Electrophoretic or bi-stable display device and driving method therefor
A bistable display and driver technology, applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as pixel deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
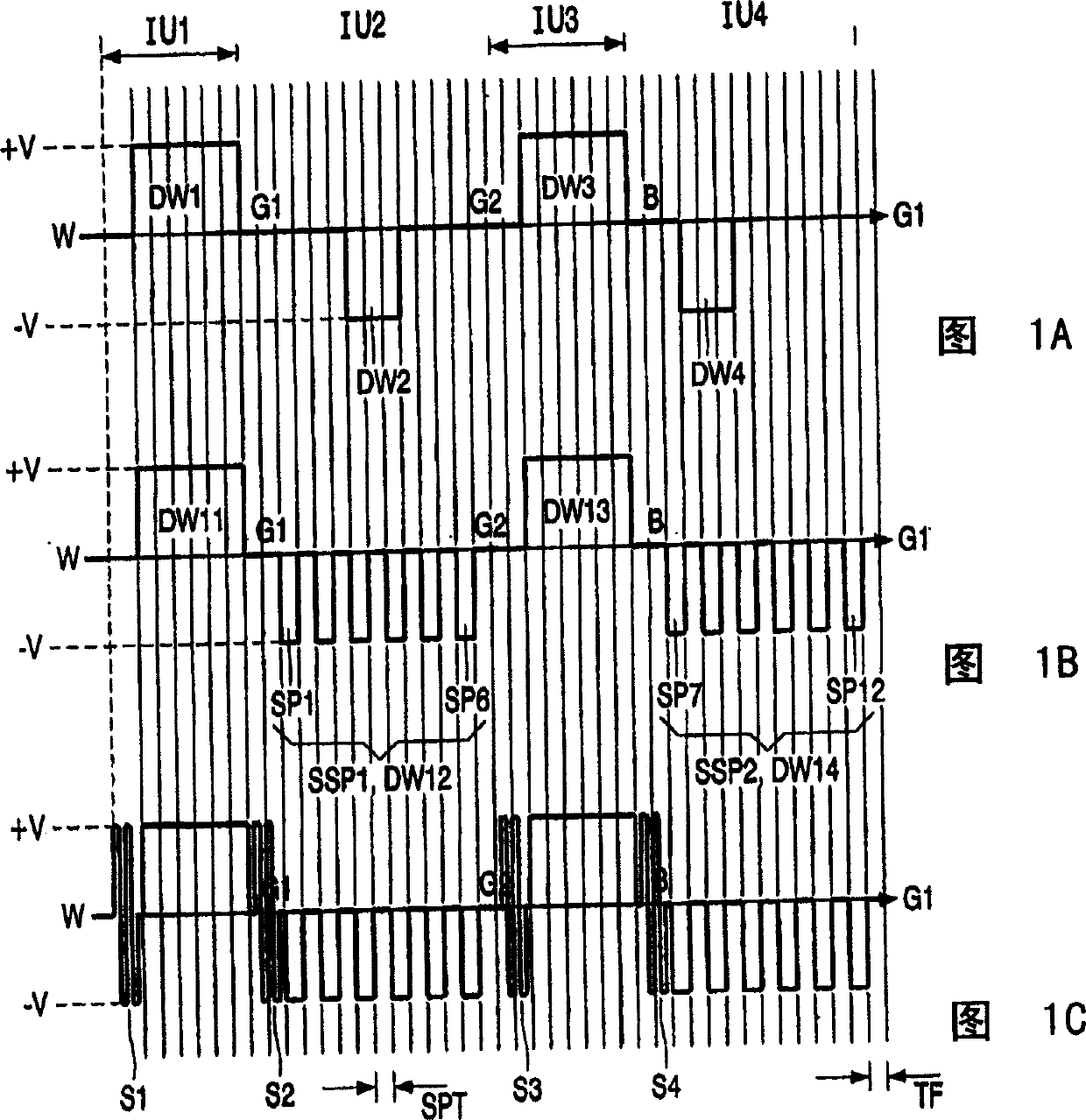
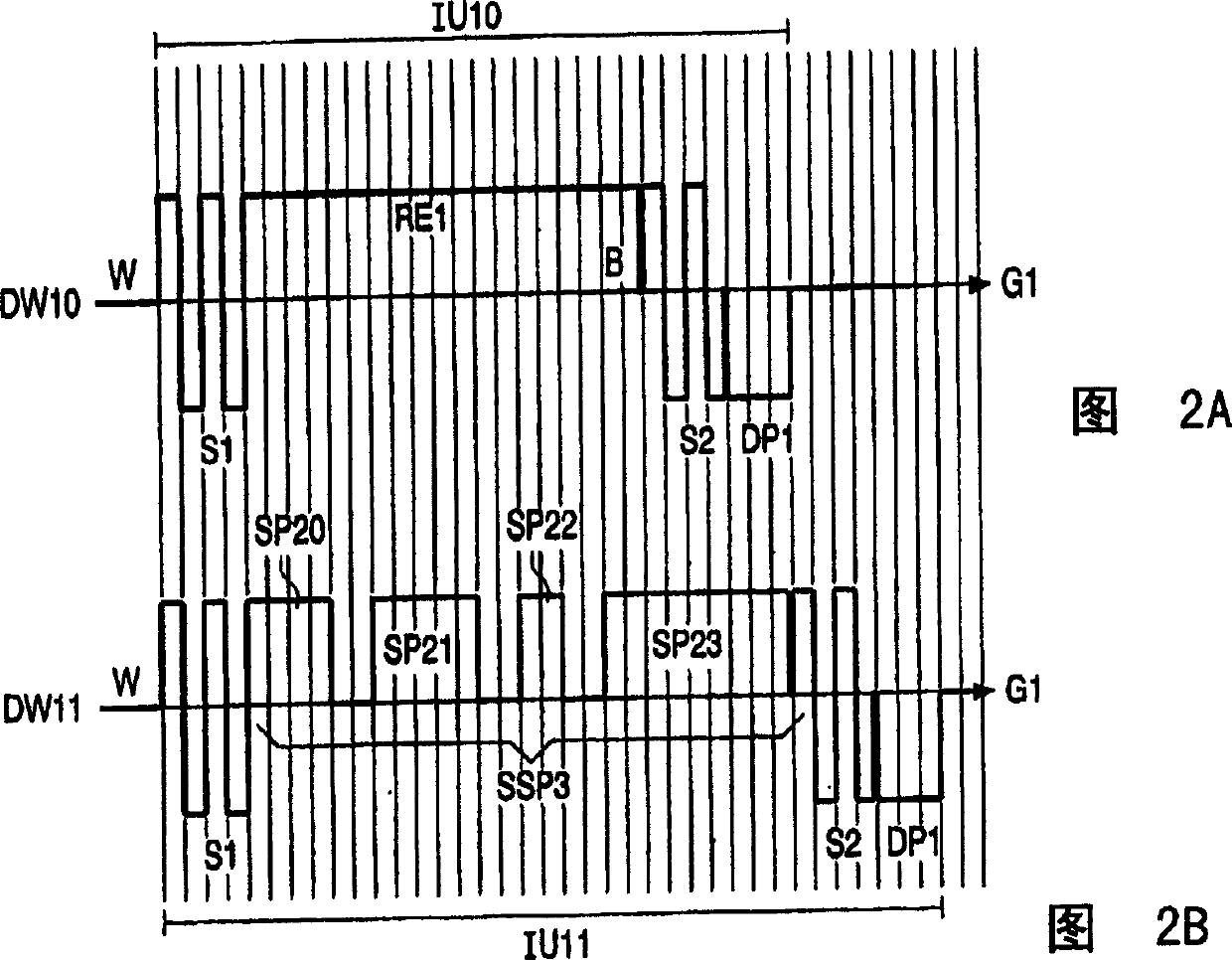
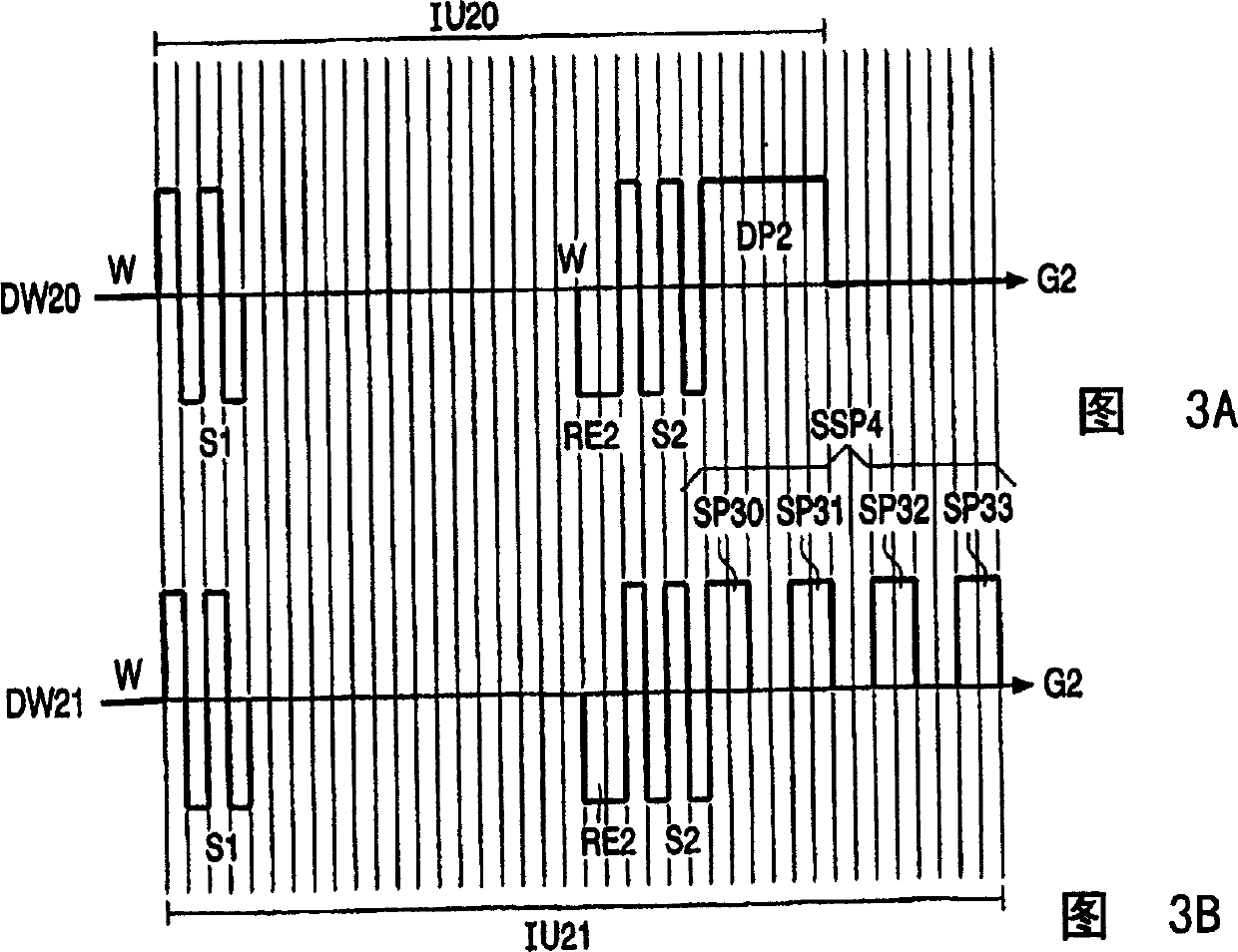
[0042] The subscripts i, j and k are used to denote specific items that are present or used. For example, pixel Pij refers to any one pixel that may be mentioned, or drive waveform DWk refers to any drive waveform. On the other hand, DW1 refers to a specific driving waveform DWk.
[0043] FIG. 1 shows drive waveforms in order to illustrate an embodiment according to the present invention in which a sequence of sub-pulses is used instead of a single drive pulse.
[0044] In electrophoretic displays it is difficult to reliably generate intermediate levels (eg gray if black and white particles are used in EInk type displays). Typically, the intermediate level is produced by applying a voltage pulse for a specific period of time, thus determined by the energy of the applied pulse. The intermediate level is largely affected by image distortion, dwell time, temperature, humidity, lateral unevenness of the electrophoretic film, etc. For example, in an EInk-type electrophoretic dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com