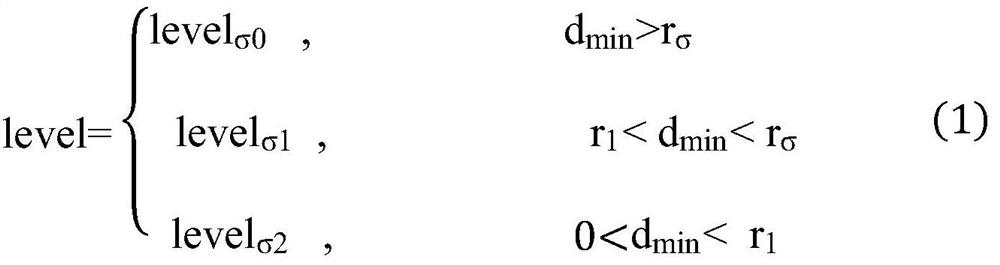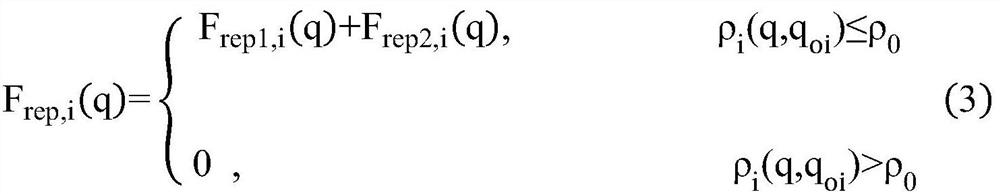Vehicle path planning method based on hierarchical monitoring domain and adaptive artificial potential field method
An artificial potential field method and vehicle routing technology, applied in the field of unmanned vehicle path planning, can solve problems such as inability to generate feasible paths, and achieve the effects of improving various performance indicators, improving safety, and optimizing computing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the technical solution of the present invention, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
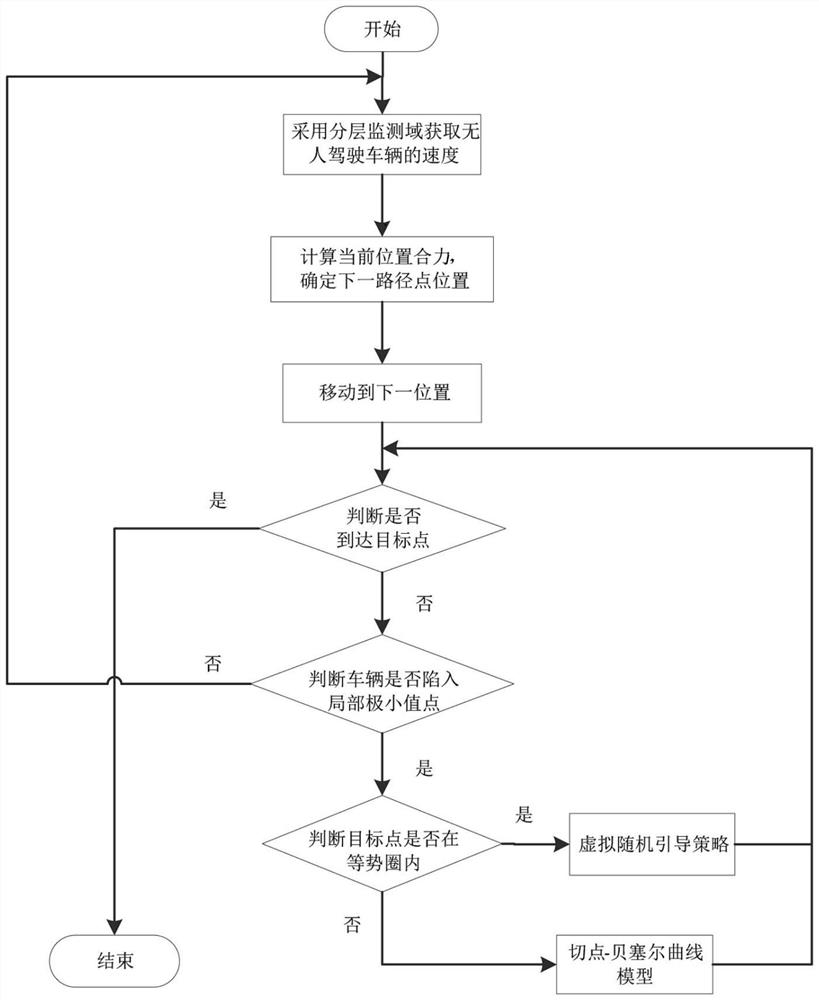
[0062] Embodiments of the present invention provide a vehicle path planning method based on hierarchical monitoring domains and adaptive artificial potential field method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0063] Step 1: Use the hierarchical monitoring domain model to obtain the speed of the unmanned vehicle: set the dynamic monitoring domain of the unmanned vehicle, and calculate the current driving speed of the unmanned vehicle according to the position of the obstacle in the dynamic monitoring domain; The layer monitoring domain model sets different warning levels for environmental changes to realize self-adaptive changes in the speed of unmanned vehicles.
[0064] The specific process of using the hiera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com