New expression system from rhodococcus
A technology of Rhodococcus and Rhodococcus erythropolis, which is applied in the determination/inspection of bacteria and microorganisms, and the introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, etc. It can solve the problems of negative effects on biotransformation efficiency and lack of specificity in response.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1. Constitutive expression of kstD after deletion of the kstR non-marker gene
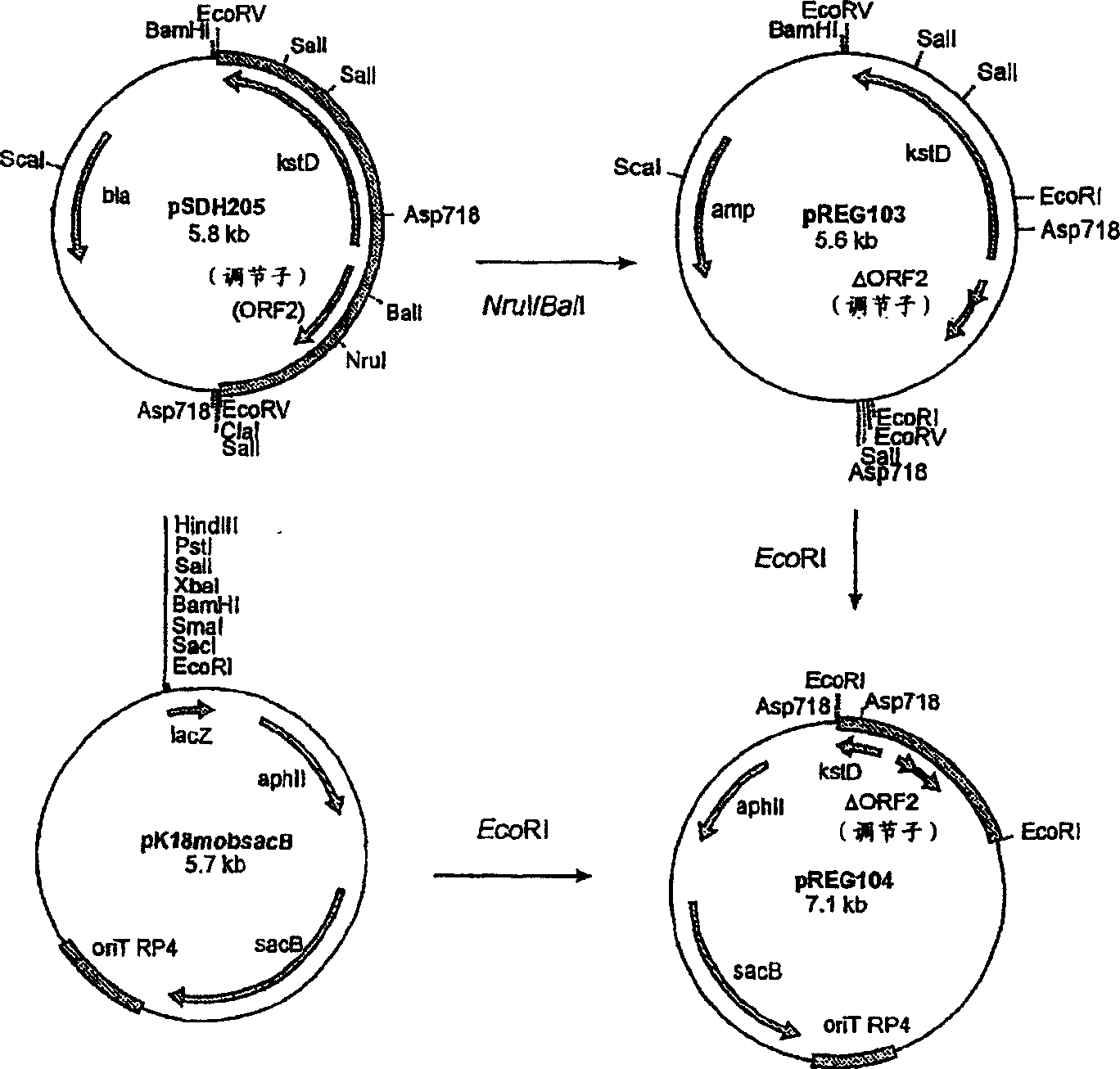
[0065] Construction of the mutagenic plasmid pREG104 for the deletion of the kstR non-marker gene, which encodes the transcriptional regulator of the kstD gene in Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 (encoding 3-sterone Δ 1 -Dehydrogenase KSTD1)( figure 1 ). Briefly, pSDH205 (Van der Geize, R. et al., 2000. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:2029-2036) was digested with restriction enzymes NruI and BalI, followed by self-ligation to generate plasmid pREG103. The EcoRI DNA fragment of pREG103 containing the deletion of the kstR gene was then cloned into the EcoRI digested pK18mobsacB vector to generate pREG104. The kstR non-marker gene deletion mutant strain Hongchuanhong was isolated from Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 by the sacB counter-selection method as described (Van der Geize R. et al., 2001. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 205: 197-202) using pREG104 coccus RG10. Authentic kstR gene deletion was c...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2. Microbial steroids Δ 1 - Constitutive expression of KstD2 upon dehydrogenation
[0069] Using pREG104 ( figure 1 , see Example 1) Construction of kstR gene deletion mutant Rhodococcus erythropolis RG9 (Van der Geize, R. et al., 2002. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 1007-1018), denoted as Rhodococcus erythropolis RG17. Strain RG17 is thus a kstD kstD2kshA1 kstR quadruple gene deletion mutant that lacks 3-sterone Δ in addition to the transcriptional regulator of the kstD promoter. 1 - Dehydrogenase (KSTD1 and KSTD2) and 3-sterone 9α-hydroxylase (KSH) activity. Due to the kstD kstD2 kshA phenotype of this mutant, strain RG17 metabolizes 4-androstene-3,17-dione (AD), 1,4-androstadiene-3,17-dione (ADD) and 9α-hydroxy-4 -Androstene-3,17-dione (90HAD) was completely blocked.
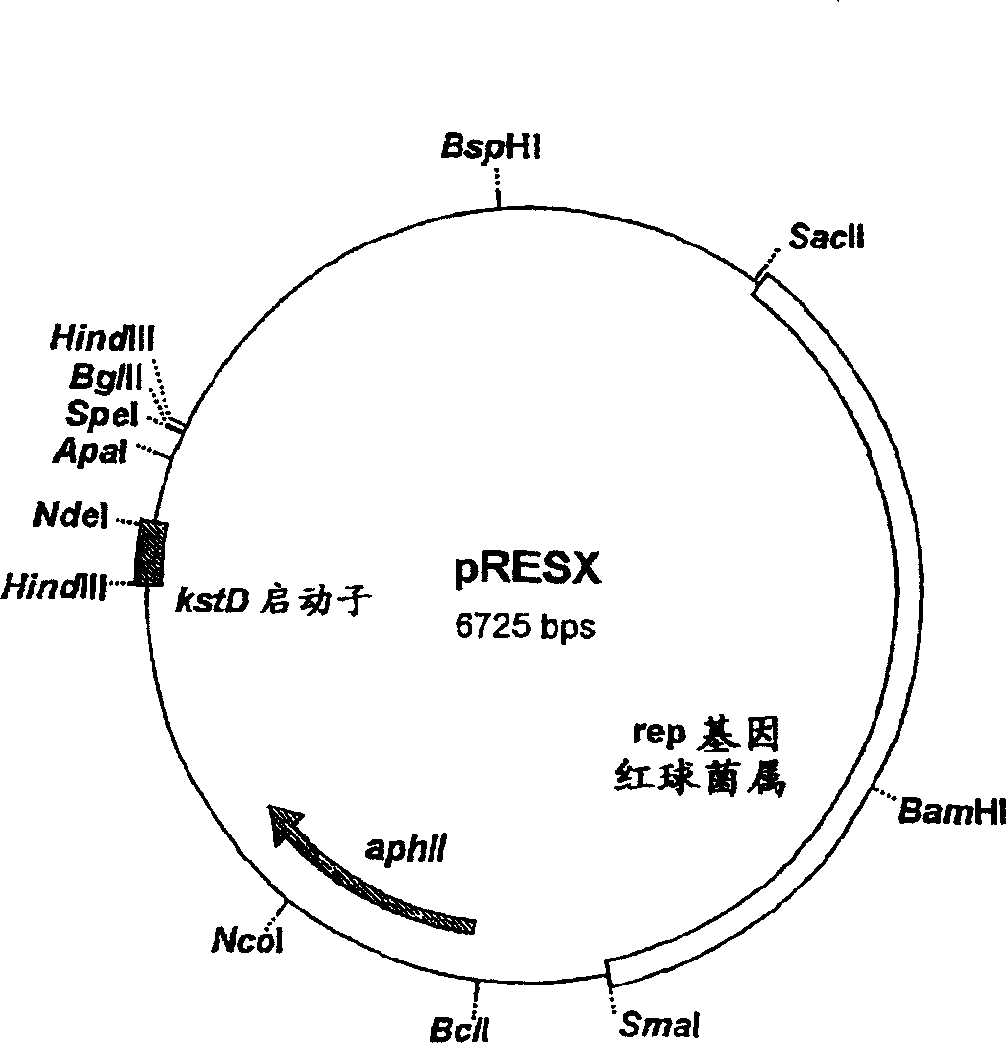
[0070]A Rhodococcus expression vector was constructed for gene expression under the control of the kstD promoter of Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 (Van der Geize, R. et al., 2000. Appl. Environ. Microbi...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3. Expression of the kshA isogene kshA2 complements the kshA mutant phenotype
[0075] Nucleotide sequencing of DNA fragments isolated from UV-induced complementation experiments of Rhodococcus mutants identified the identity of Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 (Van der Geize, R. et al., 2002. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1007-1018). Homologue of the kshA gene. Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 contains at least two kshA isogenes, denoted as kshA and kshA2.
[0076] The kshA gene deletion mutant of Rhodococcus erythropolis RG2-Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 (Van der Geize, R. et al., 2002. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 1007-1018) was shown not to supplement AD (0.25 g l -1 ) as the sole source of carbon and energy on a mineral agar plate (1 g l -1 NH 4 NO 3 , 0.25g l -1 K 2 HPO 4 , 0.25g l -1 MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 5mg·l -1 NaCl, 5mg·l -1 FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O (pH7.2), 1.5% agar). Thus, kshA2 was not expressed in RG2 under these growth conditions.
[0077] The kshA2 gene in pRESX is unde...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com