Wasserstein distance-based similar adversarial network characterization model
A technology of distance and characterization, applied in the field of characterization of similar confrontational network models, can solve problems such as large fluctuations in accuracy, limited accuracy, and limited effects, and achieve the effect of strengthening internal connections, high accuracy, and reducing conditional probability distributions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0069] The embodiments of the present invention are described below by specific specific embodiments. Those who are familiar with this technology can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the contents disclosed in this specification. Obviously, the described embodiments are part of the present invention. , not all examples. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
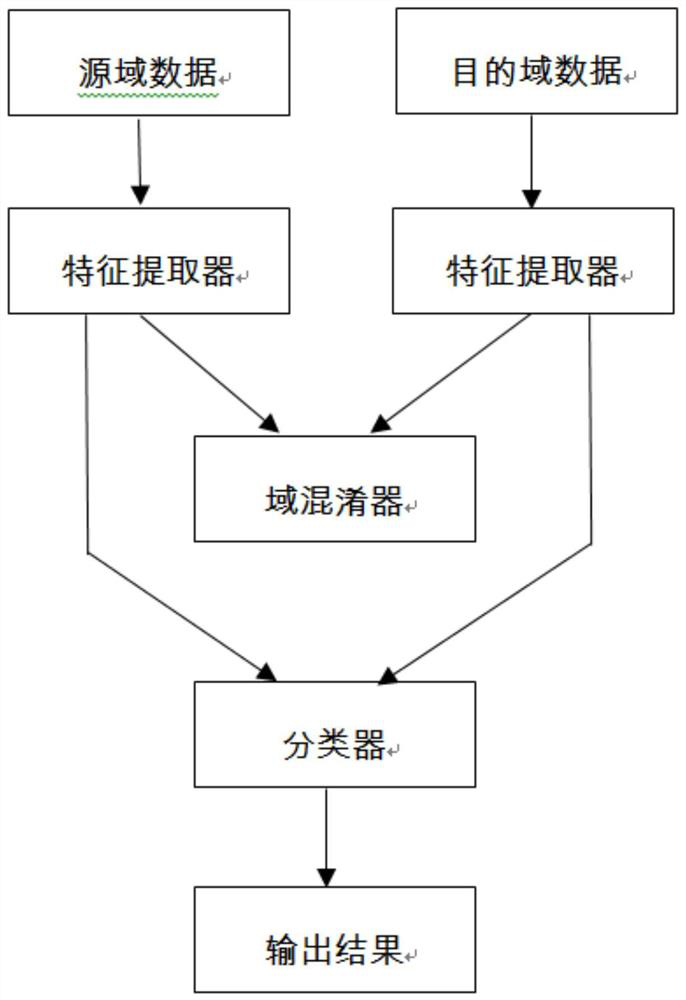
[0070] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a representation similarity adversarial network based on Wasserstein distance, which is characterized in that it includes the following steps:
[0071] S1. The EEG signal is first sampled at a sampling rate of 200hz, and the EEG signal is processed with a band-pass filter between 0.5hz and 70hz to filter out noise and artifacts, and the EEG of a sub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com