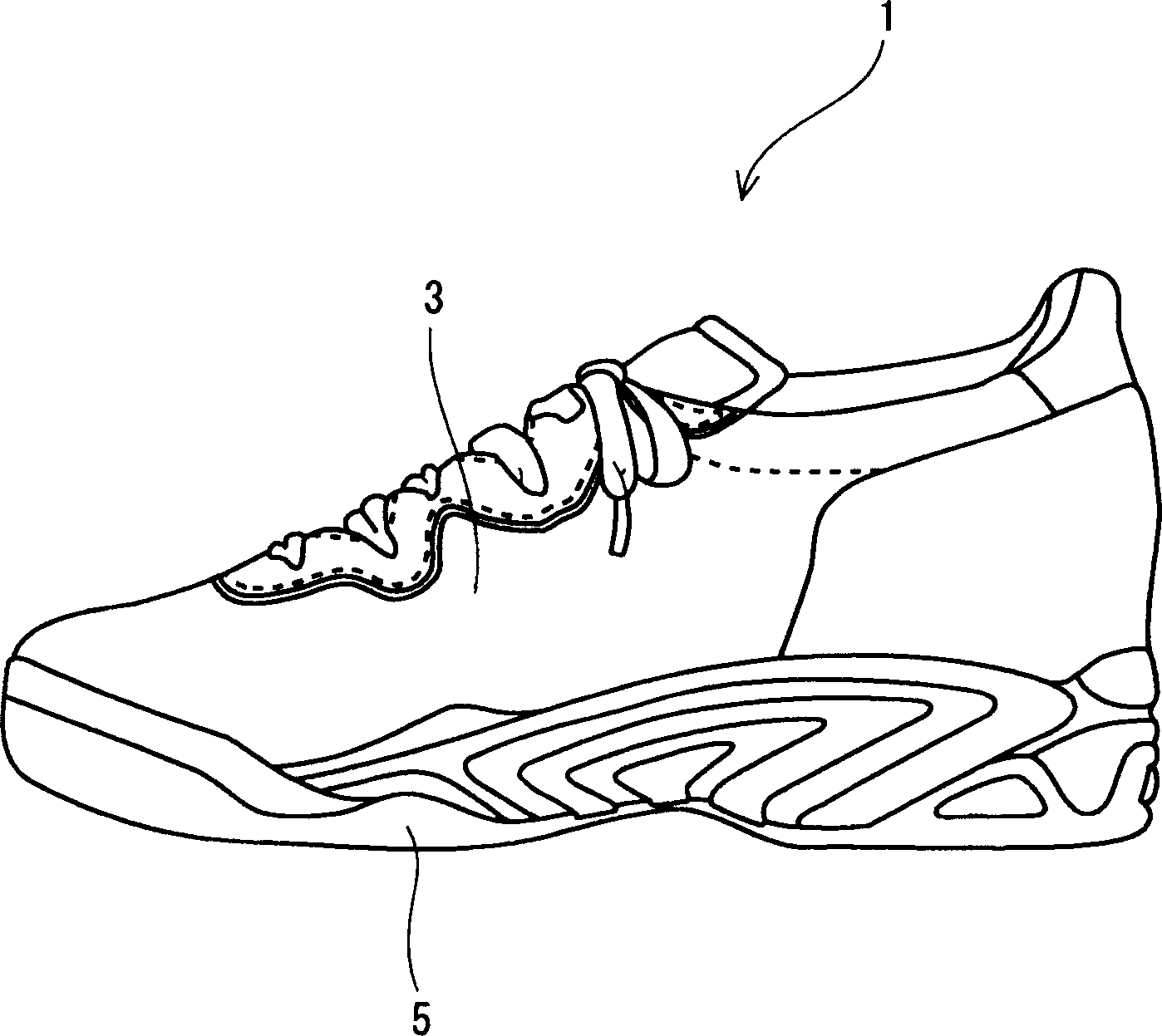
Tennis shoes
A tennis and friction coefficient technology, applied in the field of tennis shoes, can solve the problem that the anti-skid performance and sliding performance of tennis shoes cannot be fully coordinated, and achieve the effect of good anti-skid performance and good sliding performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
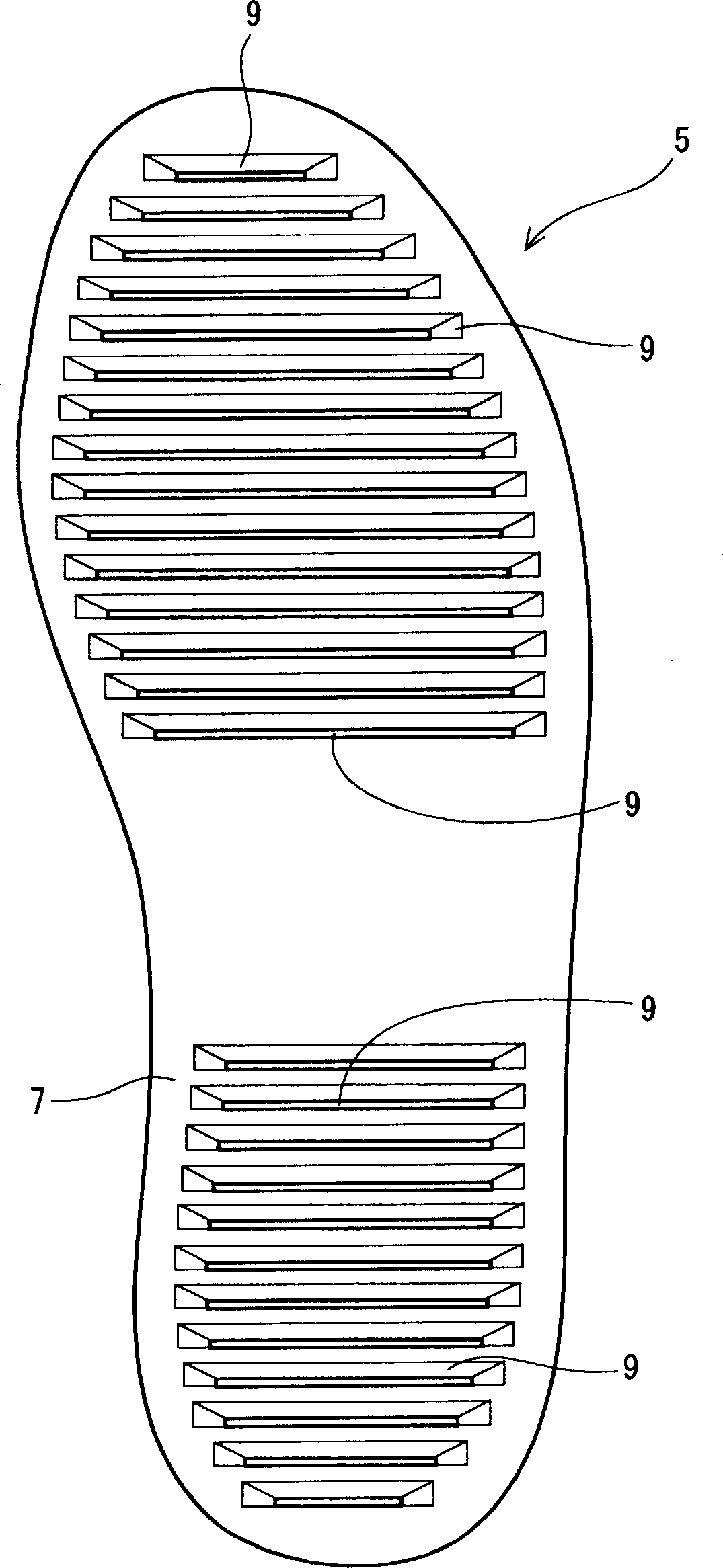
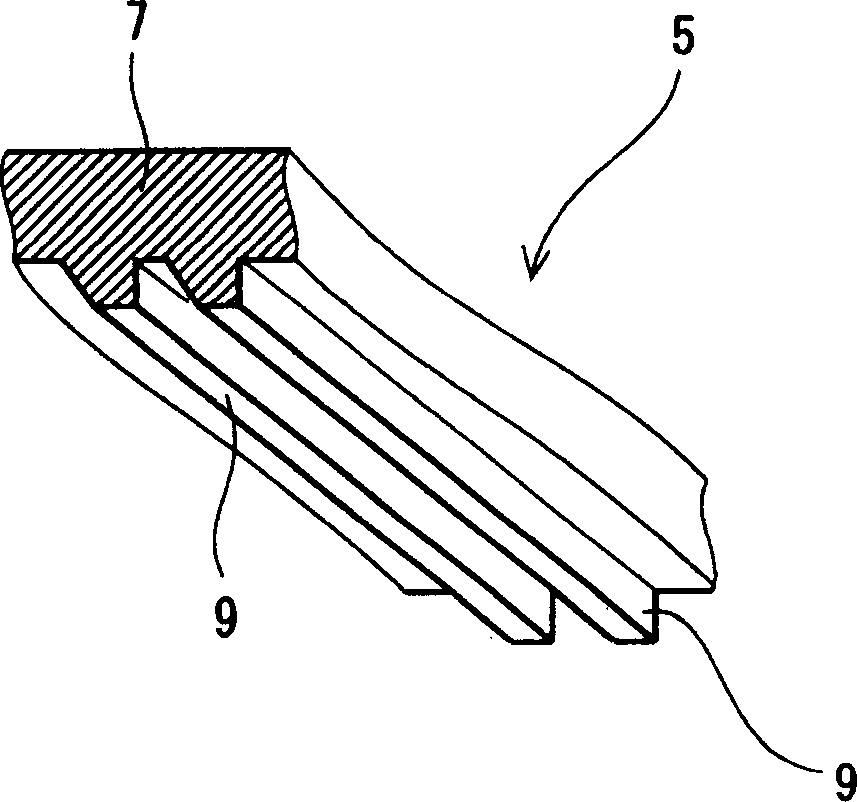
[0103] A rubber compound containing styrene-butadiene copolymer is put into a mold as a base material to undergo rubber cross-linking reaction. In this way a sole is obtained. The pattern on the underside of the sole is as figure 2 shown in . The sole has a large number of transverse ridges formed thereon. The inclination angle θa of these transverse ridges was 30 degrees, the inclination angle θb was 90 degrees, the height H was 3 mm, and L2 / L1 was 0.25. A tennis shoe according to Example 1 is obtained by attaching a midsole made of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and an upper made of cotton to the sole.
example 2 and 3, and comparative example 1 and 2
[0105] Tennis shoes according to Examples 2 and 3 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 were obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the mold was changed and a sole including transverse ridges taking the shapes shown in Table 1 below was formed.
example 4
[0107] Tennis shoes according to Example 4 were obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the mold was changed and a sole including transverse and longitudinal ridges taking the shapes shown in Table 1 below was formed. The pattern of the sole is as Figure 7 shown in .
[0108] [Actual use test]
[0109] A player is put on tennis shoes, and a tennis match is played on an artificial turf court covered with sand (trademark "OMNICOURT", manufactured by SUMITOMO RUBBERINDUSTRIES, INC.). The ease of changing direction, the anti-slip performance at the start, the sliding performance and the feeling of fatigue of the legs were evaluated on a five-point scale from "1" to "5". The highest rating is a rating of "5". Table 1 below shows the average ratings for the 10 athletes. As shown in Table 1, the outer soles according to each example had excellent evaluation results in all items.
[0110] Comparative example 1
[0111] [Experiment 2]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com