Robot passive foot with controllable angle and robot using the passive foot
A robot and foot technology, which is applied in the field of robot passive feet, can solve problems such as numerous devices, difficulty in ensuring spring rebound control, and inability to adjust the initial angle between the sole of the foot and the ground, so as to reduce weight and prevent yaw rotation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
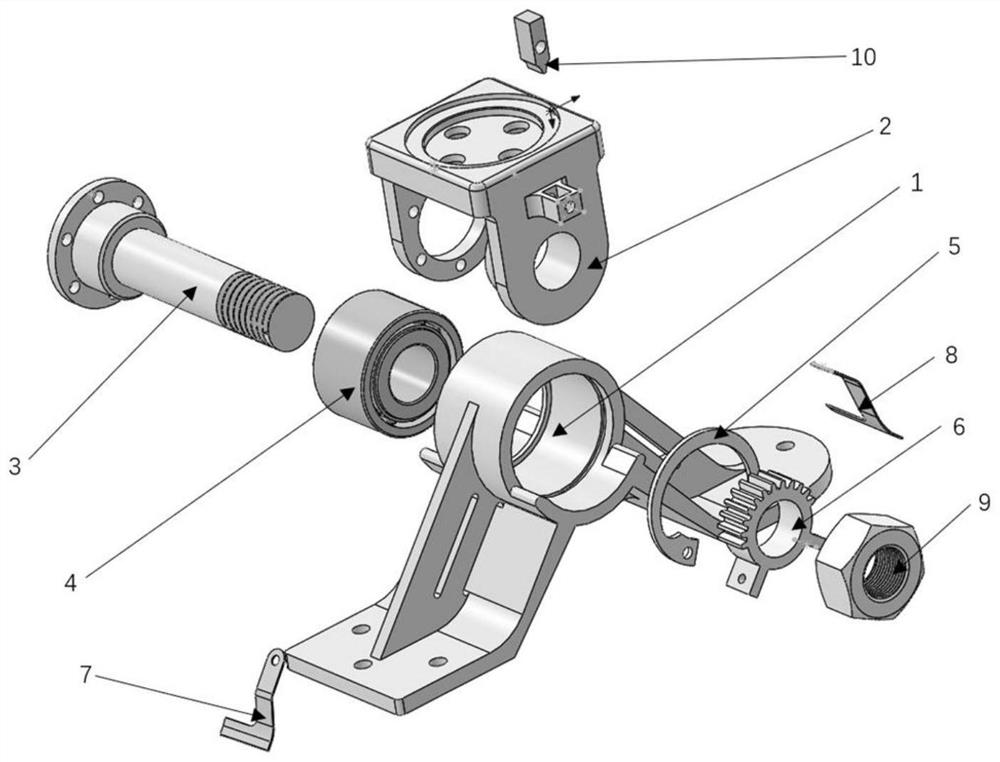
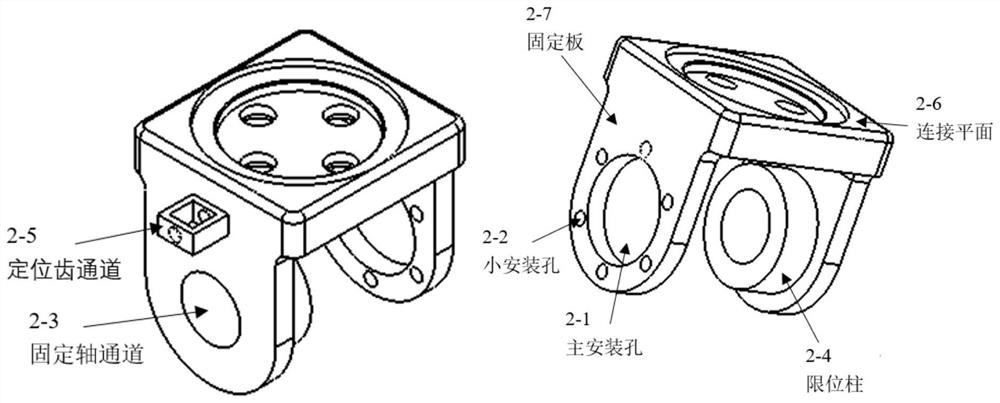
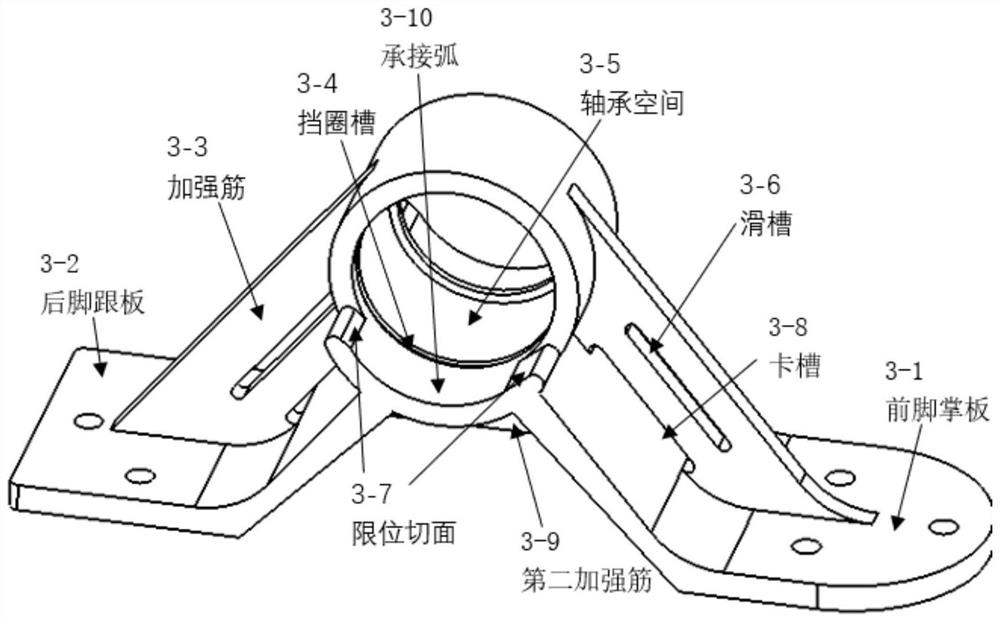
[0033] like figure 1 The shown passive foot of the robot with controllable angle includes a rotating part and a non-rotating part, and the rotating part and the non-rotating part are connected by a spring plate, so as to realize the restriction of the relative movement of the foot body while ensuring the degree of freedom and Automatic return; the rotating part includes a foot body 1 that imitates the bone structure of the human foot arch; the non-rotating part includes a leg-foot connector 2, a fixed shaft 3 and a positioning gear 6; the leg-foot connector 2 is used for Connect the robot leg and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com