Elevator control method
A technology of elevators and control methods, applied in the field of elevator landing control, can solve problems such as inability to apply elevator drives, complex solutions, and difficulties, and achieve simple and reliable adjustments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
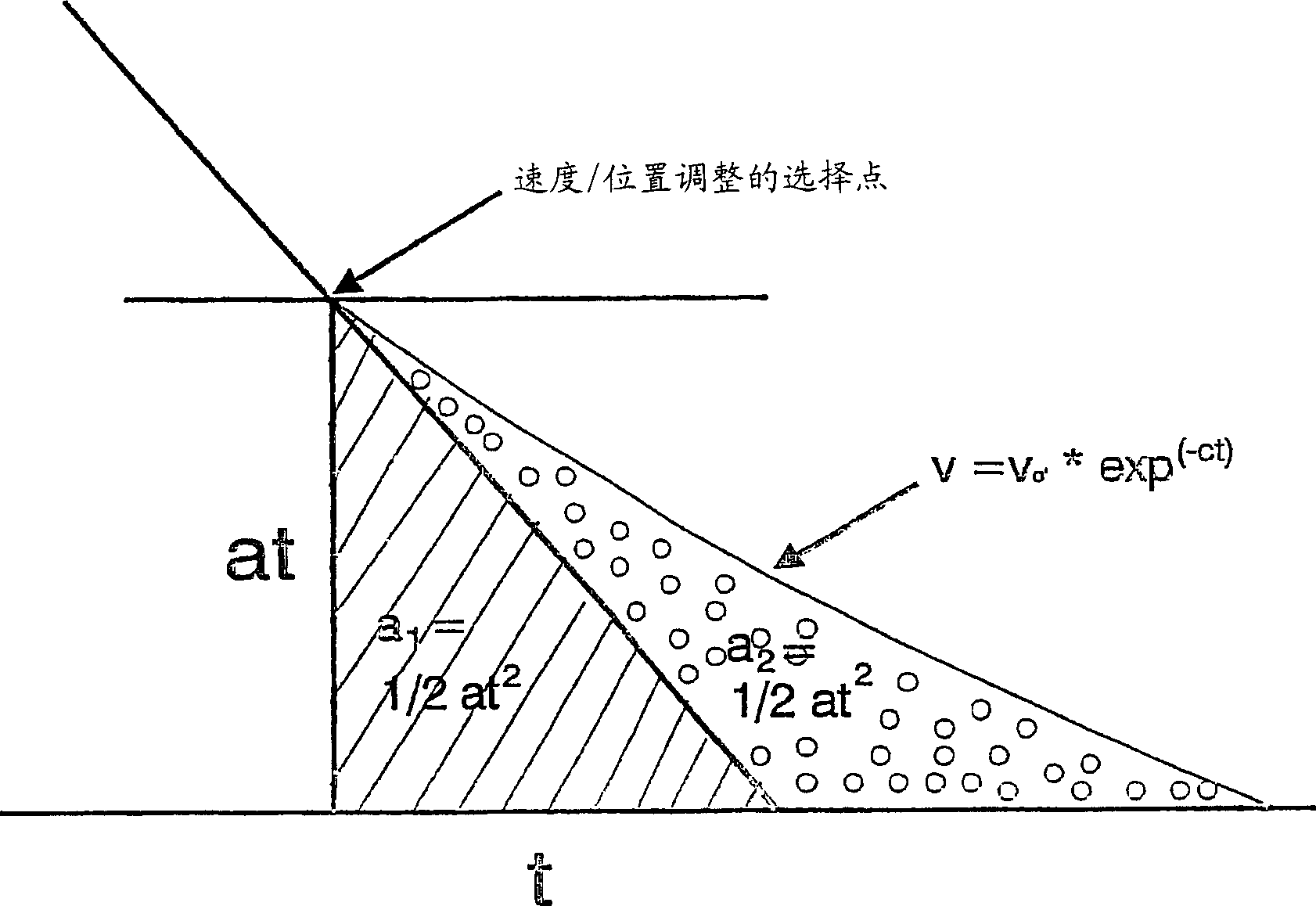
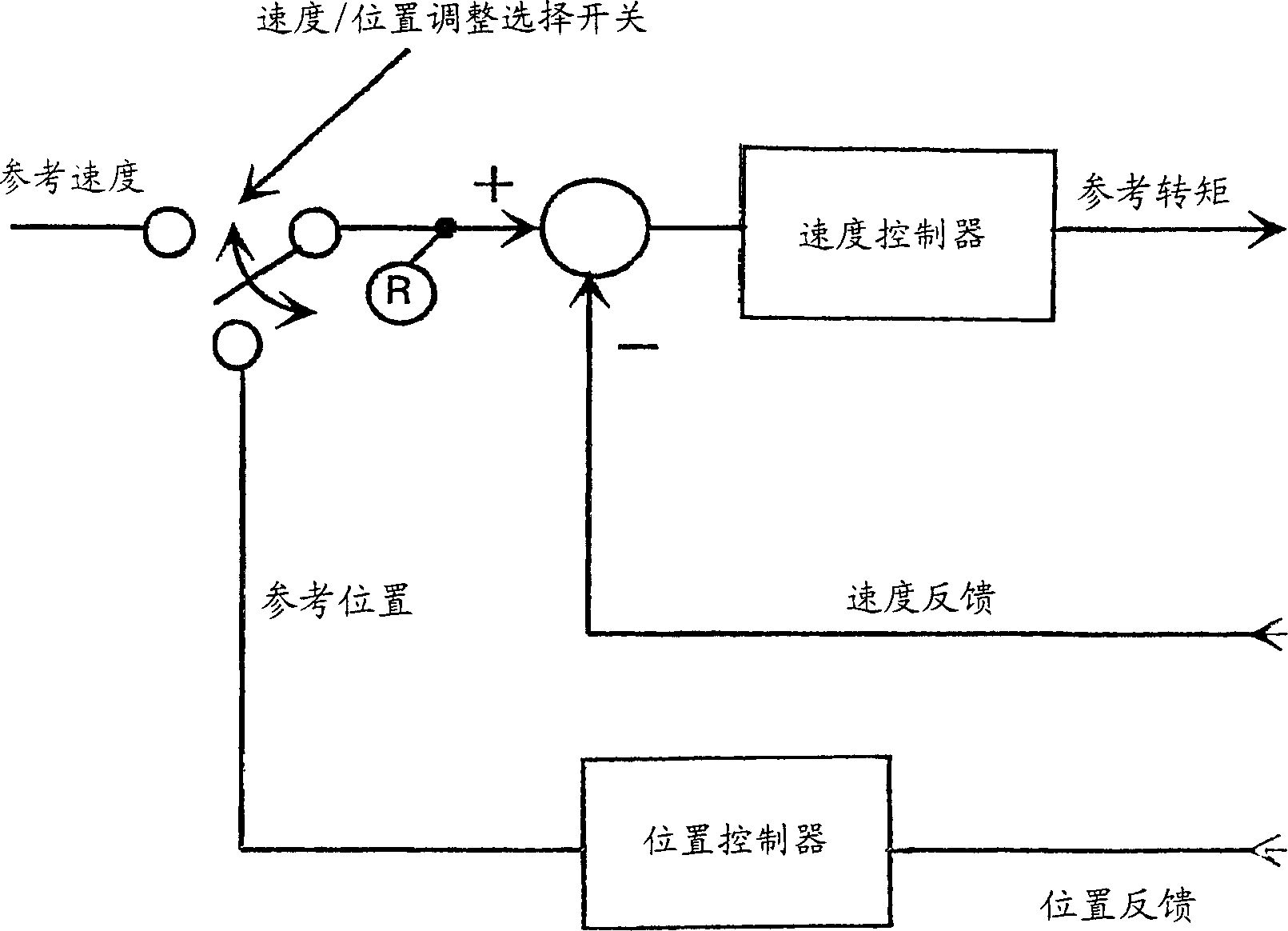
[0016] according to figure 1 , in normal operation, the elevator travel curve includes initial acceleration, constant acceleration phase, constant speed phase, constant deceleration phase, and final deceleration. During the deceleration phase, the speed of the lift etc. decreases deceleratedly, which in figure 1 V of medium speed curve a Partial representation. In the constant deceleration phase, it is well known that the equation v 1 =a*t 1 applied to velocity, where a is the deceleration and t is time, and the equation s 1 =1 / 2*a*t 1 2 Applied to the distance. In other words, when an elevator etc. comes to a decelerated stop, at time t 1 traveled within s 1 =1 / 2*a*t 1 2 distance. If, at the end of the deceleration phase, a final completion phase is added to the velocity profile, in this case the rate of change of the deceleration, that is, the deceleration rate is constant, and the value of the deceleration rate is chosen such that the stop double the distance, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com