Information sharing method, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
An information sharing and mobile device technology, applied in the field of information processing, can solve the problems of virtual key access, cumbersome return steps, inconvenient authorization credential sharing, single authorization method, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
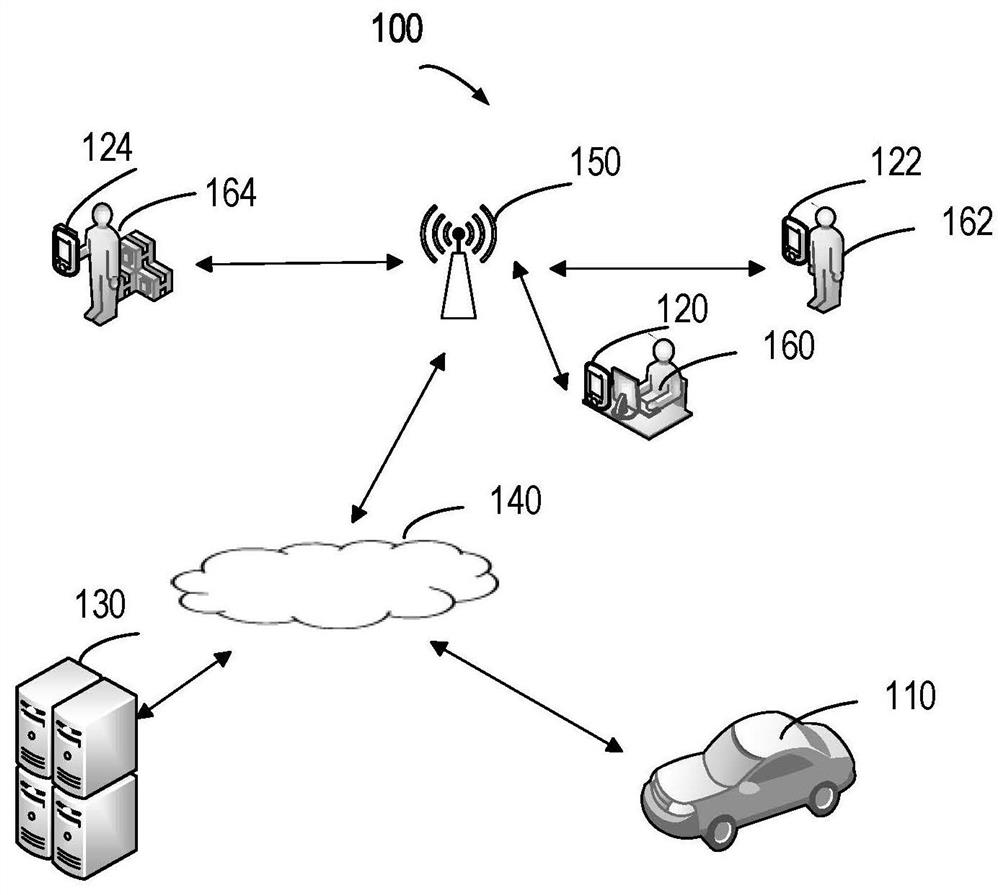
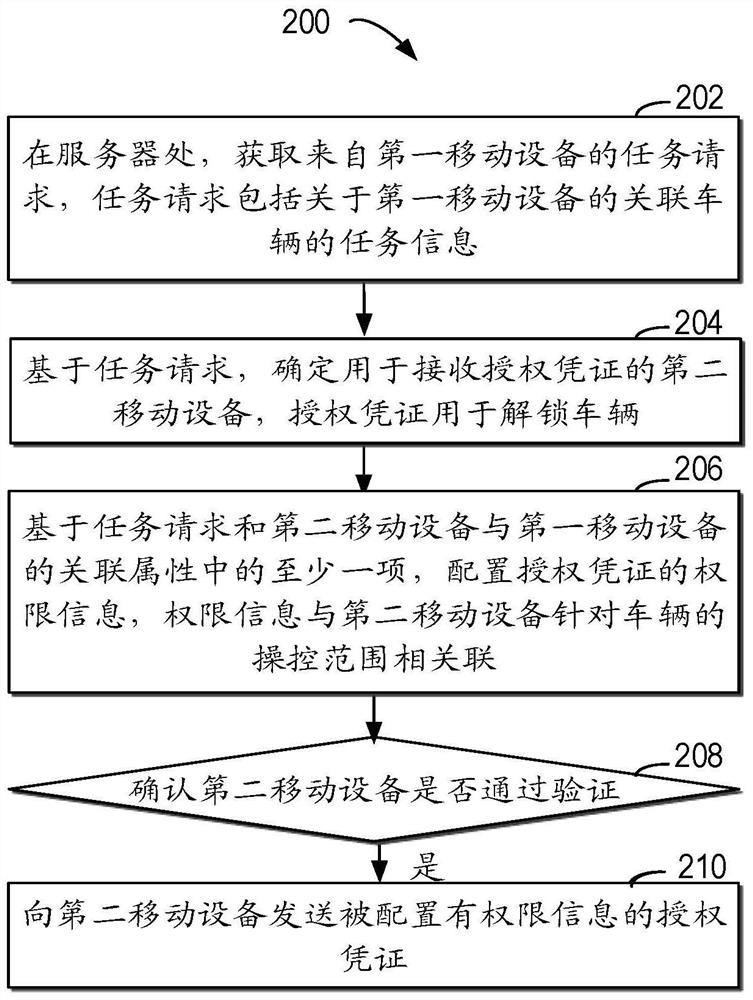
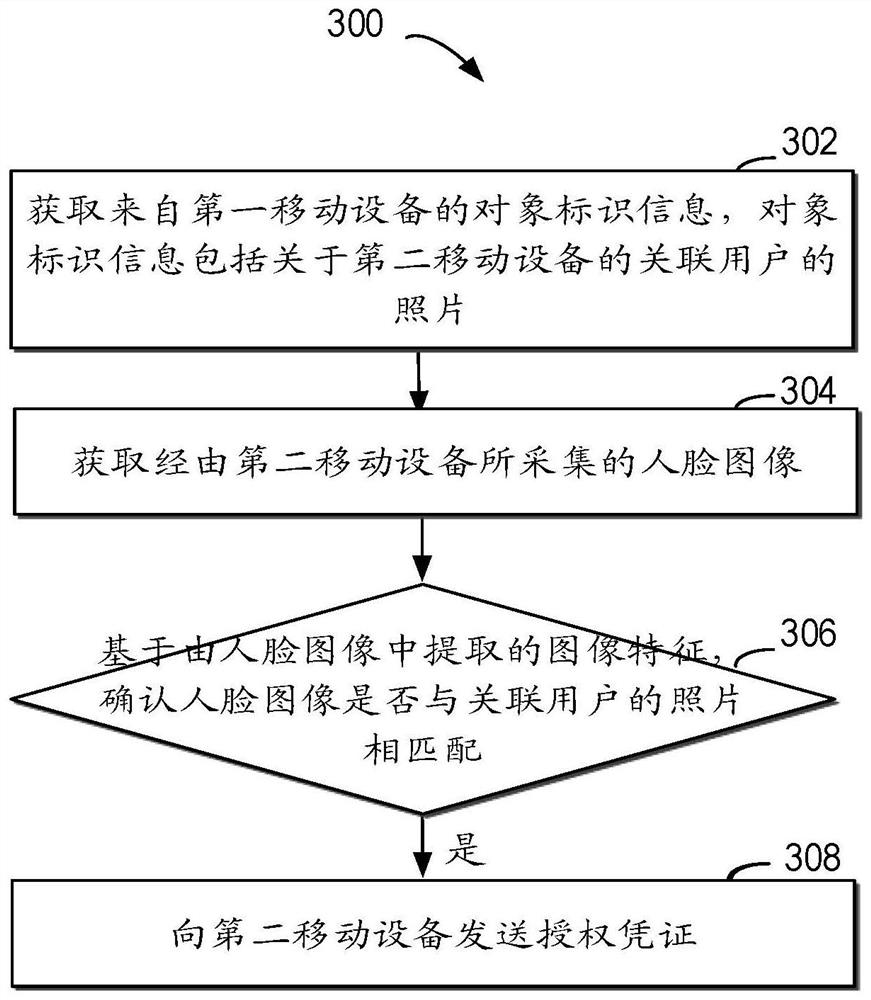
[0019] Preferred embodiments of the present disclosure will be described in more detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Although preferred embodiments of the present disclosure are shown in the drawings, it should be understood that the present disclosure can be embodied in various forms and should not be limited to the embodiments set forth herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the disclosure to those skilled in the art.
[0020] As used herein, the term "comprise" and its variants mean open inclusion, ie "including but not limited to". The term "or" means "and / or" unless otherwise stated. The term "based on" means "based at least in part on". The terms "one example embodiment" and "one embodiment" mean "at least one example embodiment." The term "another embodiment" means "at least one further embodiment". The terms "first", "second", etc. may refer to di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com