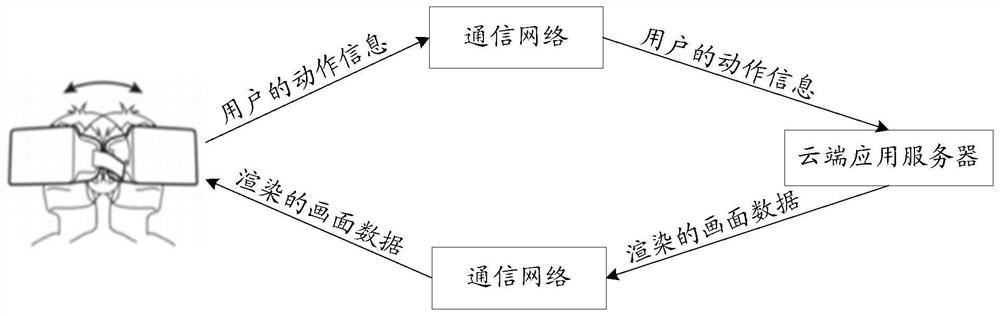
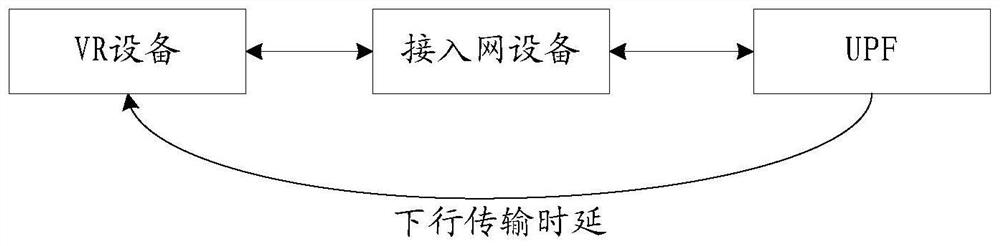
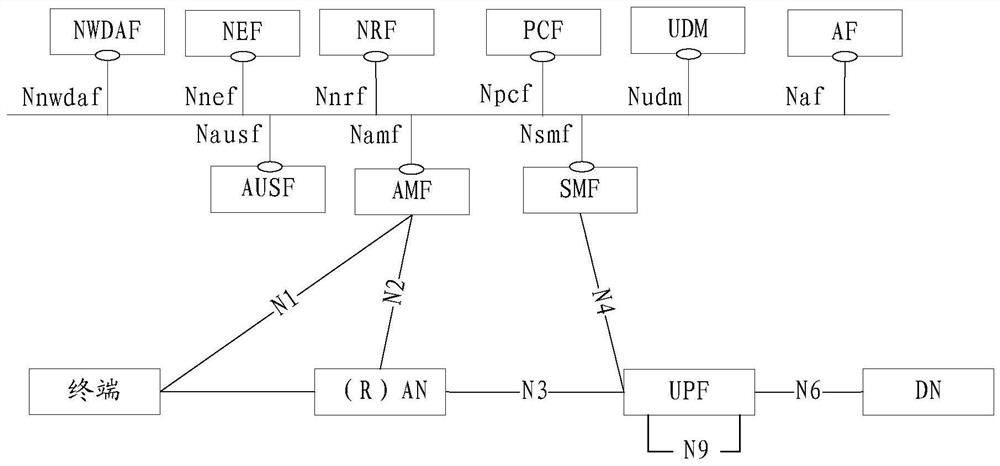
Method and device for determining air interface time delay
An air interface delay and delay technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of inaccurate delay control and inability to meet the needs of VR services.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0183] Embodiment 1 is used to illustrate the implementation process of the above-mentioned mode 1. In Embodiment 1, the loopback delay includes the delay inside the cellular network and the delay outside the cellular network.
[0184] see Figure 12 , the method that embodiment 1 provides comprises:
[0185] 1201. The terminal initiates a PDU session establishment process, so as to establish a PDU session for uplink and downlink data transmission.
[0186] 1202. The terminal sends an uplink data packet to the access network device, where the uplink data packet includes: a first identifier, a timestamp, and a loopback delay D. Correspondingly, the access network device receives the uplink data packet.
[0187] Wherein, the timestamp indicates the time T1 when the terminal sends the uplink data packet.
[0188] 1203. The access network device determines the time T1 and the loopback delay D when the terminal sends the uplink data packet according to the uplink data packet. ...
Embodiment 2
[0203] Embodiment 2 is used to illustrate the implementation process of the above-mentioned manner 2. At this time, the loopback delay includes the delay in the cellular network. In this case, the UPF needs to determine the delay outside the cellular network and send it to the access network device, so that the access network device can determine the air interface delay of the downlink data packet according to the delay.
[0204] see Figure 13 , the method that embodiment 2 provides comprises:
[0205] Steps 1301-1305 are the same as steps 1201 to 1205 respectively.
[0206] 1306. The UPF records the sending time T3 of the uplink data packet.
[0207] Steps 1307-1308 are the same as steps 1206 and 1207 respectively.
[0208] 1309. The UPF records the time T4 when the downlink data packet is received, and calculates the first time delay D1.
[0209] Specifically, the UPF can obtain the first time delay D1=T4-T3 according to T4 and T3.
[0210] 1310. The UPF sends the dow...
Embodiment 3
[0215] Embodiment 3 is different from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 in that: the UPF determines the air interface delay of the downlink data packet or the information used to determine the air interface delay of the downlink data packet and sends it to the access network device, and the access network The device schedules downlink data packets according to the information sent by the UPF. In this embodiment, the adaptation layer carries the first identifier, timestamp, and loopback delay as an example to illustrate the method provided in the above embodiment. At this time, the access network device does not need to perceive the association between uplink and downlink data transmission. , it only needs to perform downlink data packet scheduling according to the UPF instruction.
[0216] see Figure 14 , the method that embodiment 3 provides comprises:
[0217] 1401. Same as step 1201.
[0218] 1402. The terminal sends an uplink data packet, and the adaptation layer header of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com