Moving image display device and method for moving image display
A dynamic image and display device technology, applied in image communication, static indicator, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as increased cost, inability to smooth image display, and virtual images, and achieves reduction of memory capacity, suppression of dynamic image flicker, The effect of increased processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] (A-1) Hardware composition of the projector:
[0036] (A-2) The composition and operation of the intermediate frame generation circuit:
[0037] (A-3) Effect:
Embodiment 3
[0040] D. Variations:
[0041] A. Embodiment 1:
[0042] (A-1) Hardware composition of the projector:
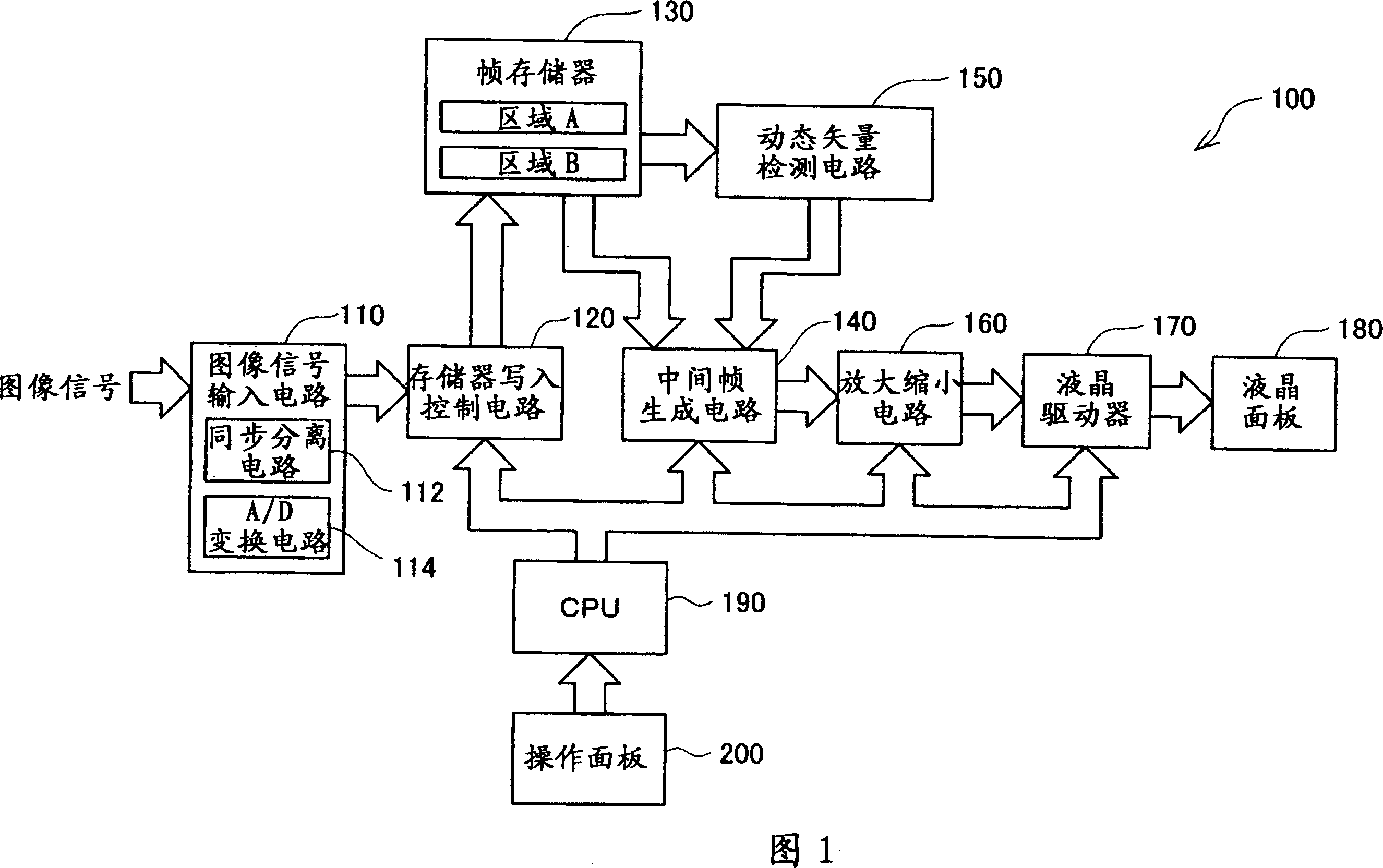
[0043] FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware configuration of a projector 100 as an example of a video display device of the present application. This projector 100 has a function of displaying a moving image at least twice the frame rate of the original moving image. A specific configuration for displaying at twice or more the frame rate will be described in detail later.
[0044] As shown in the figure, the projector 100 of this embodiment has an image signal input circuit 110, a memory writing control circuit 120 connected to the image signal input circuit 110, and a frame memory 130 connected to the memory writing control circuit 120. , the motion vector detection circuit 150 that is connected with the frame memory 130, the intermediate frame generation circuit 140 that is connected with the frame memory 130 and the motion vector detection circuit 150, the enla...
example 1
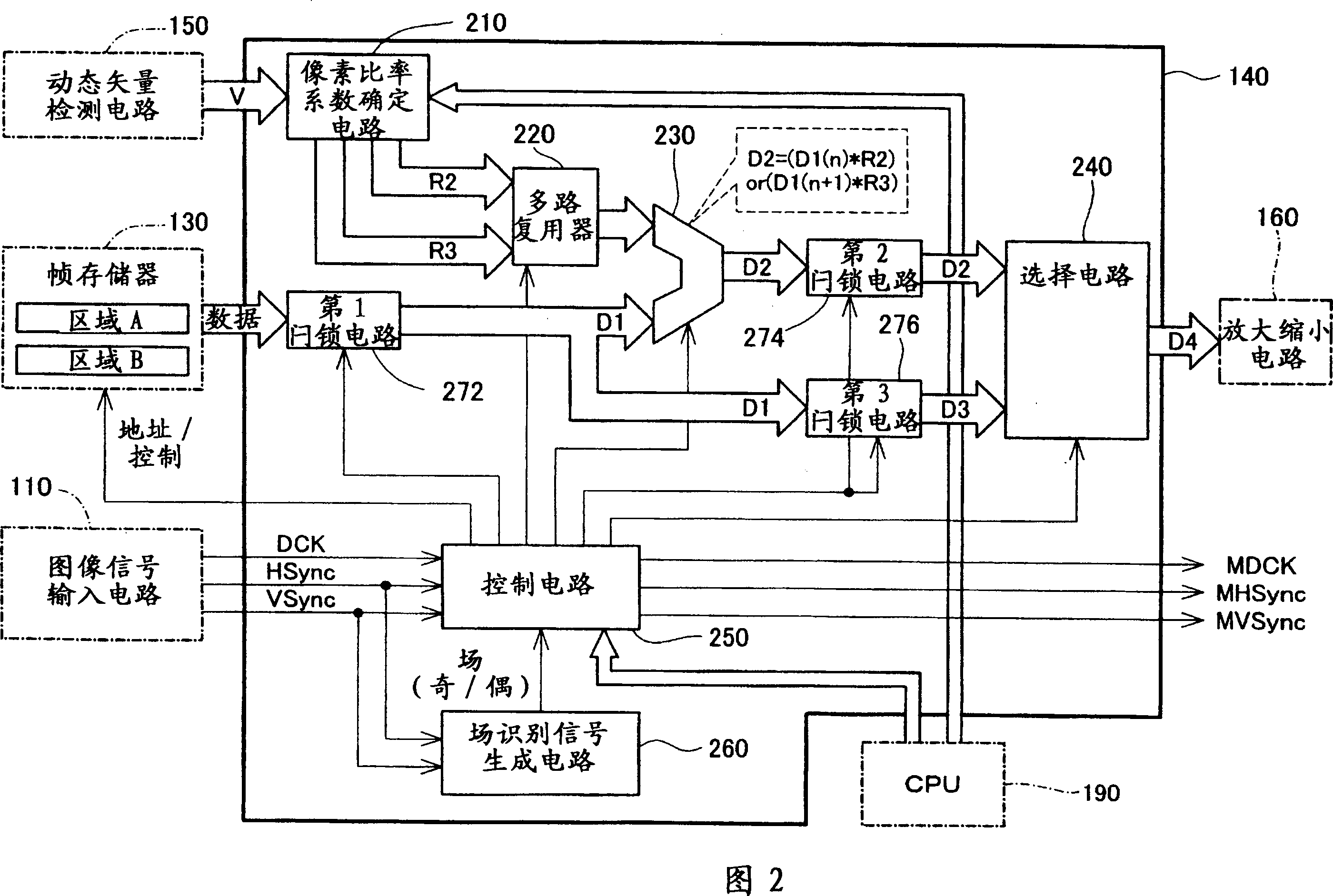
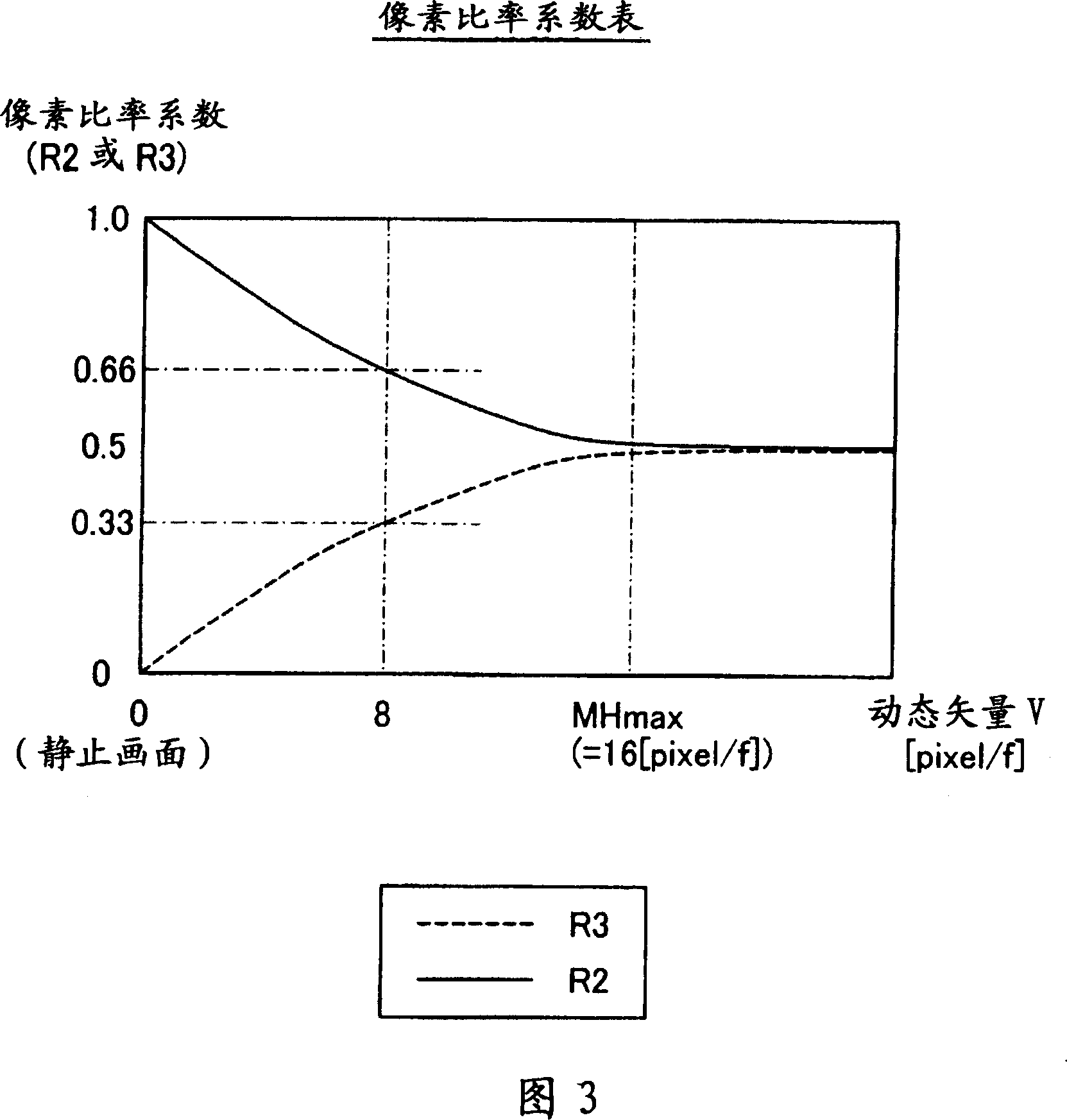
[0095] Next, a modified example of the method of determining the pixel ratio coefficients R2 and R3 will be described using FIGS. 9 to 11 . In this modified example, the pixel ratio coefficient determination circuit 210 shown in FIG. 2 determines the values of the pixel ratio coefficients R2 and R3 according to the number n of intermediate frame images to be generated and the characteristics of the sine wave regardless of the motion vector V.
[0096] In this modified example, when the number of intermediate frame images generated by the synthesis circuit 230 is set by the CPU 190, the pixel ratio coefficient determination circuit 210 determines the number of intermediate frame images to be used for each intermediate frame image according to the table shown in FIG. 9 . The angle θ(rd) (0≤θ≤π) of the pixel ratio coefficients R2 and R3 is obtained. In the table shown in FIG. 9 , values obtained by dividing the interval from 0 to π by the number of intermediate frame images a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com