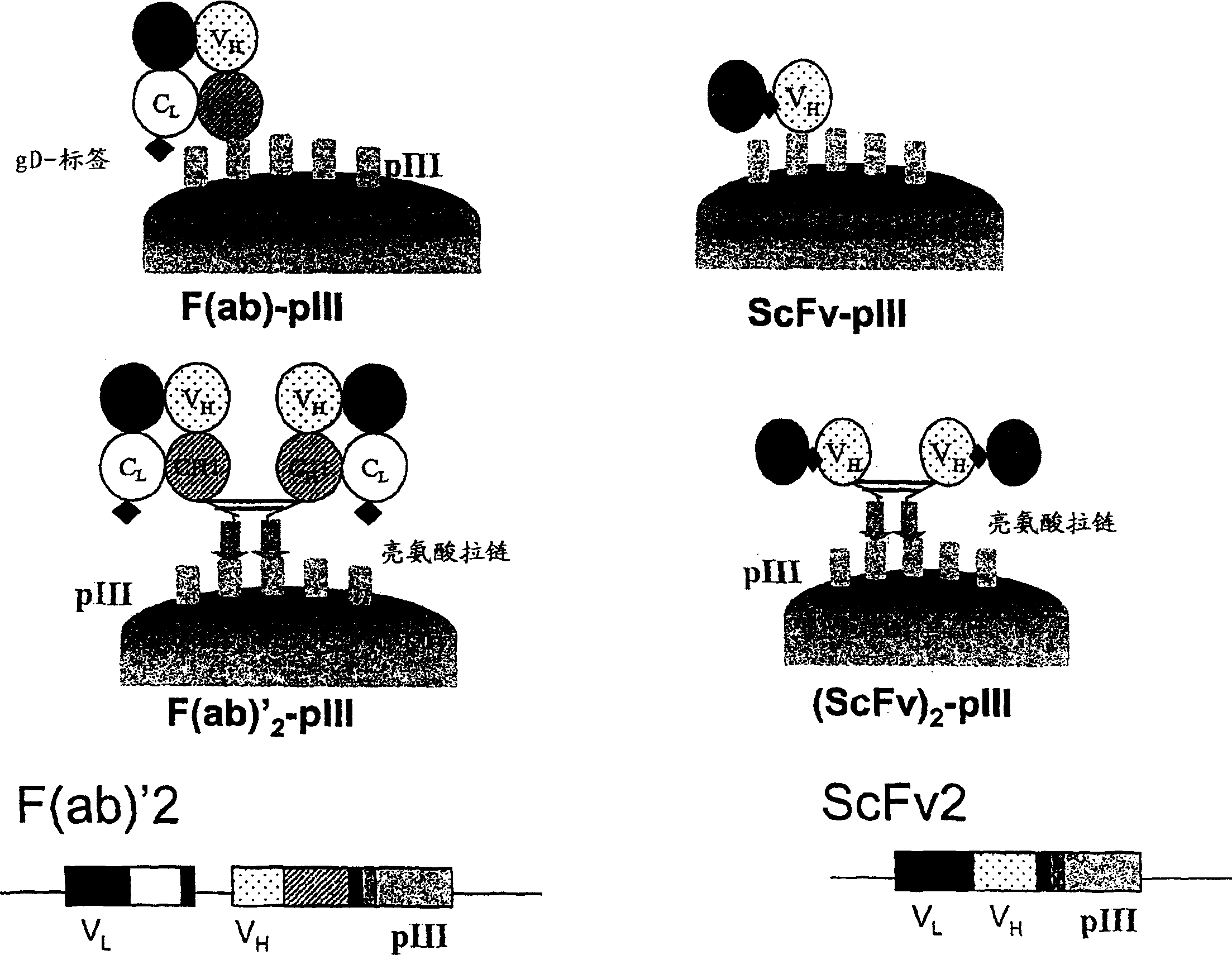
Anti-VEGF antibodies
An antibody, a technology for synthesizing antibodies, applied in the direction of antibodies, anti-inflammatory agents, anti-bacterial drugs, etc., can solve the problems of application, lack of systematic and quantitative methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-G6 and B20
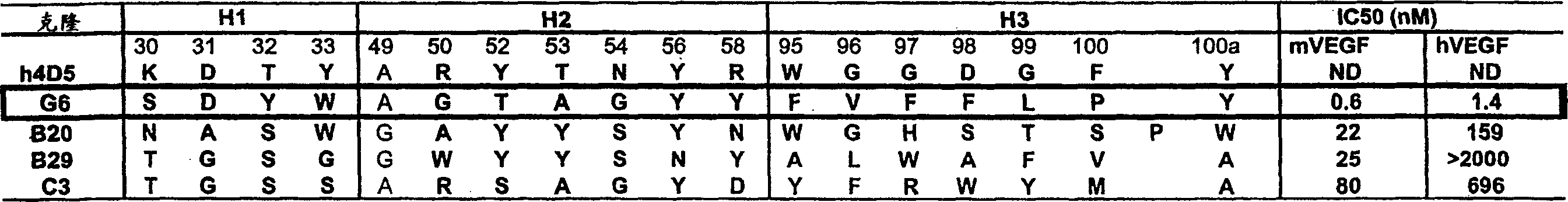
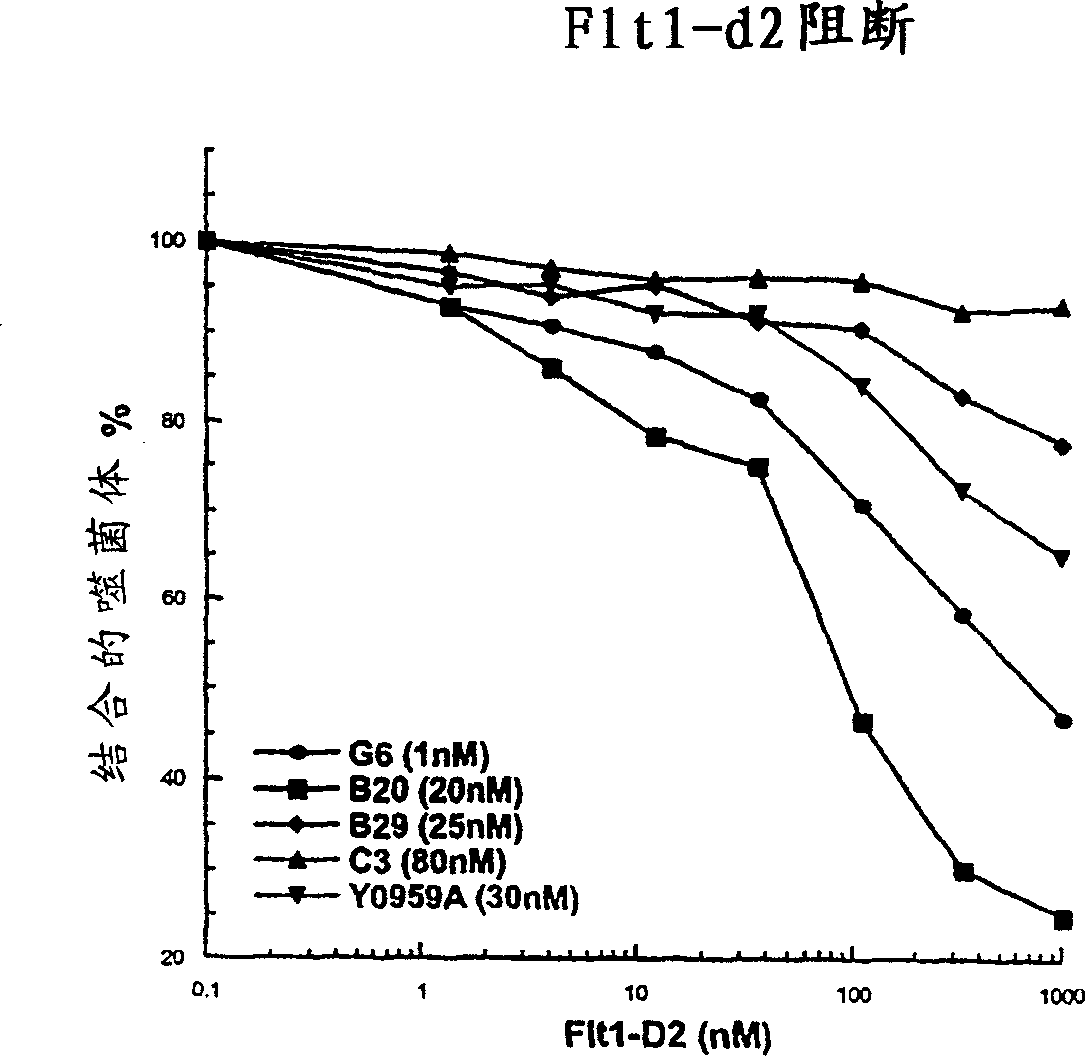
[0316] Example 1 - G6 and B20 derived antibodies
[0317] (a) Selection of high-affinity anti-VEGF Fab clones
[0318] Selection methods for high affinity anti-VEGF Fab clones involved various combinations of solid-supported and solution-bound sorting. Antibody phage libraries were panned with target antigen coated on NUNC 96-well Maxisorp immunoplates at a concentration of 5 ug / ml in solid-supported sorting. In the solution-binding sorting method, the phage library was incubated with biotinylated antigens at decreasing concentrations in solution, and then the antigens were coated on 96-well Maxisorp plates (2-5 ug / ml). Neutravidin capture. Decreasing concentrations allow for higher stringency in panning for tighter binders. For the target antigen mVEGF, a two-step sorting strategy was developed as follows, in step 1, strong binders were separated from the naive library by solid-phase-supported selection, and then in step 2, those with higher affinity Binders can be separa...
Embodiment 2-
[0350] Example 2 - Localization of VEGF Binding Sites on G6 and G6-23 Antibodies
[0351] Functional localization of G6 and G6-23 by shotgun alanine and analogue scanning
[0352] Functional mapping of G6 and G6-23 by shotgun alanine and homolog scanning was performed to identify residues important for binding hVEGF and to identify residues that could be further improved for binding VEGF Residues. We generated combinatorial phage libraries that allowed heavy or light chain CDR residues in separate libraries to be alanine or wild-type (alanine scanning), or homologous amino acids or wild-type (analog scanning).
[0353] Mutagenic oligonucleotides for shotgun scanning libraries
[0354] oligomer
sequence
H1-A
GCA GCT TCT GGC TTC ACC ATT KCC GMT KMT K
SG ATA CAC TGG GTG CGT CAG (SEQ ID NO: )
H2-A
AAG GGC CTG GAA TGG GTT GCA GST ATT RCT C
CT GST GST GGT KMT ACT KMT TAT GCC GAT AG
C GTC AAG GGC (SEQ ID NO: )
H3-A
...
Embodiment 3-G6 and G
[0380] Example 3-G6 and G6-23 derived antibodies
[0381] (a) Libraries for selection
[0382] Additional anti-VEGF antibodies were obtained by sorting phage from the shotgun alanine and homologue scanning libraries described in Example 2. Specifically, at specific residues, the residues being scanned were allowed to be changed to wild-type or alanine (alanine scanning), or wild-type or homolog residues (homolog scanning) ( Figure 14A and B). For G6, shotgun alanine and homolog scanning were performed on the G6 light and heavy chains, respectively, resulting in four libraries. For G623, shotgun alanine and homologue scans were performed on the G623 light chain and shotgun homolog scans were performed on the G623 heavy chain, resulting in three libraries. A G623 shotgun alanine scanning library was not prepared because, as discussed above, G623 is a high affinity antibody in which most of the residues critical for binding are located on the heavy chain. Mutating heavy chai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com