Establishment and induced differentiation method of spermatogonial stem cell line of Chinese sword fish
A technology of stem cell differentiation and establishment method, which is applied in the field of establishment and induction of differentiation of equine spermatogonial stem cell lines, and can solve the problems of imperfect culture technology and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
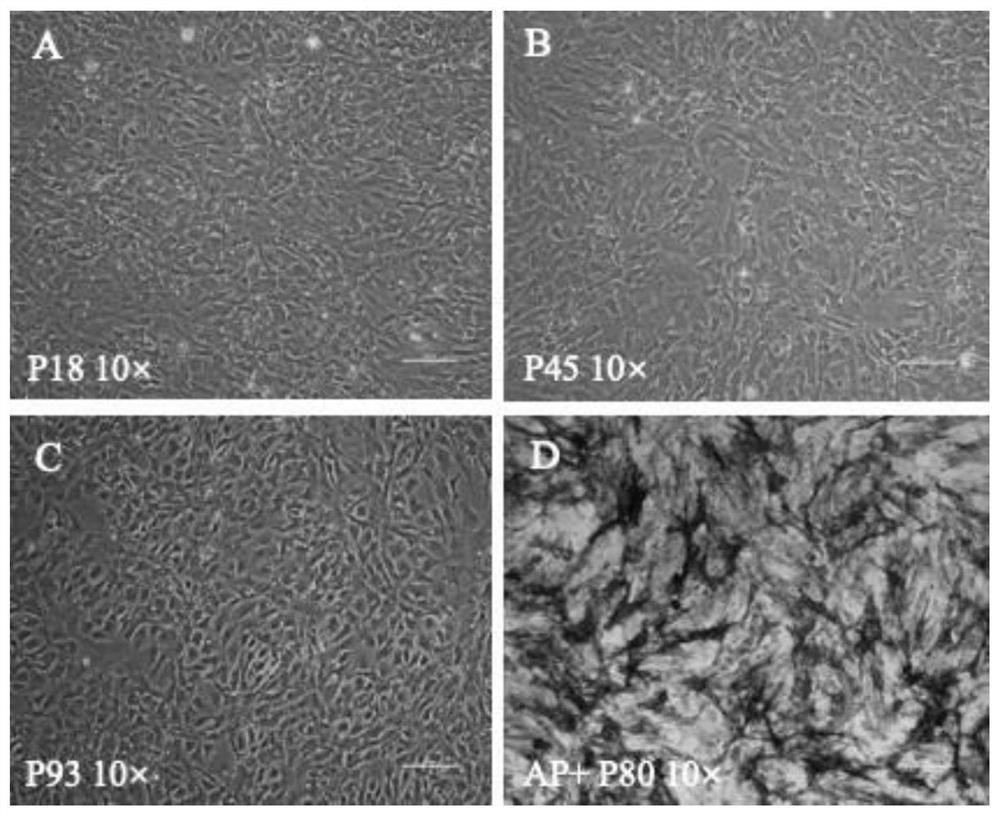
[0050] Example 1 Cultivation of Sperm Stem Cells of Snakefish
[0051] 1. Isolation and Digestion of Testis Cells from Snormouth Fish
[0052] Take juvenile horse mouth fish, soak the fish body in PBS containing 0.5% bleaching powder for 1 min, wash with PBS containing 1% double antibody, pH=7.4 for 3 times, and then dissect. Cut the belly of the fish with scissors, carefully clip out the testis with tweezers, place it in a petri dish containing 1% double-antibody PBS, carefully peel off the fat tissue on the surface of the testis with tweezers, wash 3 times with PBS containing 1% double-antibody, and transfer the testis Transfer to a 1.5mL EP tube containing 500μL of trypsin, cut the tissue properly with scissors, and place it on ice for digestion. After 1 h, 1 mL of medium was added to stop the digestion, and the tissue pieces were gently blown away with a pipette gun, and the cell suspension was transferred to a 24-well plate covered with 0.1% gelatin, and cultured at 28°C...
Embodiment 2
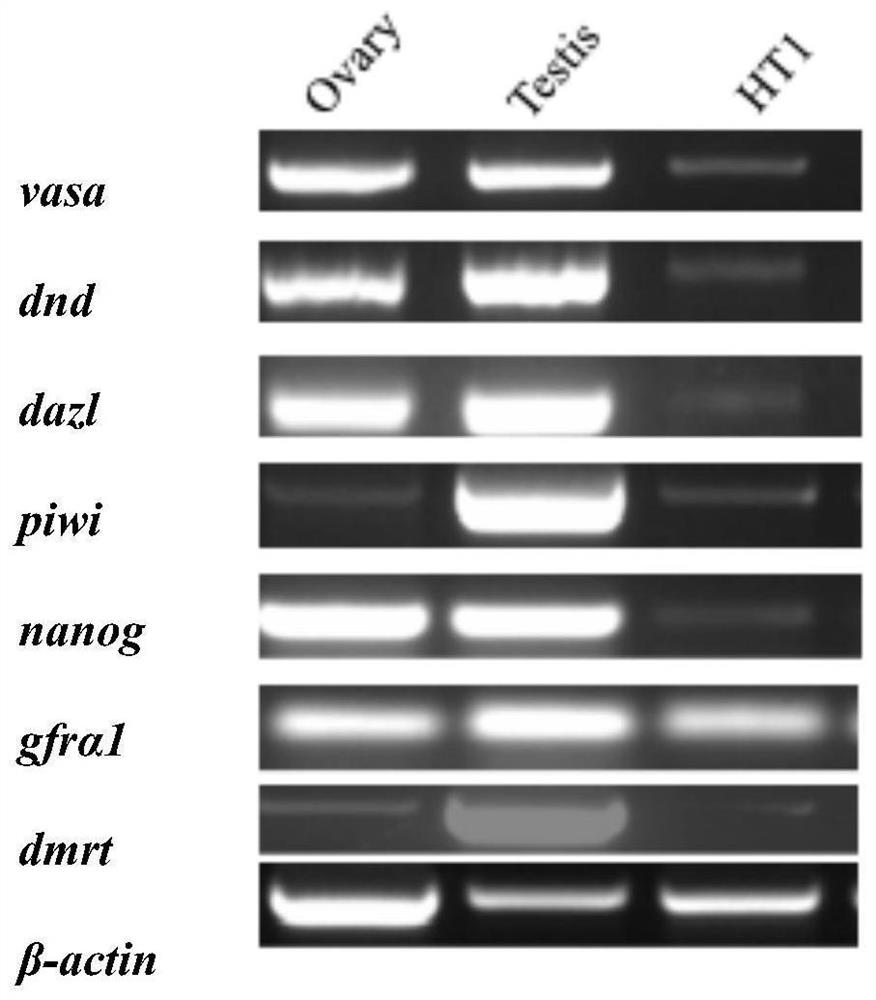
[0057] Example 2 Identification of Spermatogonial Stem Cells from Snakefish
[0058] 1. RT-PCR identification of testicular cell types in cultured Snormouth fish
[0059] In order to identify the cultured sago mouth testis cells as sago mouth spermatogonial stem cells, the RNA of the cells was extracted and reversed to cDNA for RT-PCR detection.
[0060] Primer Premier 6 was used to design primers for vasa, piwi, dnd, and dazl marker genes for spermatogonia, stem cell marker molecules nanog, gfrα1 primers, and dmrt primers for somatic cell marker genes (see Table 1 for primer sequence information). Cell RNA was extracted and reversed. Converted to cDNA, RT-PCR was used to identify the testicular cell types of the horse mouth fish. Take cells from four wells, trypsinize them, resuspend them in PBS into a 1.5mL EP tube, centrifuge at 3500g for 5min, wash once with PBS, carefully suck off the supernatant, and extract cell RNA according to the following steps. First, add 500 μL ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 Inducing the Sperm Stem Cells to Differentiate into Somatic Cells
[0083] will be 5×10 5 Spermatogonia stem cells stably expressing red fluorescent protein were inoculated into a 24-well plate not coated with gelatin. Due to the poor adhesion ability of spermatogonia stem cells, the cells were suspended in the medium and gradually aggregated into clumps, forming pseudo Embryo bodies (such as Figure 6 B). Placed at 28°C for cultivation. Replace half of the medium every other day. After 7 days of suspension culture, add 5 mM retinoic acid to the medium to a final concentration of 10 μM, place the cells at 28°C for induction, replace half of the medium every other day, and continuously induce for 7 days. Transfer the formed spheroids to gelatin-coated cells. Adhesive culture was carried out in a 6-well plate, the spheroids were blown gently with a pipette gun to disperse the cells, and the differentiation of the spermatogonial stem cells of the horse mouth ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com