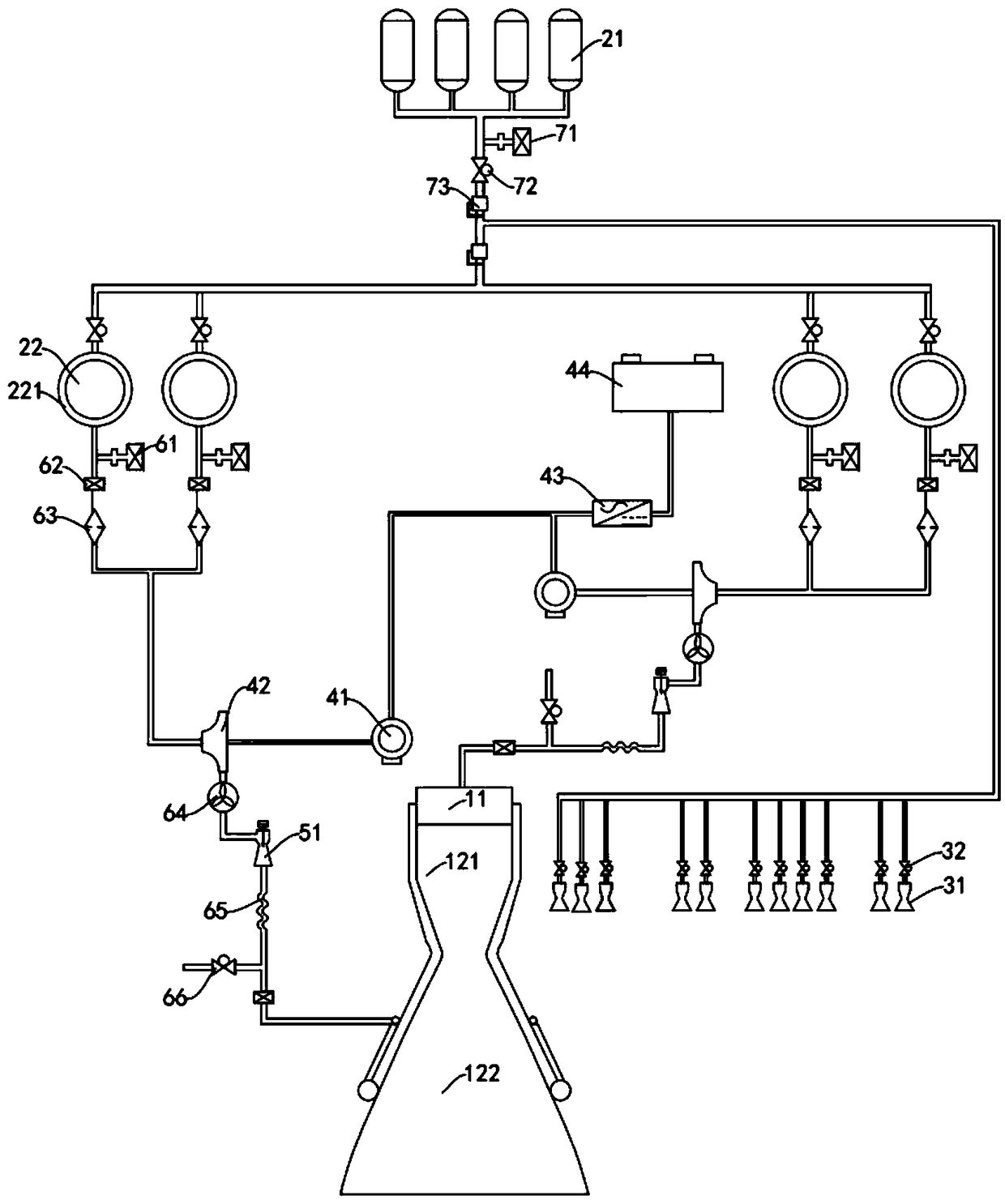
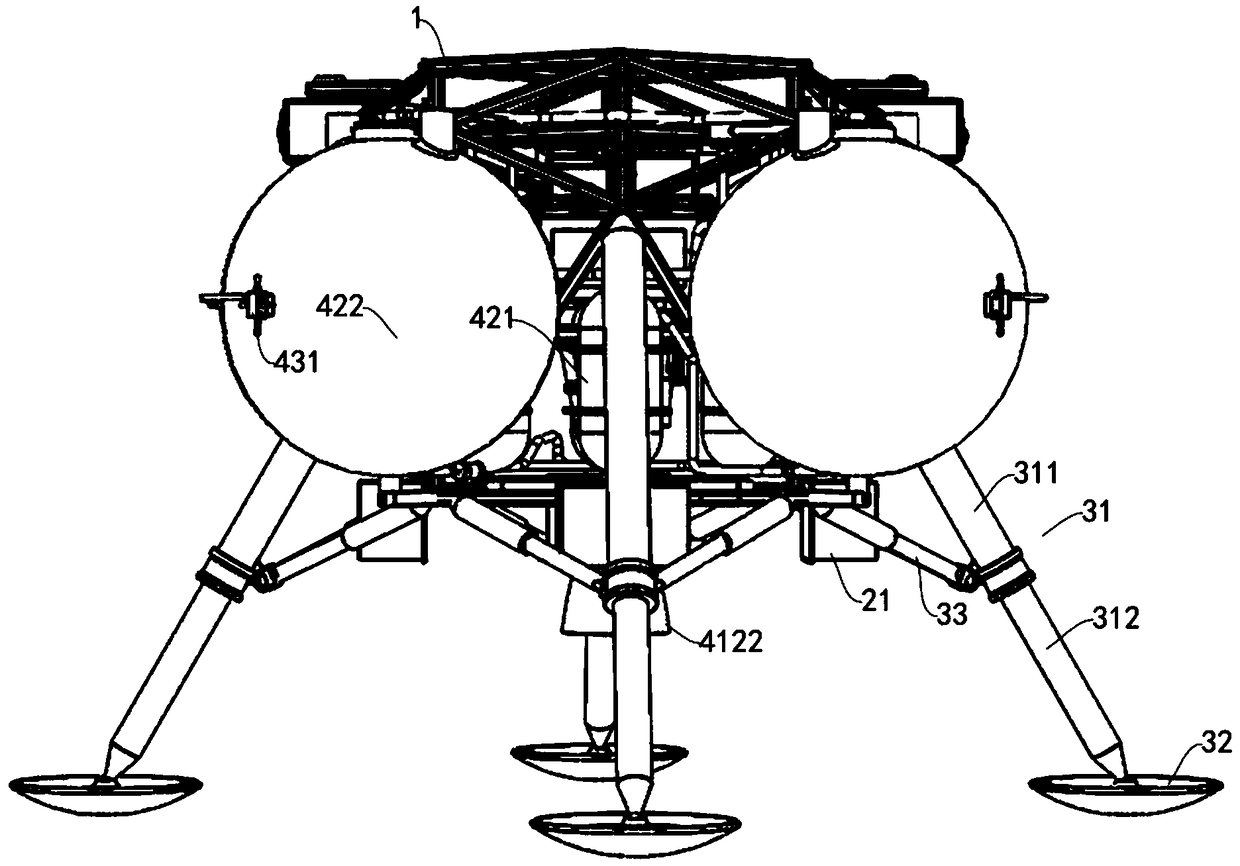
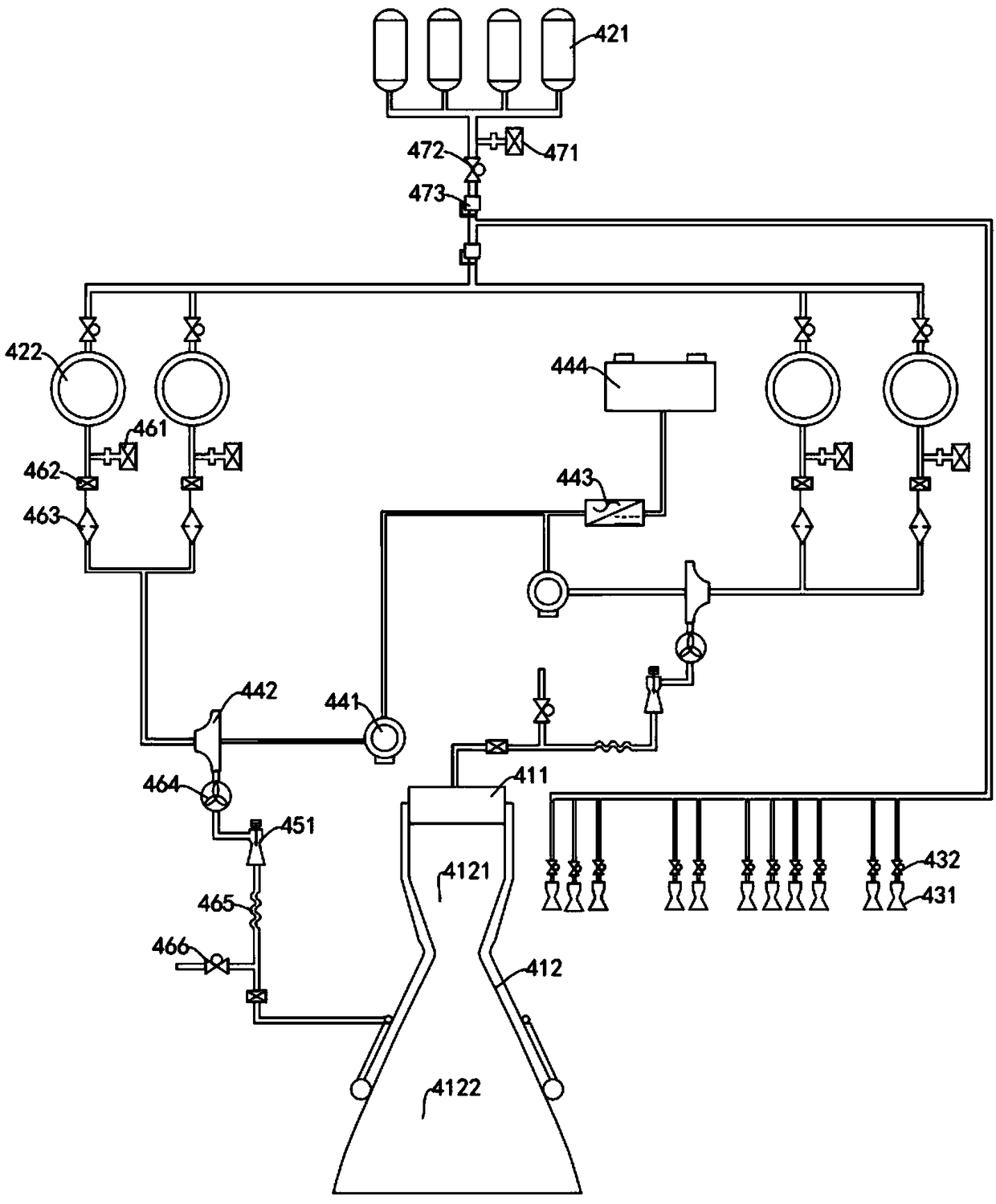
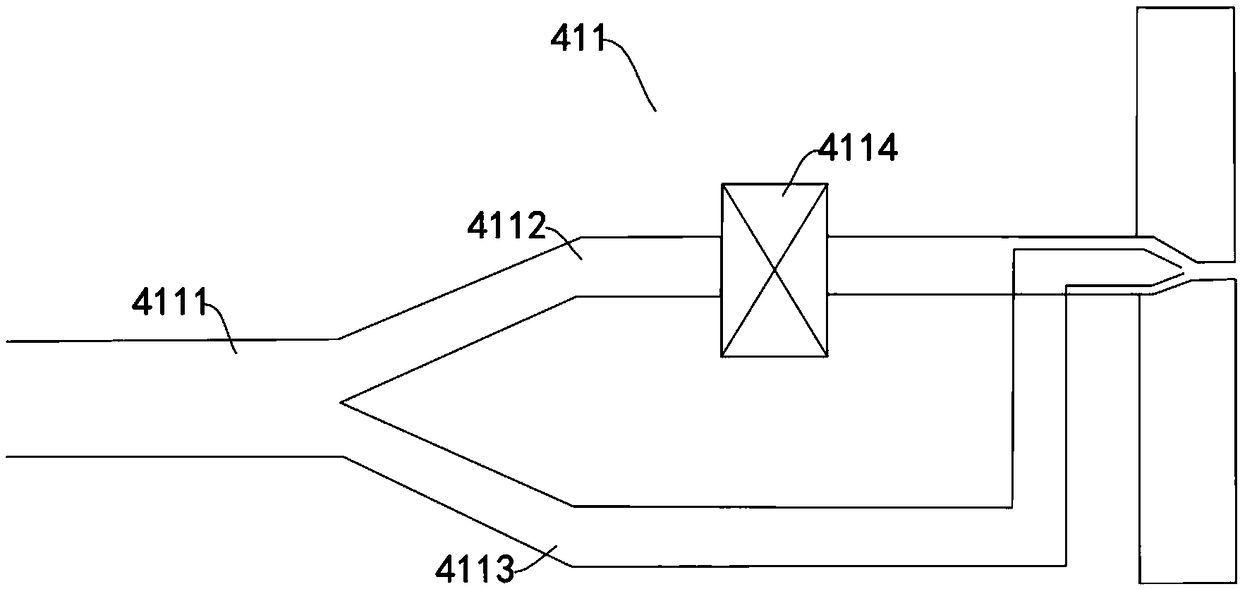
The invention provides a power system of a rocket-powered Mars transport aircraft, comprising a main engine, an energy sub-system, an attitude control sub-system, a boosting sub-system and a variablethrust sub-system. The power subsystem includes an injector, an igniter and a thrust chamber. The energy subsystem comprises a battery, a high-pressure gas cylinder and a storage tank, wherein the high-pressure gas cylinder and the storage tank are communicated with each other through pipelines, and the storage tank and the injector are communicated with each other through pipelines; The attitudecontrol subsystem comprises a plurality of attitude control engines, wherein each attitude control engine is annularly spaced on the side of a Mars transport aircraft, and a high-pressure gas cylinderis connected with each attitude control engine through pipelines. The attitude control subsystem comprises a plurality of attitude control engines, wherein each attitude control engine is annularly spaced on the side of a Mars transport aircraft. By sharing a set of high pressure cylinders with the attitude control engine and the tank, The structure of the power system is simplified, the tank pressure is reduced, the tank mass is lightened, and the pressure of the thrust chamber is increased by boosting the pressure of the boosting sub-system. The attitude adjustment function of the power system is realized by the attitude control sub-system, and the variable thrust sub-system is realized by the variable thrust sub-system, so the power system has the variable thrust function. The invention is applied to the field of planetary surface flight.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
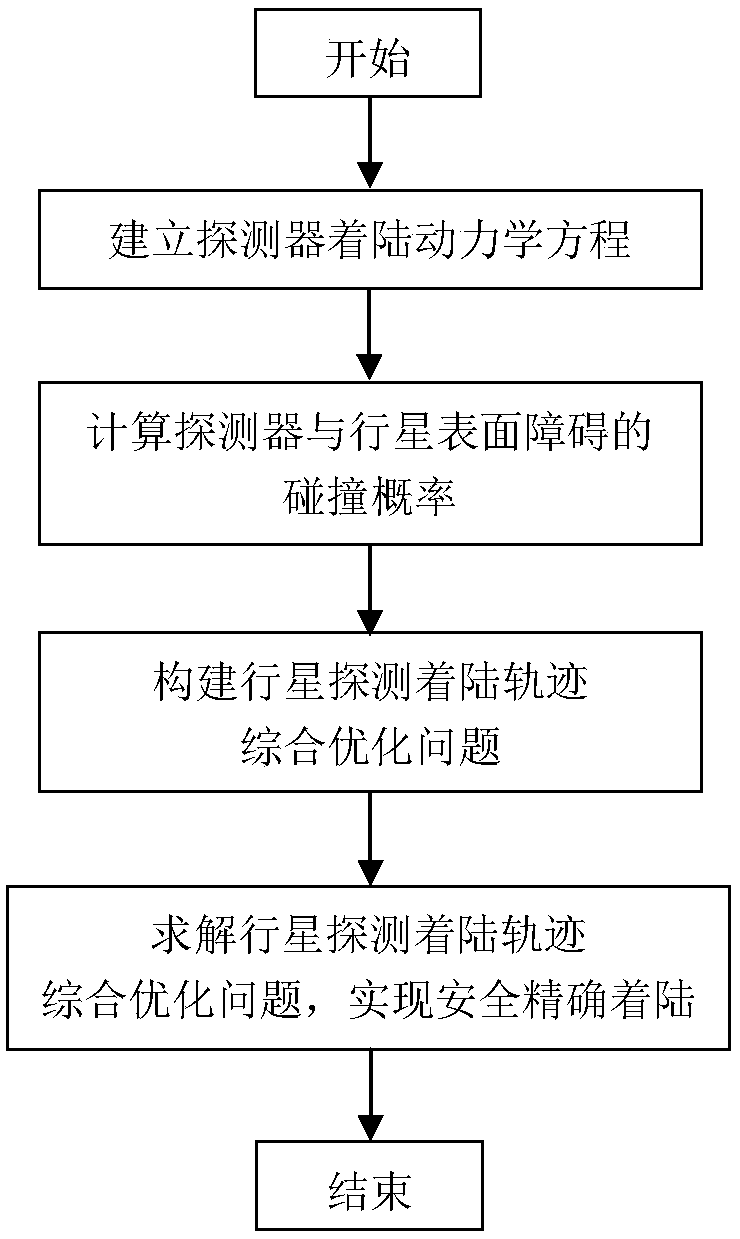
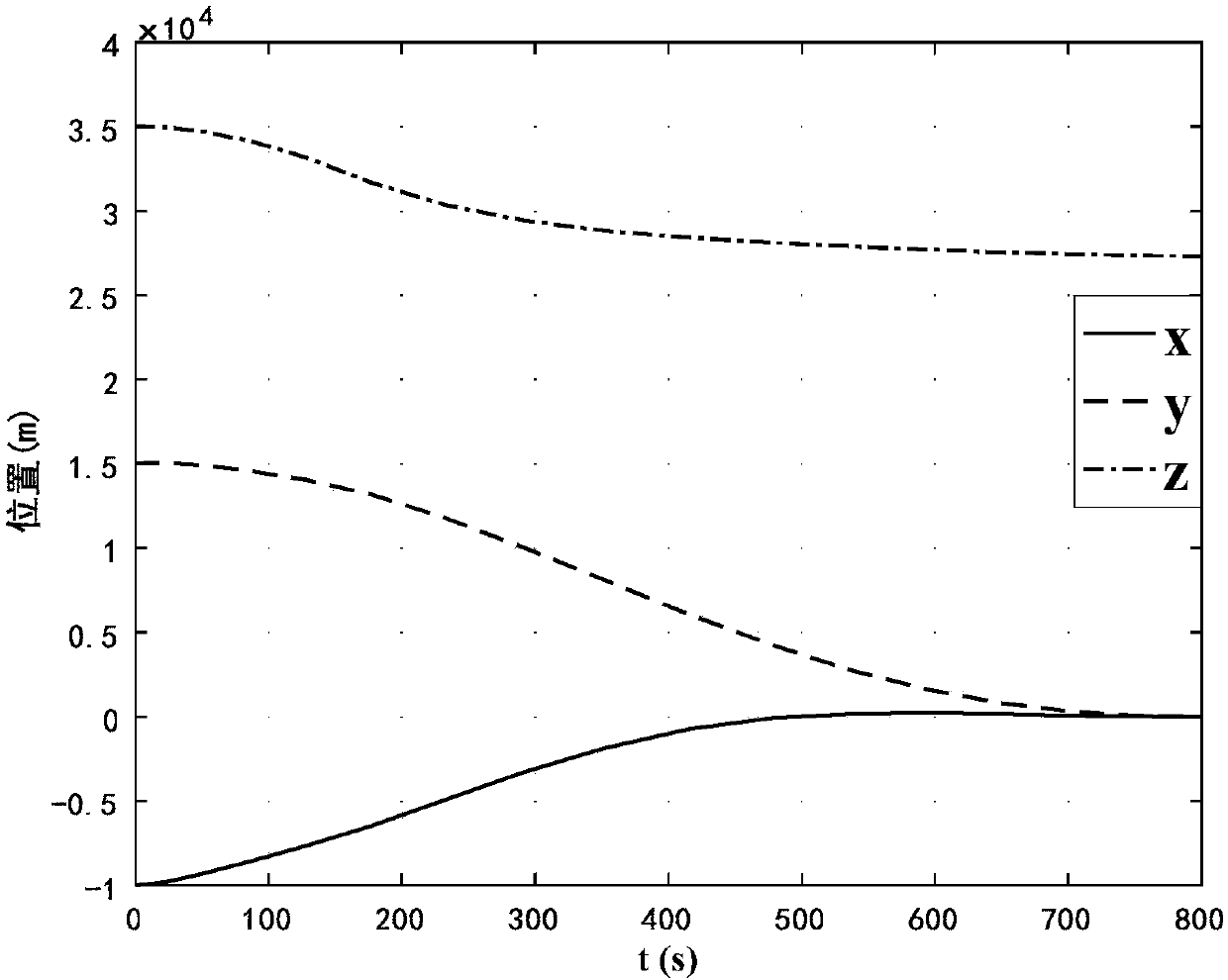
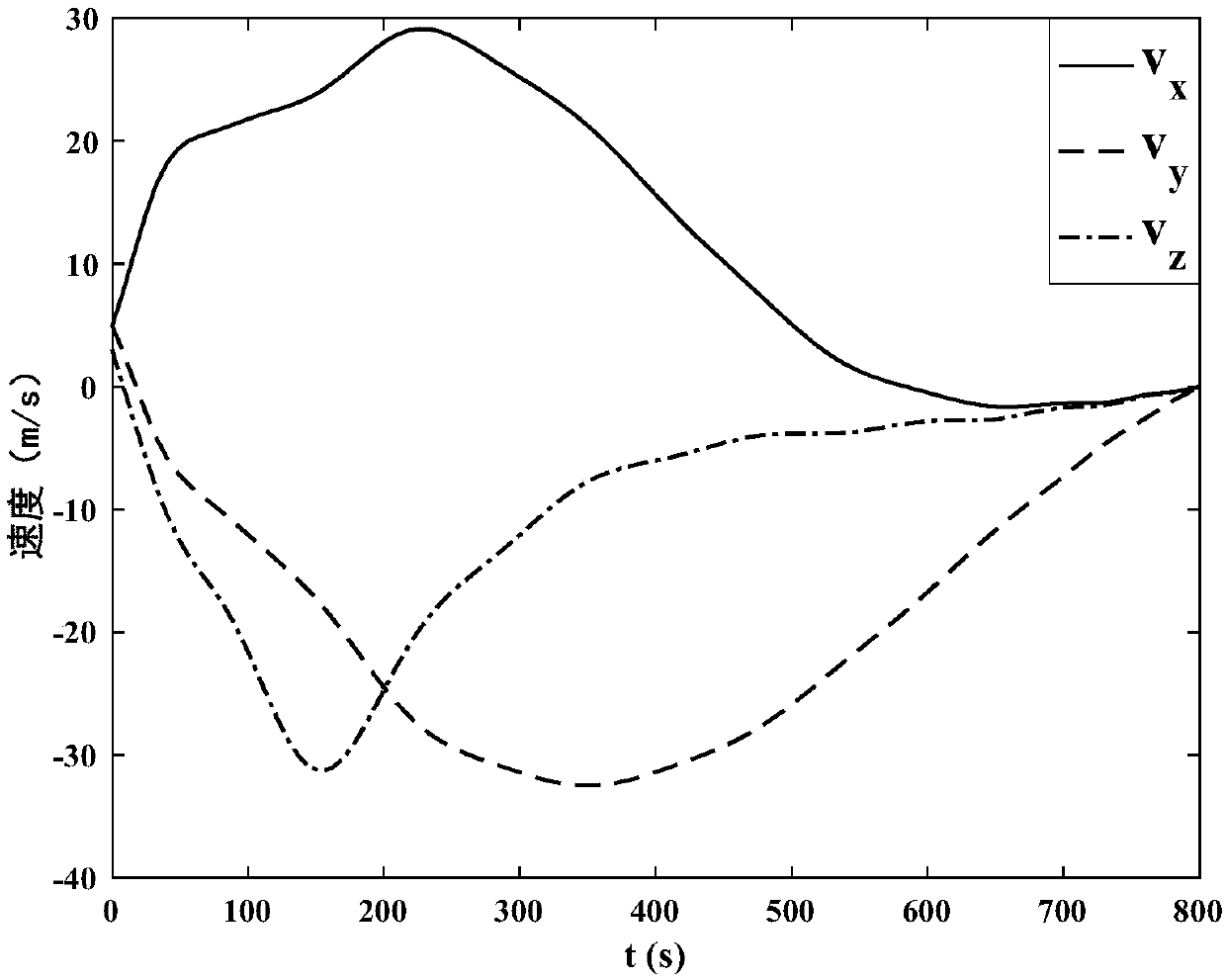
Planetary exploration landing trajectory comprehensive optimization method
ActiveCN108279011ASafe and precise landingReduce consumptionInstruments for comonautical navigationForecastingTerrainDynamic equation
The invention discloses a planetary exploration landing trajectory comprehensive optimization method, and relates to a planetary landing trajectory optimization method, belonging to the field of deepspace exploration. The method is implemented by the following steps: establishing a detector landing dynamics equation; calculating the probability of collision between a detector and planetary surface obstacles; setting up a planetary exploration landing trajectory comprehensive optimization problem by taking the uncertainty of fuel consumption performance and planetary landing as well as the complex terrain conditions of the obstacles existing on the planet surface into account; solving the planetary exploration landing trajectory comprehensive optimization problem, and completing the comprehensive optimization of the planetary exploration landing trajectory by taking the uncertainty of fuel consumption performance and planetary landing as well as the complex terrain conditions of the obstacles existing on the planet surface into account so as to realize safe and accurate landing. In addition, in the calculation of the collision probability, the description of the degree of threat tothe detector under the condition of uncertainty is more accurate. By simplifying a collision probability formula, the calculation amount is reduced and the optimization speed is accelerated under thepremise of guaranteeing accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
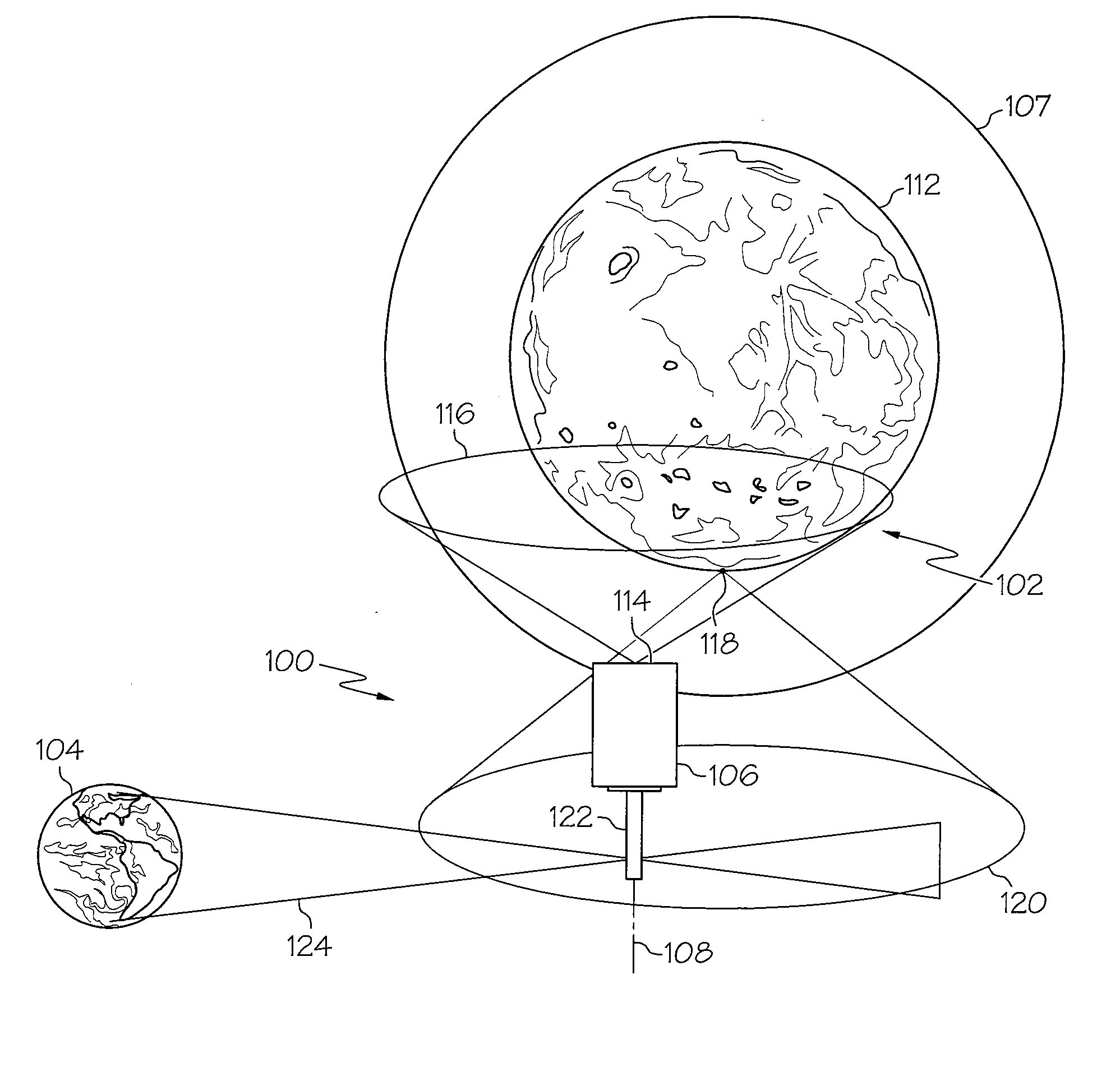
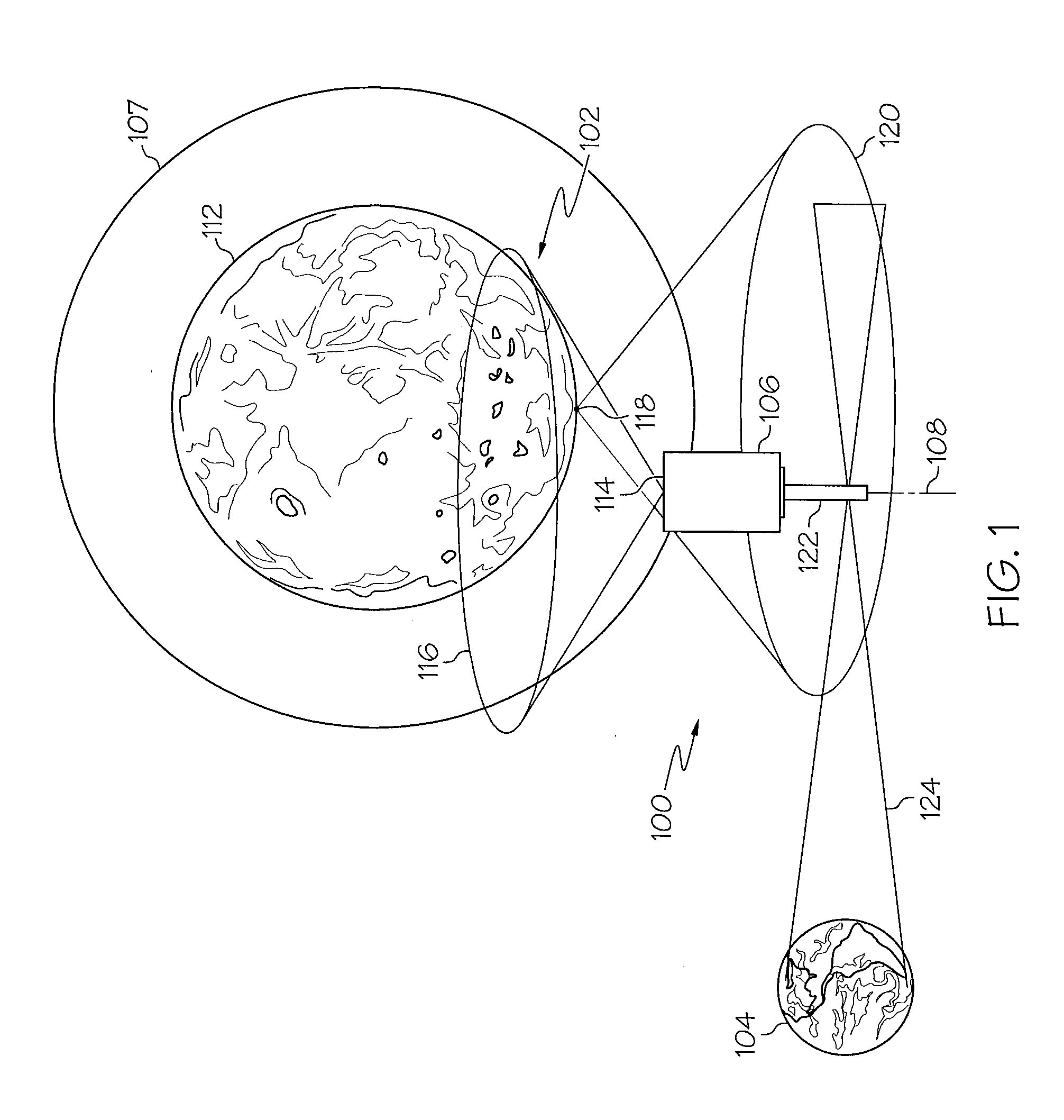
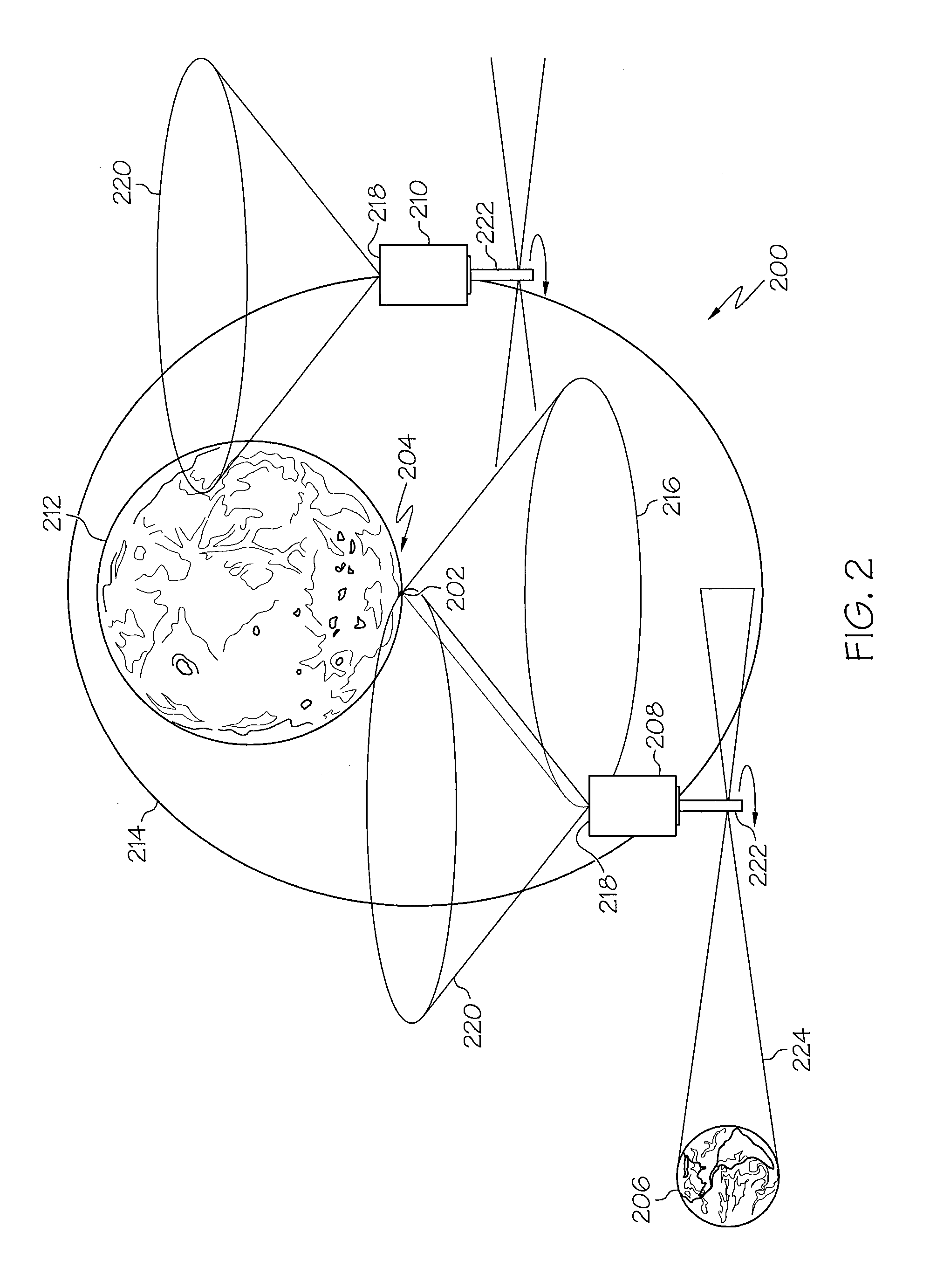
Lunar communications system
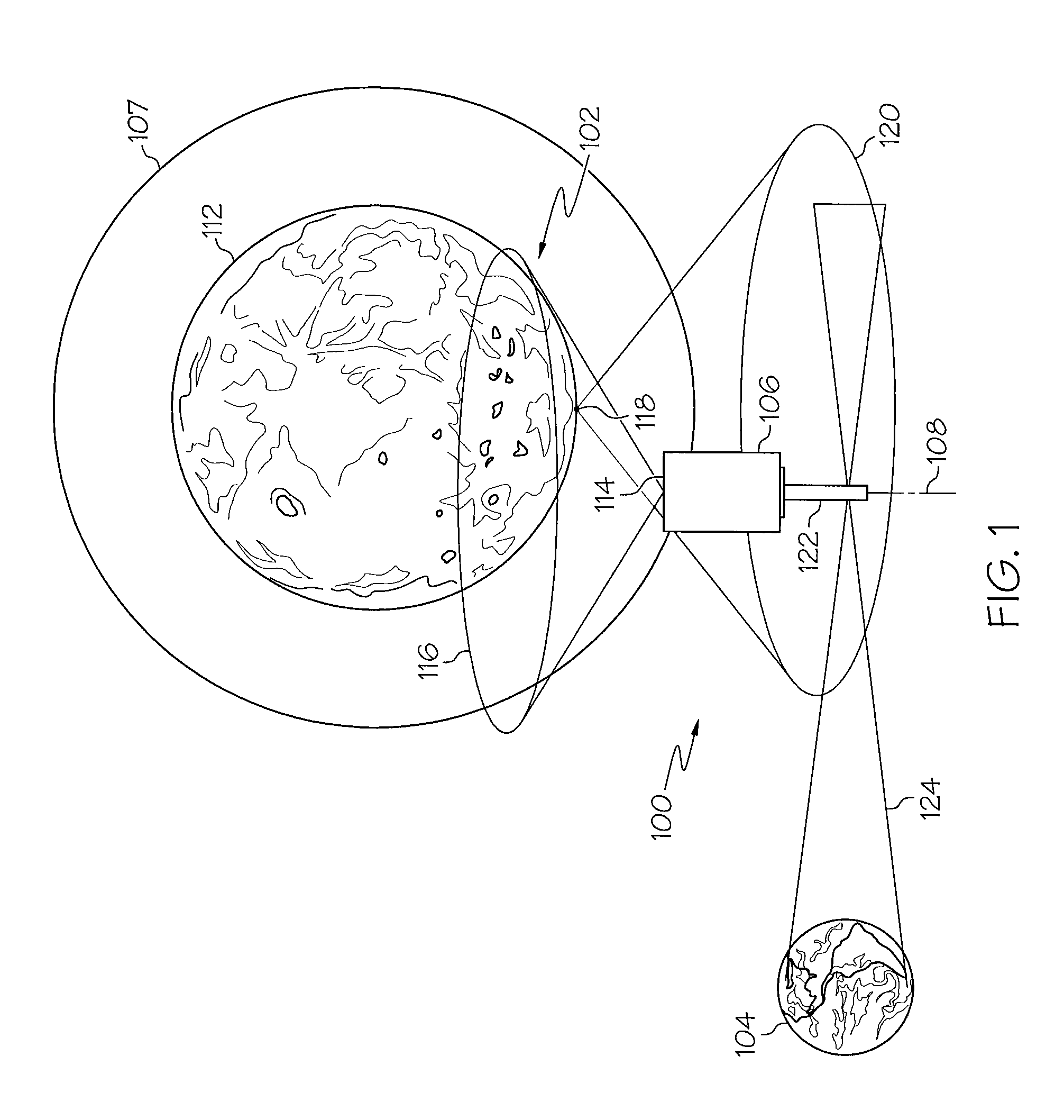
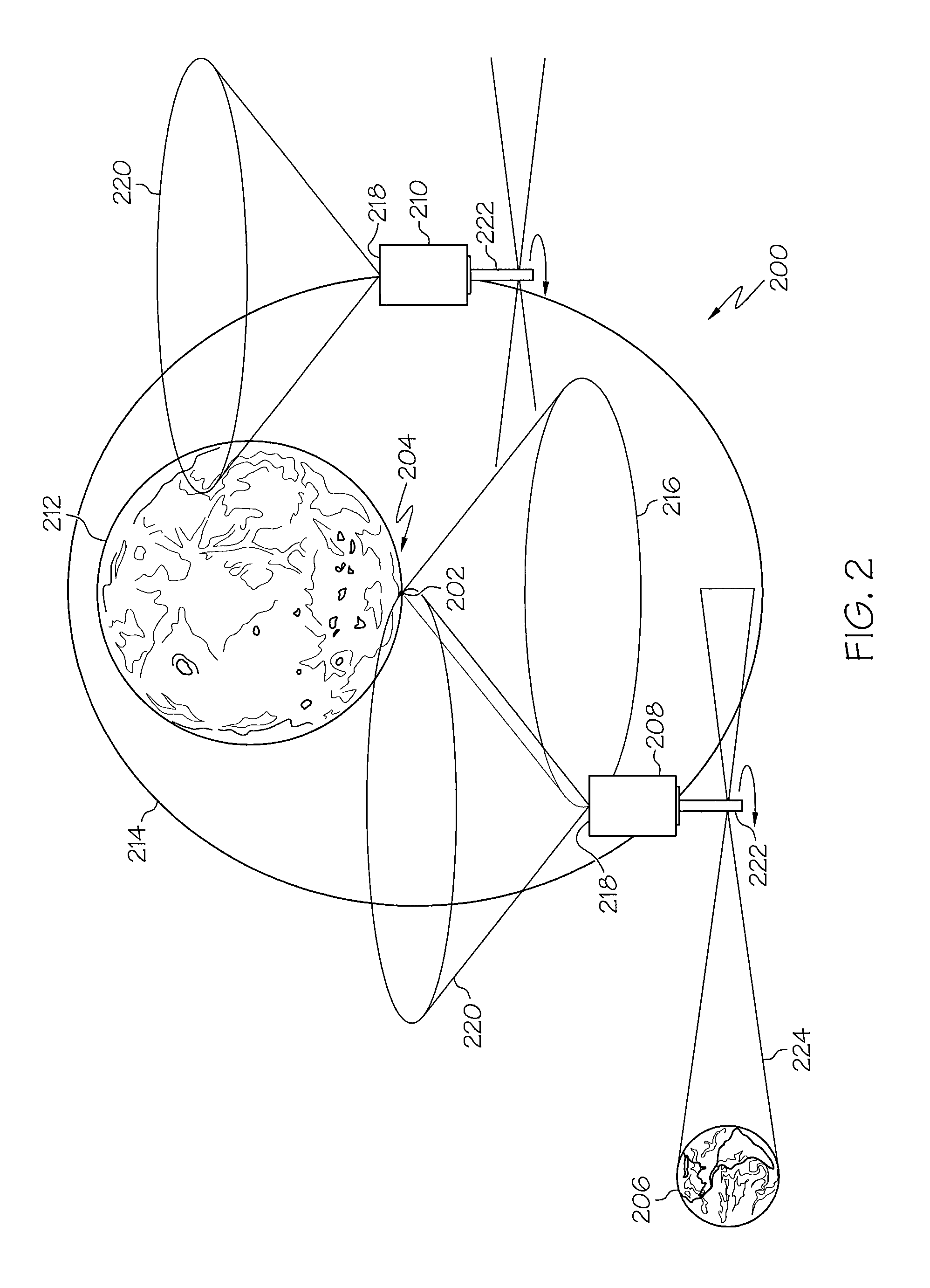
ActiveUS20110097995A1Simple designSimple solutionRadio transmissionCommunications systemCelestial body
A system for communications between a lunar or planetary surface and the Earth may include a first communications satellite adapted to be positioned in a predetermined orbit relative to a celestial body. A first antenna may be mounted on the first communications satellite. The first antenna may include a predetermined beam shape for communications between the first communications satellite and an asset on the lunar or planetary surface. A second antenna may also be mounted on the first communications satellite. The second antenna may include a selected beam shape for communications between the first communications satellite and the Earth. A communications system may be included for relaying communications between the first and second antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
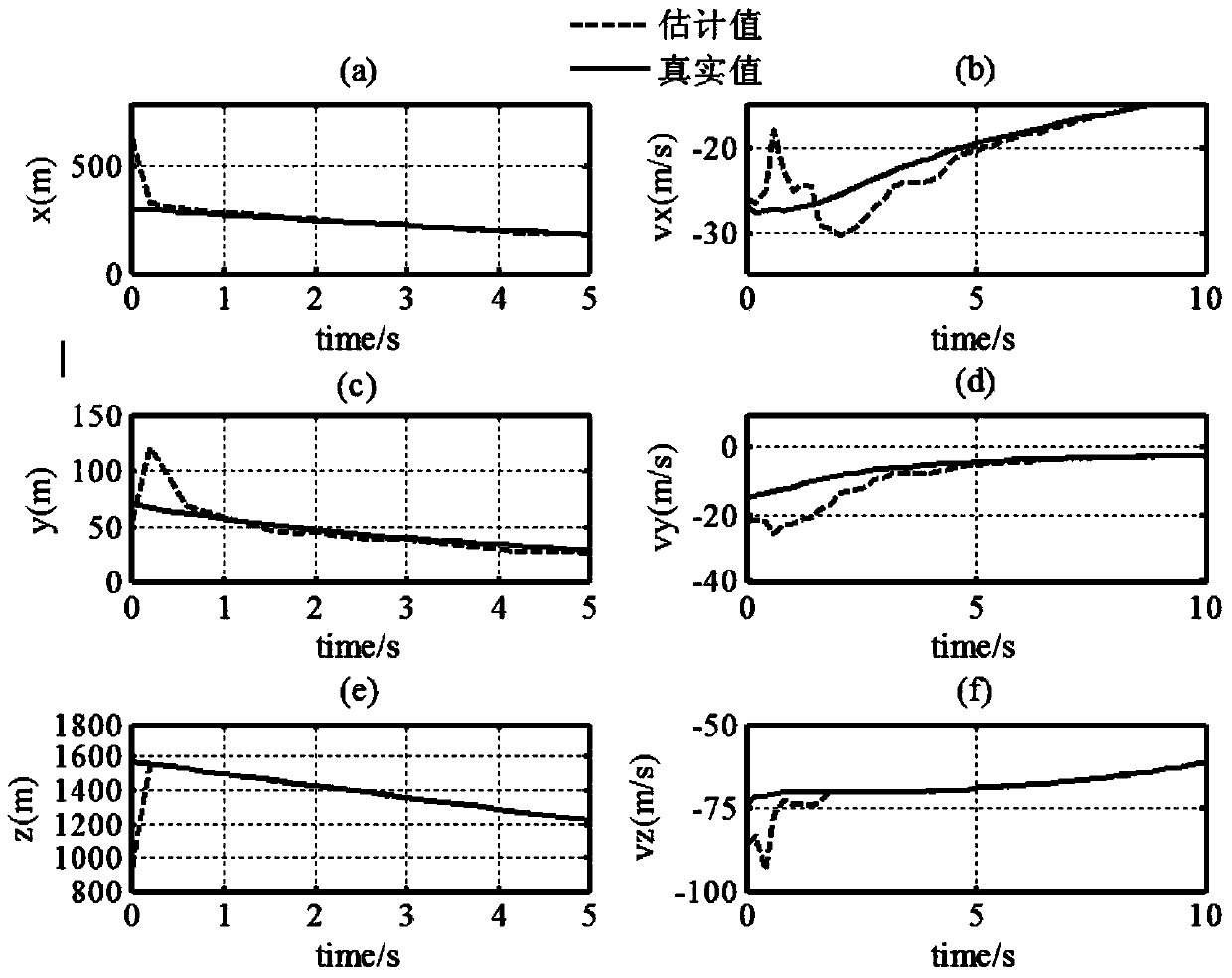
Planetary power descending branch navigation method based on TDS (total descending sensor) and image measurement
ActiveCN103438890AImprove horizontal position accuracyAccurately measure the included angleInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation systemVisual perception
The invention relates to a planetary power descending branch navigation method based on a TDS (total descending sensor) and image measurement and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. At a power descending branch, an inertial unit of a landing device navigation system is used for flight position recurrence and is a basic sensor; a Doppler radar on the TDS is used for directly acquiring distances from a landing device to the surface of a target planet in three wave beam directions and relative speeds of the landing device along the three wave beam directions and then calculating the altitude of the landing device and speeds of the landing device in three axial directions of a landing point fixedly-connected coordinate system; a navigation camera serving as a vision auxiliary navigation sensor is used for precisely measuring included angles between sight directions of different characteristic points of a landing area; the positions of the characteristic points relative to the landing point are known; the sight included angles contain horizontal position information of the landing device relative to the landing point, so that the horizontal position precision of the landing device is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A rocket-powered Mars transport aircraft
InactiveCN109018439ACompact structureLower center of gravityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsGas cylinderRocket
The invention provides a rocket-powered Mars transport aircraft, comprising a bearing system,a buffer landing system, a power system, an energy system and a navigation guidance and control system. Thebuffer landing system, the power system, the energy system and the navigation guidance and the control system are arranged on the bearing system. The bearing system comprises a truss, and the power system comprises a main engine arranged on the bottom of the frame. The energy system comprises a high-pressure gas cylinder and a storage tank, wherein the high-pressure gas cylinder is arranged in the middle of the truss, the number of the storage tanks is a plurality of and is arranged at the side of the truss in an annular interval, the high-pressure gas cylinder is communicated with each storage tank through pipelines, and each storage tank is connected with the main engine through pipelines. Adopt modular design, The landing cushion, power system, load bearing system, energy system and navigation guidance and control system are more reasonably installed on the truss, so that the load is more dispersed on the premise of ensuring that the Mars transport aircraft is more compact in structure, and the center of gravity of the Mars transport aircraft is reduced, so that the Mars transport aircraft has higher load bearing capacity. The invention is applied to the field of planetary surface flight.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
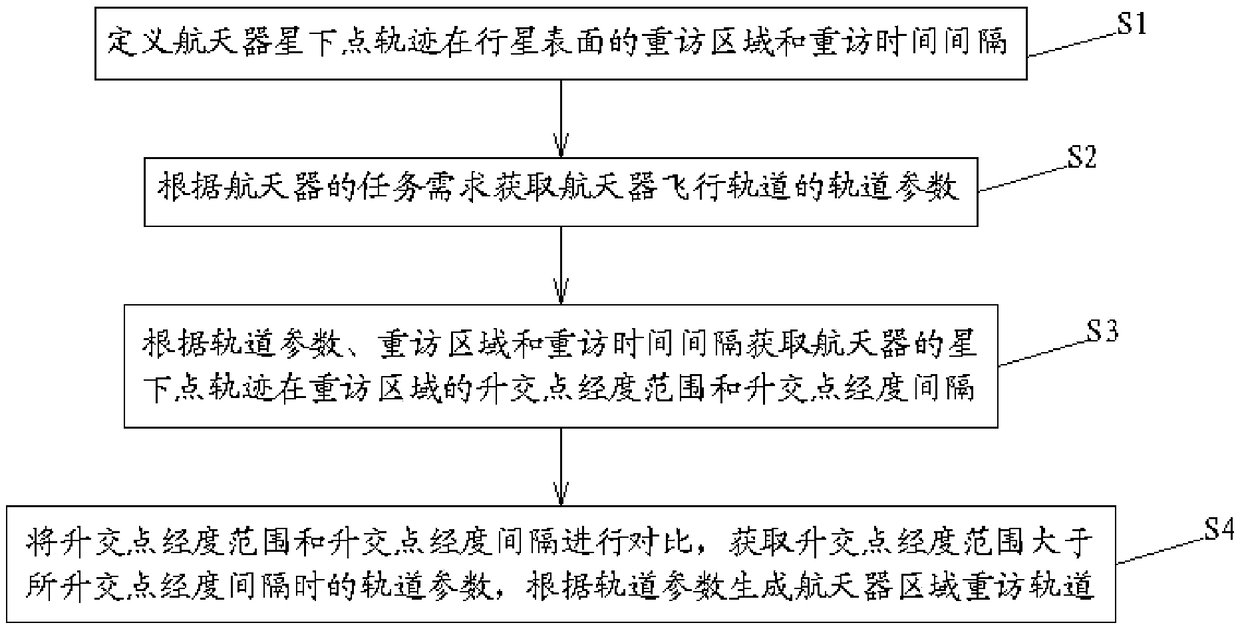
Method for designing a revisiting track of a spacecraft region
ActiveCN109110159AReduce constraintsQuick fixCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusPlanetary surfaceLongitude of the ascending node
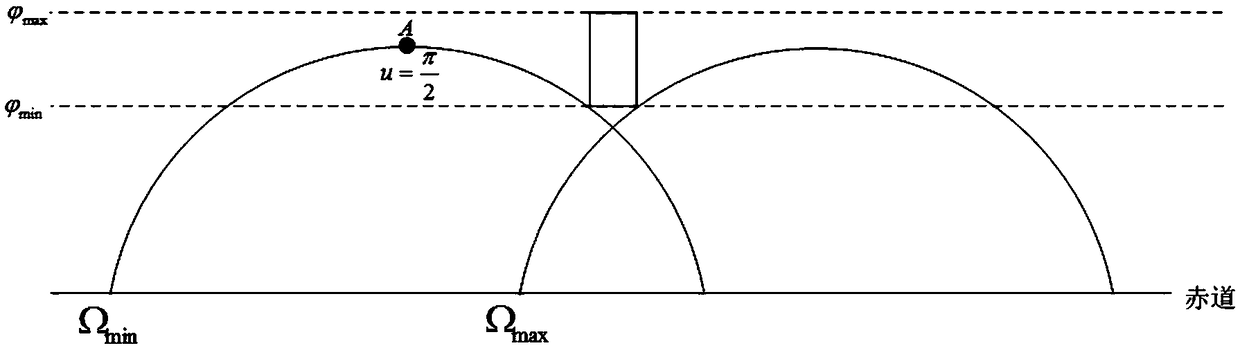
The invention relates to a method for designing a revisiting track of a spacecraft region, comprising: S1. defining a revisit region and a revisit time interval of a subsatellite point trajectory of the spacecraft on a planetary surface; S2, obtaining orbital parameters of the spacecraft flight trajectory according to mission requirements of the spacecraft; S3. according to the orbital parameters,the revisit region and the revisit time interval, obtaining the ascending intersection longitude range and the ascending intersection longitude interval of the subsatellite point trajectory of the spacecraft in the revisit region; S4. comparing the longitude range of the ascending intersection point with the longitude interval of the ascending intersection point, obtaining the orbital parameterswhen the longitude range of the ascending intersection point is larger than the longitude interval of the ascending intersection point, and generating a spacecraft region revisit orbit according to the orbital parameters. By adopting the method of matching the longitude range of the ascending intersection point with the longitude interval of the ascending intersection point to determine the orbital elements of the regional revisit orbit, the constraints among the orbital elements are reduced, and the orbital elements range satisfying the requirements of the regional revisit can be quickly determined.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Dynamoelectric controlled integrated wheel of inspection tour prober for moon surface
InactiveCN101108656ASave cabin spaceIncrease autonomyExtraterrestrial carsSurvivabilityMiniaturization
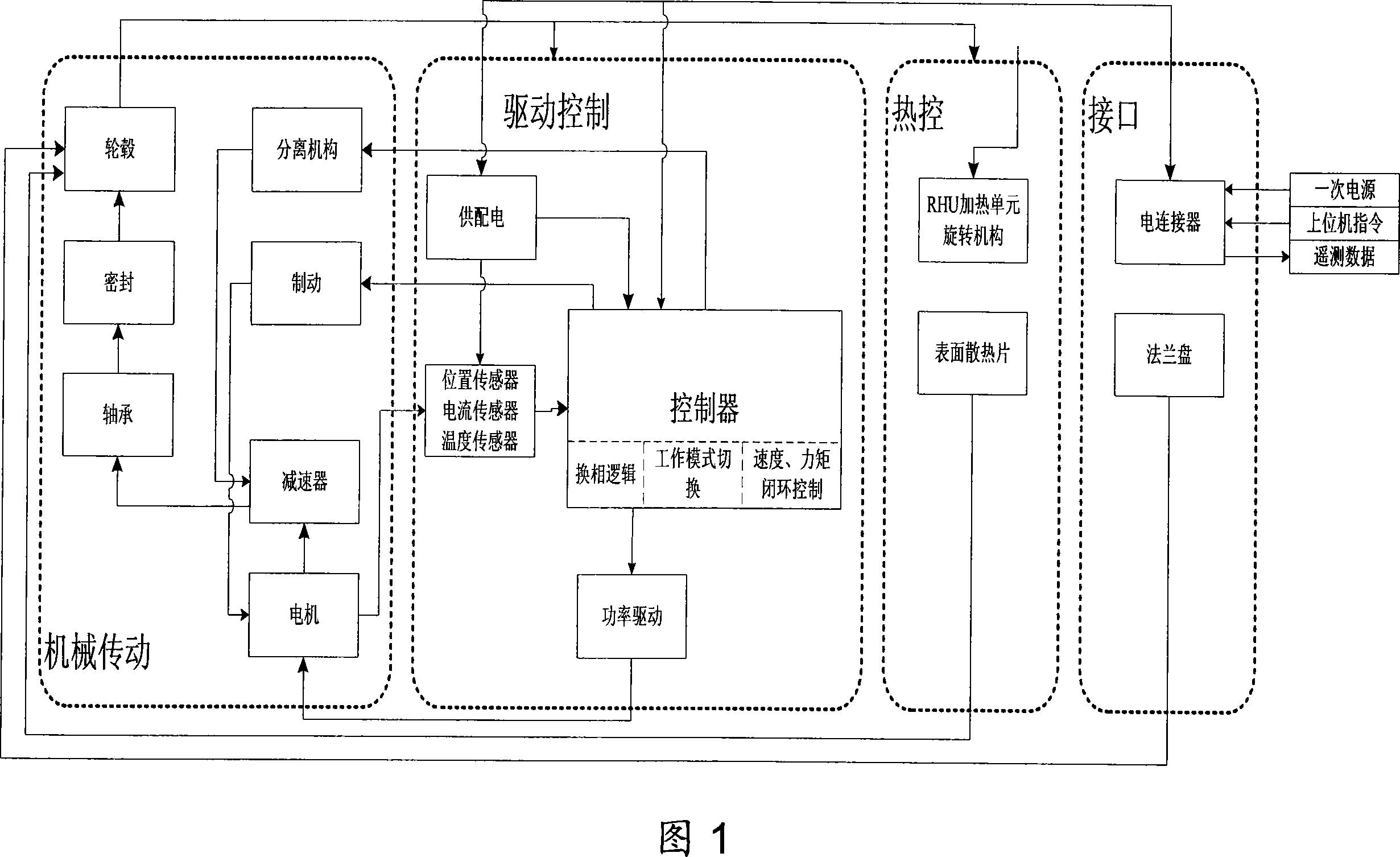
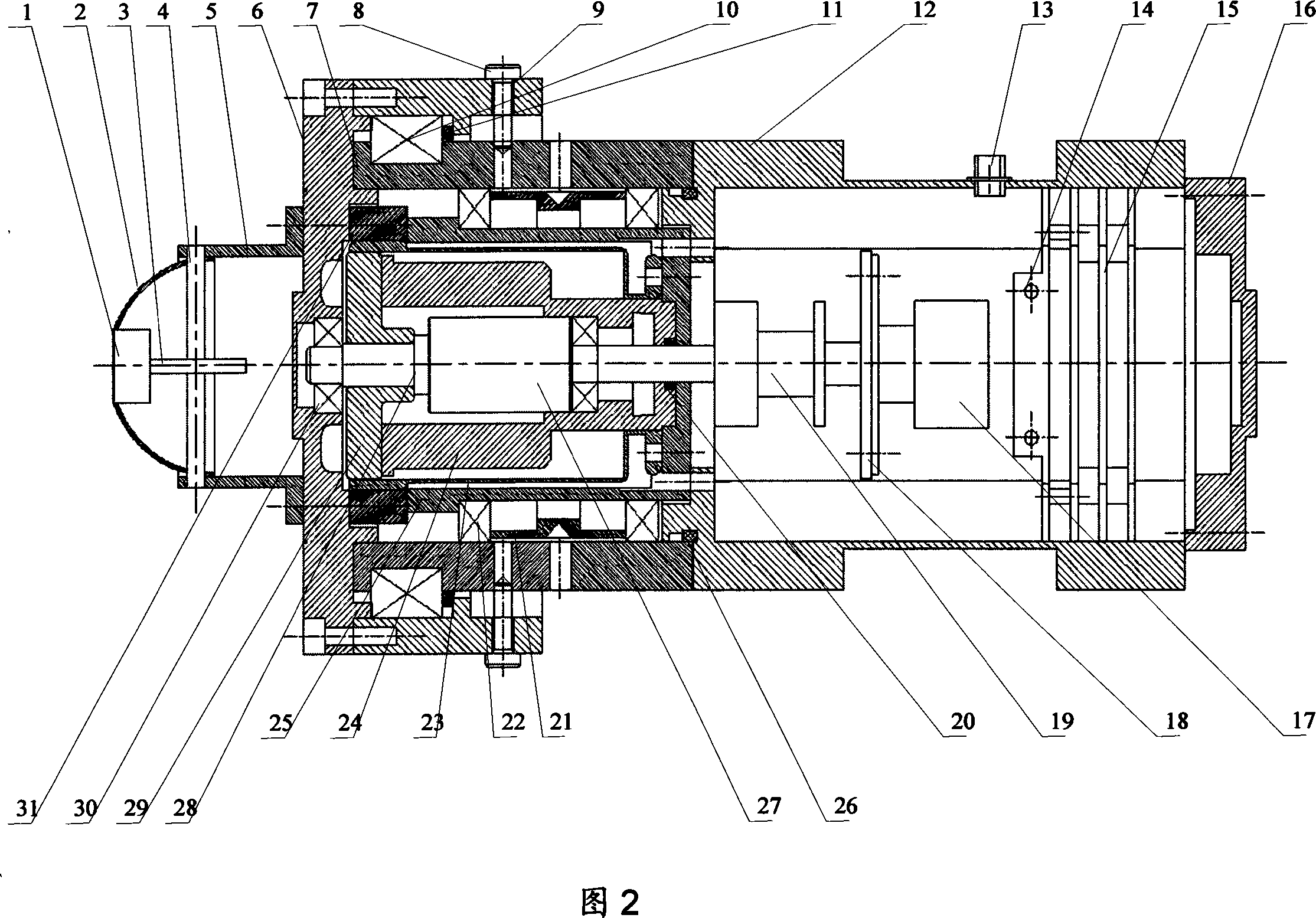
A lunar exploration rover electric-mechanic-control integration wheel is provided, which integrates a mechanical transmission unit, a drive control unit and a thermal control unit. To satisfy the requirements of the rover on the miniaturization and low energy consumption, the drive control unit is put in the wheel and communicated with an IPC through interfaces, and receives the control instruction to drive the mechanical transmission unit to control the rotation of the wheel, which not only reduces the quantities of outer leads but also improves the independence and the stability of the wheel and saves the inner cabin space of the rover; the thermal control unit is positioned on the outer surface of the wheel hub to make the wheel have the independent thermal control function and control the working temperature in the wheel at any time according to the change of the ambient temperature to increase the viability of the wheel under changeable environment. The electric-mechanic-control integration wheel can not only be used for the lunar exploration rover but also can be used for other planetary surface detectors.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
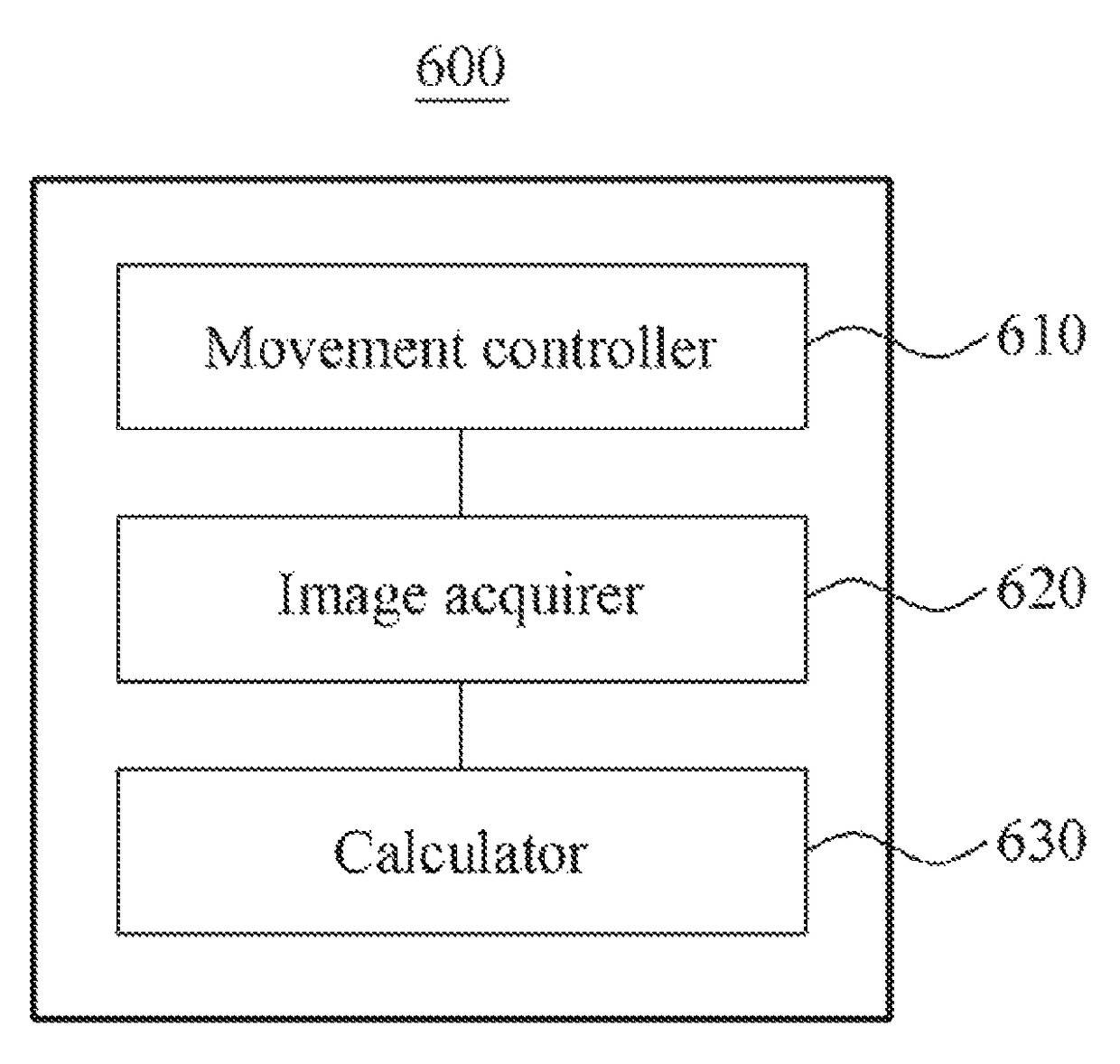
Apparatus and method for controlling a satellite
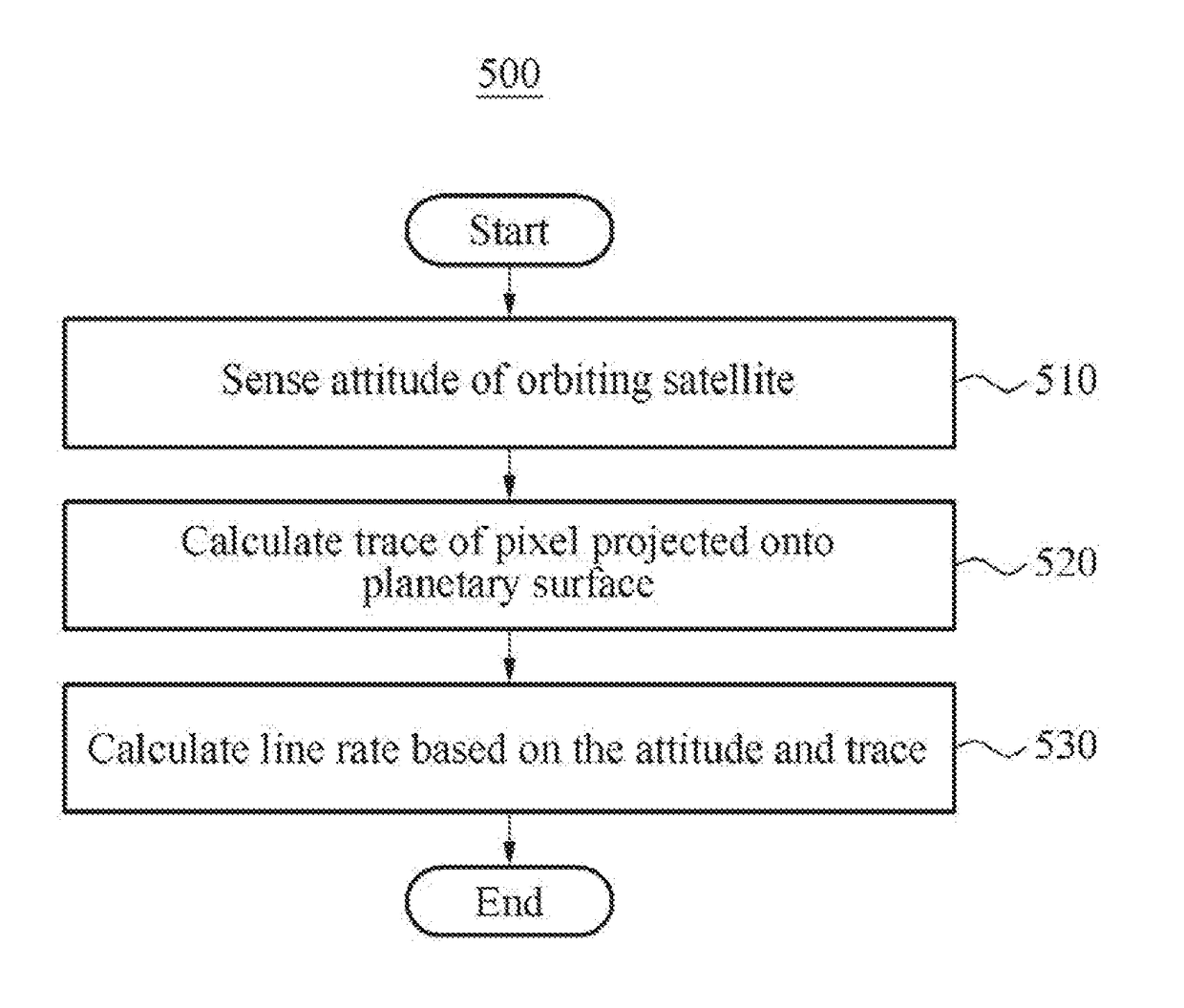
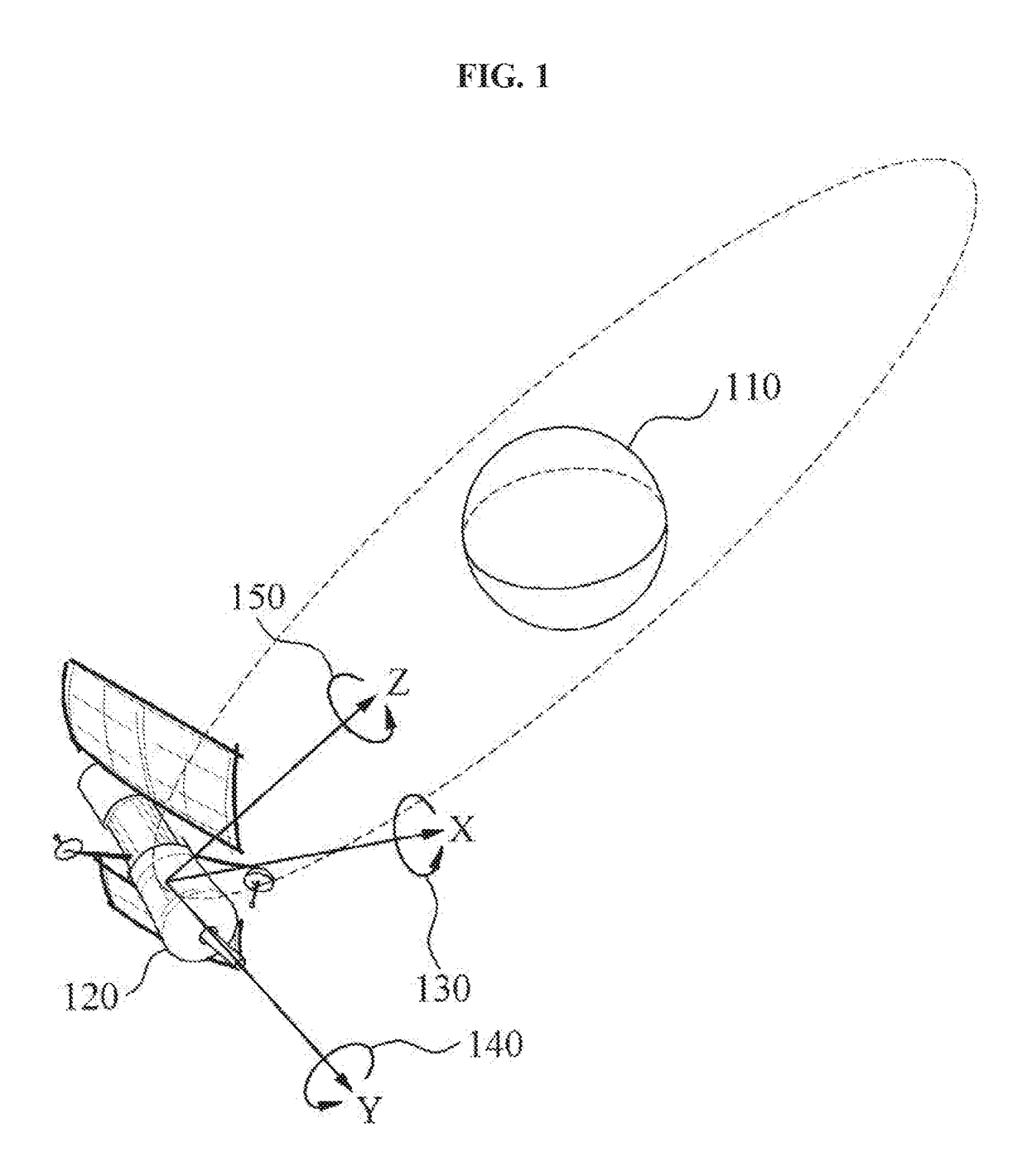
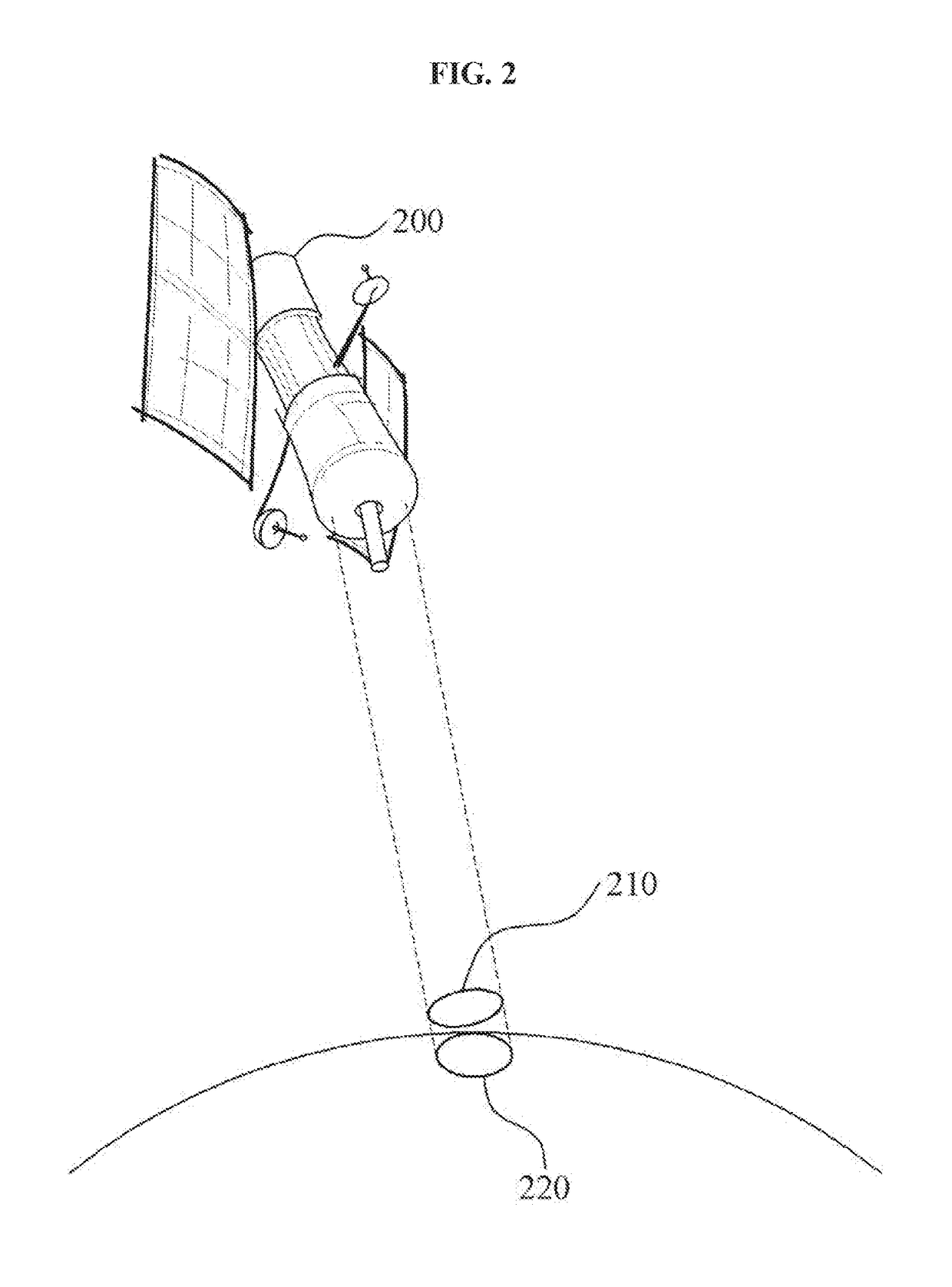
Provided is an apparatus for controlling an orbiting satellite by sensing a change in a yaw angle of the orbiting satellite and calculating a ground sample distance (GSD) based on the yaw angle. The apparatus may include a sensor configured to sense a yaw angle corresponding to yaw steering of the orbiting satellite, and a processor configured to calculate, based on the yaw angle, a GSD corresponding to a length of a pixel projected onto a planetary surface scanned by the orbiting satellite.
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
Storage of Arbitrary Points in N-Space and Retrieval of Subset Thereof Based on a Determinate Distance Interval from an Arbitrary Reference Point
InactiveUS20150058390A1Calculation can be costlyEfficient retrievalInstruments for road network navigationData conversionProximity measureData store
Systems and methods pertaining to nearness calculations of points in n-space. Among the embodiments is associating points of interest with point records in a data store, and efficient retrieval of subsets of those point records which meet arbitrary criteria. Criteria can limit retrieval to neighbors of a reference point (i.e., point records associated with points of interest whose home cells that share at least one interface with another designated home cell). Computationally expensive, at-retrieval range calculations are avoided by performing complimentary calculations at-storage and saving them with related records. The invention is appropriate for use with data storage mechanisms which limit inequality or range operations, or for which such operations result in inefficiencies. When used to model neighboring points on a planetary surface in 3-space, the invention does not suffer from polar distortion (where spherical coordinate systems have difficulty).
Owner:BOGOSIAN MATTHEW THOMAS
Cooling systems
ActiveUS9395123B1Avoid overall overheatingCosmonautic environmental control arrangementSpace suitsEngineeringThermal control system
A portable thermal-control system adapted to support space-related research and exploration. Embodiments of the present invention assist in preventing overheating of small payloads being transported from an orbiting space vehicle to a planetary surface by small atmospheric-entry vehicles. Other embodiments of the present invention provide thermal control within an extra-vehicular activity (EVA) suit. Each embodiment utilizes at least one phase-change material, cooled significantly below the freezing temperature, to absorb heat.
Owner:PARAGON SPACE DEVMENT
Storage of Arbitrary Points in N-Space and Retrieval of Subset thereof Based on Criteria Including Maximum Distance to an Arbitrary Reference Point
InactiveUS20120233210A1Affect efficiencyEffective meanDigital data processing detailsGeographical information databasesData memoryData storing
Provided are: 1) storage in a data store of points of interest in n-space along with arbitrary related information; and 2) efficient retrieval of subsets of those points meeting arbitrary criteria. Criteria can limit retrieval to neighbors of a reference point (i.e., points that are within a specified distance of that reference point). The method may be used to retrieve subsets from data stores which limit inequality or range operations. When used to model neighboring points on a planetary surface in 3-space, the method does not suffer from polar distortion (where spherical coordinate systems have difficulty).
Owner:BOGOSIAN MATTHEW THOMAS
Cooling systems
ActiveUS8342454B1Avoid overall overheatingCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringThermal control system
A portable thermal-control system adapted to support space-related research and exploration. Embodiments of the present invention assist in preventing overheating of small payloads being transported from an orbiting space vehicle to a planetary surface by small atmospheric-entry vehicles. Other embodiments of the present invention provide thermal control within an extra-vehicular activity (EVA) suit. Each embodiment utilizes at least one phase-change material, cooled significantly below the freezing temperature, to absorb heat.
Owner:PARAGON SPACE DEVMENT
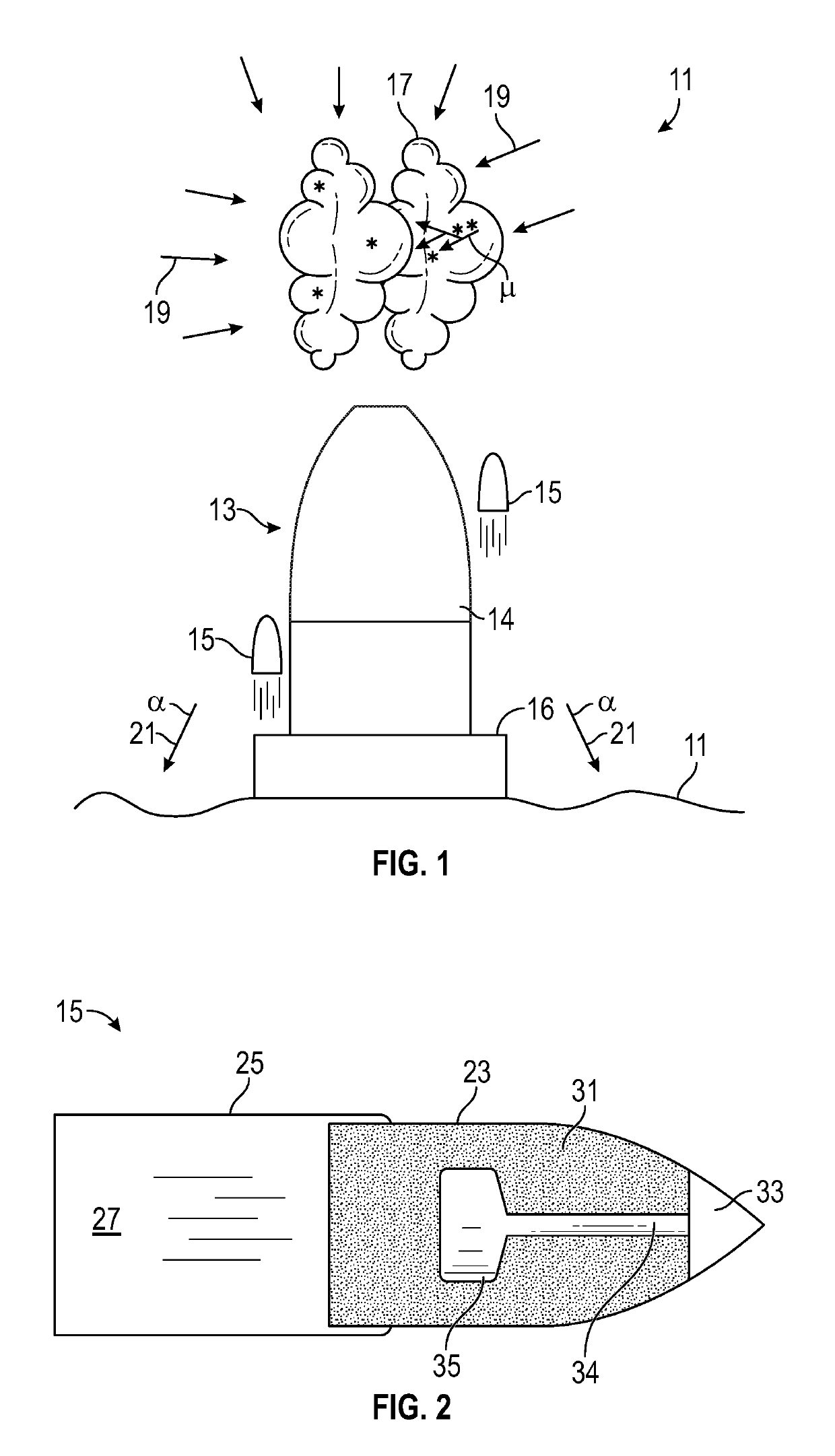
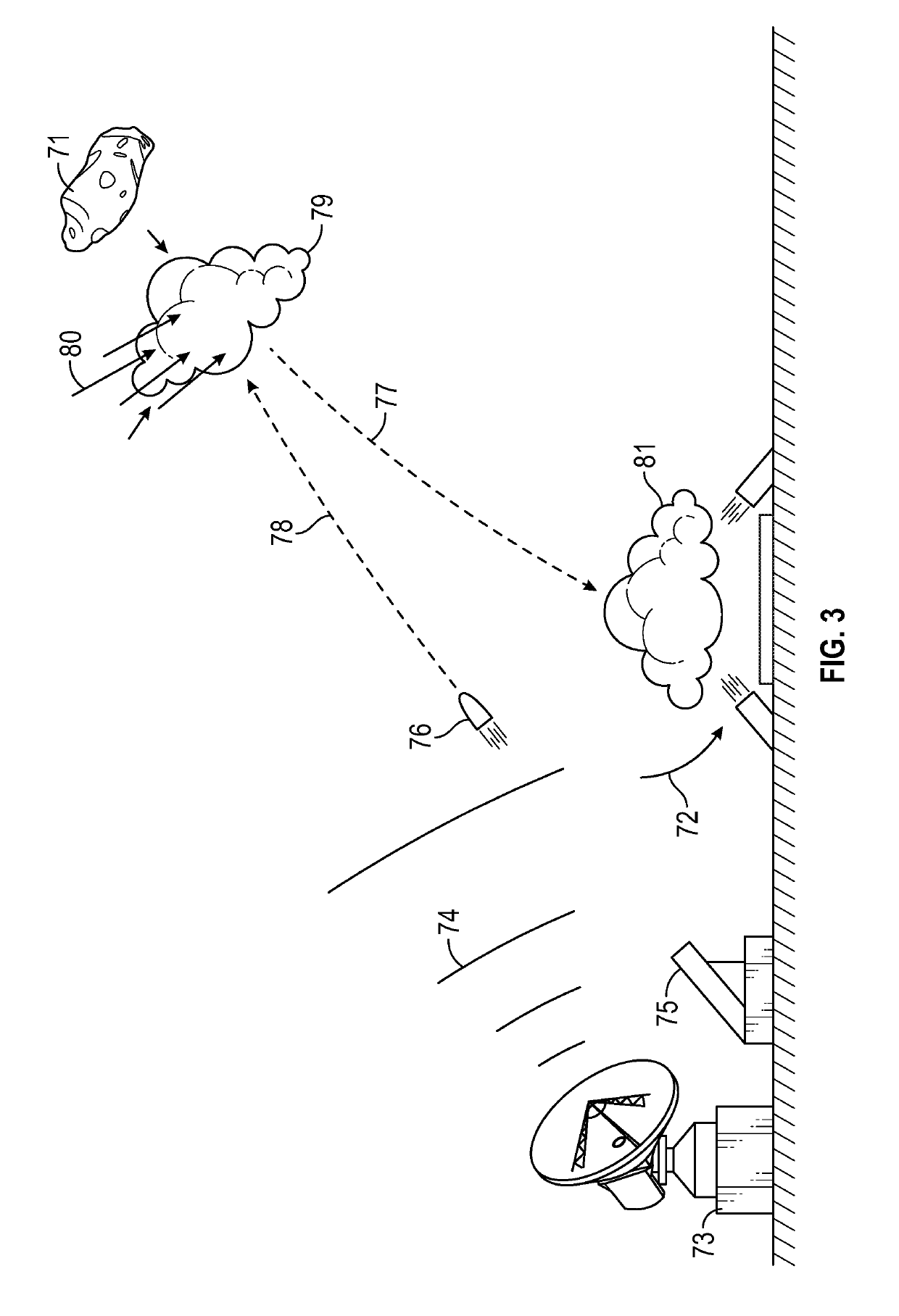
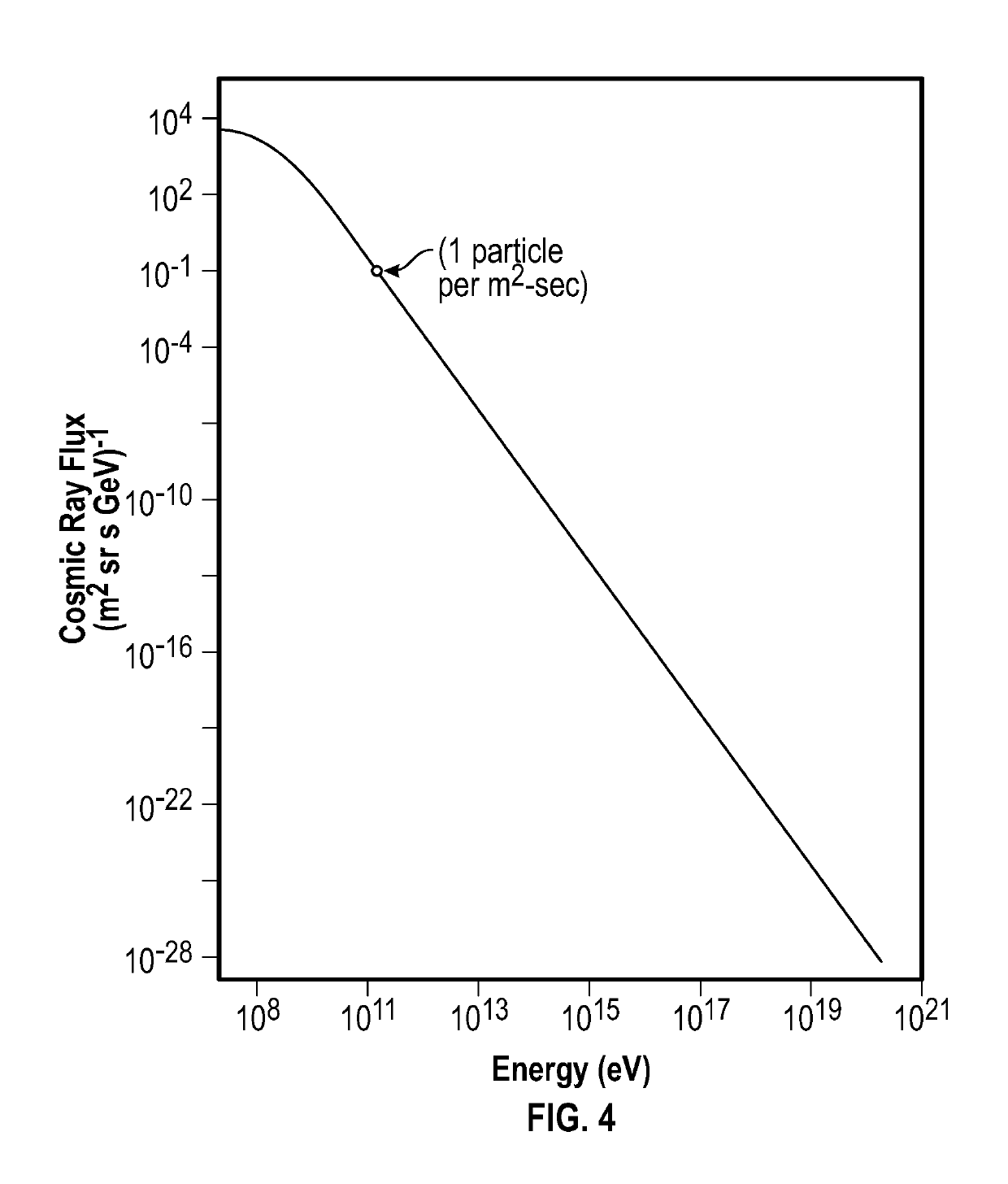
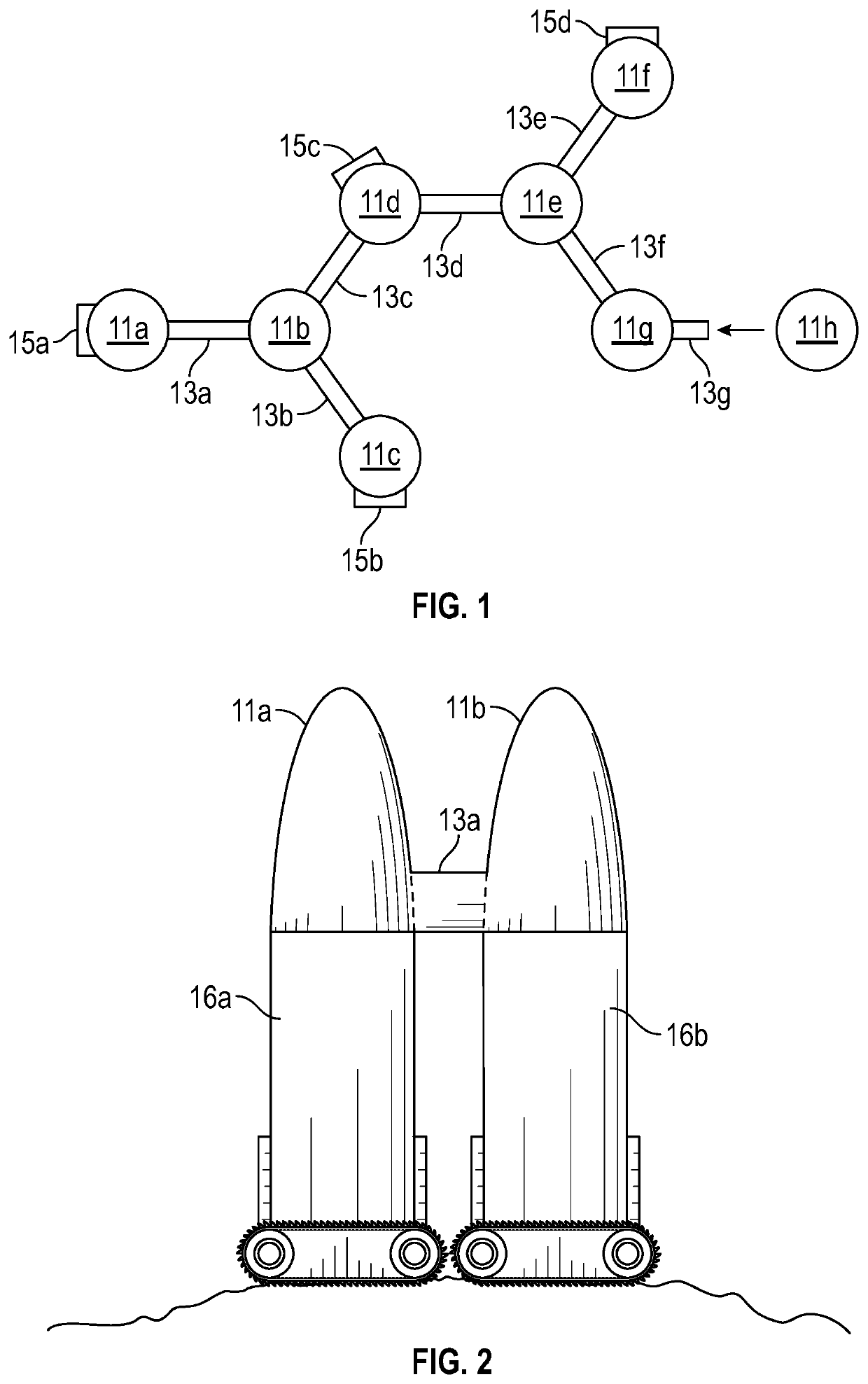
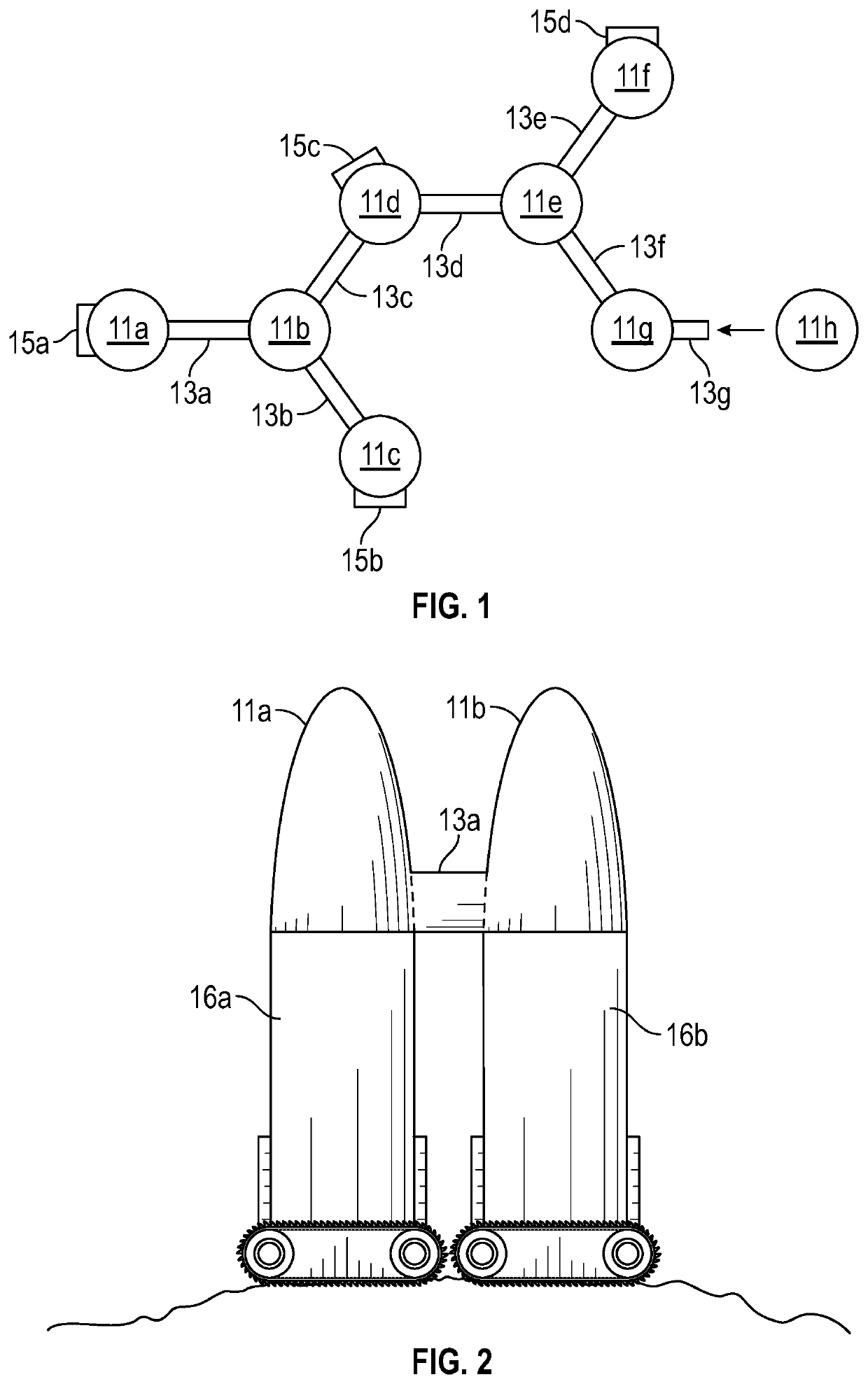
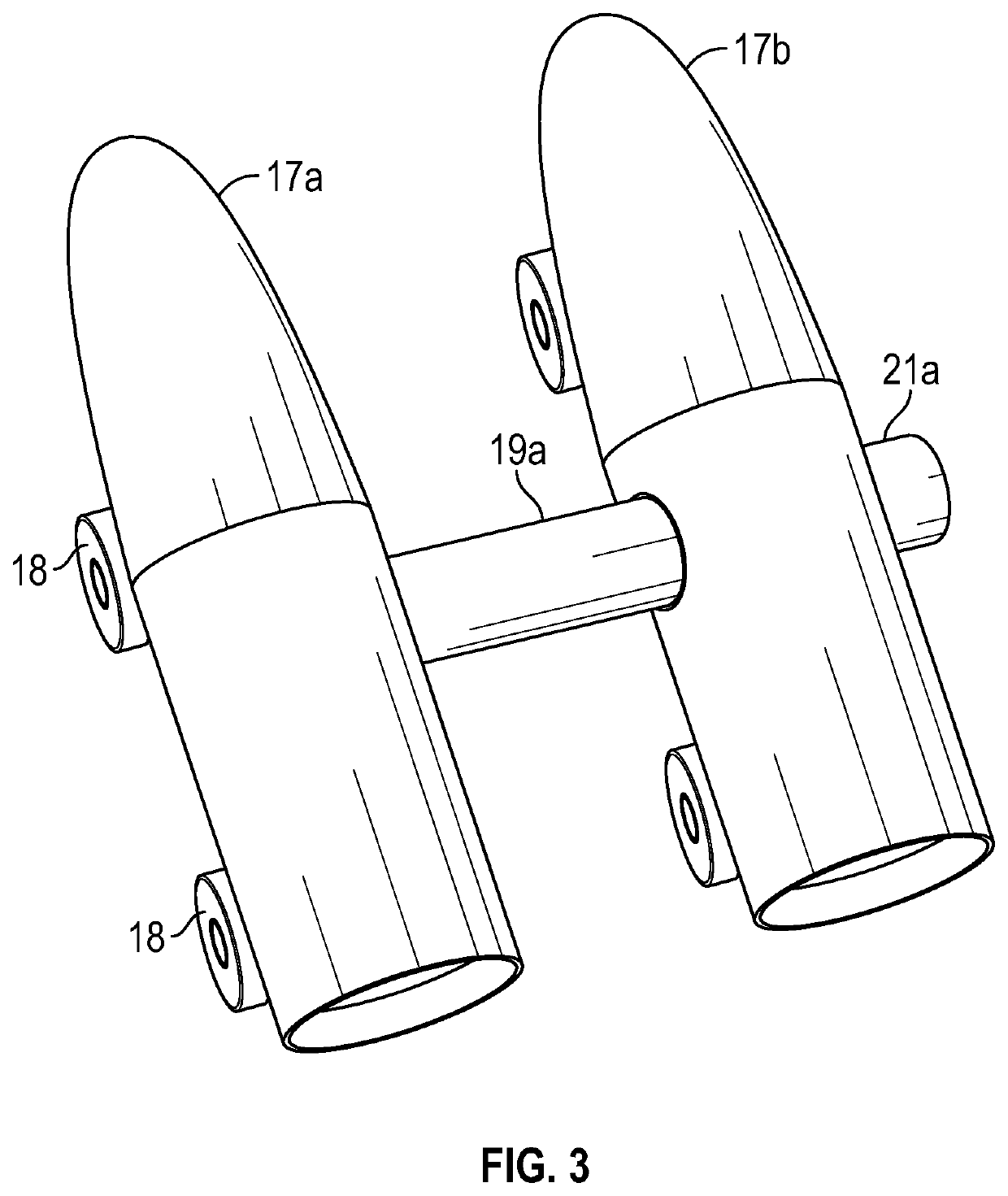
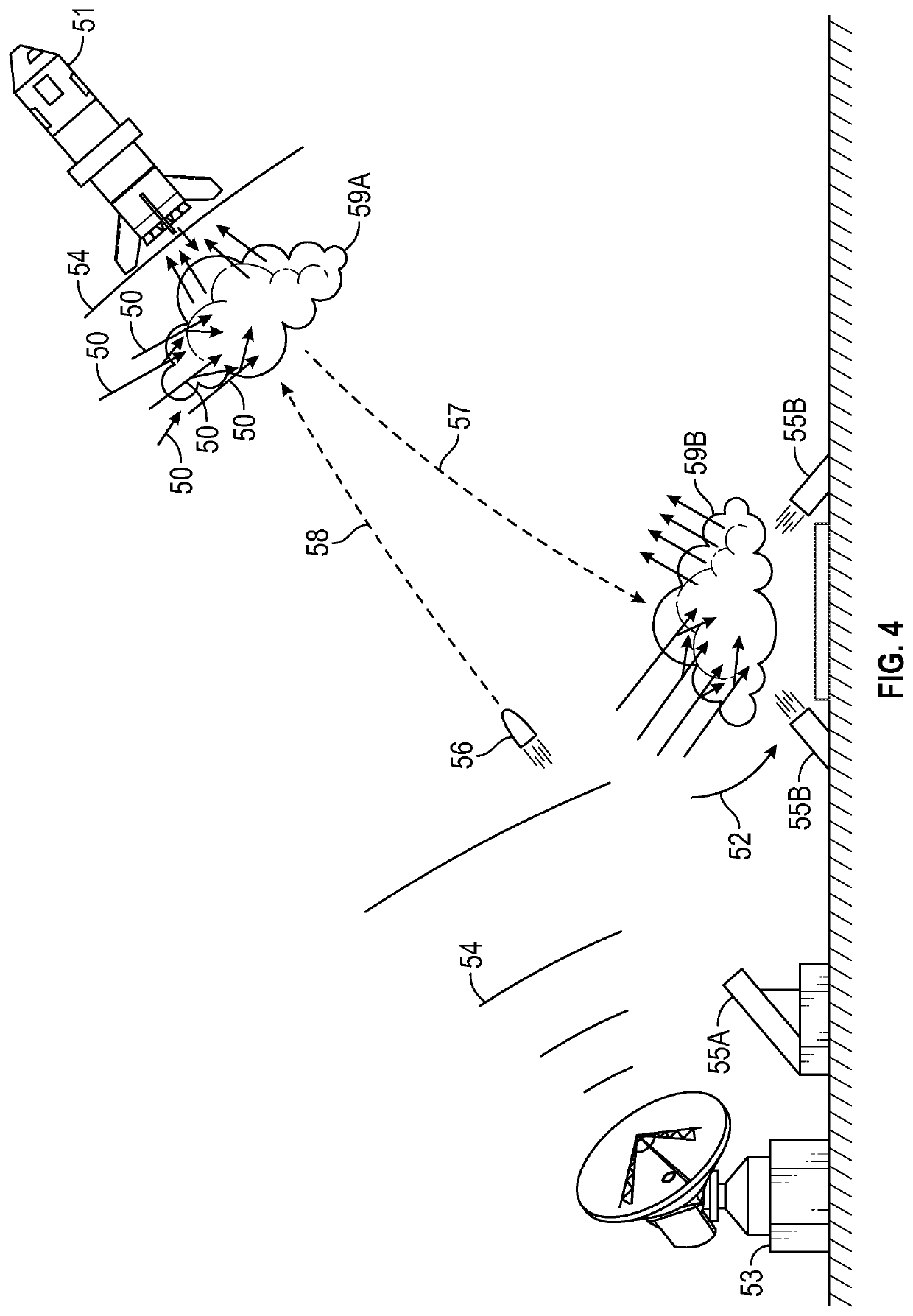
Asteroid redirection and soft landing facilitated by cosmic ray and muon-catalyzed fusion
ActiveUS20190168896A1Useful thrustCosmonautic radiation protectionLaunch systemsParticulatesMuon-catalyzed fusion
Asteroid redirection and soft-landing systems are provided that use cosmic ray and muon-catalyzed micro-fusion. These systems include a micro-fusion propulsion system providing thrust for redirecting a small asteroid, as well as providing a particle cushion at a landing site for a soft-landing. The systems deploy deuterium-containing fuel material as a localized cloud interacting with incoming ambient cosmic rays to generate energetic fusion products. Dust or other particulate matter in the fuel material converts some cosmic rays into muons that also catalyze fusion. The fusion products provide thrusting upon the asteroid. The fusion products also aid deceleration of incoming asteroids to be mined for a soft landing upon a lunar or planetary surface.
Owner:DREXLER JEROME
Disc cutter cutting sampling and air blowing sample delivery type asteroid surface star soil sampler
PendingCN111122213AReduce power consumptionLight in massWithdrawing sample devicesGas cylinderElectric machinery
The invention discloses a disc cutter cutting sampling and air blowing sample delivery type asteroid surface star soil sampler, and belongs to the technical field of asteroid detection sampling. The asteroid surface star soil sampler solves the problems that an existing planet surface star soil sampler lacks a guiding effect, so that the motion trail of a sampled product is not easy to control, and the power consumption of the sampler is high. A gas cylinder, a footage mechanism and a return cabin are respectively fixed on a detector main body, a sampling mechanism is communicated with a sample container through a sample conveying pipeline, the top of a cover body is communicated with the sample conveying pipeline, two outer rotor energy storage motors are correspondingly fixed in the cover body through two motor bases, two disc cutters are correspondingly, coaxially and fixedly connected to the two outer rotor energy storage motors, a plurality of upper nozzles are inserted into a side wall at the upper part of the cover body and run through an inner cavity of the cover body, a plurality of lower nozzles are inserted into a side wall at the lower part of the cover body and run through the inner cavity of the cover body, and each nozzle is communicated with the gas cylinder through a gas pressure pipe respectively.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Super-hard fixed abrasive lapping parameters optimization and manufacturing method based on Adams simulation
InactiveCN109702637AReduce the number of trimmingImprove processing efficiencyLapping machinesJoint simulationUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a super-hard fixed abrasive lapping parameters optimization and manufacturing method based on Adams simulation. The method comprises the steps that simulated machining joint simulation is carried out on a planetary surface lapping grinding machine model created by Solidworks by using Matlab and Adamas, optimization design is carried out by using abrasion uniformity of a lapping disc as a target by Adams, optimal grinding process parameters under given grinding conditions are obtained efficiently and cost-effectively, and an abrasion distribution model of the lapping disc is established according to the simulation results under the optimal grinding process parameters. On the basis, the lapping disc is designed and manufactured by adopting a lapping pill piece distribution technology based on abrasion resistance, so that the abrasion intensity of the lapping disc is suitable to the distribution of the abrasion resistance of lapping pill pieces, in the process after first dressing is carried out, uniform abrasion can be achieved and even abrasion is consumed, and then the original surface figure accuracy is maintained to ensure that machined workpieces have good machining accuracy in a long time, and the dressing number of the lapping disc in the use process is reduced or the lapping disc is free from dressing. The machining efficiency and utilization of the lapping machine are improved, and the comparative lifetime of the lapping disc is prolonged, and the stability of the lapping disc is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU INST OF TECH
Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar system and method
ActiveUS10649081B2High resolution measurementReduce development costsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysSynthetic aperture radarEngineering
Owner:NASA
Spacecraft-module habitats and bases
ActiveUS20200130871A1Reduce weightReduce volumeCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic ground equipmentsComputer moduleEngineering
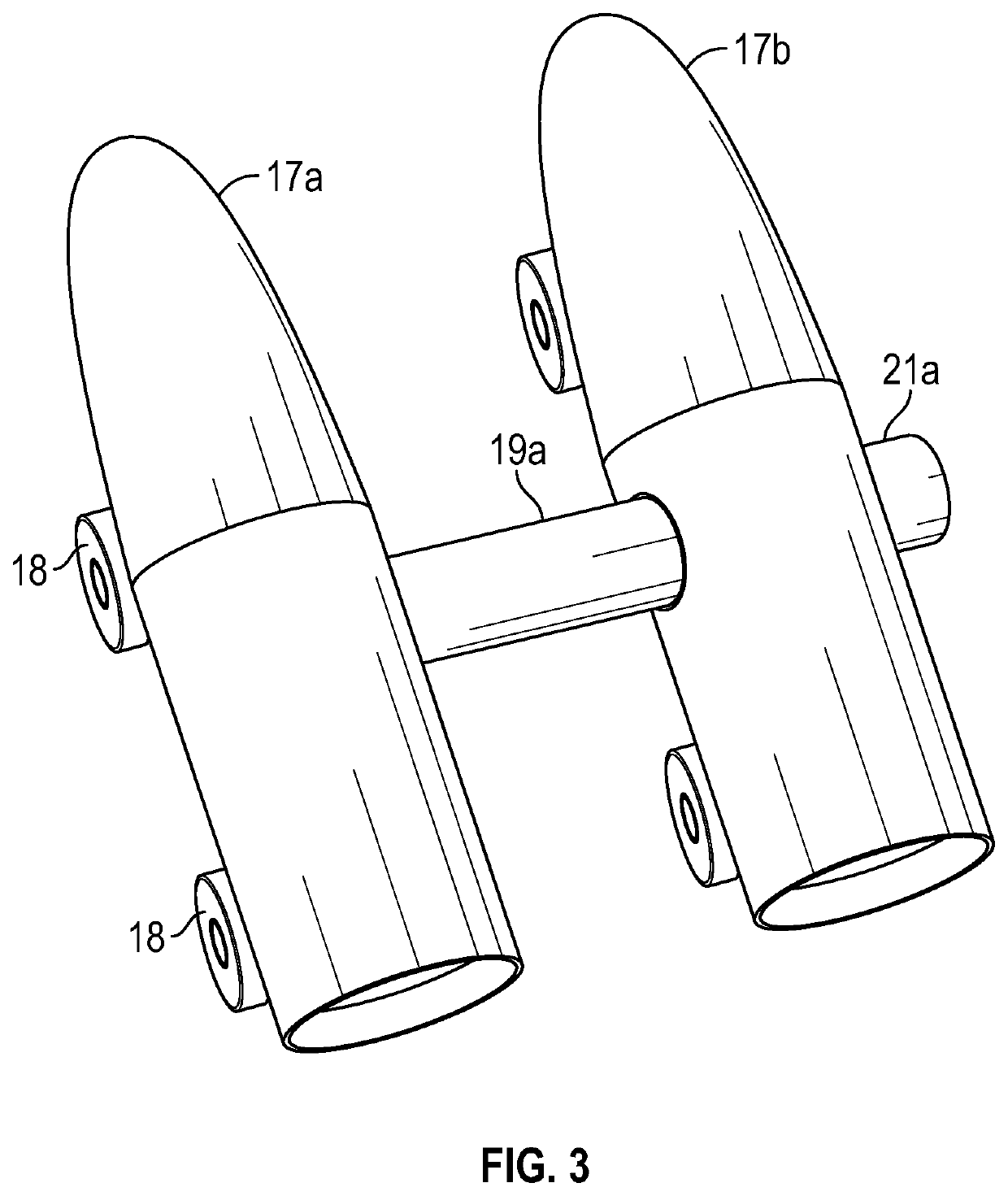
Establishing and growth of a lunar or planetary surface base involves continuing to use landing spacecraft as docked modules of the base for habitation and work. A first spacecraft is landed at a specified surface site then doubles as first module of the base. A second (and later third and subsequent) spacecraft is landed at the site a safe distance from the existing base modules then moved over the surface into a side-by-side position to dock with selected base modules. At least some of the landing, surface transport, and operational electric power is supplied by micro-fusion using ambient cosmic rays and muons interacting with deuterium-containing particle fuel material to generate energetic reaction products.
Owner:DREXLER JEROME
Spacecraft-module habitats and bases
ActiveUS10960993B2Reduce weightReduce volumeCosmonautic ground equipmentsLaunch systemsGround stationPlanetary surface
Establishing and growth of a lunar or planetary surface base involves continuing to use landing spacecraft as docked modules of the base for habitation and work. A first spacecraft is landed at a specified surface site then doubles as first module of the base. A second (and later third and subsequent) spacecraft is landed at the site a safe distance from the existing base modules then moved over the surface into a side-by-side position to dock with selected base modules. At least some of the landing, surface transport, and operational electric power is supplied by micro-fusion using ambient cosmic rays and muons interacting with deuterium-containing particle fuel material to generate energetic reaction products.
Owner:DREXLER JEROME
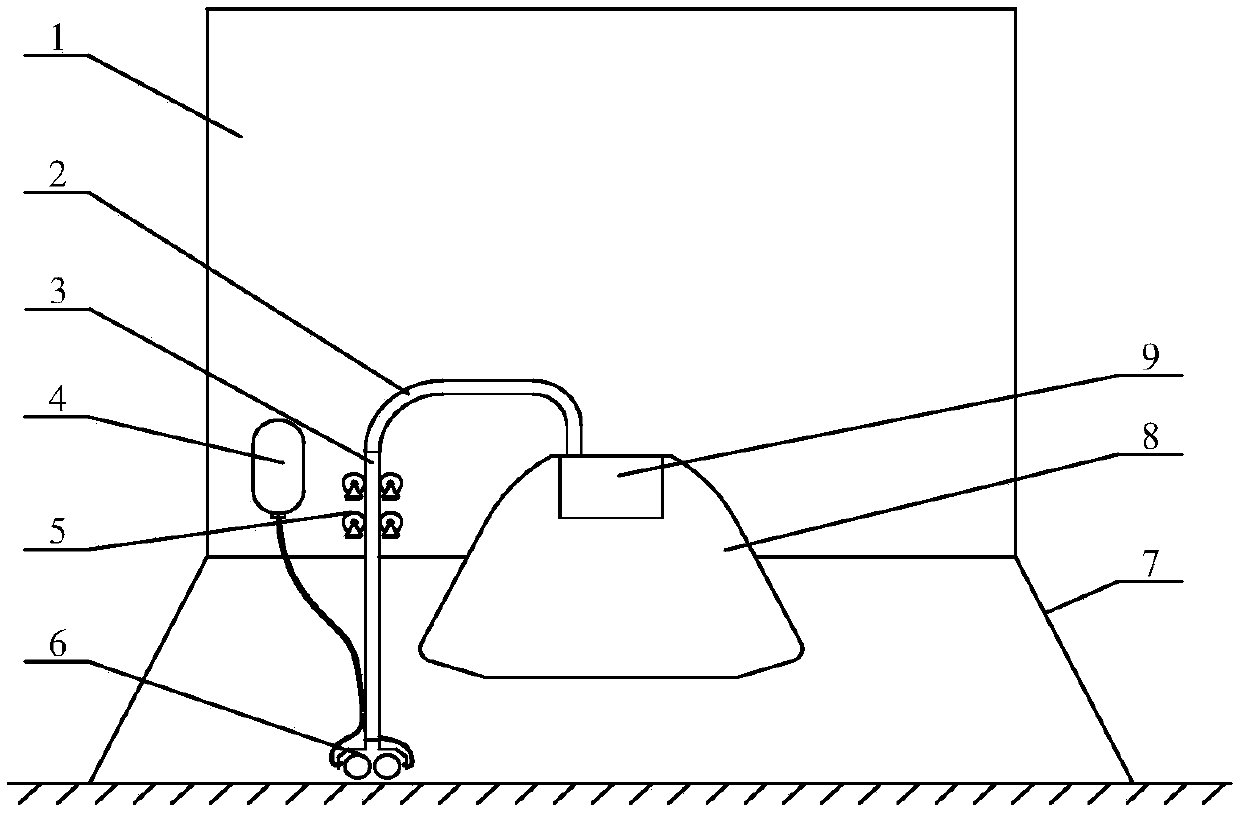
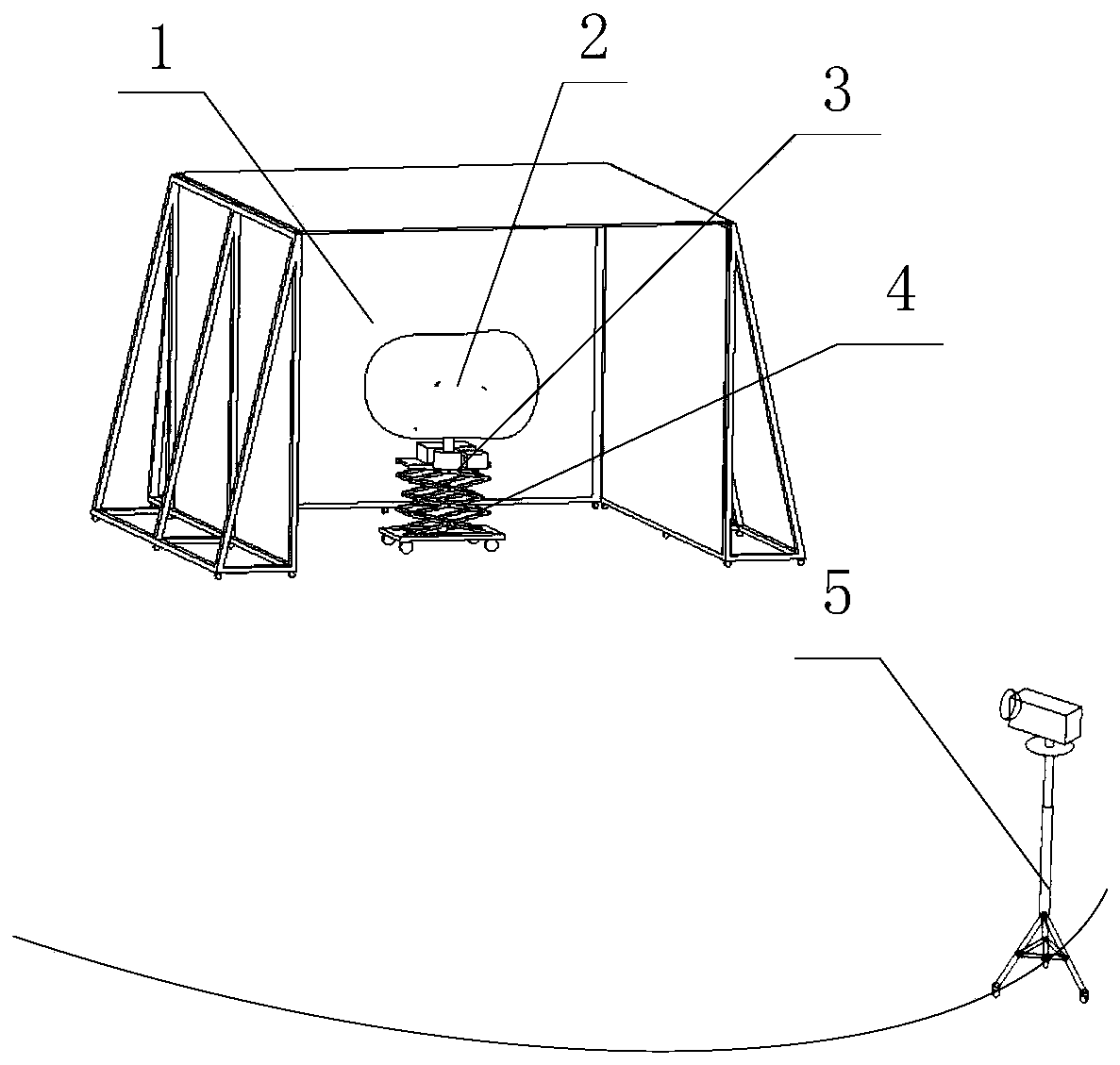
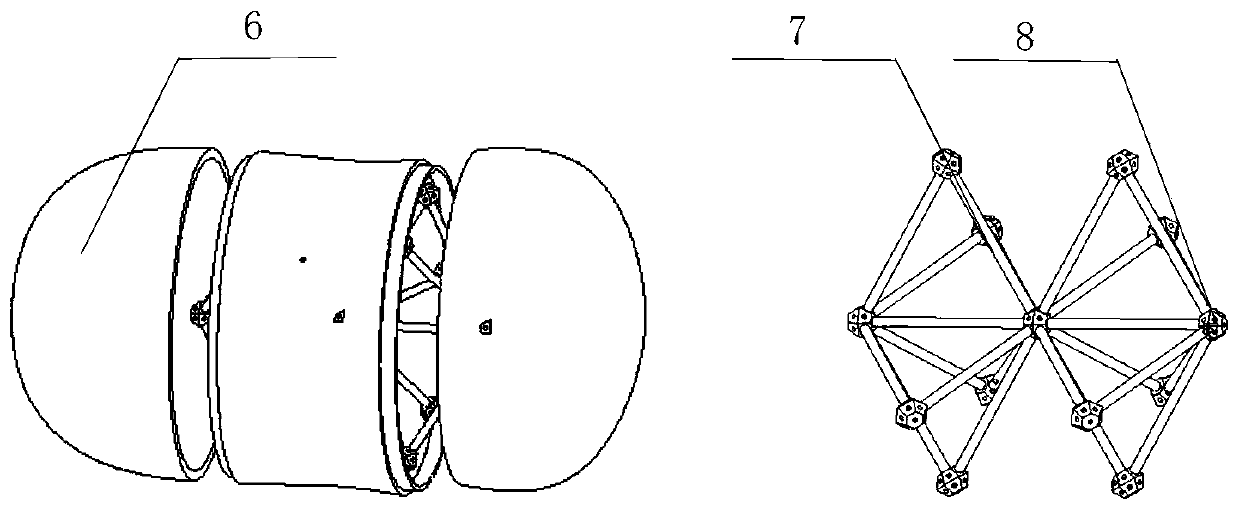
Reconfigurable small celestial body impact detection target characteristic ground simulation system
ActiveCN111453005AImprove adaptabilitySimple reconfigurable solutionCosmonautic condition simulationsCelestial bodyComputational physics
A reconfigurable small celestial body impact detection target characteristic ground simulation system comprises a deep space background simulation module (1), a reconfigurable asteroid scaling splicing model (2), an asteroid rotation axis control module (3), a movable lifting support module (4) and an asteroid surface illumination characteristic simulation module (5). The deep space background simulation module (1) is used for absorbing illumination; the asteroid rotation axis control module (3) is used for adjusting the posture of the reconfigurable asteroid scaling splicing model (2); the movable lifting support module (4) is used for adjusting the height and the position of the reconfigurable asteroid scaling splicing model (2); and the asteroid surface illumination characteristic simulation module (5) is used for outputting illumination. The simulation system provided by the invention can satisfy simulation of the small celestial body motion state and the surface illumination characteristics of an impactor in the process of impacting the target small celestial body; meanwhile, the system has high adaptability, and a reconfigurable scheme is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
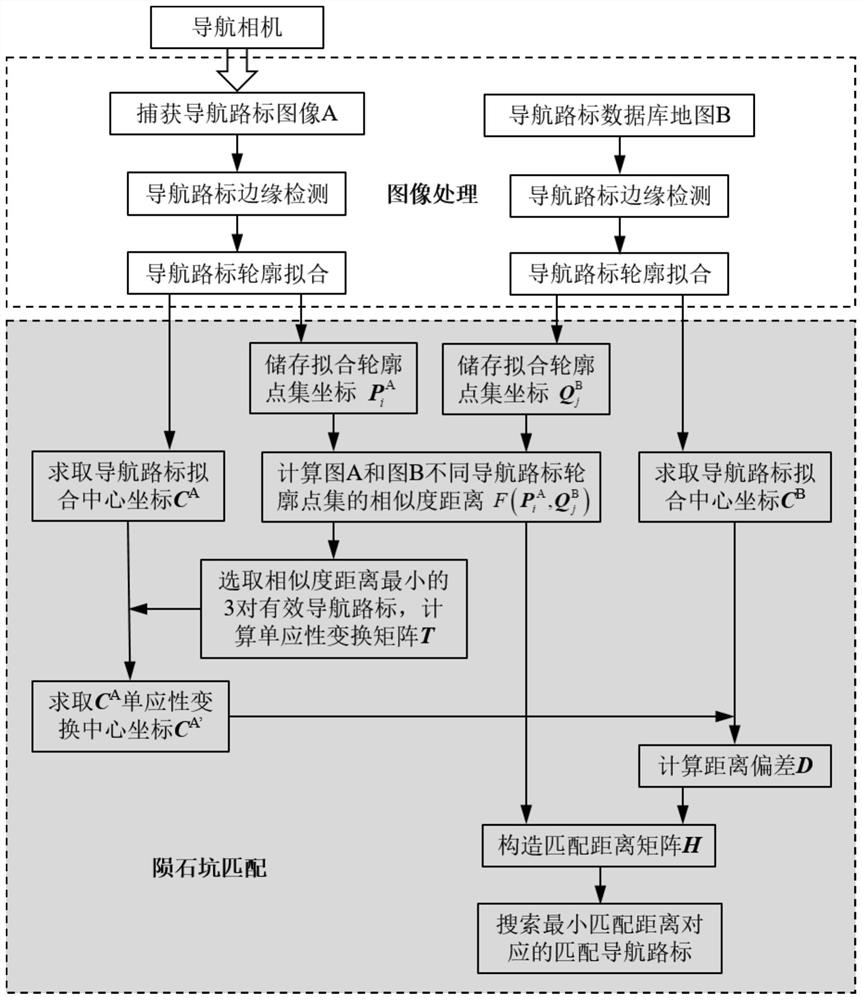
Planetary surface navigation landmark matching method based on contour point set
ActiveCN112906573ASimplify complexitySimplify calculation difficultyInstruments for comonautical navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionLandformPlanetary surface
The invention relates to a planetary surface navigation landmark matching method based on a contour point set, and belongs to the field of deep space exploration. According to the invention, the detector carries out navigation landmark edge detection and fitting on a planet surface image A and a database map B, and contour point set coordinates are obtained through navigation landmark fitting contour discretization. The similarity distance of the obtained discrete point set is calculated. Three pairs of navigation road signs with minimum numerical values in the point set similarity matrix are selected as effective matching road signs, and a homography transformation matrix is calculated; and affine transformation coordinates of the center coordinates of the navigation landmarks of the image to be matched is obtained through the homography transformation matrix, distance deviation is calculated by utilizing the center pixel coordinates of the navigation landmarks of the image, a matching distance matrix is constructed, and the navigation landmark with the minimum matching distance is searched as the matching landmark. According to the method, the matching applicable objects are wider, topographies such as meteorite craters, rocks and gullies in optical images can be matched at the same time, and the method is suitable for matching and tracking of sequence images and database maps.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Asteroid probe autonomous vision positioning system and method fused with orbit dynamics
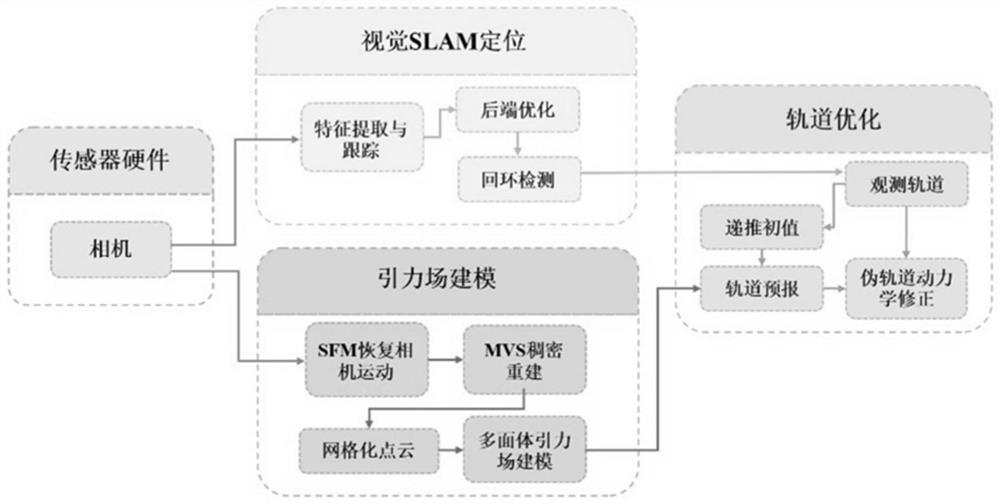
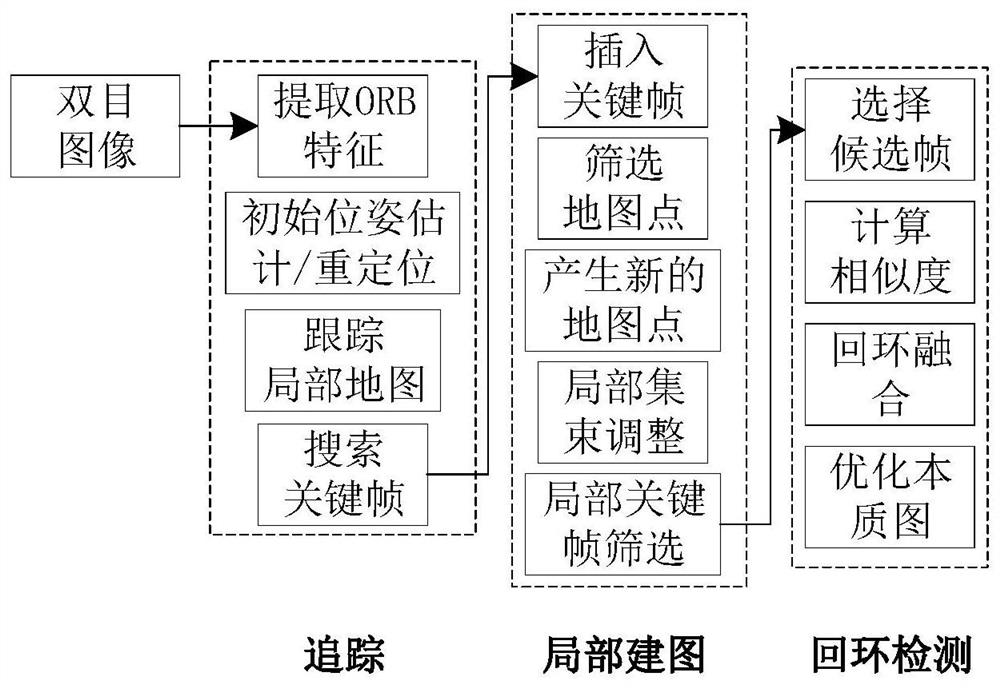
ActiveCN114485620AOptimize positioning cumulative errorGuaranteed efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationFeature extractionPoint cloud
The invention relates to an asteroid probe autonomous vision positioning system and method fused with orbital dynamics. The system comprises a visual sensor, a visual SLAM positioning module, a gravitational field modeling module and an orbit optimization module. The visual sensor is used for shooting asteroid surface images; the visual SLAM positioning module performs feature extraction matching and tracking, estimates the pose of the detector and corrects a visual accumulative error; the gravitational field modeling module reconstructs a planet surface three-dimensional model, carries out dense reconstruction, carries out gridding processing on point clouds, and then carries out modeling on an asteroid gravitational field based on a polyhedron method; the orbit optimization module analyzes and corrects the inversion vision initial orbit determination error according to the estimated detector pose and gravitational field modeling. According to the method, the irregular gravitational field of the planet is solved based on the estimated probe pose and gravitational field modeling, the propagation process of the initial vision orbit determination error in orbit dynamics is analyzed and inverted, the accumulated vision positioning error is corrected, and high-precision navigation positioning is achieved.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
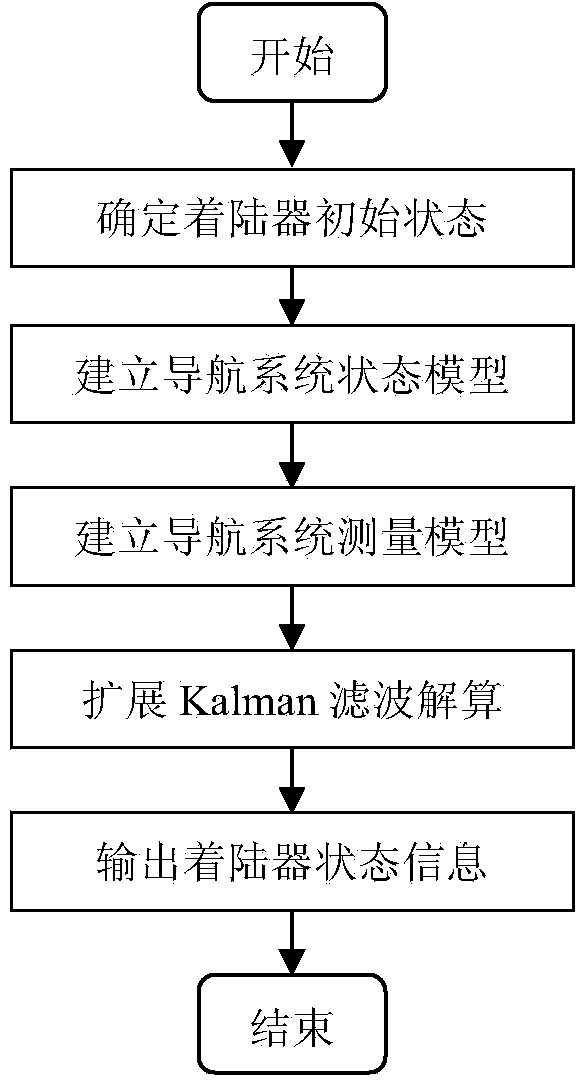
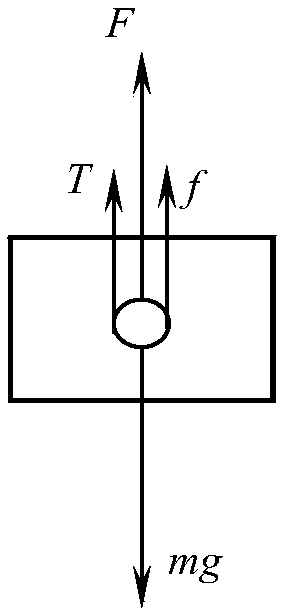
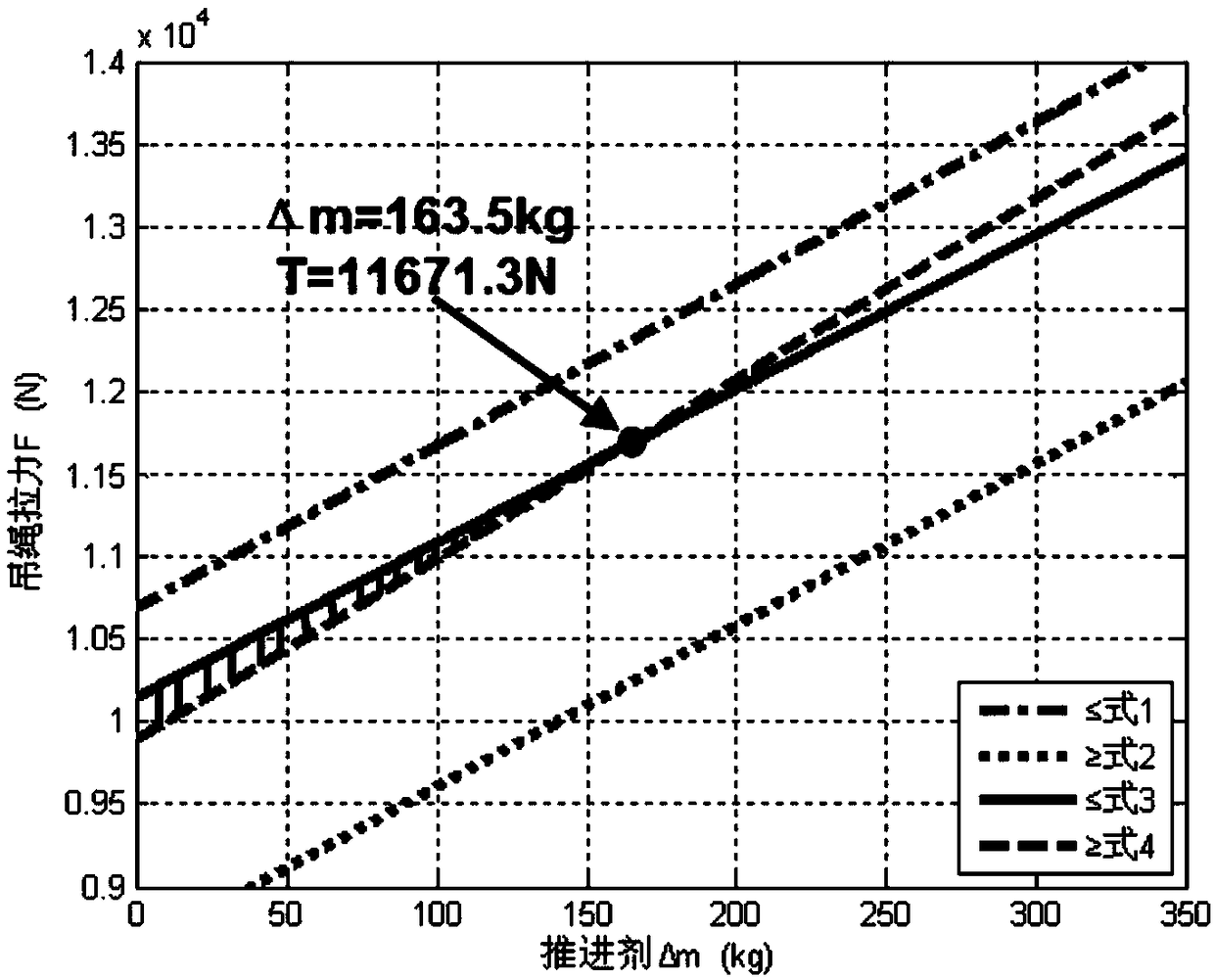
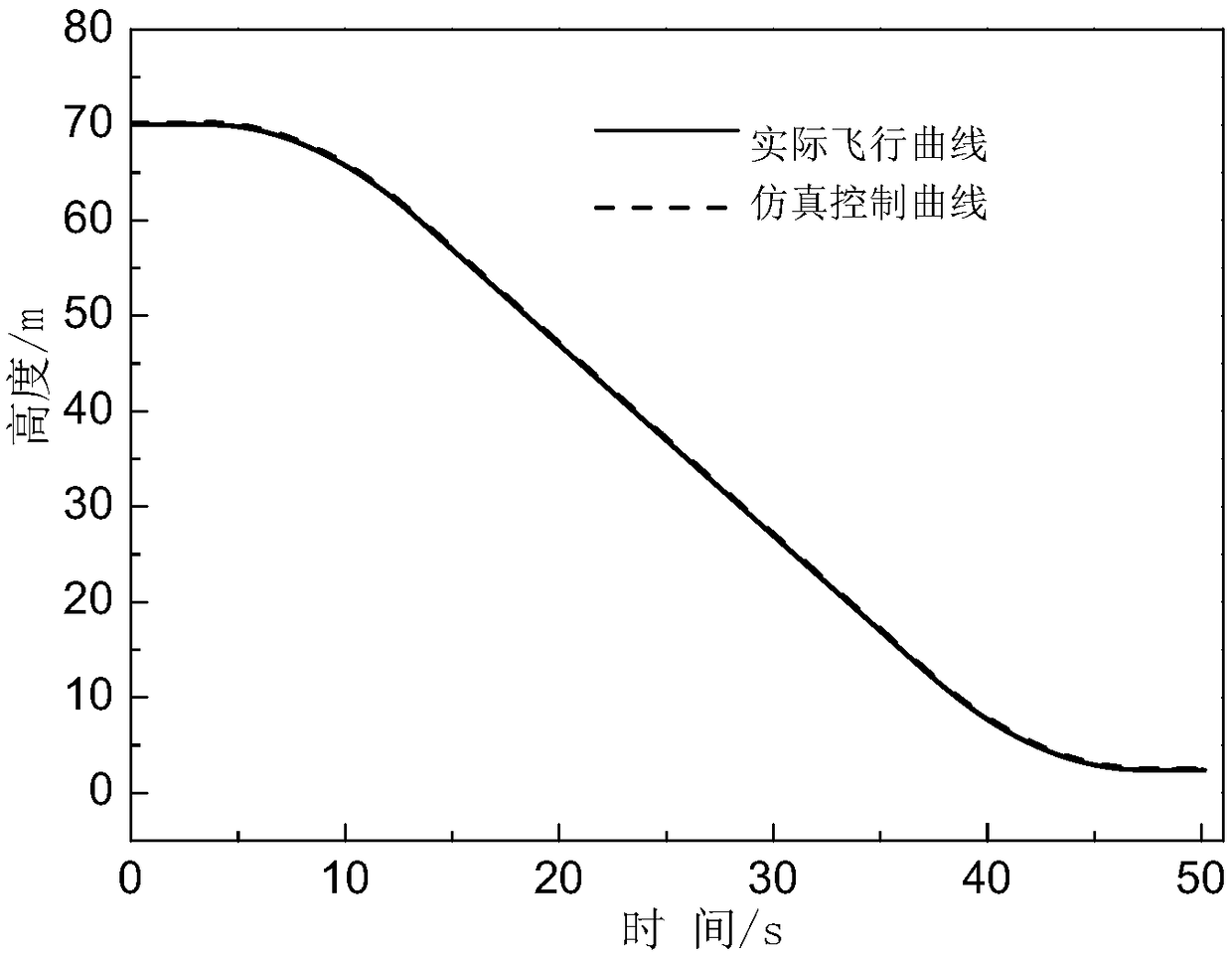
Method of simulating stress state of detector in soft landing test
The invention provides a method of simulating stress state of a detector in a soft landing test. The method of simulating stress state of a detector in a soft landing test includes the steps: throughthe engine thrust Tx of the detector and the downward and upward simulated acceleration a' up and a' down of the detector under different stress state of the detector in the soft landing test, and bymeans of assistance of the lifting rope tension, depending on adjusting and control of the engine thrust, enabling the stress state of the detector to consistent with the real soft landing process soas to accurately simulate the soft landing process in which the magnitude and the direction of the resultant force born by the detector in the vertical direction continuously changes, thus enabling the method of simulating stress state of a detector in a soft landing test can be applied to ground soft landing verification tests of other planetary surfaces, such as a lunar probe and a Mars probe.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
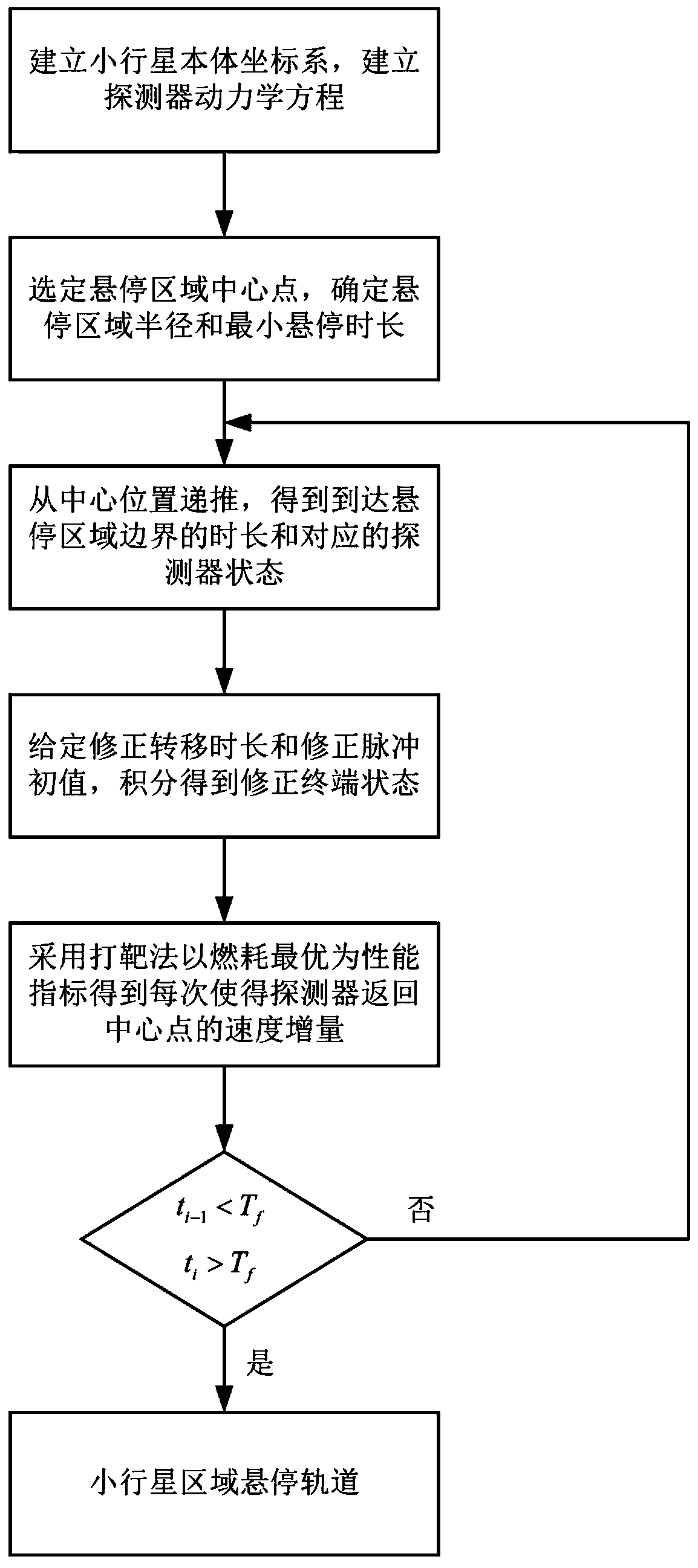
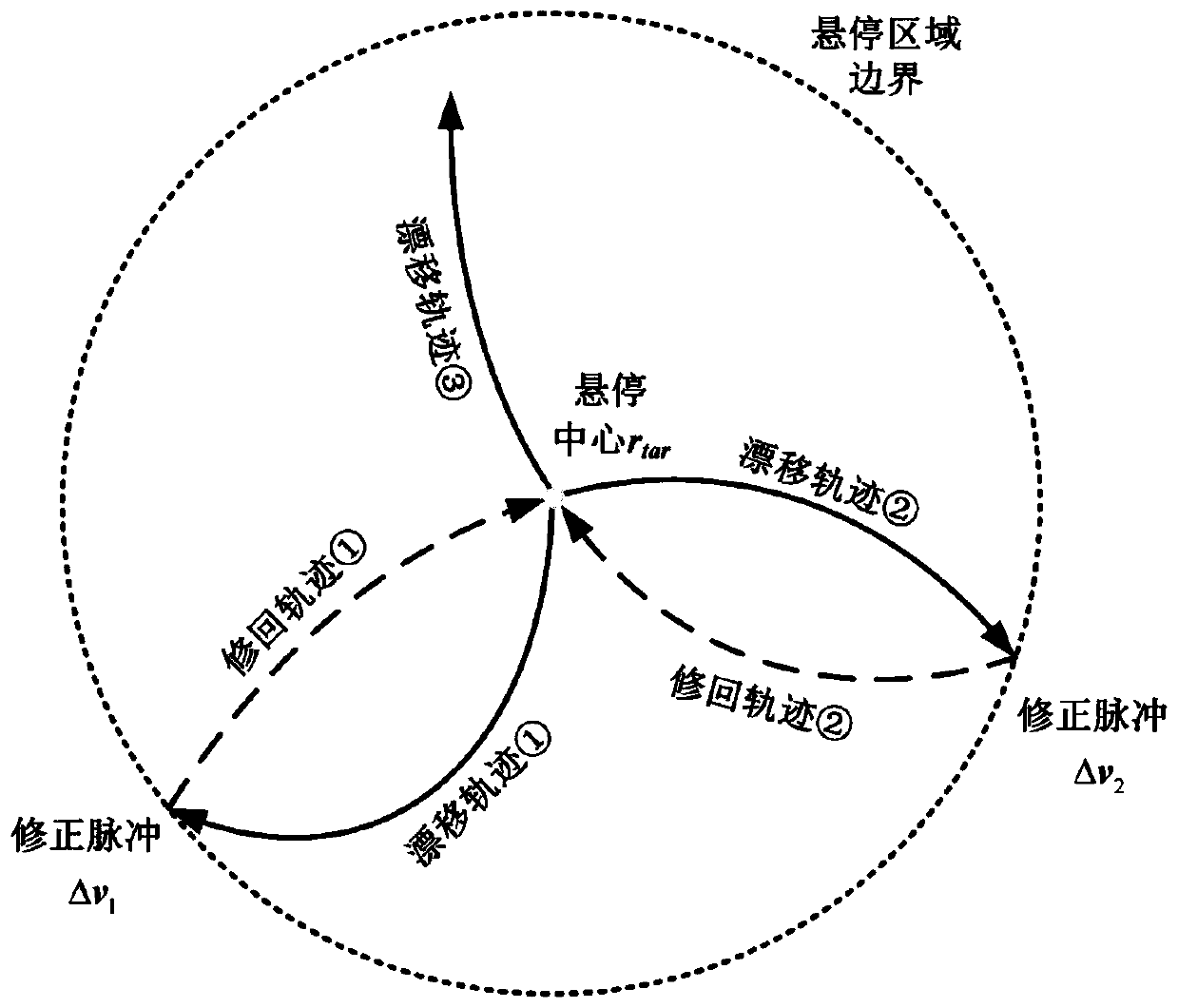
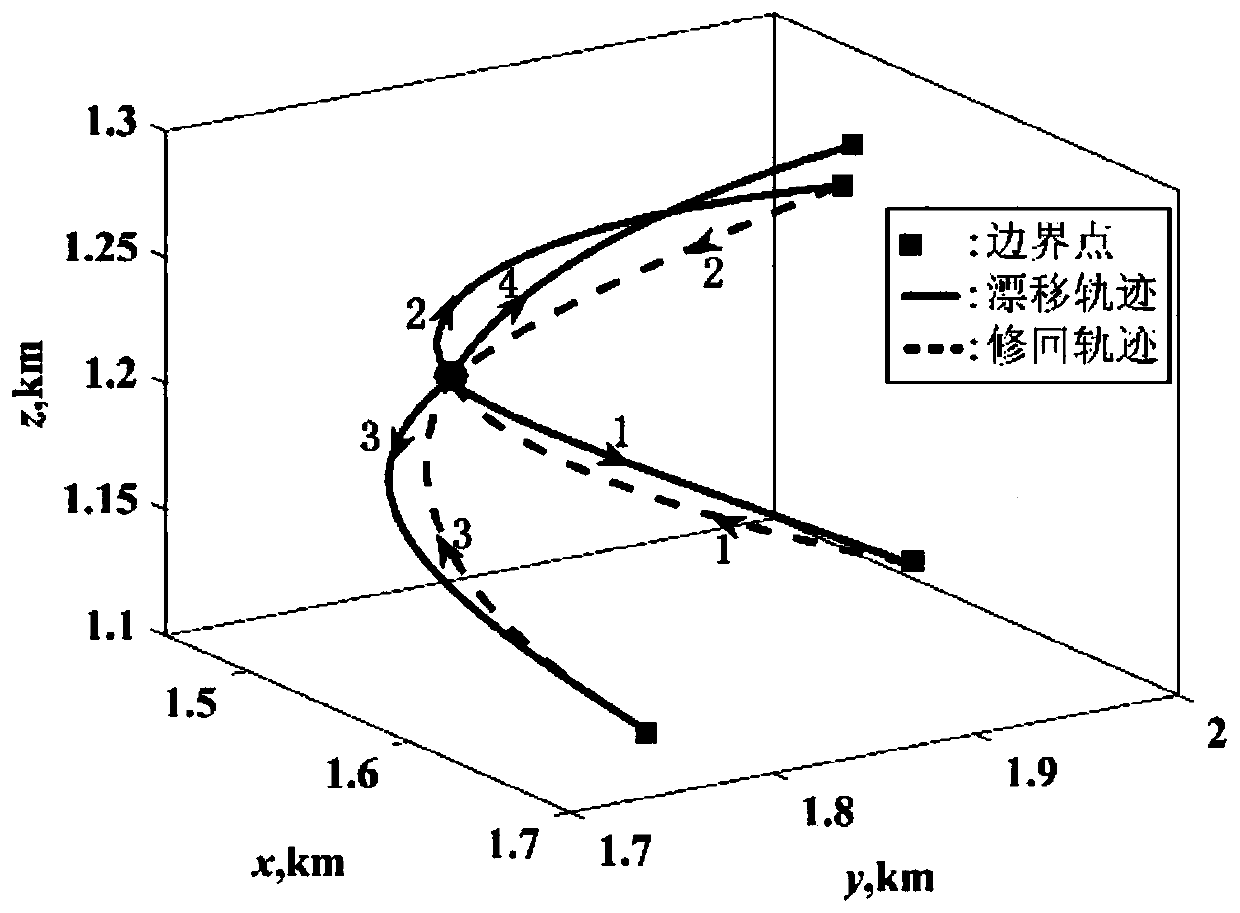
Multi-pulse region hovering method based on small planetary surface observation
ActiveCN110758775AReduce switching timesSmall total velocity incrementCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusPerformance indexAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to a multi-pulse region hovering method based on small planetary surface observation, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The multi-pulse region hovering method based on small planetary surface observation considers small planetary irregular gravity and solar radiation pressure perturbation, and designs a hovering track meeting a small planetary surface hoveringarea constraint based on a targeting method; and the optimal power consumption is the performance index, and the obtained hovering track is minimum in total speed increment under a specific correctionduration constraint. The method has the advantages of being small in required speed increment, few in application pulse times, wide in application range, capable of meeting the hovering area constraint of different sizes, and suitable for hovering track design under the constraint condition of a small planetary surface hovering area.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
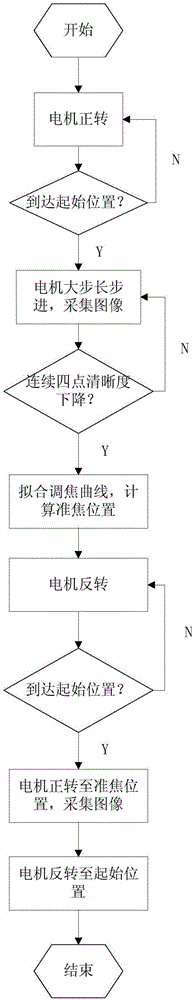
Automatic focusing microscopic imaging system for planet surface material in-situ detection
The invention provides an automatic focusing microscopic imaging system for planet surface material in-situ detection. The automatic focusing microscopic imaging system comprises a lighting unit, a microscopic imaging unit, an image acquisition unit, a focusing transmission unit and an upper computer unit; the lighting unit and the microscopic imaging unit are located in the same optical path; the microscopic imaging unit includes a microscope objective lens and a microscope lens barrel; the focusing transmission unit is a gear external-engagement transmission device; the arrangement direction of the focusing transmission unit is perpendicular to the lighting unit; the focusing transmission unit converts the transmission of gears to the movement of the microscope lens barrel; the image acquisition unit and the microscope lens barrel are in the same optical path; the image acquisition unit is connected with the focusing transmission unit; and the upper computer unit carries out definition judgment on an acquired image and controls the whole system to make the same in a focusing state. With the automatic focusing microscopic imaging system of the invention adopted, definition judgment can be carried out on the image of a sample to be detected; a focusing position can be found out quickly through a fitting a focusing function, and therefore, the speed and precision of focusing can be improved. Unitization design is adopted, so that the automatic focusing microscopic imaging system has the advantages of small size, strong function and so on.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
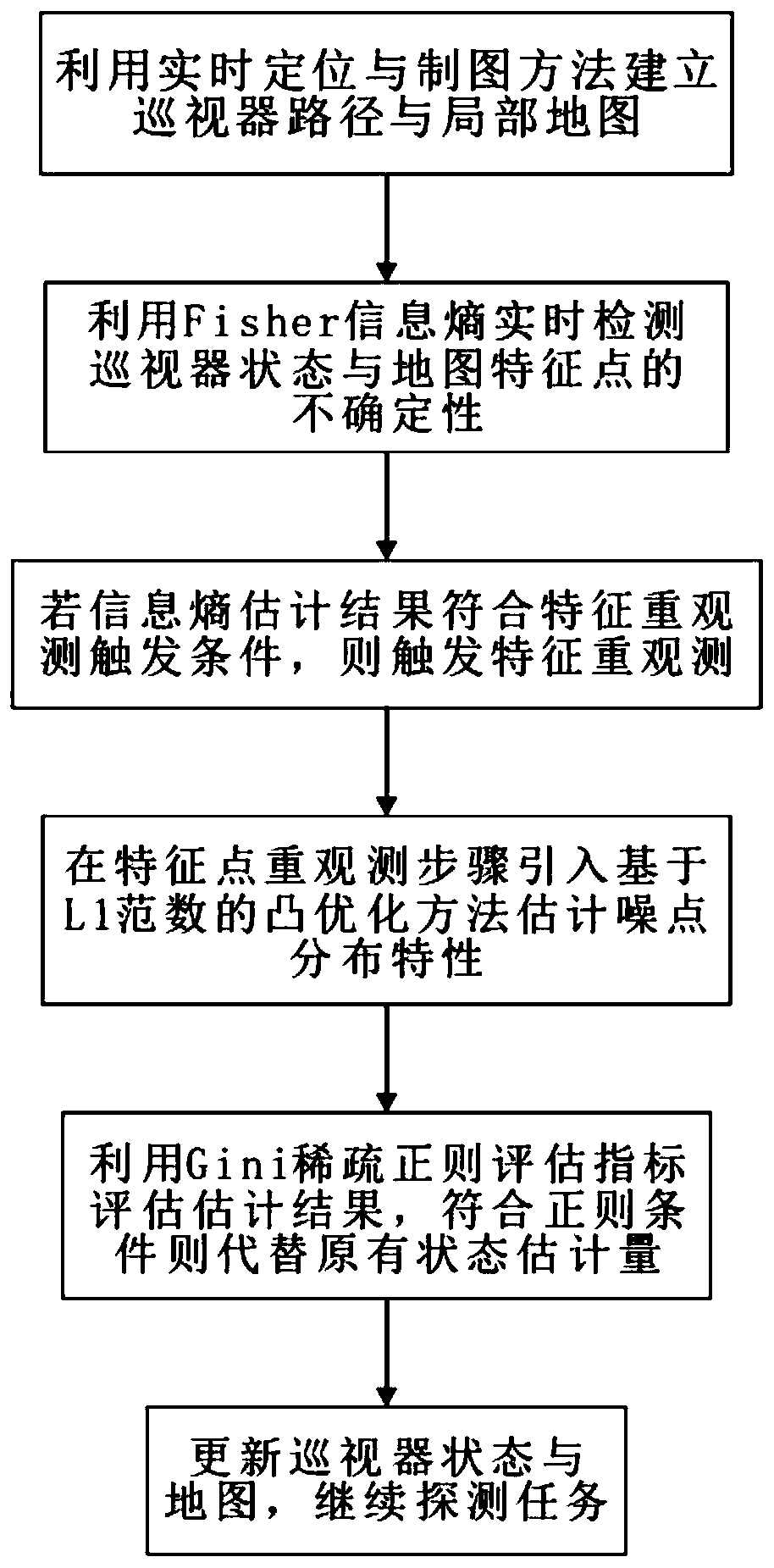
Planetary patrol device active path planning method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN110057371AHigh positioning accuracyEffective estimateInstruments for comonautical navigationPlanning approachNoise estimation
The invention discloses a planetary patrol device active path planning method based on compressed sensing. The planetary patrol device active path planning method comprises steps that: positioning andmapping of a conventional patrol device are carried out by using a SLAM method; Fisher information entropy is used for real-time examination of uncertainty of state estimation and characteristic point estimation, and a characteristic active re-observation decision mechanism is established; the compressed sensing method is introduced, when the map features are re-observed, and an L0 norm optimization problem, which is difficult to solve in the original compressed sensing problem, is replaced by an L1 norm, and noise points of non-Gaussian distribution are estimated; a Gini index function is used for examining the sparse regularities of the noise estimation sequence, and the precision of the L1 norm convex optimization method is guaranteed; and finally, the complete patrol device path planning method is established by taking the maximized Gini evaluation parameter result of the next step as an optimization index. The invention relates to the technical field of navigation guidance and control, and mainly relates to navigation guidance application for a planetary surface roaming patrol mission section.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Apparatus and method for controlling a satellite
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
Lunar communications system
A system for communications between a lunar or planetary surface and the Earth may include a first communications satellite adapted to be positioned in a predetermined orbit relative to a celestial body. A first antenna may be mounted on the first communications satellite. The first antenna may include a predetermined beam shape for communications between the first communications satellite and an asset on the lunar or planetary surface. A second antenna may also be mounted on the first communications satellite. The second antenna may include a selected beam shape for communications between the first communications satellite and the Earth. A communications system may be included for relaying communications between the first and second antennas.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com