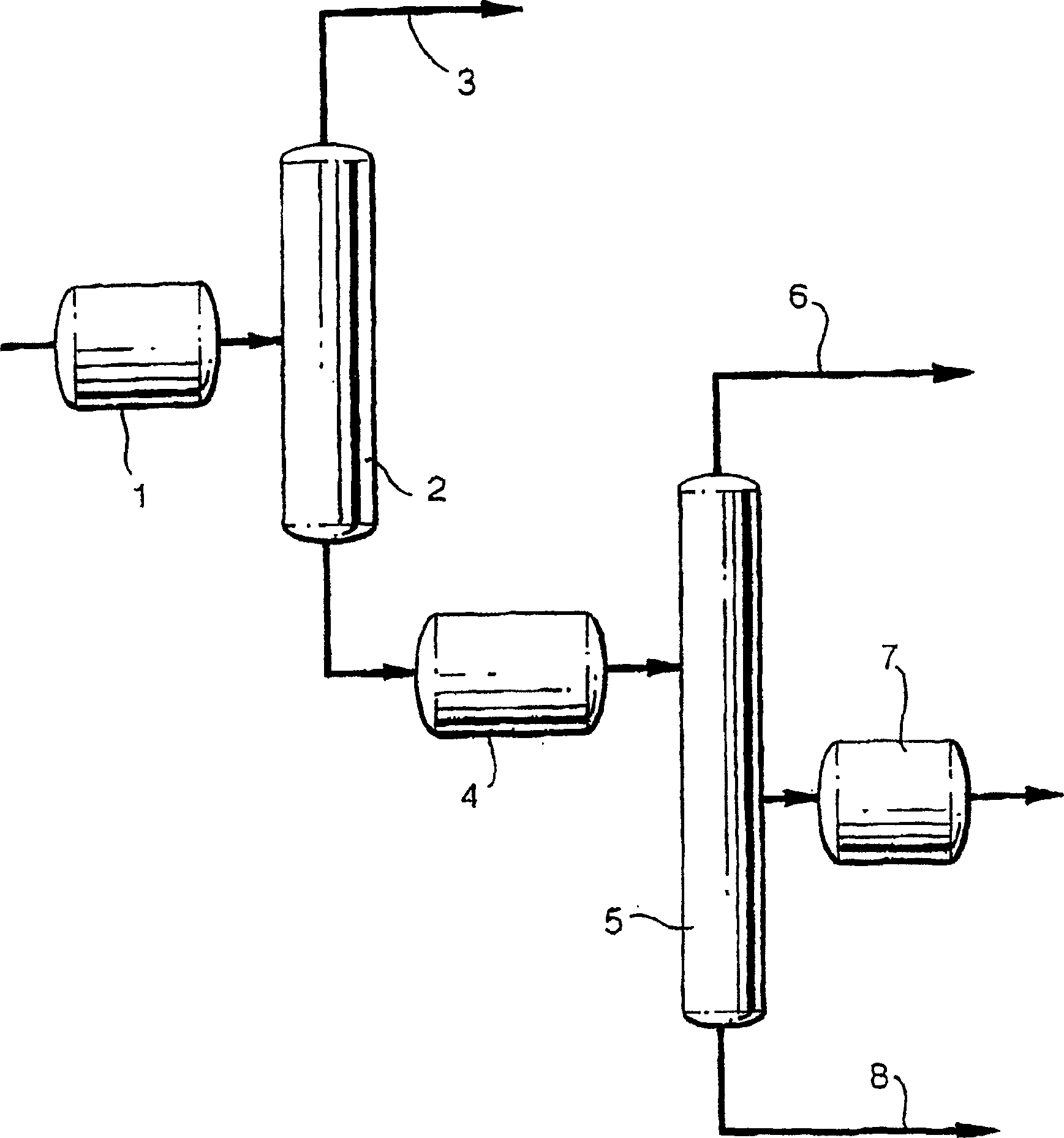
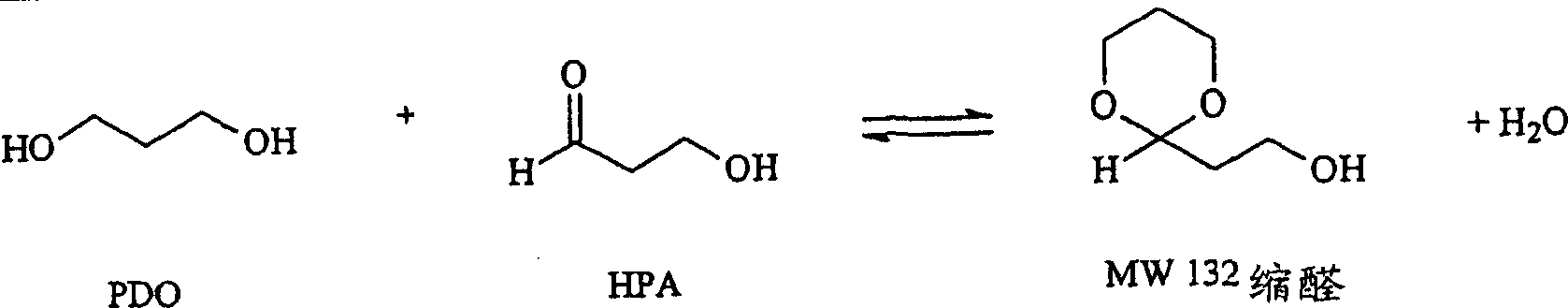
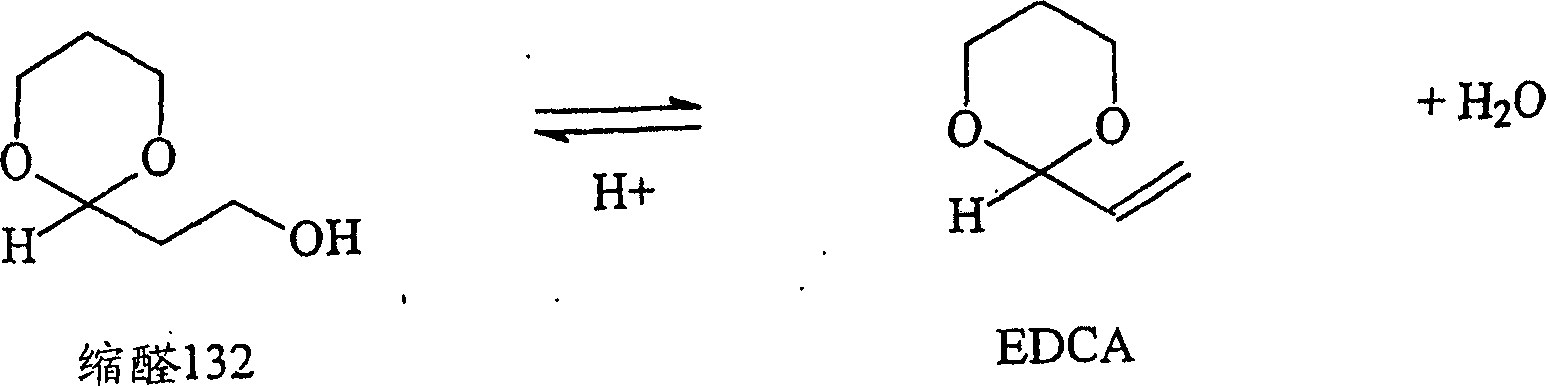Removal of impurities formed during the production of 1,3-propanediol
A technology of propylene glycol and MW132, which is applied in the preparation of hydroxyl compounds, the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the recovery rate and purity of PDO, and the low rate of combined formation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 176-1
[0059] The results in Table 2 show that treatment of a PDO sample contaminated with MW176 acetal at ambient temperature using the acid form of USY type zeolite was not effective in reverse conversion of the MW176 acetal. Room temperature inversion was demonstrated using strong acid resin A15 (AMBERLYST 15 from Rohm and Haas). High temperature treatment with zeolite overnight at 150°C resulted in elimination of MW176 to form 2-methyl-1,3-dioxane. But the formation of polyPDO (di-1,3-propanediol) with higher oligomers occurs at higher concentrations than the original MW176 acetal. Although the more difficult to isolate MW176 acetal was eliminated, the overall purity and yield decreased.
[0060] Additional timing studies were performed at 100°C using USY H+ type zeolite. The results showed the reaction conversion of MW176 acetal, especially the first gc (gas chromatography) peak MW176-1, which reacted to almost complete extent within 5 hours (MW176 acetal showed 3 peaks in gc / ...
Embodiment 176-2
[0066] The MW176 acetal impurity was treated at room temperature using a strong cationic acid ion exchange resin (AMBERLYST A35 from Rohm and Haas). The results shown in Table 3 show that the degradation of MW176 acetal forms MW102 acetal, MW18(H 2 O) and MW132 acetal.
[0067] wt%
name
MW
start
Finish
2-Methyl cyclic acetal
102
0.00
0.10
Cyclic acetal
132
0.05
0.29
Cyclic acetal diol
176
0.24
0.01
water
18
0.02
1.02
PDO
76
99.47
98.39
other
162
0.02
0.00
other
176
0.02
0.01
99.81
99.83
Molar balance
1.31
1.35
[0068] Solid acid treatment of PDO contaminated with MW176 acetal degrades this impurity into a lighter component (MW102 unhydroxylated acetal) that can be easily separated by distillation. Strong cationi...
Embodiment 132-1
[0070] Embodiment 132-1 (comparative example)
[0071] Acid resin treatment before distillation
[0072] This experiment required 1500 grams of crude PDO to be treated with 43.5 grams of dry A15 (Amberlyst A15 resin) strong acid cation exchange resin at 100° C. under nitrogen atmosphere for 3 hours with minimal separation (extraction) after distillative removal of water. The treated material is bright yellow. The MW132 acetal was only reduced from 3.2 wt% to 2.6 wt%. The treated material was distilled and successive distillation fractions showed a reduction of MW 132 acetal from 11 wt% to 2 wt%, but the final fraction formed up to 2700 ppm acrylate. Because of the strong acid treatment that liberates 3-hydroxy-propionic acid, excessive acrylate formation can be expected, resulting in substantial ester and eventual acrylate formation. This example illustrates that no significant removal of the MW132 acetal was observed for resin treatments without co-separation (extracti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com